Symptoms
BPPV develops more often in women. The most likely cause of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts (otoliths) in the inner ear canal. Head movements (tilts, turns, tilts) provoke short-term attacks of dizziness. Between episodes, the patient may experience nausea, fluctuations in blood pressure, loss of balance, and impaired thermoregulation. Regular intense attacks can cause such great inconvenience that the question of what to do with dizziness is in the first place for the patient. With timely treatment, BPPV does not cause lasting harm to health; the benign nature of the disease implies a decrease in the severity of the episodes.
Dizziness - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, therapeutic methods
The illusion of rotation that occurs in a person with dizziness is accompanied by eye movement (nystagmus). During diagnosis, the doctor uses certain methods to induce an attack in order to determine the direction of the nystagmus. This can be done using a device (a more accurate and reliable method) or visually when a feeling of rotation occurs.
There are 2 main therapeutic methods used for dizziness:
- Exercises. A special system of exercises is used to adapt the vestibular system to an unhealthy state. But this method is long-term (months of treatment), and also does not address the problems that cause dizziness.
- Maneuvers. For dizziness, positional therapeutic movements (maneuvers) are used. They (in particular, Epley's maneuvers) involve the doctor changing the position of the patient's head. With the help of maneuvers, it is possible to move the otoliths from the semicircular canals to the healthy part of the system, eliminating irritation. There is no pain during the maneuver and it usually lasts up to 30 minutes. It is often possible to get rid of dizziness after the 1st session of the maneuver; sometimes it is necessary to repeat the procedure.
Treatment of BPPV methods and exercises
Having understood the essence of the problem, the patient draws the correct conclusion: in order to avoid paroxysm, movements that shake the otoliths with the appearance of a reaction from their receptors should be avoided.
However, to rid the patient of the annoying syndrome, in addition to treating the underlying pathology that caused it, a technique of positional treatment maneuvers carried out with the help of a neurologist is used:
- Epley;
- Brandt Daroff;
- Semont or other authors.
Their essence lies in training the vestibular system by giving the head strictly sequentially changing positions.
If necessary, microsurgical interventions are used on the inner ear with filling of the affected semicircular canal with bone chips or using labyrinthectomy.
Photo and video selection of BPPV treatment methods: Brandt Daroff exercises, Epley and Semont maneuvers:
Diagnostics
In addition to a good medical history (occurrence of dizziness with typical movements) and a standardized neurological examination, the presence of characteristic nystagmus on the Dix–Hallpick test is a key factor in the diagnosis of BPPV.
Physical examination
The survey includes the following measures:
- internal (blood pressure measurement, heart rhythm disturbances, heart defects, anemia, orthostatic dysregulation: Schelling test);
- neurological (examination of cerebellar symptoms, sensory polyneuropathy with loss of position perception, damage to the trigeminal or facial nerve):
- gait study - falling on one side (on the affected side - vestibular causes, on the healthy side - cerebellar causes);
- Romberg test - positive (in the case of proprioceptive and sensory ataxia), negative (in the case of cerebral vertigo);
- Unterberger test – positive (for cerebral and vestibular damage);
- nystagmus (with the vestibular type - nystagmus in one direction, never vertical; with the central type - complex, changing direction);
- ear examination with an otoscope (herpes zoster, otitis media, perforation);
- hearing test (one-sided deafness is usually of vestibular etiology).
Instrumental studies
This method includes the following approaches:
- ECG – if there is a suspicion of heart rhythm disturbances;
- laboratory examination - blood test, glycemia, creatinine, liver tests, basal TSH (with a targeted examination, all studies are not necessary);
- if necessary, examination by an ENT specialist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, orthopedist.
What exercises can you do at home?
You need to start classes with a warm-up - perform 5-7 bends and turns of the head.
A set of exercises for BPPV at home:
- In a sitting position, fix your gaze on an object at a distance of 1 m, relax your lower jaw and tongue. Turn your head from side to side, up and down, without taking your eyes off the object
- While sitting, fully extend your arm with a pencil. Slowly bring the pencil closer to the tip of your nose, constantly watching the object with your eyes. Return to starting position. Fix your gaze on the pencil, turn your head to the side, move your hand with the object in the opposite direction. But continue to follow the object with your eyes.
- Arrange the book so that it is convenient to read. Turn your head from side to side, up and down, while reading the text out loud.
- Place 2 objects with an interval of 1 m at a distance of 1.5 m from the eyes. Look straight ahead. Then look at the left target with one eye, fix your gaze, and turn your head to the left. Without changing position, look at the right object, after fixing your gaze, turn your head to the right.
- Sit on a chair. Place the ball on the side of the chair with your right hand and straighten up. Bend over, pick up the ball, return to the starting position.
- Toss the ball from hand to hand at eye level.
- Bend over, transfer the ball from hand to hand behind your knees.
- In a standing position, legs together, arms extended in front of you, turn your head to the sides. Then open and close your eyes on the count of 3.
- Stand on one leg for 10 seconds. Gradually increase the duration to 30 seconds.
- In a standing position, put one leg forward, arms crossed, palms resting on your shoulders. Change the position of your legs, fixing the position for 10 seconds.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, arms along the body. Tilt your torso slightly forward, tilt it back, move it from side to side. Repeat with eyes closed.
- Walk at your usual pace, turning your head to the right and left.
- Walk along the line facing forward, then backwards for 1 minute.
Symptoms
BPPV develops more often in women. The most likely cause of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts (otoliths) in the inner ear canal. Head movements (tilts, turns, tilts) provoke short-term attacks of dizziness. Between episodes, the patient may experience nausea, fluctuations in blood pressure, loss of balance, and impaired thermoregulation. Regular intense attacks can cause such great inconvenience that the question of what to do with dizziness is in the first place for the patient. With timely treatment, BPPV does not cause lasting harm to health; the benign nature of the disease implies a decrease in the severity of the episodes.
Indications for use
The Epley maneuver is prescribed by a doctor only after examination, examination and an accurate diagnosis. It is also worth remembering that these exercises can only be recommended for stable, non-progressive illness.
Among these pathologies:
- period after a stroke;
- benign positional paroxysmal vertigo;
- violation of movement coordination;
- osteochondrosis;
- recovery period after injury to the spine or brain;
- ear diseases;
- infectious pathologies.
Gymnastics does not affect muscle function in any way
Its main goal is to teach a person to control attention, so regular use does not cause any unwanted manifestations
Vestibular exercises for dizziness
The best workout is the swing. Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness must necessarily include swing riding. In this case, you need to start gradually, with rocking with a small amplitude. Each time it is necessary to increase the training time and the amplitude of the swings. Each person benefits from riding about 15 minutes a day.
Another possible way to simply train the vestibular system is to walk along a curb. We've all done this as children, trying to maintain balance for as long as possible. In adulthood, this exercise will help rid the body of seasickness. It is worth saying that vestibular gymnastics should be regular and progressive. After you have reached the limit, you need to rest for a week or two so that your body gets used to training, and then start exercising again.
The third simple exercise of vestibular gymnastics for dizziness is turning around yourself. It is necessary to turn around its axis in both directions about 10 times. After this you need to walk along a straight line. With each workout, you should increase the number of turns and the length of the straight line. Training the vestibular apparatus will quickly affect the general condition of the body, and dizziness will go away.
Vestibular gymnastics goes well with yoga. In order to get rid of nausea, it is enough to learn to breathe correctly
You need to study with trusted masters and in good centers, so that attention is paid not only to exercises, but also to breathing techniques and adjusting your way of thinking
In yoga there is one very good vestibular gymnastics breathing exercise that will quickly bring you back to normal. This technique does not require any special skills other than concentration. The exercise is performed with a completely straight back. It is necessary to exhale deeply with great effort, as if expelling the air from yourself. As you inhale, you should lower the diaphragm, inflate your stomach and fill the lower sections of your lungs with air to the limit. After this, you need to forcefully expand the chest, letting air into the middle sections of the lungs. Finally, due to the movement of the neck, the upper sections of the lungs are filled. Exhalation should be smooth, occurring in the same order: first the stomach, then the chest and neck. Remember to inhale through your nose and exhale through your mouth.
Vestibular gymnastics for the elderly has its own characteristics. They should avoid riding on swings, walking on curbs, and breathing too deeply. In various diseases, this can cause unpleasant or painful sensations in the body. Vestibular gymnastics after a stroke can be carried out only after examination by a doctor and his permission to practice. Therapeutic and preventive gymnastics under the supervision of an experienced specialist is the best solution for older people.
Vestibular gymnastics at home should be structured as follows:
The first week you need to practice turning your head in different directions, in circular movements. Do not be afraid of nausea, because this is quite normal. The main thing is to continue studying. The second week should be devoted to bending your torso back and forth and left to right.
At the same time, it is important to monitor your breathing and remember that you exhale when bending over. After 20 days, the training is supplemented with light boxing
You need to clench your fists and bend your elbows and box with an invisible opponent. Remember that your torso should also turn after your hand. The hand throw should be done with force. After this you should add walking. Step forward and then, without looking back. 10-15 repetitions will be enough.
At the same time, it is worth knowing that people who move little often get motion sickness.
This is why it is so important to play sports and run more. Great for active ball games
Vestibular gymnastics exercises
In such diseases, where there is tinnitus and various hearing impairments, gymnastics for the vestibular apparatus should be a mandatory attribute of treatment. If you experience dizziness, again, it would be a good idea to consult a specialist to identify the true cause of this phenomenon.
In any case, before performing the next set of exercises, you should consult with a specialist, and if severe pain occurs during the exercise, then the exercise should be stopped. Almost all exercises are performed 5-7 times and before performing them, do a little exercise in the form of arm swings, rotation of the shoulder girdle and squats.
- The starting position of the body is to stand straight, with your heels and toes together. The back is straight, the arms are lowered, and the stomach is slightly retracted. In this position, you need to raise your arms straight and close them above your head. This pose is held for five to seven seconds, after which you can return to the starting position and repeat.
- Standing straight on your feet, you need to alternately raise your left and right legs, holding for five seconds. Then, after successfully completing these actions, the exercise is complicated as follows: the raised leg is pressed against the other leg so that the heel is closer to the groin area and the toe is pointing down. In other words, the leg bent at the knee needs to be pressed against the other leg, while clasping it with both hands. Make sure that the bent leg is in the same plane with the other leg. Balance must also be maintained in this way for five to seven seconds.
- The essence of the exercise is to turn your head to the side and fixate at the extreme point for five seconds. At the same time, be careful and do not allow pain to arise in the neck.
- The head is tilted and raised: the top of the head is pulled up, after a delay at the extreme point for several seconds and returned to the starting position. Head tilts are performed in the same way.
- Tilt your head to the side - try to press your ear to your shoulder, without moving your shoulders. Fixation at the extreme point is also necessary here.
- Grab yourself by the shoulders and lean forward, trying to stretch the ligaments and muscles of the spine as much as possible.
Physician Epley Method
This exercise was developed by doctor Epley, after whom this exercise is named. It is also prescribed as vestibular exercises for BPPV (benign positional paroxysmal vertigo). Starting position: lying on the bed, arms along the body. The head must be turned 90 degrees in any direction and held in this position for 30 seconds. After waiting the allotted time, turn your head in the other direction and hold again for 30 seconds. Then, without changing the position of your head, turn to your side, while looking down. Again we delay for half a minute.
Therapeutic measures to eliminate pathology and discomfort
Conservative treatment without the use of drugs includes the following methods:
Brandt-Daroff method.
The patient can perform this exercise independently at home.
To carry out this technique, the patient needs to sit in the center of the bed and bend several times from side to side. Then the patient is injected back into a horizontal position and repeats the movements in a supine position.
It is necessary to rest the body for a minute, then repeat the indicated Brandt Daroff exercises.
The method for treating the disease is repeated three times throughout the day. The duration of the procedure is determined individually depending on the general well-being of the patient.
Semont maneuver
This technique can be performed either independently or with the help of a qualified specialist.
The patient sits on the bed, the doctor takes the patient's head with both hands and turns it sharply, then injects it on the same side without changing the position of the head relative to the original plane.
The patient should lie down until all discomfort disappears.
After rest, without changing the fixed position of the patient’s head, the patient is returned to a sitting position, the head is turned and placed on the opposite side, the patient should also rest. This exercise is repeated 2-3 times, once a day.
In cases where a patient suffering from benign paroxysmal vertigo has a life history of pathologies from the cardiovascular system, cardiac tonic drugs are administered before the procedure as a specific predication.
If nausea and vomiting occur during the procedure, patients are prescribed antiemetic drugs.
Epley maneuver
A procedure of this nature is carried out only by qualified specialists. The peculiarity of this method is that the procedure is carried out using smooth and slow body movements.
The patient should initially sit on the couch, the doctor takes the head with both hands and fixes the head, turning it to the side in the same position, the patient’s head is placed on his back. After this, the person’s body is turned over on its side, and then slowly seated in its original position.
This method of non-drug treatment is very effective and in most cases, repeating two or three sessions can help completely get rid of the pathological condition.
The effectiveness of this method depends entirely on how professional the specialist performing this procedure is.
Lempert maneuver
This technique is carried out exclusively by a qualified specialist. The initial position of the patient should be sitting along the couch. Turning the head forty-five degrees, fix it in the plane of the horizontal body on the side of the focus of the pathological condition.
After this, the patient is placed in a supine position on his back and the position of the head is slowly changed in the opposite direction, then the head is turned to the other side and the position of the body is changed from back to stomach, while the head should rotate together with the human body.
The exercise can be repeated several times, but with the condition of maintaining a rest period.
Surgical technique for treating the disease
Surgical intervention is performed in cases where conservative treatment of the disease has shown absolutely no positive results.
This treatment method is carried out very rarely and in quite exceptional cases.
For this purpose, surgical intervention techniques such as:
- filling the lumen of the semicircular bony canal of the inner ear with fragments from the bone structure, which is taken from another part of the skeleton of the human body. The most optimal bone for transplantation is the tibia;
- selective removal of nerve endings that innervate the vestibular canals of the human inner ear;
- total removal of structures and spongy substance of the bone labyrinth;
- destructive destruction of labyrinth structures using specially selected laser installations.
Absolutely all surgical methods are extremely traumatic for humans and therefore should be performed only for special medical indications.
After surgery, the patient must undergo antibacterial therapy in order to prevent the development of complications of an infectious nature.
To prevent dysentery as a side effect of antibiotics, the patient is prescribed probiotics in combination.
Diagnostic methods
The study of equilibrium functions is carried out through a comprehensive examination.
Physical examination
Physical examination methods:
- Detailed anamnesis. The nature and type of equilibrium disorder is determined.
- Study of spontaneous vestibular phenomena: standing, when walking, deviation of the limbs (the patient should stand straight, walk in a straight line for several steps, etc. - this allows you to control which side he is leaning towards, what feelings of dizziness he has). The examination provides important information about the external manifestations of balance disorders.
Instrumental studies
Instrumental research methods:
- If an organic cause is suspected, X-rays, CT, MRI (damage to the brain stem and cerebellum) are performed.
- Orientation study of brain nerve function to compare the functions of the right and left equilibrium apparatus.
- Stimulation testing of equilibrium functions (electronystagmography) usually requires special devices.
- Audiometric examination.
Damage to the lateral semicircular tubule
A lesion of the lateral RCC is detected with the patient lying down by turning the head in the plane of the canal from right to left and vice versa (roll test). Horizontal nystagmus occurs, with a clonic component directed downward, mainly when the affected ear is turned downward; if the healthy ear is located below, nystagmus also occurs, the clonic component of which is directed downward, but less pronounced.
In a quarter of patients, canalolithiasis in the lateral RCC is combined with canaloliasis in the posterior RCC. In contrast to downward-directed nystagmus, the clonic component of evoked nystagmus is directed toward the overlying ear. This form is combined with the location of otoliths in the anterior part of the lateral ACC or the otolith fixed to the cupula, while with freely moving otoliths, nystagmus occurs directed towards the underlying ear.
Test results may be influenced by cervical spinal canal stenosis, radiculopathy of the cervical segments of the spinal cord, severe kyphosis, restrictions of movement in the cervical spine: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Paget's disease, spinal cord injury, morbid obesity, Down syndrome. In this case, it is possible to use a Barany swivel chair.
If the test results are negative, a preliminary diagnosis of BPPV is made based on complaints of positional vertigo and is confirmed by successful performance of vestibular maneuvers.
If examination reveals a nystagmus that differs from that described above, as well as other neurological symptoms, it is necessary to exclude other lesions of the nervous system.
A number of types of dizziness and nystagmus appear only when the position of the head in space changes - they are positional.
Nystagmus and rotational vertigo can cause both central (for example, associated with damage to the brain stem or cerebellum) and peripheral (canalolithiasis, vestibular neuronitis, damage to the ear ganglion, perilymphatic fistula) lesions of the vestibular analyzer, as well as combined damage to central and peripheral structures - meningitis, intoxication.
Dizziness can be caused by circulatory disorders: thrombosis of the vestibular arteries, migraine, orthostatic hypotension, paroxysmal heart rhythm disturbances.
The relevance of the differential diagnosis of these causes is due to the fact that the central forms require special intervention.
The most commonly ordered test is an MRI of the brain. In some cases, diagnosis may require an orthostatic test, blood pressure and ECG monitoring, duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries/transcranial Doppler sonography, radiography of the cervical spine, and an ophthalmological examination.
Positional maneuvers are also used to treat the patient. Treatment is carried out with the participation of a doctor and takes into account the location of the otolith according to the diagnostic maneuver.
Patient reviews
Anzhelika Rogonova, 35 years old:
Frequent dizziness began and it was impossible to get out of bed. I sinned on the blood vessels, but after Dix Hallpike’s test, the doctor revealed the diagnosis. I’ve been going to physical therapy for a month now and doing exercises for BPP, the Brandt Daroff method, and I feel positive changes.
Alesya Rumyantseva, 28 years old:
She suffered from the flu very badly, and began to have heart problems, which also caused dizziness. But it turned out that it was otolithiasis and inflammation of the inner ear. I do Brandt Daroff vestibular gymnastics, go to the pool, treatment has just started, but I feel like life is easier.
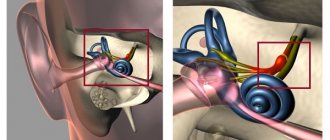
The vestibular apparatus is an organ that perceives changes in the positions of the head and body in space.
This organ is located in the inner part of the ear.
With poor development of the vestibular system, a person experiences nausea, vomiting, disturbances in consciousness, fainting and dizziness when changing position.
At a young age, such manifestations are rarely observed, but as a person ages, changes occur in the body that disrupt the functioning of this organ, so it becomes more susceptible to any changes in the coordination of human movements.
Vestibular gymnastics for benign positional paroxysmal vertigo
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder of the inner ear that causes paroxysmal dizziness in certain head positions. The main method of treating BPPV is to carry out the so-called rehabilitation maneuver - a special complex of vestibular gymnastics.
It should be noted that self-medication is possible only after a doctor has reliably diagnosed BPPV, since in cases of tumor or ischemic brain damage, as well as a high probability of compression of the vertebral artery, self-medication can complicate the provision of timely professional medical care and worsen the patient’s condition. The most adapted for the patient to perform independently are the Brandt-Daroff and Epley-Simon gymnastics.
Brandt-Daroff gymnastics
1. In the morning, after sleep, sit on the bed, straightening your back (Position 1) 2. Then you need to lie on your left (right) side with your head turned up at 45° (to maintain the correct angle, it is convenient to imagine the person standing next to you at a distance of 1 .5 meters and keep your gaze on his face) - Position 2 3. Stay in this position for 30 seconds or until the dizziness disappears 4. Return to the starting position while sitting on the bed 5. Then you need to lie on the other side with your head turned up 45 ° — Position 2 6. Stay in this position for 30 seconds 7. Return to the starting position while sitting on the bed (Position 1) 8. Repeat the described exercise 5 times
If dizziness does not occur during the exercise, it is advisable to perform it only the next morning. If dizziness occurs at least once in any position, then you need to perform the exercises at least two more times: in the afternoon and in the evening.
Epley-Simon Gymnastics
1. Sit on the bed with your back straight (Position 1) 2. Turning your head towards the affected labyrinth, stay in this position for 30 seconds (Position 2) 3. Lie on the bed with your head thrown back 45°, stay in this position for 30 seconds (Position 3) 4. Turn your head in the opposite direction, stay in this position for 30 seconds (Position 4) 5. Turn on your side with your head turned with your healthy ear down, stay in this position for 30 seconds (Position 5) 6. Return in a sitting position on the bed with legs down
The correct execution of the complex is shown in the following video clip:
It should be noted that independent implementation of the Epley-Simon complex is difficult at first due to the patient’s ignorance of the side of the diseased labyrinth; in addition, the opposite side may also be involved in the pathological process. In this regard, it is highly advisable to only continue the classes started by the doctor, and not self-medicate.
When to expect an effect
As experts and patients themselves say, a positive result after using gymnastics using the Brandt-Daroff method can be expected after completing the first set. You need to perform the maneuver 5 repetitions each morning, afternoon and evening.
Each set should take no more than 10 minutes. If an episode of dizziness has occurred, then it is better to perform the maneuver for 2 weeks. But doctors say that within a day after the gymnastics, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Vestibular gymnastics, regardless of which of the Brandt-Daroff or Epley maneuvers was used, is a safe and most effective way to independently reduce, and in some cases completely get rid of, the symptoms of dizziness.
If maneuvers do not help, then it is better to seek qualified help. The doctor will help you choose a different set of exercises and, if necessary, prescribe medication.
Step by step guide
The physician performing the Epley maneuver manually moves the person into a series of positions. This can also be done at home by a person who is experiencing symptoms of CDB. The steps for both versions are detailed below.
Steps of the Epley maneuver performed by a physician.
When a doctor performs the Epley maneuver, he or she does the following:
- Have the person sit upright on the examination table with their legs fully extended in front of them.
- Turn the patient's head at a 45-degree angle to the side of the dizziness where they experience the worst dizziness.
- Quickly move the person back so that their shoulders are touching the table. The person's head is pointed in the direction most susceptible to dizziness, but now at an angle of 30 degrees, so that it is raised slightly from the table. The doctor holds the patient in this position for 30 seconds to 2 minutes until the dizziness stops.
- Rotate the person's head 90 degrees in the opposite direction, stopping when the opposite ear is 30 degrees away from the table. Again, the doctor holds the patient in this position for 30 seconds to 2 minutes until the dizziness stops.
- They then turn the person in the same direction they are facing, onto their side. The side they experience the worst dizziness on will be facing upward. The doctor holds the patient in this position for 30 seconds to 2 minutes until the dizziness stops.
- Finally, the doctor returns the patient to a sitting position.
- The entire process is repeated up to three times until the patient's symptoms disappear.
Steps of the Epley maneuver performed at home.
It is best to have a doctor perform the Epley maneuver if the person experiencing BPSD has not previously used this technique.
After the doctor performs the Epley maneuver, the patient may want to repeat the procedure at home if they experience other symptoms.
A person experiencing HPV symptoms can follow these steps to get relief at home:
- Sit in bed with their legs extended in front of them and turn their head 45 degrees to the side where they feel most dizzy.
- Lie down with your head turned to the side and raised at a 30-degree angle from the bed. They should remain in this position for 30 seconds to 2 minutes until the dizziness stops.
- They should then turn their head 90 degrees to the other side and stop when it is 30 degrees away from the bed on the other side. Again, the person should hold this position for 30 seconds to 2 minutes until the dizziness stops.
- They should now roll onto their side towards the head, maintaining this position until the dizziness stops.
Treatment
At the moment, the treatment of otolithiasis often involves actions that facilitate the extraction of the otolith from the semicircular canal back into the vestibule. This allows you to relieve existing symptoms, but does not guarantee that the attack will not recur.
In situations where removal of the otolith is impossible, specialists resort to the method of repeated provocation of dizziness, which makes it possible to reduce the severity of symptoms (or even get rid of them altogether) thanks to central compensation.
After the attending physician has carried out the necessary actions, it is usually necessary to reduce vestibular excitability. For this purpose, special vestibulolytic drugs are used.
Most often, specialists prescribe betahistine dihydrochloride (Betaserc) to patients. The medication affects histamine receptors located in the inner ear and the vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system.
Betaserc improves blood flow and normalizes lymphatic pressure inside the cochlea and labyrinth. In addition, the drug helps increase serotonin levels, which also makes the vestibular nuclei less active. The optimal dosage of the drug is 24 mg twice a day.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe additional medications that will help eliminate nausea, dizziness and emotional stress, and will also help normalize blood circulation in general.
One of the most significant points regarding overcoming a disorder of the vestibular system is associated with performing sets of exercises that represent special vestibular gymnastics.
It is equally important to begin treatment as early as possible, as well as to provide rational psychotherapy, since in some cases (as, for example, with phobic pastural vertigo), the main cause of the disease can be psychological disorders, without eliminating which the entire process will be meaningless. It should also be taken into account that patients may require not only medication, but also surgical treatment
Health-improving gymnastics
First of all, we are talking about rotatory (facing the affected ear) tilts of the head. A lying or bending person holds the position for 10-15 seconds. Then he sits down, simultaneously turning his head in the direction opposite to the painful area.
You can also make turns by vertically rocking forward and backward. The desired result is felt already 1-2 days later in approximately 75% of patients.
Next, you should switch to specially designed therapeutic exercise programs:
Epley maneuver.
You need to sit on the couch in a sitting position and turn your head approximately 45° towards the sore ear. The specialist fixes the resulting position and places the patient on his back, also tilting his head to 45°. After this, you need to turn it in the opposite direction, and the entire body on the side where the healthy ear is.
The last step is to take the starting position, tilt your head and turn to where you feel dizzy. Repeat the entire complex 3-4 times.
Semont maneuver.
While sitting, keep your legs perpendicular to the ground. Turn your face 45° towards the ear that does not hurt. Fix the pose with your hands and lie on the side opposite to the side in which you turned your face.
You must remain in this position until the attack completely passes, and then, with the help of a doctor, lie on the other side without changing the position of your head. Wait until the attack is over again, then take the starting position. Repeat as needed.
Lempert maneuver.
Sitting on the couch, turn your head at the standard angle for such exercises in the direction where the pathological area is located. The physician must hold the patient's head throughout the maneuver. The person needs to be placed on his back and his face turned in the opposite direction. Then turn your head to where your ear is great.
Next, the body of the person who came to the appointment is turned so that he lies on his stomach. The head should be turned so that the nose points perpendicularly downwards. Turn the patient on the other side, and place the head so that its painful side is facing down. Return to the starting position through the healthy side.
Such techniques are usually quite sufficient to overcome the disease, so you should not resort to independently obtained folk recipes for treating dizziness, especially without obtaining the approval of a specialist.
Epley maneuver
The essence of the Epley maneuver is to position your head so that the dizziness stops.
To treat dizziness, the exercise therapy complex includes the Epley maneuver or maneuver. You can perform the exercise yourself, but a specialist should show all the basic techniques.
The essence of the Epley method for dizziness is to place your head at an angle so that gravity stops making you dizzy. Improvements occur after the first implementation of the complex, but provided that the person follows all the doctor’s recommendations for several days.
Indications: BPPV, period after a stroke, loss of coordination, osteochondrosis. Gymnastics speeds up the recovery process after head or spinal injuries and helps with ear diseases. Contraindications – confusion, disorientation, problems with breathing, heart, blood vessels. You will have to abandon the complex if after performing the maneuver your health deteriorates significantly.
The Epley maneuver is used as a diagnostic method if it is not possible to accurately diagnose BPPV, but there are all signs of pathology. The exercise can only be done with negative Hallpike tests.
Studies have shown that with regular performance of the Epley maneuver for dizziness, unpleasant symptoms quickly disappear. The technique is considered simple and safe. When performing exercises, the otoliths do not dissolve, but change their position in the inner ear and do not irritate the organ of balance. Relapses occur in only 20% of patients.
How to do it correctly
When changing body position, the head must be kept at an angle of 45 degrees.
Exercises must be performed quickly, but without jerking. The neck should be straight so that calcium salts do not enter the semicircular canal again. The appearance of slight dizziness is a sign of correct execution of the maneuver. The duration of the gymnastics is 10 minutes.
Technique for performing the Epley method for dizziness:
- Sit up straight with your feet on the floor.
- Turn your head to your ear at an angle of 45 degrees.
- Don't turn your head at the right angle, lie down on the couch, tilt your head back a little. Remain in this position for at least 1 minute.
- Turn your head the other way 90 degrees. Hold the position for half a minute.
- Turn your body and head in the same direction another 90 degrees, your face should be pointing down. Stay in this position for 30 seconds.
- Return to original position.
After the maneuver, you need to sit quietly for a quarter of an hour so that the otoliths do not move. For the rest of the day, you need to wear a neck or travel pillow to limit head movements and record the results of the gymnastics. For the next 2-3 days you need to sleep with your shoulders back and your head turned at an angle of 45 degrees. During the day after performing the exercise, you should not throw your head back.
Exercises are performed in a bright room without sharp, dangerous objects. Clothes and shoes are comfortable, the surface is smooth and soft. It is not recommended to do the maneuver alone, as you may feel very dizzy, feel nauseous, and will need help. Doctors recommend taking 100 mg of Dramamine half an hour before classes.
The lack of the desired result when performing exercises for dizziness may be due to insufficient neck extension, with blockage of the posterior semicircular canal. The therapeutic effect does not appear if the diagnosis is incorrect or if BPPV transforms from the posterior canal to the anterior one.
Symptoms of BPPV
An attack of dizziness can also occur when you turn your head with a jerk, as if you were shouting sharply.
The attack may have the character of a feeling of uniform swaying, as in “sea sickness,” and may, like it, cause nausea.
The recorded duration of the seizure does not exceed half a minute, although to those suffering from the pathology it seems equal to several minutes.
The attacks are either single or occur repeatedly at equal intervals of time, the frequency ranging from several per week to several over the course of a day.
Features include the short duration of the attack, the absence of dizziness in a constant position, and the absence of other accompanying symptoms in BPPV:
- severe headache;
- deafness in the problematic ear;
- noise in the ear.
Disorders of the vestibular system are characterized by paroxysmal attacks that last from 30 seconds to several minutes. The following symptoms usually appear:
- dizziness when changing head position;
- headache;
- feeling of objects moving around, swaying;
- weakness;
- lack of coordination;
- hearing impairment;
- nausea, rarely vomiting.
Tinnitus
- Sudden attacks of dizziness, especially during movements and spinning
- The duration of the attack is no more than 30 seconds
- The patient feels acute pain in the ears; the ear on the side of which the disorder occurred will hurt
- Feeling of nausea, vomiting
- Blurred visibility
- Sweating and fever
- Pale skin
- Dizziness occurs irregularly: the attack can be repeated several times during the day, or maybe a couple of times a week
If you lead a calm lifestyle and do not make sudden movements of your head, then attacks of dizziness may not bother you at all.
This condition is very easily confused with migraine aura and other types of dizziness that can occur with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as infectious diseases. In modern medicine, the following features are identified that help recognize positional vertigo:
- The disease occurs in attacks. The dizziness is not gradual. Each attack is unexpected for the patient and there is no justification for its beginning or end.
- This condition does not last more than a day.
- The disease may be accompanied by vegetative symptoms - pallor of the skin, increased sweating, elevated body temperature, nausea, and others.
- If the patient does not have an attack, then the state of health is stable, without any abnormalities.
- The course of treatment lasts no more than thirty days. The body quickly recovers from this pathology.
Essence and basic principles
The Epley maneuver or exercises are a special maneuver used to treat benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
This procedure is often carried out in a physiotherapy office, but it can also be done at home after a specialist shows all the basics of the technique. This maneuver was developed by Dr. John Epley, after whom it was named. The first time it was talked about was back in the 80s of the last century.
The Epley maneuver is a series of exercises that help relieve symptoms of dizziness. Numerous studies have proven that this technique is the simplest, safest and most effective in the treatment of dizziness caused by the deposition of calcium salts in the inner canal of the ear.
All these exercises do not eliminate the presence of otoliths, but only change their location. Such manipulations cause them to move to other areas of the inner ear that do not cause dizziness.
As a result, it turns out that this maneuver relieves all symptoms, but you need to do the set of exercises several times. The thing is that the first time the crystals can move a small distance.
There are a number of rules that must be followed:
- classes should take place in a well-lit room;
- there should not be any objects with sharp corners, carpet paths, or objects that could cause a person to fall near the patient;
- It is better to perform the exercise on a soft surface; a couch, yoga mat, or thick-pile carpet are suitable for this;
- the clothes a person wears should be loose, not restricting movements, so that he can move easily and freely;
- shoes on feet should be without heels;
- while performing exercises, someone must be present next to the person; it is unknown how his body will react to the exercise; someone needs to provide backup;
- if a person feels unwell or has symptoms of other diseases, then therapy is postponed until the person feels better;
- Even after the Epley maneuver is successfully performed, when the results sought are obtained, you will need to visit the doctor several more times to prevent a relapse.
Experts who recommend the Epley maneuver to their patients for symptoms such as dizziness note that after the first use of a set of exercises, serious changes are observed. The symptoms go away, but only if you follow all the prescribed recommendations for several days after them.
Prevention of cupulolithiasis
There are many reasons for the occurrence of BPPV; without provoking them, you can avoid an unpleasant disease. Dizziness of any etiology is not scary if you follow a healthy lifestyle, do exercises in the morning and hardening. Benign positional vertigo syndrome is more complicated, since the causes of its occurrence are not always clear. However, a general set of actions will help avoid not only DDZ:
- If the patient has already had the disease, then therapeutic maneuvers should be performed several times a week so as not to provoke a relapse.
- Maintaining a daily routine that requires 7-8 hours of sleep.
- Active lifestyle, training to strengthen the body.
- Proper nutrition with a minimum content of salty, fatty, spicy foods.
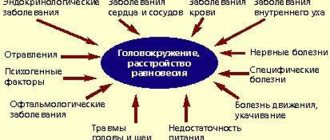
Etiological factors in the development of functional dizziness (causes)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), a very complex condition in etiology, in some cases it is not possible to establish the true cause of the disease.
The most common causes of BPPV include:
- traumatic injuries of the skull and concussions;
- inflammatory processes in the labyrinth of the inner ear;
- undergone surgical interventions in the head area.
Features of symptomatic manifestations
Symptomatically, benign paroxysmal vertigo manifests itself in the form of a feeling that objects around are rotating, this feeling appears after a sudden change in body position.
Paroxysmal dizziness usually manifests itself in the morning after sleep; it is difficult for a person to navigate in space after getting out of bed.
The duration of the paroxysmal period is, as a rule, no more than three minutes, then it goes away on its own without the use of auxiliary techniques.
An important aspect in diagnosing the disease is that benign positional vertigo is not accompanied by syndromes of organic disorders of the nervous system.
With this pathology, no pathologies develop in the organs of hearing, vision or smell. Thus, the disease does not pose a particular threat to human life, but causes some discomfort.
Causes of otolithiasis
Otolithiasis is attack-like (paroxysmal) dizziness. Its characteristic feature is the factor that provokes dizziness - this is a change in the position of the head. Otoliths in the ear, namely the inner ear, irritate the receptors, causing the patient to experience various ailments.
Unidentified causes
In 40-50% of cases, it is not possible to establish the exact cause of dizziness. This is due to the fact that there are many diseases that cause dizziness.
Meniere's disease
It is a non-inflammatory process in the inner ear. It most often occurs in people aged 30-50 years and is unilateral in nature, which usually becomes bilateral.
Dizziness occurs systematically with severe attacks, accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting. If the patient tries to change the position of the body, the condition worsens.
Taking ototoxic antibiotics
Ototoxic antibiotics affect the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and hearing. The destructive property of such drugs is their destructive effect on the cells of the ear and auditory nerve. The disease begins with hearing impairment, and then attacks of dizziness occur.
Viral inflammation of the vestibular apparatus
Viral diseases include vestibular neuronitis, when the vestibular nerve becomes inflamed. It occurs against the background of some previous infection. Inflammation affects the superior branch of the vestibular nerve.
Alcohol intoxication
Alcohol intoxication is a poisoning of the body that affects all its functions. Dizziness appears already in the middle stage of intoxication, when alcohol begins to affect neurological functions and organs. Alcoholic drinks disrupt the transmission of impulses between neurons.
Traumatic brain injury
Such injuries are dangerous for the brain because they cause serious deviations in its activity. Symptoms vary depending on the extent of the injury. Dizziness is a common symptom and occurs even at the lowest level.
Spasm of the labyrinthine artery during migraine
The labyrinthine artery supplies blood to the vestibular apparatus. The spasm may occur due to a migraine. Therefore, people with frequent migraine attacks feel dizzy, have a feeling of objects moving around, and feel nauseated.