Causes of headaches in the crown area
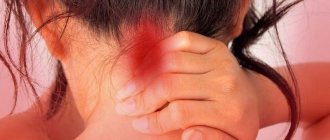
Among the causes of parietal headaches are acute and chronic diseases of the hearing organ, nerves, muscles and joints, as well as the vascular system. Vital organs are concentrated in the area behind the ears, so ignoring painful sensations is dangerous. You should pay attention to the time of occurrence and nature of the headache in the crown, its intensity - this information is important for the attending physician during diagnosis.
Diseases of the hearing organ
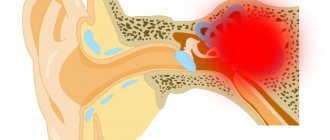
If the parietal part of the head hurts on one or both sides, a hearing test must be performed. It has a complex structure, and disorders or inflammatory processes in any area can lead to painful sensations behind the ears. The difficulty of the examination lies in the fact that the internal parts of the hearing organ are not visible to the naked eye even when using standard diagnostic techniques. However, new diagnostic methods make it possible to accurately determine the cause of pain in the parietal part of the head associated with diseases of the hearing organ.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear in any of its parts. The cause of the disease can be injury, bacterial infection, or mechanical blockage of the ear canal. In children, chronic otitis media is often caused by hypertrophy (abnormal growth) of the adenoids. Inflammation can be acute or chronic, aseptic or purulent. It is important to treat the disease in a timely manner, since otitis often becomes chronic and worsens with hypothermia or colds, and also causes hearing impairment.
There are several types of otitis, depending on the location of the inflammatory process:
- Otitis externa - affects the ear canal and the outer surface of the eardrum, rarely spreading to the auricle. This is the most common and safest type and can be easily treated with ear drops. The pain becomes more severe when opening the mouth.
- Otitis media is an inflammation of the auditory tube and other components of the middle ear. The disease is accompanied by acute pain, which often intensifies at night. Patients also complain of a sharp deterioration in hearing, pain in the temples and frontal part of the head, noise and ringing in the ears.
- Internal otitis (labyrinthitis) is a rare, but most dangerous type. If the process spreads to the inner ear, it can lead to inflammation of the auditory nerve and hearing loss. Treatment is complex and includes a course of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
With inflammation of the outer ear, the pain is one-sided, throbbing, spreads to the parietal region and intensifies during head movements. If the cause is a bacterial infection, discharge from the ear canal appears. When the internal parts are damaged, the pain spreads to the entire surface of the head. Treatment of otitis involves the use of anti-inflammatory ear drops and tablets, and also includes a course of antibiotic therapy.
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The disease often manifests itself as a complication of otitis media and is of bacterial origin. It is diagnosed in both adults and children of any age. This is a dangerous disease, since a bacterial infection causes purulent melting of tissues and, without appropriate treatment, can spread to important formations, including brain structures.
Mastoiditis can be identified by the following symptoms:
- the onset of clinical signs – some time (from several days to several weeks) after the development of otitis media;
- pain in the parietal region of the head and ears;
- increase in general body temperature;
- the appearance of purulent discharge from the auditory canals;
- protrusion of the auricle, possible redness of the skin and the appearance of a painful swelling behind the ear.
The basis of treatment for mastoiditis is a course of antibiotic therapy. At the same time, a regimen is prescribed aimed at relieving inflammation and pain. In the absence of timely therapy, the process can spread to the structures of the inner ear and cause purulent melting of tissues. Typical complications are perforation of the eardrum and the formation of a postauricular purulent abscess under the periosteum. Rarely, a bacterial infection with mastoiditis spreads to the temporal lobe of the brain or to the neck area with the formation of an abscess.
Blockage of the ear canals
The main cause of mechanical blockage of the auditory canals, which leads to pain in the parietal part of the head, is cerumen plug. It is formed either due to lack of hygiene and ear care, or due to increased formation of wax. In addition, the process can be triggered by the incorrect structure of the ear canals, their narrowing due to anatomical features.
In some patients, the wax plug is visible to the naked eye. It is a collection of gray or brown dense mass that completely blocks the ear canal. However, it may be located in the far part of the outer ear. Its presence can be assumed by characteristic symptoms:
- gradual deterioration of hearing, including one-sided;
- the appearance of sensations of noise, ear congestion;
- nausea and vomiting that occurs regardless of food;
- headaches in the parietal part of the head.
Blockage of the ear canal can be caused by foreign objects. More often they get into the ears of children, causing pain and hearing impairment over time. If a child complains of headaches in the parietal part of the head, it is necessary to contact an otolaryngologist to check the contents of the ears. Foreign objects are removed with special tools. It is not recommended to carry out the procedure at home, so as not to damage the eardrum.
Meniere's disease
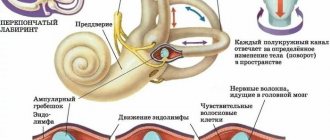
Meniere's disease is a chronic disease of the inner ear in which the amount of endolymph in the labyrinth increases. This value is not constant, it may increase due to deterioration in the removal of fluid from the body, poor diet, or taking certain groups of drugs. The disease often manifests itself in acute form in patients aged 20 to 50 years and may have a hereditary origin. Also, increased pressure in the inner ear can be caused by head injuries or allergic diseases.
Meniere's disease can be recognized by the following signs:
- attacks of dizziness that last from 1 to 6 hours, rarely longer;
- nausea and vomiting, increased sweating;
- unsteadiness of gait, loss of coordination of movements;
- pain in the ears and in the parietal part of the head.
The labyrinth is a formation in the inner ear formed by the bones of the skull. It has a complex structure and performs several functions simultaneously. It picks up sound vibrations and transmits information to the brain, but is also a center of balance, thanks to the regulation of the amount of endolymph. Treatment of the disease is symptomatic, often the doctor prescribes diuretics and a low-salt diet. These principles allow you to stimulate the removal of excess fluid and prevent its accumulation in the body.
Fungal diseases
Otomycosis is a fungal disease that can cause pain in the crown and behind the ears. Its causative agents are various representatives of human fungal microflora. The disease can develop when an infection enters from the outside or when it spreads from other existing foci. It can also penetrate during trauma and surgery. Otomycoses often occur in humid and dusty climates. This air contains a large number of microorganisms, and after they enter the ear, an optimal environment is created for their development.
Otomycoses are classified according to the place of their occurrence and typical clinical signs:
- otomycosis of the outer ear is the most common type, manifested by itching and soreness of the auricle;
- mycotic otitis media is a dangerous disorder that is a fungal complication of bacterial otitis;
- fungal myringitis - damage to the eardrum, which can lead to thinning and perforation;
- otomycosis of the postoperative cavity - antibiotics and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs create a suitable environment for the development of fungal microflora.
Otomycosis progresses rapidly without the use of antifungal drugs. The infection causes pain in the ears and crown of the head, itching and hearing loss. The diagnosis is made based on the examination of smears, in which various representatives of fungal microflora are found.
Cochlear neuritis
Cochlear neuritis is inflammation of the auditory nerve. This is an acute or chronic disease that leads to acute pain and hearing impairment. Acoustic neuritis can be caused by inflammation of the inner or middle ear, as well as various infectious diseases. In addition, its damage is observed in cases of poisoning, as a result of traumatic brain injuries and operations during which nerve fibers are damaged.
With cochlear neuritis, there is acute pain in the ears and head, which can be concentrated in the parietal region. Nausea, vomiting, and loss of coordination of movements also develop. Patients complain of a sharp deterioration or complete loss of hearing, tinnitus and other auditory hallucinations.
Inflammatory diseases
Pain in the parietal part of the head is the body’s response to various inflammatory reactions. Vital formations are located in this area, so it is important to undergo an examination and determine the causes of discomfort. There are several inflammatory diseases that can be diagnosed in adults and children with pain in the parietal part of the head.
- Inflammation of the temporomandibular joints is a common cause of pain in the crown area. These joints are located symmetrically near the ears and connect the upper and lower jaws. Their inflammation can be a consequence of injury or dental disease.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. These are cavities formed by the bones of the skull, normally filled with air. This group includes sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sphenoiditis, as well as combined forms. When inflammation occurs, the cavities become filled with contents, which in advanced cases must be removed surgically.
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. The process is often associated with previous infectious diseases, since the lymph nodes are an organ of immune defense. Lymphadenitis can also develop with congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies.
- Meningitis is a dangerous disease in which inflammation of the membranes of the brain occurs. The pain is acute, girdling, spreading to the parietal region and the entire surface of the head.
Inflammatory diseases should be treated in the early stages. Otherwise, they can progress and spread to surrounding organs and tissues. For therapy, a course of anti-inflammatory drugs is selected that will eliminate the main cause of pain in the parietal part of the head.
Infectious diseases
A viral or bacterial infection that enters the body from the outside is one of the main causes of pain and inflammation. Its representatives cause inflammation and pain, as well as various additional symptoms. There are several diseases that can cause pain in the parietal part of the head.
- Infectious mumps (mumps) is an inflammation of the parotid salivary glands caused by viruses. The disease most often occurs in children. The typical clinical picture includes symmetrical enlargement of the salivary glands under the ears, increased temperature and a general deterioration in health. Specific prevention includes vaccination.
- Shingles is a viral disease that causes severe headaches. In chronic cases, hearing loss may occur.
- Flu, sore throat, ARVI - viral diseases of the respiratory tract can also cause pain in the parietal region. After some time, fever, rhinitis, cough and other characteristic signs of a cold are added to the symptoms.
Infectious diseases often worsen and cause headaches in the crown of the head during the cold season and in the off-season. This is due to a decrease in vitamin intake, insufficient sunlight exposure to the skin (the main source of vitamin D), as well as a weakened immune system. Treatment is specific, prescribed based on the symptoms of the disease and an accurate diagnosis; a course of antibiotics may be required.
Other reasons
Soreness in the crown area is a typical symptom for various diseases. They have different origins and may be accompanied by additional symptoms. It is important to conduct a complete differential diagnosis in order to exclude the possibility of developing even rare pathologies and determine the exact cause of pain. The examination may reveal the following abnormalities:
- osteochondrosis – a disease of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae, which is accompanied by compression of blood vessels and nerves, acute headaches;
- migraine – attacks of unilateral headaches that have a chronic recurrent course;
- high blood pressure;
- dental diseases, including caries, incorrect position of wisdom teeth - the cause of pain that spreads from the upper jaw to the area behind the ears.
Treatment and prevention methods differ for different disorders. The attending physician will be able to select the appropriate tactics. The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders that are accompanied by pain in the parietal part of the head.
Most common reasons
Among the many factors mentioned above, there are causes of pain in the top of the head that are particularly common and have the most specific manifestations.
Occupational pain or tension pain
Both children and adults are susceptible to this type of headache, which most often affects the crown of the head. A dull pain presses on the head from above, compresses it and absorbs it entirely. There is a feeling as if an invisible helmet, helmet or spacesuit is being worn on top. The nature of occupational pain lies in the fact that a person remains in an uncomfortable position for a long time, without moving, in the presence of poor lighting, or in the workplace not meeting ergonomic standards and requirements.
Solution:
- Change working conditions - adjust the height of the chair, adjust the lighting, position the computer at the correct distance from the eyes.
- After every hour of work, get up from the table and do a little exercise, stretching your neck and shoulders.
- Regularly ventilate the room, maintain normal humidity and temperature.
- Perform a light self-massage of the head.
During the week, a person spends most of his time at work. To avoid headaches in the workplace, you need to properly organize your work-rest schedule and create suitable working conditions.
Neuroses and psychoemotional disorders
Over half of the complaints about pain that occurs where the crown of the head is located in a person is associated with neurotic diseases and disorders. If a squeezing or constricting headache occurs, often accompanied by dizziness and even numbness of the limbs, then this is a serious reason to consult a specialist.
Take care of your nerves. They cause most diseases
Approximately 60% of people diagnosed with neurasthenia or hysteria suffer from pain in the upper part of the head. Painful sensations are constant or periodic, they can intensify or weaken, but they always accompany the patient and do not leave him for a long time.
A person suffering from neurosis experiences emotional instability and is prone to panic attacks, and the fear is always very specific. Someone is afraid of getting a certain disease, someone is worried that they might lose a loved one, etc.
Unfortunately, a person with a neurotic disorder is constantly in a vicious circle of “fear-pain”. Fear increases pain, and pain causes new fears. Most often, people who experience prolonged stress or psycho-emotional stress suffer from neuroses.
Solution: seek help from a psychotherapist or psychiatrist and undergo a course of medication.
Post-traumatic conditions
People who have suffered even minor traumatic brain injuries complain that the top of their heads hurts. At the same time, there is a decrease in memory, performance, concentration and an increase in psycho-emotional exhaustion. The nature of such pain is dual in nature: physiological and psychosocial.
Physiological manifestations of pain are determined by the following factors:
- disturbance of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid;
- compression of the nerve roots;
- excessive pressure on the membranes of the brain.
The psychosocial component consists of increased suspiciousness of the victim, fear of complications after injury, and mistrust of doctors.
Solution: treatment from specialized specialists and consultation with a psychologist.
Vascular pain
Often the parietal area of the head suffers from pain that occurs with hypertension, hypotension, and vegetative-vascular dystonia. Decreased or increased vascular tone prevents them from performing their functions of maintaining optimal blood pressure. Either compression of the nerve cells by the vascular walls or vasospasm occurs.
- Equalizing blood pressure with medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Dieting.
- If the pain takes you by surprise, then people with high blood pressure need to lie down in bed and put a high pillow under their head, and people with low blood pressure need to put it under their feet.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose pain in the parietal region, instrumental and laboratory techniques are used that make it possible to determine the exact cause of the discomfort. A simple examination reveals inflammatory processes, neoplasms, abscesses, as well as symptoms of infectious diseases. However, to understand the full picture of the disease, the following tests may be prescribed:
- examination of smears and scrapings from the ears, skin, and mouth;
- blood tests to determine pathogens of viral diseases and pathologies of individual organs;
- consultation with an otolaryngologist - instrumental techniques will allow you to identify various diseases of the hearing organ;
- examination by a dentist - prescribed if caries, abscesses, or incorrect position of teeth during their growth are suspected;
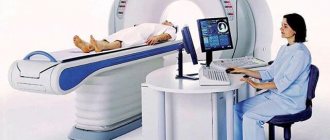
- CT, MRI of the head - these techniques are used to diagnose brain tumors.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment that allows for accurate and high-quality analyzes. There is also the opportunity to consult with general and specialist doctors who specialize in various areas.
Stress
Headache in the parietal region begins to bother you with emotional problems, stress, and depression. This pain may radiate to the neck and shoulders. It proceeds moderately and does not intensify with increasing load. Stable periods are followed by exacerbations, during which stabbing sensations appear.
Hard mental and physical work, accumulated fatigue are obvious factors that provoke pain in the center of the head. Even with simple muscle fatigue or sitting for a long time in an uncomfortable position, this pain can manifest itself.
Moreover, if the head hurts on top of the skull, then the pain is accompanied by additional symptoms: malaise in the chest, burning, increased heart rate, tachycardia, dizziness and even numbness of the limbs. Among the variety of causes of this condition, doctors identify psycho-emotional disorder and neurosis.
Thus, the body gives a signal to a person that he is working at the limit of his strength and capabilities.
As a treatment, doctors recommend forgetting intense work for a while, falling into a long sleep and giving yourself a good rest. Yoga classes, breathing exercises, quiet walks, head and neck massage - all this will help get rid of headaches. If the headache continues, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of parietal headaches
Treatment tactics are selected individually, depending on the exact diagnosis. Most diseases can be treated conservatively, using tablets, injections, ointments and drops. The scheme may include the following steps:
- anti-inflammatory therapy - tablets and injections help relieve inflammation and pain;
- antibiotics - prescribed for bacterial infections, as well as to prevent its occurrence in inflammatory diseases;
- additional methods - the doctor may prescribe means for removing excess fluid, antifungal and other drugs;
- physiotherapy – a set of techniques to improve hearing in case of ear diseases;
- surgical methods are necessary for removing foreign bodies from the ear canals, treating purulent sinusitis, as well as for removing abscesses and neoplasms.
At the Clinical Brain Institute there are opportunities to undergo inpatient or outpatient treatment. The regimen will include only those drugs and procedures that will help quickly get rid of the cause of pain and symptoms of the underlying disease. At home, it is important to follow all the recommendations of doctors in order not only to relieve pain, but also to prevent further development of the disease.
Head injuries
Pain in the crown may occur after a traumatic brain injury. This problem can become chronic. A person feels the first manifestations a week or two after receiving an injury.
Similar symptoms may be present if the pathology has a hidden course. Therefore, you cannot do without the help of a specialist if you have:
- visual impairment;
- deterioration of memory and general condition of the body;
- increased pain;
- vomiting and severe dry mouth;
- high body temperature.
Only a doctor can prescribe the appropriate treatment depending on the severity of the injuries.
With traumatic brain injuries, pain may appear immediately or some time after the impact. If the crown of the head does not hurt too much, and there are no other symptoms, then we are most likely talking about a soft tissue bruise that does not require medical treatment.
Otherwise (dizziness, excruciating pain in the crown of the head, bleeding, loss of consciousness, etc.), you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
After a traumatic brain injury, the top of the head usually hurts. Even with a minor impact, pain can occur.
In addition to pain, injury manifests itself in the form of decreased memory, performance, and concentration. Sharp pain in this local area (on the top of the head) can manifest itself based on a psychological factor.
If a sick person is suspicious by nature and is afraid of a number of complications, then the headache can only get worse.
With a concussion, the headache is chronic. As accompanying symptoms: memory loss, fever, blurred vision, general weakness of the body.
The appearance of a headache can be a consequence of an injury, and the pain can be of any kind: shooting, stabbing, and even loss of consciousness is possible. Sometimes this happens when a person has already forgotten about the injury (fall, etc.).
Methods for preventing parietal headaches
To prevent diseases of the hearing organ, it is necessary to maintain ear hygiene and immediately consult a doctor if foreign objects get into the ear canals. It is also important to strengthen your immune system, get enough vitamins and lead an active lifestyle at any time of the year. To prevent swelling and high blood pressure, you need to monitor your diet and avoid large amounts of salt and spices.
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute emphasize that timely prevention will help prevent most viral diseases, dental problems and hearing impairment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 10 votes
Share article on social networks
Features of traditional treatment
Simple remedies that our ancestors used can reduce the intensity of attacks and spasms.
Effective traditional medicine recipes:
- The easiest way to relieve pain is cabbage leaf. Apply to the problem area for 30 minutes.
- Place your feet in a bowl of hot water. The procedures help to quickly eliminate acute spasms, especially if cold is applied to the head.
- Herbal soothing decoctions - effectively neutralize aching pain: marjoram, mint and medicinal valerian.
- Relaxation: massage, yoga, spa treatments and aromatherapy - lavender, sage, marjoram or mint.
- Beads and bracelets made of amber are good for relieving migraine attacks.
- Cucumber masks, lemon or orange peel. You can simply eat citrus - it helps reduce the intensity of pain.
If, after diagnosis, the general practitioner has not determined why the top of the head hurts, for additional examination he will prescribe a consultation with specialized specialists - a neurologist or psychotherapist, and MRI diagnostics.
Alternative treatment for painful headaches is also very popular. The effect of some has not been proven by science, but is successfully used at home.
- A chopped cabbage leaf with the juice released has long been used as a means of relieving pain and relieving swelling. It is applied to the affected area and held for at least 30 minutes.
- To relieve pain, you can immerse your feet in a container of hot water, while at the same time wrap your head in a cool, damp towel.
- A cold compress on the head is considered very effective.
- To prepare drinks that generally have a mild sedative effect, mint, chamomile, valerian or marjoram are used.
- Some people also benefit from aromatherapy using mint, lavender and sage scents.
- Sports activities based on relaxing movement, for example, yoga, massage, breathing exercises, etc.
- Wearing amber, usually in the form of beads or bracelets, has an unconfirmed effect by science.
Since medications are not always indicated for young patients, tea based on medicinal herbs can be used to combat pathology.
Naturally, before this you need to find out whether the child can drink such drugs. If the doctor allows it and the baby does not have allergies, then the following recipes will be useful:
- Tea of lemon balm, oregano and mint. All herbs can be used in combination or separately. Plant leaves can also be added to ready-made tea.
- A mixture of oregano, mint and fireweed. All ingredients are taken in equal proportions. A tablespoon of the mixture should be poured with half a liter of boiling water and left for 30 minutes (after wrapping it up). You need to take half or a whole glass several times a day when an attack begins.
- Weak black or green tea. It has a calming effect.
- Menthol oil. You just need to apply it to your temples and forehead, and the pain will go away fairly quickly.
To get rid of migraines. you need to combine 6 parts of dill seeds, 3 parts each of lemon balm, linden, tansy flowers. You need to pour 2 tablespoons of the presented mixture in a thermos with half a liter of boiling water. You need to insist for 1.5 hours. After straining, the product is consumed up to 4 times a day, a quarter or half a glass. To make the liquid more pleasant to the taste, it is fashionable to add honey to it.
Hypertension or hypotension
Increased blood pressure often causes headaches in the crown area. This is a serious disease that can cause hemorrhage and other pathological conditions. You cannot do without the help of a doctor if:
- the head often hurts and throbs, especially in the morning;
- it seems that the ears are blocked;
- seeing double;
- colitis heart;
- sleep is disturbed;
- often feel dizzy;
- memory has deteriorated.
To make you feel better, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Headache from above: pressing and throbbing? Perhaps the reasons lie in low or high blood pressure. Moreover, the pain syndrome can spread to the crown area. In addition, insomnia, blocked ears, shortness of breath and decreased vigilance are possible. If you ignore all of the above symptoms, this may lead to a cerebral hemorrhage.
If the pressure is high, then it is necessary to take medications to reduce pressure, as well as drugs with antispasmodic and analgesic effects.
With low blood pressure, you may experience nausea, weakness, and a headache in the top center as if it were being squeezed by a hoop. Often the pain is localized in one place and pulsates. In this case, it is necessary to increase blood pressure: drink Citramon or strong coffee without sugar.
Cluster pain
DescriptionCluster headache is a rare but very distressing condition. which occurs in approximately three out of a thousand people.
Typically, attacks are typical for men aged 20-40 years, and their causes, as in the case of migraines, are not fully understood. Nature of pain Patients suffering from this syndrome have a headache from above, in the temple or orbit, and the pain is burning, excruciating.
It builds up very quickly, reaching a peak within 5-10 minutes and can last from 15 minutes to 3 hours.
Diagnosis and treatment There are no special measures that can accurately determine cluster pain, so the diagnosis is made after excluding other causes of pain in the upper part of the head. Treatment is symptomatic - taking painkillers, massage, inhaling oxygen.
If you have a headache on the upper left in one place, then this often characterizes a cluster type of pain. It can last up to several hours. Men predominantly suffer from cluster pain. In women, this type of headache can occur during PMS or menopause.
Among the signs of this pathology are the following:
- redness of the eyes;
- cluster pain intensifies during physical activity;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sensitivity manifests itself to light and noise.
The pain is not constant, has a sinusoidal nature: increases/decreases.
Occurs in 1.5% of the population. An intense headache at one point can bother a person for several months in a row, affecting the area of the temples and eye sockets. The attack lasts from a minute to 3 hours. Pain at night can wake a person. Main features:
- Nasal congestion with mucus discharge.
- Tearing of the eye on the side where the headache hurts.
- Nausea, dizziness.
- Excruciating pain syndrome, after which the patient needs time to recover.