Double vision is often confused with blurred vision. However, fog in the eyes is a visual impairment in which a person sees one blurry, unclear image, and with double vision, one object is perceived as two images of it.
Diplopia manifests itself in different ways. Some patients report this condition from time to time, others live with it constantly. In some cases, people claim to experience double vision only when they look in a certain direction (vertical or horizontal plane).
Vision system
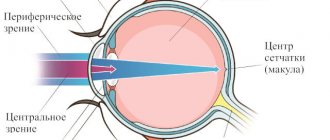
We rarely think about how exactly vision works until problems arise with it. In a normal state, the visual process occurs like this:
- the object is projected onto the retinas of both eyes, right and left,
- the brain combines information from both eyes, producing a complete picture.
Otherwise, this connection is broken, and the image doubles.
Let's take a closer look at the causes and treatment of double vision.
What is diplopia
Diplopia (double vision) is the inability to see a single image of objects located in the vision zone.
The brain provides a binary image of a single object. The image can be deformed in different ways: vertically and horizontally or diagonally. In this regard, a person is not able to see a clear, unified picture of an object. The pathology causes very unpleasant sensations for patients, causing eye fatigue, dizziness and disorientation in space.
It is important to understand that this is not an independent illness, but a concomitant signal of a systemic disease. In medical practice, almost all causes of double vision have been studied, and proper treatment in most cases leads to a positive result.
Nature of appearance and types of diplopia
In order to diagnose diplopia, it is enough to consult an ophthalmologist. After all, sometimes this illness is a consequence of other, more serious neurological or oncological diseases.
This defect occurs when a visible object is projected onto asymmetrical areas of the retina. Therefore, the brain, when processing the signal, does not reduce it into a single picture. The image can bifurcate in different directions and, as a rule, is a consequence of dysfunction of the oculomotor system. The muscles bring the eyeballs into non-identical positions, causing different focus.
If you notice symptoms of diplopia, you should definitely consult a specialist. Especially if the disease has been with you for a long time.
Persistent double vision comes in two forms:
- Binocular . The most common violation. A defect caused by the lack of parallelism of the visual axes in the eyes. Often accompanied by or resulting from strabismus. Often occurs after injury, but is not always permanent.
- Monocular . A rarer form that can begin against the background of organ injury, corneal degeneration (astigmatism), damage to the visual cortex of one of the cerebral hemispheres, or clouding of the lens. The main difference from the binocular form is that double vision can occur even when the affected eye is closed.
There are also forms of diplopia that are temporary:
- Strong-willed . Conscious “defocus” of the gaze. Thanks to which, the ability to look, as it were, “through” an object appears.
- Temporary . Typically caused by alcohol intoxication, traumatic brain injury, or a side effect of certain medications. However, if the symptoms become permanent, it is necessary to check the organs of vision and systematically treat the disease.
Diagnostics
During the initial examination by an ophthalmologist, the type of diplopia is first determined. If when closing one eye the symptoms disappear, then we are talking about the binocular form. In the monocular version, double vision persists when the second eye is closed. To establish the etiology of diplopia, specific examination methods are performed:
- Visometry.
Visual acuity is measured at distance and at the patient's working distance with and without correction. In this case, it is necessary to find out at what distance ghosting occurs and whether its characteristics change with glasses or when the head is tilted. - Computer autorefractometry.
Subjective refraction is studied with the selection of a trial correction. After instillation of cycloplegics, the study is repeated to obtain objective refraction values. - Biomicroscopy of the eye.
It is necessary to examine in detail the anterior segment of the eye and assess the condition of the refractive media of the eyeball. In pseudophakia, the position of the intraocular lens should be determined. - Ophthalmoscopy.
Examination of the fundus can reveal signs of intracranial hypertension (congestion of the optic nerve head, dilated tortuous veins, narrowed arteries). After vitreoretinal interventions, distortion of the retinal surface is possible. - MRI of the orbits and optic nerves.
The technique makes it possible to visualize thickening of the extraocular muscles, which is observed in orbital myositis and thyroid ophthalmopathy. With concomitant proptosis, it is important to exclude pathological changes in the fiber. - X-ray of the orbit.
It is performed in direct and lateral projection in the presence of a clinical fracture of the bone walls of the orbit. If there are difficulties in diagnosis, computed tomography is recommended. - Laboratory research .
If thyroid ophthalmopathy is suspected, measurement of TSH, T3, free T4 and the level of antibodies to thyrotropin receptors is indicated. In myasthenia gravis, the level of autoantibodies to the muscle acetylcholine receptor should be assessed. - Pharmacological tests.
The essence of the tests comes down to the subcutaneous administration of an anticholinesterase drug for the clinical picture of myasthenia gravis. The test is considered positive if clinical signs are fully or incompletely compensated.
Ophthalmological diagnostics
Photos of treatment stages
Patient : 30 years old
Diagnosis : Double vision + strabismus after an accident
1. Several operations to compensate for double vision (the last two at the Hemholtz Research Institute of GB)
2-3. The results of the operations are not visible after a year; double vision progresses.
4-5. Double vision remained plus the lack of eye mobility towards the temple was added
6. Prismatic glasses were prescribed to compensate for double vision and restore eye mobility when worn continuously for a year, treatment continues.
Need specialist advice?
Operating procedure
Clinical picture of double vision
Many modern clinics offer intervention services for vision problems. But few can guarantee that the patient will not gradually begin to lose visual acuity after a year. That is why it is so important to understand everything and make the correct diagnosis.
Pathology has an extremely long list of causes for its occurrence. Starting from traumatic brain injuries, alcohol intoxication, migraines and abscesses, ending with stroke and oncological diseases such as cancer and brain tumors.
In most cases, double vision indicates a neurological condition and requires treatment of the underlying cause at the level of the peripheral nervous system or brain.
Stages of the disease
Regardless of the cause of its appearance, pathology always develops in several stages. At the initial stage, unpleasant symptoms make themselves felt, but not constantly. When overworked, a person experiences a decrease in visual acuity and an inability to focus on an object. But after a short rest, the signs inherent in diplopia disappear.
The progressive stage is characterized by a pronounced splitting of the picture, a strong decrease in visual function, and loss of strength. Even after a long rest, the patient notes that the unpleasant symptoms do not go away. The advanced stage of the disease increases the signs of pathology; a person’s vision decreases greatly.
Symptoms appear with varying degrees of intensity. In some cases, the patient does not notice the progression of the pathology, but most often problems begin to appear at the initial stage.
Causes of double vision
Speaking about the monocular form of the disease, it is worth considering the following reasons for its occurrence:
- Astigmatism, since with it only one eye has a split.
- Corneal dysfunction. Such as dryness, scarring and various infections.
- Also, against the background of clouding of the lens, a possible cause may be cataracts.
As for the binocular shape, the main reasons may be:
- Strabismus. It can be both a cause and a consequence of a disease.
- Various diseases characterized by impaired vascular function - cerebral aneurysm, stroke, hypertension.
- Diabetes. Due to damage to nerve endings.
- Autoimmune diseases such as myasthenia gravis and multiple sclerosis, which affect the central nervous system.
- Injuries. Traumatic brain injury is an extremely common cause of diplopia.
Considering a wider range of causes, diplopia can be caused by the following diseases:
- Neuropathy caused by B vitamin deficiency.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
- Migraine, epilepsy, hypertensive crisis, stroke.
However, double vision has other causes. A correct clinical picture is possible only with timely diagnosis and detection of the localization site. For example, there is also a paralytic form of diplopia, it is characterized by paralysis of one or more eye muscles:
- When the rectus ocular muscles are damaged, the patient sees a parallel bifurcated image.
- With pathology in the oblique muscles, the image is located one above the other.
Often, the provocateurs of this visual disorder are also:
- Complications of various infectious diseases.
- Aneurysm of the carotid artery, leading to compression of the optic nerve.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Tumors inside the skull.
- Endocrine ophthalmopathy.
- Inflammation in the brain: meningitis, encephalitis.
Reasons for the development of amblyopia
As a rule, amblyopia develops in one eye (cases of bilateral amblyopia are much less common). The immediate cause may be any obstacle in the optical system of the eye, leading to sensory deprivation (stimulus deficiency), severe asymmetric refractive pathology (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism), accommodation disorders, etc. However, the most common cause-and-effect relationship is amblyopia and strabismus. It is noteworthy that this connection can be both direct (amblyopia develops in the initially squinting eye) and reverse (the “lazy” eye, along with degrading visual functions, loses motor coordination with the movements of the healthy eye and begins to squint).
The main clinical characteristics of amblyopia include:
- decreased visual acuity and clarity;
- loss of binocularity (the ability to perceive stereoscopic space);
- disturbance or, less commonly, absence of central gaze fixation.
Double vision: treatment and diagnosis
Consultation cost 3000 rubles
The risk of developing an underlying disease and irreversible visual changes is a sufficient reason to immediately consult a doctor. Identifying the causes will create the prerequisites for the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment regimen.
Diagnostics
- History taking
When compiling a medical history, first of all, attention is paid to the patient’s most recent injuries and illnesses.
- Detecting the form of diplopia
At the next diagnostic stage, the form of diplopia (binocular/monocular) is determined by tests.
- In-Depth Study
It is necessary to identify the degree of discrepancy between the patient’s images (vertically, horizontally) through a test.
- Quantitative Research
At this stage, the prism compensator allows you to correct diplopia by combining double images to set the number of prism diopters.
- Diagnostic analysis
The degree of functionality of the extraocular muscles is assessed using the Haabu method. Namely, by the method of infrared videooculography and electrodynamic scanning, as a result of which hyperfunction of the oculomotor muscles is detected.
Prevention
To protect yourself from diplopia, it is enough to follow a number of simple rules:
- If possible, completely give up cigarettes or minimize their use;
- control blood sugar levels;
- walk 1.5-2 km every day;
- wear dark glasses on bright sunny days;
- promptly treat ophthalmological diseases;
- control the level of thyroid hormones.
Yes, prevention will not help to get rid of the pathology 100%, but it will significantly reduce the rate of its development.
Basic principles of treatment
Binocular disorders
- Depending on the underlying cause of the disorder, treatment will be prescribed by a specialist in a specific field. However, a neurologist and a neurosurgeon are the doctors you should consult first.
- In case of injury to the organ of vision, a comprehensive examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary.
- Corrective therapy involves wearing sphero-prismatic glasses, which neutralize the double vision syndrome. Regular eye exercises will be an effective addition.