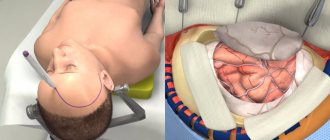
Main symptoms and indications for surgery
Seeking professional help is important for any type of defect.
They are classified by size (small - up to 10 sq. cm, medium - up to 30 sq. cm, large - up to 60 sq. cm, extensive - more than 60 sq. cm) and by localization (occipital, parietal, frontal, temporal, combined ). In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev (Moscow) cranioplasty is prescribed only after a comprehensive diagnosis using CT, MRI, radiography, and determining the nature of the problem. The main symptoms indicating the possible need for surgical intervention include:
- headaches and local pain in the area of the defect, which arise as a result of changes in weather and even air temperature;
- protrusion of the contents of the skull during physical exertion, sneezing, coughing or sudden movements of the head;
- memory and sleep disturbances, emotional agitation, difficulty performing intellectual tasks and concentrating;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system and problems with blood vessels of the neuro-endocrine system.
Experts include the elimination of cosmetic defects and sealing of the cranial cavity as indications for cranioplasty. In the second case, at least two goals are pursued: to normalize cerebral hemodynamics and liquorodynamics, to protect the brain from the effects of external factors.
Preparation for surgery and postoperative period
Preparation for cranioplasty includes a standard list of examinations in the form of:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test;
- blood clotting studies;
- tests for hepatitis, HIV infection;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- electrocardiography, fluorography.
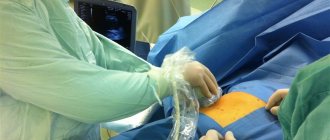
Cranioplasty surgery can take a long time and lasts on average 2-3 hours, so it is important to prepare the patient as well as possible. General anesthesia is used for pain relief. 2 weeks before the operation, anticoagulants are canceled, the day before the patient is given a cleansing enema, and in the evening food and water intake is stopped. The hair from the head in the intervention area is shaved off.
In the operating room, the surgeon treats the scalp with an antiseptic, makes an incision in the soft tissue and begins to restore the structure of the skull using prepared materials. After fixing the graft, coagulation or suturing of the bleeding vessels is performed, the soft tissues are stitched in the reverse order, and the sutures are treated with an antiseptic.
The course of the postoperative period is determined by the type of cranioplasty and the nature of the pathology. In the first days, the person undergoing surgery may be bothered by a headache and pain in the suture area, a feeling of a foreign body and discomfort in the head, so the attending physician prescribes analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. To prevent infectious complications, broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated.
The consequences of cranioplasty depend on the nature of the pathology that led to the operation, as well as on the skill of the surgeon. The most common adverse effects are infectious complications, inflammatory changes in the wound area, bleeding, and excessive scarring in the area of graft placement.
Hospitalization in the absence of complications and a smooth course of the postoperative period lasts one and a half to two weeks. During this time, the tissues grow together, and on days 10-14 the sutures can be removed. Every day the wound is treated with an antiseptic and the bandage is changed.
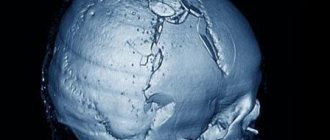
examples of cranioplasty results
There are no significant restrictions in the lifestyle after cranioplasty, however, the person operated on should be careful when playing sports, the types of which are dangerous for injury are prohibited. Avoid possible injuries and head impacts, which could damage the implant or cause it to dislodge. Otherwise, the lifestyle after cranioplasty is the same as for all other people.
Features of the operation
Surgical intervention should not be started when inflammatory processes are detected in the cranial cavity, in the meninges or brain. Contraindications also include noticeable mental abnormalities of the patient, the presence of a piece of bone tissue or a foreign object in the cranial cavity, and bulging of the brain in the problem area. If visual examination and diagnosis do not reveal any of the listed points, surgery is prescribed.
Skull plastic surgery after trephination and other similar manipulations are called cranioplasty. It is aimed at restoring the integrity of the skull after decompression and stabilization operations, gunshot wounds, falls from a height, and mechanical damage. The choice of intervention technology depends on the timing of the plastic surgery, and it can be primary (1-2 days after injury), primary delayed (up to 2 weeks), early (up to 8 weeks), late (more than 2 months).
There are several rules that must be followed during any type of cranioplasty surgery:
- maximum possible preservation of bone tissue elements;
- use of separated fragments as an autograft;
- strict correspondence between the plate size and the size of the closure area;
- absence of sharp and too thin parts of the skull.
Elimination of a skull defect is a rather complex and responsible operation, the first step of which will be excision of the meningeal scar. All manipulations are performed as carefully as possible to avoid trauma to the brain tissue. For good adhesion of the skull bones and the implant, the edges of the entire problem area are exposed, and the material is necessarily installed “flush” with the skull bones. To prevent such a negative phenomenon as graft displacement, reliable fixation is carried out. Conventional soft tissue suturing is not enough.
Types of implants for plastic surgery
If you believe historical data, a description of materials for plastic surgery of a trepanation defect first appeared in the medical literature back in 1565. At that time, the choice of specialists settled on gold plates. Modern doctors have a significantly increased choice of materials. Main types of implants:
- Autografts. This involves the use of patient tissue, which is taken during the initial operation. It is possible to produce material of the required size from the bone of the cranial vault or rib. If the problem area is small, preliminary crushing of bone fragments is performed to achieve the desired size.
- Allografts. In this case, the doctor uses materials that have been canned, frozen, or decalcified. Materials refer to bones and dura mater taken from corpses and carefully processed.
- Xenografts. This type of transplant refers to materials taken from animals. This group also includes inorganic materials, implants made on the basis of hydroxyapatite (a mineral from the apatite group, an analogue of chlorapatite and fluorapatite).
When choosing, it is important to consider the following requirements: biocompatibility, plasticity, resistance to mechanical stress, no risk of infectious complications, compatibility with modern neuroimaging methods.
Today, such a service as skull plastic surgery with a titanium plate is quite popular. It is possible to manufacture a graft from titanium alloy, stainless steel, chromium- and cobalt-based alloy. But practice shows that the most suitable option is the patient’s own bone tissue. Therefore, the task of reconstructive neurosurgery specialists is to preserve skull fragments as much as possible during the primary operation.
Depending on the situation in the neurosurgery department of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev's methods are used: the uatoplasty method using a pedicle graft, free autoplasty, bone-saving method, adhesive osteosynthesis, grinding of fragments with subsequent placement on the dura mater.
Types of cranioplasty
Depending on what materials will replace the bone tissue, there are:
- cranioplasty with implantation of tissues of biological origin;
- plastic surgery of the defect using artificial materials.
If the patient’s own tissue is used during cranioplasty, then they speak of autoplasty. In the case of using biological preserved materials or tissues from animals, we are talking about alloplasty or xenoplasty.
Artificially created synthetic materials for cranioplasty are called explants. They can be made of metals (gold, platinum, steel, titanium, etc.) or acrylic resins (plexiglass, ethacryl, polakos K and R).
The list of synthetic materials used as implants on the skull is quite wide. They are considered inert, safe and quite durable, but are not without certain disadvantages, since they have both mechanical and biological effects on the human tissues surrounding them.
comparison of some types of transplant materials
Based on the time period from the moment of injury to the plastic surgery of skull defects, they are distinguished:
- primary cranioplasty - performed within the first two days from the moment of injury as the final stage of primary wound treatment;
- primary-delayed - carried out in the first 2 days - 2 weeks after the initial treatment of the wound, the tissues can be fused with loose connective tissue;
- early - no later than two months after the injury, during this period pronounced adhesions can be observed;
- late - after 2 or more months after receiving skull damage.
Autoplasty using one's own tissue can be free, when the tissue for transplantation is taken from a neighboring area of the head or another part of the body altogether. The disadvantage of the method can be considered the lack of nutrition in the transplanted tissue, which is why it may not take root. In other cases, autoplasty is performed with grafts on a feeding pedicle, which take root faster than a free tissue fragment due to preserved trophism through connection with the donor tissue. The disadvantage of the second method of cranioplasty is the impossibility of its use for large defects and the need for a repeat operation to separate the already established flap from the feeding pedicle.
Alloplasty, when the surgeon uses foreign materials, is much more widespread than autotransplantation. The source of material for skull plastic surgery can be bone, the dura mater of the brain, taken from a donor, specially processed and preserved.
When choosing a cranioplasty method, the surgeon is based on the parameters of the defect (diameter, nature of the edges, adequacy of treatment for wounds), the patient’s condition, the characteristics of the skin at the site of the proposed plastic surgery, the presence or absence of protrusion of brain tissue into the through defect of the skull, and the technical capabilities of the clinic.
If the patient’s condition allows, surgeons try to resort to bone-sparing cranioplasty operations for skull fractures. The necessary conditions for such operations are the satisfactory condition of the patient, the preservation of all vital functions, the absence of brain edema and protrusion of its tissue into the resulting bone defect.
To firmly connect bone fragments of any shape and size to each other, the method of adhesive osteosynthesis is widely used. Large fragments of the bones of the calvarium are preserved, while small fragments separated from the periosteum are first removed and treated with antibiotics, and then adhesive osteosynthesis is performed.
For injuries to the skull bones with the formation of free-lying bone fragments, surgeons can use the grinding technique, when bone fragments are turned into shavings placed on the dura mater of the brain, a film of fibrin, a thin sheet of gold, etc. The shavings of the patient’s own bone can be mixed with blood and special polymer. The grinding method is classified as a bone-preserving operation, since islands of bone chips subsequently serve as a source of new bone tissue formation.
Possible complications after surgery
If the patient’s own biomaterial is used during the operation, then the risk of any exacerbations will be minimal. The recovery period in this case will last less than with the installation of alternative grafts. Possible consequences of cranioplasty after trepanation:
- bleeding (reducing blood loss is achieved through infiltration of the skin);
- development of purulent-inflammatory processes (most often due to rejection of an artificial implant);
- infection of the problem area (the main reason is insufficient treatment of the operated area with disinfectants).
The capabilities of modern neurosurgery, a wide variety of surgical methods and materials make it possible to eliminate defects in the skull of any shape, size and level of complexity without consequences.
Are you interested in the price of skull surgery? Call our clinic and make an appointment with a neurosurgeon. Contact phone number. All further actions can be learned only during a face-to-face consultation.