Content:
- Why withdrawal syndrome occurs: mechanisms of formation of nicotine addiction.
- Clinical picture of withdrawal syndrome.
- Why is treatment for nicotine addiction important?
- How to ease the symptoms of withdrawal symptoms.
“Quitting smoking is easy! I've done this a thousand times! It is this statement by Mark Twain that accurately characterizes numerous attempts to get rid of the almost irresistible craving for cigarettes. Despite a lot of information about the dangers of tobacco smoke, smoking is often perceived as a completely harmless (and until recently, fashionable) habit. Usually it all starts as an innocent indulgence - a couple of cigarettes when talking with friends, discussing the latest news in the smoking room in the office, and many do not notice how a few pieces gradually grow into a dozen, or even a pack a day. And quitting is no longer so easy: in addition to psychological, nicotine causes physical dependence. And without competent psychotherapeutic and medication assistance, it is very difficult to cope with withdrawal symptoms when quitting smoking.
How can smokers cope with unpleasant symptoms?
If such ailments have become an integral part of smoking, you should urgently consult a doctor, as these symptoms may indicate a serious illness - hypertension.
The best solution in the fight against dizziness, nausea and weakness is to give up cigarettes. It is best and most effective to do this under the supervision of a narcologist. The doctor will be able to choose the right course of treatment and appropriate medications for you.
Will help relieve the condition:
- sound, long sleep;
- green tea every morning;
- cold and hot shower;
- walks in the open air;
- no stress, if possible.
If you feel very dizzy due to cigarette consumption, you can cope with the problem with the help of massage. During an attack, it is necessary to press on specific acupuncture sites, which are:
- on the earlobes;
- in the temporal region;
- on the upper lip near the wings of the nose;
- at the base of the nose at the level of “3 eyes”.
Slow, circular movements with slight pressure on the points will relieve you of the unpleasant symptom and associated nausea.
A herbal infusion will be no less effective in combating the problem. To do this you need:
mix 20 g of cloves with ½ liter of vodka;- add 200 g of granulated sugar to the composition;
- grate 2 lemons with zest and add them to the grounds;
- pour the composition into 3 liters of water and leave in a cold place for at least two weeks;
- strain the extract and drink 30 milliliters three times a day 20-25 minutes before eating.
The medicinal method is quite widespread. Some of the most popular drugs at the moment are :
- Tabex, the average price in Moscow and the region varies within 1000 rubles. per package.
- Nicorette patches, with an average price of 800-900 rubles. for packaging in St. Petersburg, 1000-1100 in Moscow and the region.
- Antidepressants.
I would like to emphasize that every smoker should definitely quit the bad habit, but if nicotine causes nausea and dizziness when inhaling, you should listen to your body and part with the cigarette once and for all.
Why does withdrawal syndrome occur: mechanisms of nicotine addiction formation
After inhaling tobacco smoke, approximately 25% of nicotine immediately penetrates the systemic bloodstream and reaches the brain within 10–15 seconds. Thus, in terms of the speed of onset of the effect, smoking is comparable to intravenous drug administration. One of the features that causes physical addiction to tobacco is its rapid destruction in the body (half-life does not exceed 2 hours). This explains the frequent desire to smoke again and again.
Like other psychostimulants, smoking, like one of the main neurotransmitters acetylcholine, affects dopamine structures in the brain. A powerful release of adrenaline, norepinephrine, endorphin and some hormones (in particular, adrenocorticotropic hormones, cortisol) has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system. This creates a kind of “positive” effect for the smoker and a desire to repeat it again.
SMOKING and cerebrovascular accidents
The high prevalence of tobacco smoking continues to be one of the important causes of morbidity and premature mortality in the population, primarily from heart disease, cerebral stroke and malignant tumors. As indicated in the special document “Towards a Healthy Russia” [1], the number of smoking men aged 20 to 54 years in different cities ranges from 55 to 65% (see diagram). The resolution of the World Health Organization conference held in Beijing in 1997 noted that quitting smoking could save over 100 million lives in the next 20 years [2]. Data were cited according to which in developed countries, for example in the USA and Great Britain, half of smokers die from diseases associated with this addiction, with 25% at the age of 35-69 years.
Regarding this global health problem, we will consider only the research results related to cerebral vascular lesions.
The pathogenic effect on brain cells is based on rapidly occurring changes in the composition of the blood or the so-called systemic effects of smoking [3]. Within seven seconds after inhaling tobacco smoke, nicotine reaches the brain cells, exerting a specific effect on them. Under its influence, as well as under the influence of carbon monoxide and other substances (in total, smoke contains about 3,400 compounds [4]), blood pressure increases, heart rate, and the concentration of catecholamines and free fatty acids increase. Smoking can increase blood clotting, affecting red blood cell aggregation, hematocrit, viscosity, fibrinogen, and hemoglobin content. The function and activity of blood platelets are impaired [5]. In men, a violation of the hemorheological properties of blood is associated mainly with viscosity, which in turn can cause an increase in fibrinogen levels. In women, these disorders are predominantly associated with an increase in hemoglobin levels. These changes in hemorheological parameters indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases in smokers, deterioration of blood flow and microcirculation [6]. Nicotine affects different levels of the central nervous system, its autonomic formations, and therefore vascular tone and the ability of blood vessels to adapt to other factors are disrupted [7].
| Inhaling tobacco smoke increases blood pressure and causes emphysema. This effect increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in smokers by 2.5 times. Mortality from subarachnoid hemorrhage is especially high among those who smoked a pack or more of cigarettes daily and drank alcohol every day. |
Nicotine can also act locally, for example by releasing norepinephrine from chromaffin tissue near blood vessels and thereby causing their construction [8], or act directly on vascular smooth muscle [9].
It has been experimentally proven that large doses of nicotine can cause degenerative changes of the anoxic type in the walls of arteries and arterioles [10].
| Percentage of smokers among men 20-54 years old in various cities of Russia (1984-1986)* |
Smoking significantly reduces local cerebral blood flow [11]. The risk of blockage of the great vessels of the head increases. Atherosclerotic plaques can form in them, narrowing the lumen of blood vessels, worsening the conditions of blood supply to the brain. The activity of the heart is impaired. These changes in the cardiovascular system contribute to the development of both chronic (initial manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, vascular dementia) and acute (transient cerebrovascular accidents, minor stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes) cerebrovascular lesions.
Early signs of cerebrovascular pathology in the presence of an underlying vascular disease (atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension) may include frequent complaints of headaches, dizziness, noise in the head, memory impairment, and decreased performance. If these complaints are noted quite regularly over a long period of time (at least once a week over the last three months), then, according to the “Classification of vascular lesions of the brain and spinal cord” [12], developed by the Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, a diagnosis of “initial manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain.” This is a serious risk factor for developing cerebral stroke. Even with this early form of vascular brain damage, patients are strongly advised to quit smoking in order to reduce the possibility of disease progression and stroke development.
Incidence of acute cerebrovascular accidents and prevalence of smoking in the population of men aged 40-49 years**, % | ||
| (according to seven-year prospective observation in the Tushinsky district of Moscow) | ||
| Groups | Examined | % of smokers |
| ONMK* | 80 | 43,75 |
| Without ONMC | 167 | 20,96 |
| * ACVA - acute cerebrovascular accidents: strokes, transistor ischemic attacks, cerebral type hypertensive crises ** Age at the beginning of the examination For seven years, we observed a group of men aged 40-49 years selected from the population by random sampling. When assessing the results of this work at the final stage, it was found that smokers were significantly more likely to develop acute cerebrovascular accidents | ||
Numerous studies conducted both in various population groups and in medical institutions reveal the mechanisms of the harmful effects of tobacco smoking. Ph. Wolf et al. [13] believe that inhalation of tobacco smoke contributes to increased blood pressure and the occurrence of emphysema. This effect increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke among smokers compared to non-smokers by 2.5 times and by 2.8 times when eliminating (using mathematical modeling) other associated factors: age, levels of diastolic blood pressure and cholesterol in the blood serum, alcohol consumption , hematocrit values and body weight. Long-term, long-term smoking abuse has a particularly harmful effect. Thus, American neurologists [14] concluded that for people aged 60 years who have smoked for 40 years, the risk of having severe atherosclerosis increases approximately 3.5 times compared to non-smokers. Evidence has been obtained that pathology of the great vessels of the head progresses more slowly in people who quit smoking compared to smokers.
Of particular interest is the examination of 265 thousand Japanese, among whom over 25% of deaths in both men and women were caused by vascular lesions of the central nervous system. A very large material was analyzed - over 6000 cases of death of patients with these diagnoses, which made it possible to calculate mortality separately for cerebral thrombosis, cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage and other vascular lesions. It has been proven that the occurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhages is directly related to smoking; This is especially true for those who smoked a pack or more of cigarettes every day and drank alcohol every day.
Nicotine addiction in smokers manifests itself in various symptoms. Quitting smoking in some people is accompanied by anxiety, irritability, nervousness, and increased fatigue. Currently, the basic mechanisms of neuroendocrine regulation of emotional reactions have been established, in which the reticular formation plays an important role. One of the areas of this formation - the “substantia nigra” - releases the neurotransmitter dopamine. It is believed that it contributes to the emergence of pleasant sensations when smoking, euphoria, making it difficult to give up the habit, which, as is known, promises many troubles and is a serious risk factor in cases of a number of major non-communicable diseases [16].
Among measures to combat smoking, much attention is paid to psychological assistance. Basic tips for overcoming this addiction are given in the report of the WHO Expert Committee [15]. The dose of tobacco smoke can be reduced:
- smoking fewer cigarettes;
- taking a shallow puff;
- leaving large cigarette butts, since the concentration of the most harmful components of tobacco smoke increases as the cigarette is smoked;
- taking fewer puffs from each cigarette;
- taking out the cigarette after each puff.
I would like to note that, unfortunately, the fight against smoking is still a very difficult problem. Medicines that make it easier to quit smoking contain nicotine without other harmful ingredients of tobacco smoke: Nicorret or nicotine gum, Nicotinella in the form of skin applications, etc. However, the use of medicines in most cases does not give the desired effect.
A review of foreign literature indicates that, despite the widespread use of self-control methods, hypnosis, acupuncture, general programs, analysis of behavioral reactions, and prescription of medications, a positive effect was achieved only in 10-40% of cases [3].
There are tens of millions of smokers in our country, and their number is steadily increasing. Over the past decade, the number of women and schoolchildren who smoke has increased sharply [17]. Depressing fact!
According to leading manufacturers and sellers of tobacco products, the Russian market is one of the largest in the world. However, if such trends continue, we can “catch up and overtake” in this regard, gaining the dubious reputation of “leaders”. Although currently the country sells tobacco products for every taste - both domestic and imported, the import of which is poorly controlled.
Medical measures to combat smoking alone are clearly not enough, especially considering the flow of deafening, intrusive cigarette advertising. What kind of effectiveness of these measures can we talk about if patients sometimes see doctors smoking even in the office where they are receiving treatment?
At the same time, our four-year epidemiological program for stroke prevention showed that active health education work can achieve certain results in the fight against smoking. During this period, the intervention population became less likely to smoke compared to the control group (15.9% and 24.1%, respectively).
Smoking can be fought not only and not so much by developing and actively implementing effective preventive programs that take into account modern living conditions, but by carrying out government measures that help solve the problem of smoking, the importance of which is so obvious.
Literature
1. Towards a healthy Russia. M. 1994, p. 27. 2. Aleksandrov A. A. Smoking and health // Doctor. 1998. No. 2. P. 17-22. 3. Shultsev G.P., Vasin A.N. Systemic effects of smoking: Foreign review. lit. // Wedge. honey. 1992. No. 2. P. 17-22. 4. Hoffman D., Winder E. L. Chemical composition and bioactivity of tobacco smoke. In the book: Smoking and health (MAIR materials)/Ed. D. G. Zaridze, R. Peto. M., 1989, pp. 168-191. 5. Kanareikin K. F., Bakhur V. T., Manvelov L. S. Alcohol and smoking as risk factors for cerebral stroke // Klin. honey. 1987. No. 1. P. 17-23. 6. Ernst E., Koenig A., Matrai B., Filpiat B., Stieber J. Blood rheology in healthy cigarette smoker Results from the MONICA Project // Augsburg. J. of vascular biology and thrombosis. July - August, 1988. Vol. 8, No. 4. R. 385-386. 7. Laeson PS, Haag HB, Suvette H. Tabacco. Experimental and Clinical Studies. Baltimore, 1961. 8. Burn JH, Leack EH, Rund MJ, Thompson JWJ // Physiol. 1959. Vol. 148. R. 332-352. 9. Haimovici H. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. 1948. Vol. 68. R. 516-520. 10. Hueper WC Arch. Path. 1943. Vol. 35. R. 846-856. 11. Kubota K., Yamaguchi T., Abe J. et al. // Stroke. 1983. Vol. 14. R. 720-724. 12. Shmidt E.V. Zhurn. neuropathol. and a psychiatrist. 1985. No. 9. P. 1281-1288. 13. Wolph Ph., Cobb JL, D. Agostino RB Epidemiology of stroke in stroke. // Pathophysiologi. Diagnosis and Management. Second Edition. H. J. Barnet, J. P. Mohr. BM Stein, FM 14. Whisnant JP, Homer D, Ingall TJ et al. Duration of cigarette smoking is the strongest predictor of severe extracranial carotid artery atherosclerosis // Stroke. 1990. Vol. 21. No. 5. R. 707-714. 15. Smoking and its impact on health. Report of the WHO Expert Committee. 16. Bloom F., Leiserson A., Hofotedter L. Brain, mind and behavior. M. Mir, 1988, p. 248. 17. Russian statistical yearbook, State Statistics Committee of Russia. M., 1994.
Clinical picture of withdrawal syndrome
The first signs of withdrawal syndrome appear very quickly - 2–2.5 hours after the last cigarette smoked, reaching a peak within 24 hours. How long nicotine withdrawal lasts depends on many factors, in particular, on the smoking experience and the character of the smoker. Typically, the main symptoms persist for 2–3 weeks, with individual manifestations lasting up to several months. Often, addicts admit that they don’t mind smoking even 2–3 years after their last cigarette.
In addition to the passionate, almost irresistible desire to go on a smoke break, the acute period of withdrawal syndrome manifests itself:
- malaise;
- weakness;
- irritability, intolerance, anxiety;
- worsening mood;
- increased appetite, and the smoker usually prefers snacks, candies, etc., rather than full meals;
- headache.
A cough appears a little later, it is difficult for a person to focus his attention on anything, he suffers from insomnia at night, and on the contrary, drowsiness during the day. Also, withdrawal syndrome when quitting smoking is typically characterized by a decrease in blood pressure and exercise intolerance. Independent attempts to quit smoking are often accompanied by the appearance of extra pounds, since the desire to “binge” smoke breaks persists for many months.
Why is it important to treat nicotine addiction?
On average, one cigarette contains up to 0.5 mg of nicotine; the conventionally lethal dose for humans is about 60 mg.
Physiological effects of tobacco include:
- narrowing of peripheral vessels;
- increased peristalsis;
- general decrease in the speed of metabolic processes;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased excitability;
- tachycardia and palpitations.
In the long term, smoking negatively affects the functions of almost all organs and systems. First of all, this addiction is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Of course, the respiratory tract is the first to be affected. But smokers are more often diagnosed with malignant neoplasms of the larynx and trachea, stomach, intestines, and liver.
There is a high probability of developing:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- heart attack;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- gastric ulcer, nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- obstructive pulmonary disease.
When smoking, respiratory viral infections are much more severe, women experience menopause earlier, and the risk of osteoporosis increases. The pathological habit does not have the best effect on the appearance and condition of the teeth.
How to relieve withdrawal symptoms
As practice shows, about 90% of smokers declare their desire to get rid of this bad habit, but only 5–7% succeed without professional help. The most common cause of relapse is the influence of stress factors and other external circumstances. Moreover, serious health problems do not deter many from returning to tobacco.
At Ugodiya, the specialists know perfectly well how to help not only get rid of the symptoms of withdrawal symptoms when quitting smoking, but also cope with the disease in general.
There are several methods to treat nicotine addiction. This:
- replacement therapy;
- consultations with a psychologist;
- coding;
- physiotherapy.
As a rule, monotherapy does not bring the desired result, so doctors prefer complex treatment. To relieve acute symptoms of withdrawal, medications containing minimal doses of nicotine are indicated, which are available in the form of tablets, chewing gum, patches, and sprays. They do not differ in their mechanism of action; a specific agent is chosen solely on the basis of the patient’s personal preferences.
As the symptoms of withdrawal syndrome ease, the dose of nicotine-containing drugs is reduced. To eliminate nervousness, anxiety, restlessness and correct sleep disorders, sedatives are used. Plant-based sedatives are the safest, however, with a long history of addiction and pronounced manifestations of withdrawal, the effect of medicinal herbs is usually not enough.
In such cases, the specialist individually selects antidepressants and/or sleeping pills. Application begins with a minimum dose, which is then either left unchanged or increased to a therapeutically reasonable dose. At the same time, a course of cognitive behavioral psychotherapy is started.
After eliminating the main symptoms of withdrawal syndrome, acupuncture and coding are recommended. This approach allows you to achieve a positive result in the shortest possible time and avoid relapse.
Smoking treatment
In our clinic you can undergo a full course of treatment for nicotine addiction, which includes medication and psychotherapeutic treatment. We have helped many smokers quit cigarettes, even with a long history of addiction. Please note that daily nicotine intoxication is dangerous in itself, and also leads to chronic respiratory diseases. Therefore, every day that you continue to smoke, the cost of treatment will increase.
We strongly recommend that you seek help today, thereby maintaining your health and saving on smoking cessation treatment. At any time, you can call our call center, its number is listed on the website page, or fill out the feedback form, and we will call you back. Get rid of the painful addiction to cigarettes and breathe deeply.
Bibliography:
- Andreeva T.I. Tobacco and health.
- Amirov N.B. Tobacco epidemic: pharmacological control options.
- Melnichenko G.A., Butrova S.A., Larina A.A. "The effect of tobacco smoking on health and body weight." Federal State Institution Endocrinological Research Center, Moscow.
- Kovaleva G.M., Kozachenko V.F., Makiev A.G., Bogachenko S.M. The effectiveness of treating nicotine addiction (tobacco smoking) using various methods. KDP FGKU "1602 VKG", Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, Rostov-on-Don.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
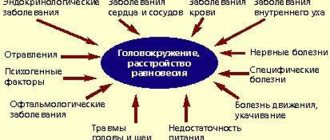
Dizziness from smoking
It doesn’t matter what you prefer to smoke: convenient portable cigarettes, aristocratic cigars, a fashionable vape, a hookah or a pipe. Sooner or later you have to figure out why you feel dizzy when you smoke.
This question arises for almost everyone. To be clear, we are talking about tobacco and its derivatives, not marijuana or other things that some people use.
The symptoms are probably familiar to most people who have inhaled tobacco smoke. After smoking, the smoker often feels dizzy and staggers. There are other side effects: it may simply make you feel nauseous, or it may even lead to vomiting. You might even lose your balance and fall.
Let's understand the physiological causes of the phenomenon in order to understand how to deal with this effect or, at least, weaken and reduce it
First of all, it is important to realize: if you start to shake, feel dizzy or feel tense, this is normal and you should not panic. These effects can be dealt with in accessible ways.