: Reading time:
A psychotherapist with more than 14 years of experience, Krailina Irina Sergeevna, talks about effective methods of self-help for panic attacks, how they work, and the role of psychotherapy.
A person who has experienced a panic attack for the first time thinks that something extraordinary, terrible, catastrophic has happened to him.
Many of my patients, when they learn ways to control their emotions, thoughts and body, exclaim: “Oh, if only when this happened for the first time, someone told me that this is a disorder well known to doctors and psychologists, that it can be treated, and most importantly “They don’t die from it!”
After all, then, at the very beginning, there was one most terrible thought that covered everything in the world like a black cloud: “No one knows what’s wrong with me. I will die".
Therefore, a person tries to get first aid by calling an ambulance, or going to a therapist or cardiologist.
Many people try to fight this disorder on their own, looking for recommendations and advice on how to get rid of panic attacks. Usually on the Internet. There is a lot of information there, often it is scattered and contradictory.
Therefore, I will try to systematize information on recommendations and methods of self-help and talk about the benefits of psychotherapy.
For those who want to better understand the topic, the article contains “More details” blocks: you need to click/tap on them for additional information to appear. If your goal is to learn only about self-help techniques, just read the plain print.
Learn more about the mechanism of development and symptoms of panic attacks
Click on the title to read the text
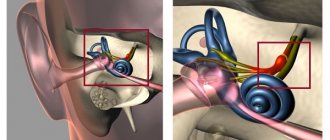
A panic attack is an unpredictable attack of acute anxiety (panic) with bodily symptoms for which the autonomic nervous system (hereinafter referred to as the ANS) is responsible.
Scheme 1. How the autonomic nervous system (ANS) works
In an individual, these symptoms may be present in full or in part:
- heartbeat;
- rise in blood pressure;
- frequent shallow breathing;
- feeling of suffocation, tightness in the chest;
- goosebumps;
- cold extremities;
- dizziness;
- pallor;
- sweating;
- urge to defecate;
- nausea;
- trembling in hands.
These symptoms are a manifestation of autonomic crises (sympathetic-adrenal, vagoinsular or mixed). Often the attack is accompanied by fear of death, loss of control or madness, as well as a feeling of unreality of what is happening or change in one’s self.
Lasts for minutes and ends with the passage of a large amount of light-colored urine. The person feels broken and empty.
Vegetative crises can be a manifestation of certain somatic diseases (endocrine, cardiovascular system), can occur during pregnancy, taking certain medications, or occur as isolated episodes against the background of overwork or alcohol abuse.
When doctors have ruled out somatic pathology, but panic attacks recur, it is more correct to call it a panic disorder.
The reason for the recurrence of panic attacks is a special form of thinking (when anxious traits are combined with perfectionism, the need to control everything) plus instability of the autonomic nervous system (what doctors used to call vegetative-vascular dystonia).
After the first panic attack, a person is in constant anxious anticipation of its repetition. The slightest unpleasant sensation in the body or just a thought can trigger a cascade of somato-vegetative reactions that support and reinforce each other through the mechanism of a vicious circle and lead to panic.
To clearly explain how different self-help methods work, let’s consider a person as an integral system and highlight 4 components:
- the human body;
- his emotions;
- thoughts;
- the external environment with which it interacts.
These components interact with each other and influence each other.
An example of the interaction of body, emotions, thoughts and environment
Click on the title to read the text
For example, support from the environment, family, gives confidence (the thought) that help will be provided in any case. The level of anxiety (emotions) temporarily decreases and vegetative symptoms go away (body). The trouble is that environmental support does not completely eliminate panic disorder. She only supports the belief that one cannot cope with the disorder on one’s own.
Read in the article:
- Stress: causes, symptoms and consequences
- How to cope with stress?
- The essence and principles of breathing exercises
- Why do breathing exercises help relieve stress?
- Preparing to do breathing exercises
- Effective breathing techniques
- Additional benefits of breathing exercises
Breathing exercises can significantly improve the condition of the body. It is believed that breathing helps unite the body and mind, relax, relieve anxiety and stress, cope with insomnia and solve a number of other problems.
Stress: causes, symptoms and consequences
Stress is a condition in which the body uses all its reserves. This is how the reaction to various factors manifests itself.
A little stress can sometimes even be beneficial, as it triggers the release of adrenaline into the blood, which helps to cope with difficult situations. However, a prolonged stressful state has an extremely negative effect on the body, reduces immunity and causes mental problems.
Stress can be caused by a variety of situations:
conflicts, dissatisfaction with oneself or others, life in general, lack of proper rest, loneliness, etc. It is unrealistic to eliminate all factors, so sufficient attention should be paid to the prevention of such conditions and recovery from them.
Main symptoms
, indicating the presence of stress, are considered:
- irritability, attacks of anger for no apparent reason;
- attempts to avoid any communication;
- lethargy, passivity;
- increased fatigue;
- insomnia;
- panic attacks;
- tearfulness;
- nervous tic.
The list goes on and on, but stress manifests itself differently for everyone, so it is not always easy to recognize.
In addition, there is a condition with similar symptoms: burnout syndrome
. It manifests itself in loss of motivation, reluctance to do usual things, and a negative attitude towards them. Fatigue and signs of exhaustion quickly appear, there is a feeling of guilt and attempts to justify oneself. The syndrome may also be accompanied by physical manifestations: disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, sleep problems and headaches.
In both situations, simply eliminating the symptoms is not enough. It is necessary to identify the causes of anxiety, fatigue and depression, and try to eliminate them, and if this is not possible, change your attitude.
Tics and obsessive movements
It was believed that nervous tics arise during age-related crises (new stages of independence), which are observed at 3-4 years and 7-8 years.
It is at this time that children first encounter developmental crises:
- new skills are acquired;
- the child's behavior changes;
- personal characteristics are being formed.
The cause of this condition is, on the one hand, instability of work, immaturity of the nervous system as a result of:
- Chronic intrauterine hypoxia:
- maternal diseases during pregnancy (blood diseases, cardiovascular pathology, diabetes mellitus);
- Intrauterine infections:
- Acute hypoxia during childbirth:
- Birth injuries.
- Taking medications by the mother during pregnancy.
- Prescribing medications for a newborn after birth.
- Bilirubin encephalopathy as a result of prolonged jaundice.
The cause of tics and obsessive movements can be regular long-term spending of time in front of a TV screen or at a computer - this disrupts the alpha rhythm in the brain, which is responsible for the calm and tranquility of the baby.
As well as low physical activity of the child.
Acute stress is considered the main provoking factor:
- acute or chronic traumatic situation that the child cannot cope with on his own;
- constant noise or other irritants;
- psychological trauma in a child;
- frequent somatic diseases.
Anxiety is considered a protective mechanism of the brain to prepare in advance for the onset of a dangerous event and speed up reflex activity.
Therefore, during this period, the baby’s brain is in a state of constant anxiety and anticipation of danger. At the same time, the ability to voluntarily suppress the excessive activity of brain cells is gradually lost.
It must be remembered that tics cannot occur in an infant - any obsessive movements at this age are associated with organic pathology of the nervous system and brain and require immediate diagnosis and treatment.
The danger lies in the fact that these movements become fixed in the form of a pathological habit, which over time transforms into tics, and subsequently into the neurosis of obsessive movements.
For mild cases of the disease, sometimes a course of sessions with a neuropsychologist, psychologist or behavioral therapist is sufficient. But you definitely need:
- temporarily limit computer use and TV viewing;
- spends more time outdoors with the child;
- examine your health condition and eliminate all possible somatic causes. If necessary, various sedatives are prescribed;
- organize more movements and physical activity;
- art therapy activities, music therapy, neurocorrectional classes have a beneficial effect;
In addition, you need to realize that the causes of this disease lie in the psycho-emotional sphere. Very often, tics and obsessive movements are just the tip of the iceberg, which is visible to the naked eye, and the problems lie deeper. And if you try to eliminate the manifestations of (i.e.) tic, the problem (failure, conflicts, stress, overexertion, low neurodynamics, lack of communication skills, school “failure”) may worsen, and the SOS signal for others and parents may become louder and stronger - develop into enuresis, logoneurosis, encopresis. Therefore, ignoring or trying to solve the problem of obsessive movements by keeping silent, making comments, or pulling back can lead to an even greater intensification and complication of the problem.
How to cope with stress?
One of the most effective ways to prevent stress is a healthy lifestyle: proper nutrition, physical activity, and giving up bad habits play an important role in preventing stress.
Yoga, relaxation techniques and special breathing exercises for stress can help cope with stress. This complex includes breathing exercises that are performed in a certain sequence. However, it should be remembered that if performed incorrectly, the exercise can cause harm, so it is advisable to consult a doctor and choose a complex, taking into account the characteristics of the body.
The essence and principles of breathing exercises
To understand the essence and principles of breathing exercises, it is worth understanding the types of breathing itself. It happens:
- upper
, when the diaphragm practically does not tense, breathing occurs through the upper part of the chest; - medium
- air enters due to the expansion of the middle part of the chest, the diaphragm moves slightly downwards; - lower
– maximally lowered diaphragm and relaxed abdominal muscles; - complete
- a combination of all of the above types with maximum filling of the lungs with air; - reverse
, when when inhaling, the abdominal muscles tense and the diaphragm lowers.
There is also the option of delayed breathing, when there is a pause between inhalation and exhalation. This is the option used in yoga. The founders of this teaching believed that strength and energy fill the body while holding the breath.
Breathing exercises also come in various types, but the essence of any of them comes down to three points: artificial difficulty, holding and slowing down breathing. Thus, the benefits of exercise are based on weakening breathing.
Why do breathing exercises help relieve stress?
Situations often arise in life that cause strong feelings and anxiety. This is just a stone's throw away from real stress, which becomes chronic over time. One of the simplest and most accessible ways to deal with stress is through special sets of breathing exercises.
Numerous studies have proven that breathing techniques really help relieve nervous tension, forget about insomnia and get rid of depression. With a conscious method of breathing, the heart rate slows down, which makes it possible to calm down and better control oneself, emotions and sensations.
Stress relief also occurs due to muscle relaxation, activation of the production of endorphins - “happiness hormones”, lowering blood pressure, and stimulating the functioning of the lymphatic system. Special exercises help restore your voice and recover from a cold.
When should you do breathing exercises?
You need to start breathing correctly in advance, as soon as you feel that a panic attack is approaching. But how to recognize it? What are its symptoms? Experts identify several signs of the onset of a panic attack:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- feeling of lack of air;
- sense of anxiety;
- excitement;
- confusion of thoughts and consciousness;
- a person ceases to control his actions;
- sensation of goosebumps under the skin;
- heavy sweating;
- rapid pulse;
- rapid heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of a lump in the throat;
- rapid rapid breathing.
Very often, it is difficult for a person who suffers from this illness to recognize the onset of a panic attack. Most people cease to understand what is happening around them when a feeling of fear arises.
Preparing to do breathing exercises
At first glance, using breathing techniques is very simple, but in fact some preparation is required. To begin, try concentrating on your own breathing and observing it. As soon as you think about the rhythm and depth of your breathing, you will immediately feel that it is changing.
In such a situation, the speed of inhalation and exhalation slows down, and the normal rhythm evens out. Usually we use only the upper abdomen and the area near the lower ribs when breathing. But breathing practices involve opening the whole body. To start:
- Choose a comfortable position (sitting or lying down).
- Place your hands so that your fingertips are in your lower abdomen.
- Try directing a few breaths there, expanding the abdominal area.
- Gradually increase the depth of inhalation.
- Relax your throat completely.
- Try to direct your breath to your spine, feel how the back of your torso fills with air and “deflates” as you exhale.
Even 5 minutes of such breathing helps cope with stress. To achieve a more noticeable effect, you should master and regularly perform special exercises.
Getting acquainted with breathing techniques should start with the simplest exercises. For example, immediately after waking up, sit up in bed and close your eyes. With your mouth open, take 3 loud breaths in and out, trying to feel the contraction of your abdominal muscles. Imagine that you are breathing on a mirror so that it fogs up. Inhale and exhale through your nose for a few more minutes.
Pay attention to how you breathe while concentrating, when you are very nervous. At such moments, breathing becomes intermittent and shallow. To cope with stress, inhale through your nose, hold your breath for a few moments, and exhale.
Relaxation, restoration, calmness
The benefits of such exercises are undeniable. Deep breaths saturate the body with oxygen to the maximum, which means that metabolism noticeably improves, the functioning of all systems and organs is normalized, the skin is evened out, a healthy glow appears, and the head becomes clearer. Inhaling and exhaling slowly helps calm the nervous system. But often it is frayed nerves that are blamed for various diseases.
Article on the topic The Science of Relaxation. How to help yourself with stress
With the help of special exercises you can overcome stress, relax your muscles, restore your voice, and even fight a cold. The main thing is to follow a number of simple rules.
It just seems like there is nothing complicated in the breathing process. In fact, not everyone knows that you should breathe smoothly, without jerking, so that both the chest and the diaphragm take part in the process. Inhalation must be done through the nose, because... It is in the nasal cavity that the air is heated and humidified, as well as cleansed of dust. True, in some cases, for example, with a runny nose, it is allowed to breathe through the mouth.
Ideally, you need to do breathing exercises in the fresh air. And in the summer this can be done. In general, it is recommended to exercise outside while the air temperature is within +5 degrees. When it is lower, there is a risk of catching a cold - in this case you need to train in a well-ventilated area.
5 simple breathing exercises that will help you cheer up
More details
Effective breathing techniques
There are many stress-relieving exercises based on breathing techniques. You can try different methods and choose those that best affect your emotional state and give the most tangible effect:
- Diaphragmatic breathing
- Lying on your back, place your palms on your stomach and take a deep breath through your nose. Concentrate on the breathing process and the anterior abdominal wall. Exhale long through your mouth, pressing your palms onto your stomach. - While sitting, lying on your back or standing, inhale for 3 counts, hold your breath for 1-2 seconds, exhale for 7 counts.
- Sitting on a chair, close one nostril with your thumb, inhale slowly through the other, pause for a second and exhale. Repeat the cycle with the other nostril.
- While lying down, place your hand on your stomach and inhale slowly through your nose, feeling the abdominal wall rise. Push the air out completely by contracting your abdominal muscles.
- Inhale and exhale through your nose as quickly as possible, keeping your mouth closed.
- Find a square-shaped object. Look at its upper left corner and inhale, then at the upper right corner - hold your breath. Look at the lower right corner and exhale, look at the lower left corner - relax and smile.
If signs of dizziness appear, you should stop exercising and take a break. If you do the exercises regularly, over time your dizziness will stop.
First aid for acute stress
If you find yourself in a stressful situation unexpectedly (someone made you angry, your boss scolded you, or someone at home made you nervous), you begin to experience acute stress. First, you need to gather all your willpower and command yourself “STOP!” in order to sharply slow down the development of acute stress. To be able to get out of a state of acute stress and calm down, you need to find an effective way of self-help. And then in a critical situation that can arise every minute, we will be able to quickly navigate by resorting to this method of helping with acute stress.
Here are some tips that can help you get out of acute stress.
- Anti-stress breathing. Slowly take a deep breath through your nose; At the peak of inhalation, hold your breath for a moment, then exhale as slowly as possible. This is a calming breath. Try to imagine. That with each deep inhalation and long exhalation you partially relieve stress.
- A minute of relaxation. Relax the corners of your mouth, moisten your lips. Relax your shoulders. Focus on your facial expression and body position: remember that they reflect your emotions, thoughts and inner state. It's only natural that you don't want others to know that you're stressed. In this case, you can change your “facial and body language” by relaxing your muscles and breathing deeply.
- Look around and carefully examine the room you are in. Pay attention to the smallest details, even if you know them well. Slowly, without rushing, mentally “go through” all the objects one by one in a certain sequence. Try to fully concentrate on this “inventory”. Say to yourself mentally: “Brown desk, white curtains, red flower vase,” etc. By focusing on each individual subject, you will be distracted from internal stress, directing your attention to a rational perception of the environment.
- If circumstances permit, leave the room in which you are experiencing acute stress. Go to another place where there is no one, or go outside where you can be alone with your thoughts. Mentally disassemble this room (if you went outside, then the surrounding houses, nature) “piece by piece”, as described in paragraph 3.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, lean forward and relax. The head, shoulders and arms hang down freely. Breath calmly. Hold this position for 1-2 minutes, then very slowly raise your head (so that it does not become dizzy).
- Engage in some activity - no matter what: start washing clothes, washing dishes or cleaning. The secret of this method is simple: any activity, and especially physical labor, in a stressful situation acts as a lightning rod - it helps to distract from internal tension.
- Turn on soothing music, the one you love. Try to listen to it, concentrate on it (local concentration). Remember that concentrating on one thing promotes complete relaxation and evokes positive emotions.
- Take a calculator or paper and pencil and try to calculate how many days you live in the world (multiply the number of full years by 365, adding one day for each leap year, and add the number of days that have passed since your last birthday). Such rational activity will allow you to redirect your attention. Try to remember a particularly remarkable day in your life. Remember it in the smallest detail, without missing anything. Try to calculate what this day of your life was like.
- Talk about some abstract topic with any person nearby: a neighbor, a workmate. If no one is nearby, call your friend or girlfriend on the phone. This is a kind of distracting activity that is carried out “here and now” and is designed to displace the internal dialogue saturated with stress from your consciousness.
- Do some anti-stress breathing exercises. Now, having pulled yourself together, you can calmly continue the interrupted activity.
What are these breathing exercises?
Autoregulation of breathing.
Under normal conditions, no one thinks or remembers breathing. But when, for some reason, deviations from the norm occur, it suddenly becomes difficult to breathe. Breathing becomes difficult and heavy during physical exertion or a stressful situation. And vice versa, when they are very frightened or tensely expecting something, people involuntarily hold their breath (hold their breath). A person has the opportunity, by consciously controlling his breathing, to use it to calm down, to relieve tension - both muscular and mental, thus, autoregulation of breathing can become an effective means of combating stress, along with relaxation and concentration. Anti-stress breathing exercises can be performed in any position. Only one condition is required: the spine must be in a strictly vertical or horizontal position. This makes it possible to breathe naturally, freely, without tension, and fully stretch the muscles of the chest and abdomen. The correct position of the head is also very important: it should sit straight and free on the neck. A relaxed, upright head stretches the chest and other parts of the body upward to a certain extent. If everything is in order and the muscles are relaxed, then you can practice free breathing, constantly monitoring it.
We will not go into detail here about what breathing exercises exist (they are easy to find in the literature), but we will present the following conclusions:
- With the help of deep and calm autoregulated breathing, you can prevent mood swings.
- When laughing, sighing, coughing, talking, singing or reciting, certain changes in the rhythm of breathing occur compared to the so-called normal automatic breathing. It follows that the method and rhythm of breathing can be purposefully regulated through conscious slowing down and deepening.
- Increasing the duration of exhalation promotes calm and complete relaxation.
- The breathing of a calm and balanced person is significantly different from the breathing of a person under stress. Thus, by the rhythm of breathing one can determine the mental state of a person.
- Rhythmic breathing calms the nerves and psyche; The duration of individual breathing phases does not matter - the rhythm is important.
- Human health, and therefore life expectancy, largely depends on proper breathing. And if breathing is an innate unconditioned reflex, then, therefore, it can be consciously regulated.
- The slower and deeper, calmer and more rhythmically we breathe, the sooner we get used to this method of breathing, the sooner it will become an integral part of our life.
Additional benefits of breathing exercises
Breathing exercises not only help fight stress. They activate lung ventilation, reduce blood acidity, and this causes additional blood flow to the brain. As a result, concentration improves and a feeling of calm appears.
Such techniques are worth mastering for people who have sleep problems. For example, in a lying position, with one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach, you need to inhale through your nose for 4 counts. At the same time, it is important to ensure that when you inhale, it is not the chest that rises, but the anterior abdominal wall. Then you need to take a few regular breaths and exhale and repeat the exercise.
The benefits of various types of breathing techniques have been known since ancient times. Special exercises help cope with anxiety and insomnia and other symptoms of stress. But you need to perform such exercises correctly and regularly in order to feel their positive effects.