Signs of migraine
Migraine is characterized by the onset after the appearance of precursors - weakness, weakness, unpleasant odors or other sensations. This is the so-called “aura”. If the aura is followed by pain on the right side of the head, the doctor will first consider a diagnosis of migraine.
Migraine pain is characterized by paroxysmal, burning sensations: the patient experiences pressure on the right eye, photophobia occurs, and nausea appears. The pain is sharp, intensifies, and is localized on the right side of the head. Unfortunately, it is still unclear why migraines occur; it is only clear that the problem is neurological in nature. Usually doctors look at the whole picture and strive to eliminate possible causes: psycho-emotional stress, overexertion, trauma.
Why it worries: reasons
Headache over the right eye is caused by various pathological and physiological factors. Severe pain often occurs in women when the balance of hormones in the body is disturbed. This condition is often recorded when carrying a child or during menopause. Other causes can also affect pain above the eye that occurs in the right hemisphere:
- Underwent plastic surgery. Pain often occurs in patients who have had unsuccessfully removed wrinkles in the frontal area or the outer eye area.
- Neuralgic disease of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the left eyebrow is most often affected and hurts, but there are also unpleasant sensations on the right side.
- Increased intracranial pressure. With this disorder, a person may experience severe pain in the area of the nose, above the right eye in the temples.
- Neoplasms of various types. Pain is triggered by tumor processes, in which pathological manifestations often spread to the back of the head.
- Traumatic brain injuries. Pain above the eyes may begin to bother the patient after a blow to the head of varying intensity. In this case, nausea and dizziness may also occur.
- Diseases of the ENT organs. An inflamed sinus or larynx can cause a person to experience aching pain in the bridge of the nose and above the right eye.
- Infectious foci. With the flu or an acute viral infection, the body gets rid of the pathogen, which can cause similar unpleasant symptoms.
- Poisoning of the body. Signs of intoxication may appear after excessive intake of medications, alcoholic beverages, spoiled or low-quality foods.
Eye pathologies
Sometimes this symptom occurs against the background of conjunctivitis.
Often the source of pain above the eyes are ophthalmological abnormalities, which include:
- The appearance of stye and the progression of chalazion. In the latter case, damage to the cartilage tissue and sebaceous gland is recorded. Often the inside of the tear duct is damaged, which can cause a person to experience pain in the area above the right eye.
- Conjunctivitis. The disease is characterized by an inflammatory reaction of the mucous membrane. The pathology is allergic, viral and bacterial in nature.
- Phlegmon of the orbit. A diffuse purulent inflammatory process is observed. Often the pus spreads to the brain tissue, posing a threat to life.
- Myositis of the eye. The right side above the eye can hurt due to an inflammatory reaction in the muscles of the eyes. Deviation can be caused by hypothermia, injury, stress factors, or prolonged sitting at the computer.
Sinusitis and other ENT inflammations
Chronic and acute ENT infections often lead to severe headaches. For example, the cause of pain in the head on the right can be sinusitis - inflammation of the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses. In addition to direct pain, symptoms of sinusitis include nasal discharge, fever; it usually appears from an untreated runny nose and develops into an unpleasant chronic disease. If your headache is combined with nasal discharge, contact an infectious disease specialist or therapist at your place of registration - he will tell you how to cope with the disease.
Why does the right side of my head hurt?
Physiological reasons
Episodic hemicranias are detected in many healthy people and disappear after taking an anesthetic, sleep, and rest. There is a connection with external circumstances and no tendency to relapse. Provoking factors are considered to be acute and prolonged stress, mental and physical overload. The right side of the head can also hurt due to alcohol intoxication, frequent smoking, or abuse of caffeine-containing drinks.
Migraine
A distinctive feature of migraine is paroxysmal unilateral pain with periodic change of half of the head. For unknown reasons, the disease most often manifests itself as pain in the right side of the head. Painful sensations are localized in the area of the eye, forehead, temple, and less often in the occipital region. They often start in one place and then cover the entire half of the head.
For most types of migraine, symptoms persist for a period of several hours to 3 days. Some signs depend on the type of disease:
- Simple migraine.
The most common. Accompanied by classic attacks without an aura, sometimes preceded by a prodrome in the form of impaired performance, deterioration of the emotional state. Nausea, vomiting, light and sound phobia are noted. - Migraine with aura.
Paroxysms are the same as in the previous case. They are preceded by an aura, which is most often represented by visual disturbances. There may be unusual sounds and smells, sensory disturbances, and difficulty speaking. - Vestibular migraine.
A typical feature is dizziness, which occurs at the prodrome stage and may persist or disappear with the onset of the headache. Sometimes different variants of the aura are observed. - Ocular migraine.
Along with visual disturbances (flickering, the appearance of scotomas, loss of parts of the visual field) that precede cephalalgia and persist for 10-20 minutes, this type of migraine differs from others in its atypical duration - less than 3 hours. - Ophthalmoplegic migraine.
Another variant of the disease with ophthalmological disorders and unusual duration. Symptoms persist for more than a week. Disturbances from the oculomotor, and less commonly, trochlear or abducens nerves occur on days 1-4. Diplopia, mydriasis, strabismus, and drooping eyelids are possible.
If the duration of a migraine attack (except for types with ocular symptoms) is more than 3 days or paroxysms during this time continuously occur one after another, migraine status is diagnosed. This condition is characterized by high pain intensity, wave-like decrease and increase in symptoms, and progressive dehydration caused by repeated vomiting.
Paroxysmal hemicrania
It occurs with episodes of extremely intense pain in the right or left half of the head with the epicenter in the orbit, temporal zone, crown, back of the head, and forehead. It can be provoked by sudden turns of the head, drinking alcohol, or strong emotions. Pain sensations are stabbing, boring, burning, pulsating, aching. The duration of the episode is 5-45 minutes; in severe cases, up to 40 attacks occur during the day. Paroxysmal hemicrania is accompanied by autonomic disorders: lacrimation, local hyperhidrosis, feeling of heat, nasal congestion.
Pain in the right side of the head
Hypnic headache
This primary cephalgia is characterized by its occurrence only during sleep. Separately, the right or left half of the head is affected in 40% of patients; in other cases, the pain is bilateral. At the beginning of the attack, the patient awakens, after the end of the paroxysm he falls asleep again. Hypnic headache is dull, moderate, rarely severe. Diagnosed in people of the older age group, once it appears, it continues to bother throughout life.
Cluster headache
Unlike migraines, the left side of the head is affected more often than the right, but right-sided cephalgia is also possible. The majority of patients are young men. Attacks of cluster headaches develop suddenly, increase within 1-3 minutes, and stop after 15-120 minutes. The painful sensations are extremely intense. Localized mainly in the orbital area, stabbing, burning, tearing, pressing. They decrease with moderate physical activity, so during paroxysm patients constantly move.
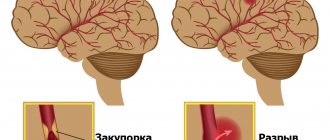
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Pain in half of the head is typical for the spondylogenic form of the disease. The left and right halves are affected equally often, the localization is determined by the side on which blood flow disturbances occur in the vertebral artery. The pain is provoked by movements of the neck, its severity clearly depends on the position of the head. Painful sensations with vertebrobasilar insufficiency appear in the back of the head, cover the temple, forehead, orbit, and radiate to the upper limb. Accompanied by autonomic and cerebellar disorders, visual and hearing disorders.
Other cerebral pathologies
Pain in the right side of the head is observed with brain tumors, limited arachnoiditis of the corresponding localization. With neoplasms, it appears in the early stages of the disease, strong or moderate, bursting, deep, often observed in the form of attacks. With arachnoiditis, it occurs chronically, gradually progresses, worries mainly in the morning, and is supplemented by neurosis-like symptoms.
Other reasons
Right-sided cephalgia can be detected in the following diseases:
- Sinusitis.
The pain syndrome is bursting, pulsating, provoked by sinusitis or sinusitis of the right paranasal sinuses. It is more pronounced in the forehead area, extending to the temple. Nasal discharge and general signs of an inflammatory process are characteristic. - Mastoiditis.
Manifests simultaneously with acute purulent otitis media or a few days after its onset. There is intense pain behind the ear, spreading to adjacent parts of the head, increased temperature, and drainage of pus from the ear. - Temporal arteritis.
Rheumatic pathology is caused by damage to the temporal artery and is accompanied by throbbing, dull pain in the temple. The pain intensifies at night and gradually progresses. Combined with general intoxication manifestations. - Spinal diseases.
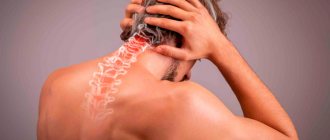
Pain in the right side of the head is caused by right-sided compression of nerves and blood vessels. It is detected in patients with osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia. Neck pain is typical and gets worse with movement. Possible muscle weakness, numbness of the right hand.
Problems in the temporomandibular joint
The lower jaw is connected to the skull by a cartilaginous disc, which can become inflamed or “wear out” because it is a moving part. A problem with the temporomandibular joint is quite easy to recognize: in addition to acute pain localized on the right, there are sensations of “shooting” in the eye and ear, the face may become asymmetrical, a burning sensation in the mouth, dryness or increased salivation may appear. If you suspect this pathology, you should contact your dentist - he will prescribe a diet, medications and, if necessary, refer you to a surgeon. If the joint is completely destroyed, it is replaced with an implant.
Spinal problems
If we talk about pain in the lower back on the right, the first thing that comes to mind, of course, is “the most popular diagnosis” - osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. The pain is usually aching, occurs on one, less often on both sides, intensifies during physical activity, prolonged stay in a monotonous position.
Another common cause is a herniated disc, which most often occurs in the lumbar spine, due to the fairly high mobility and high loads that the lower back has to experience. The pain usually occurs on one side, spreading to the buttock, down the back of the leg.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Neuralgia pain
Neuralgia pain is provoked by cold water, air, and sudden movements. For example, when washing with cold water, a sharp pain in the head on the right may occur, which undoubtedly indicates neuralgia.
Pressing, burning, bursting and dull pain in the head on the right appears with the same migraine. Often it can spread to other areas of the head and spread to the entire skull. There are other, more rare causes of headaches on the right.
In order to help a patient with such pain, it is undoubtedly necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. Migraine can be successfully treated with both medications and osteopathic craniosacral techniques. Neuralgia is quite difficult to treat; medications, as a rule, do not help. But, fortunately, many types of neuralgia can be corrected using osteopathic techniques.
So, if pain in the head on the right is caused by a pinched nerve in the exit channel, then alignment and balancing of the skull bones can completely relieve the patient of this problem. In our center, Dr. Malyutin A.G. can see you with this problem. and others. Make an appointment!
Diagnostics
Determining the pathology that causes pain in the right side of the head is the responsibility of a neurologist. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to an otolaryngologist, rheumatologist, or oncologist. To identify focal symptoms, a neurological examination is performed. Diagnosis of primary cephalgia is based on compliance of the clinical picture of the disease with certain criteria. Additional techniques are used during differential diagnosis. For other pathologies, the list of procedures is determined taking into account the nature of the disease. May be assigned:
- Ultrasonography.
Duplex and Doppler sonography are informative in assessing the condition of blood vessels. In case of vertebrobasilar insufficiency, they are performed to study the cervical and intracranial vessels, determine the localization and extent of stenosis. In other cases, they are prescribed to exclude vascular diseases. - Tomography.
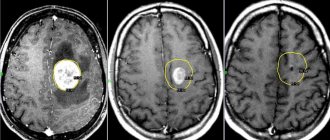
Patients with arachnoiditis and tumors are referred for MRI of the brain. If the vertebral artery is damaged, MR angiography is performed. Spinal diseases are diagnosed using CT or MRI of the cervical spine. - Otolaryngological examination.
Necessary for sinusitis, mastoiditis. Along with an external examination, anterior rhinoscopy, otoscopy, and diagnostic puncture of the accessory sinus can be performed. - Radiography.
Images of the cervical spine are recommended for disc herniation, osteochondrosis, and suspected compression of the vertebral artery by surrounding hard structures. X-rays of the temporal bone are indicated for mastoiditis, and of the paranasal sinuses for sinusitis.
Electroencephalography
Treatment methods
Doctors will select an individual treatment regimen that will help relieve not only the pain syndrome, but also its cause. Depending on the cause and nature of the headache, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases, the following techniques may be prescribed:
- drug treatment: for mild headaches, use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen), as well as painkillers (Analgin);
- antibiotics - indicated for purulent otitis and other diseases that are accompanied by bacterial infection;
- physiotherapy - a course of procedures designed to improve blood circulation and innervation of certain areas;
- nootropics are substances that improve blood supply to the brain and are used as an addition to the main therapy regimen.
The Clinical Brain Institute provides treatment for headaches of various origins in inpatient or outpatient settings. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of specialists, with constant assessment of its effectiveness and the dynamics of the patient’s condition. Doctors warn that self-medication can be dangerous and lead to complications, so at the first symptoms it is important to seek medical help.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 13 votes
Share article on social networks
Diagnosis of shooting pain in the head on the right side
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of headaches. If it bothers you often or occurs with high intensity, it is recommended to consult a therapist. Based on the results of the examination and medical history, additional consultation with an ENT doctor, neurologist and other specialized specialists may be required. To determine the cause of headache, the following examination methods are prescribed:
- blood tests (clinical and biochemical) - will indicate an increase in the concentration of leukocytes (indicators of inflammation), an imbalance of microelements, an increase in glucose levels and other pathologies;
- MRI, CT of the brain is a modern technique, thanks to which you can obtain a three-dimensional image of the area under study, identify areas of ischemia, neoplasms, and blood supply pathologies;
- ECG (electroencephalography) - analysis of bioelectrical conductivity of nervous tissue;
- ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck;
- special examination techniques by an otolaryngologist to exclude otitis media and other hearing diseases.
Timely and accurate diagnosis is the key to correctly prescribing a treatment regimen. At the Clinical Brain Institute you can undergo a full examination using modern equipment and get the most accurate results.