In this article we will tell you:
- Stress concept
- Psychological theories of stress
- Types of stress conditions
- Psychological causes of stress
- Stages (phases) of stress
- Psychodiagnostics of stress/Symptoms of stress
- Methods for mild correction of stress
- Prevention of stress conditions
Psychology of stress - why is it important to know as much as possible about it? It's simple. The pace of life has become increasingly faster lately, and stress – both physical and psychological – is constantly growing. It is not surprising that being in a permanent state of stress has become almost the norm for many people.
Stress concept
Stress is a nonspecific response of the body to any change in conditions that requires adaptation. In simple words, some changes in the external environment require us to adapt. It got colder outside, warmer, we moved to a different climate, met other people - all this requires physical and mental effort from us. In general, this phenomenon can be described as stress. If adaptation occurs, it means there is stress.
The concept of stress is translated as load, tension, pressure, a state of increased tension, and it is so. But not every state of tension is stress. Only when you need to turn on the body's reserves for adaptation.
Stress is our internal mechanism of adaptation of the body and its way of survival.
If a person steps on glass with his heel, a stress response will begin in his body. That is, stress is an adaptation mechanism itself. The body begins to make some changes in order to adapt to this situation. He notices that there is glass in the heel, thickens the blood so that it begins to clot and prevent blood loss.
But if the system of reactions to stress and attempts to adapt to it remains turned on for too long, this leads to illness.
Stress is anything that disrupts our homeostatic balance. Homeostasis is the body’s self-regulation system, which allows us to maintain consistency within our systems. Usually here we are talking about maintaining body temperature, blood glucose levels, approximately the same blood pressure and various other processes within the body.
When stress somehow upsets our balance, the body, with the help of neurotransmitters, hormones, and the nervous system, tries to adapt to this and restore balance back.
If, in the case of animals, stress is only a violation of the homeostatic balance that already exists at a given time, i.e. This is a factor that is affecting right now, then everything is more complicated with a person. When a wild dog Dingo grabs a jerboa by the spine, this is a stress factor for him. In the case of a person, everything is different; it may also be the thought that the homeostatic balance may be disturbed, that is, this is not stress itself, not the stress factor itself, but thoughts about what could happen.
1.What is acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a rapidly developing and life-threatening condition in which the lungs are so damaged that they can no longer perform their direct function of oxygenating the blood.
Causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS.
ARDS can occur when small blood vessels in the body, including those in the lungs, are damaged due to injury or severe inflammation. As a result, the lungs lose their ability to fill with air and cannot provide oxygen to the bloodstream.
Damage to the lungs can be direct or indirect. Direct lung injury
possible, for example, in the following situations:
- Inhalation of smoke or toxic chemicals;
- Inhalation of stomach contents into the respiratory tract (aspiration);
- Drowning;
- Pneumonia;
- Lung infections.
Indirectly
affect the condition of the lungs and
cause ARDS
:
- Bacterial blood infection (sepsis);
- Drug overdose;
- Large number of blood transfusions;
- Being on artificial circulation;
- Infection or irritation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- Severe bleeding due to injury (for example, as a result of a traffic accident);
- A strong blow to the chest or head.
In practice, the most common causes of ARDS are sepsis, traumatic injury, or pulmonary infections such as pneumonia. However, it should be noted that the presence of these factors does not necessarily indicate the imminent development of ARDS. Each case is individual, and the pathological process may well not begin.
A must read! Help with hospitalization and treatment!
Psychological theories of stress
For the first time in 1915, American psychophysiologist Walter Bradford Cannon spoke about a condition that is now associated with the concept of stress, and called this reaction “fight or flight”. And he even described this phenomenon in the book “Body changes during pain, hunger, fear and anger.” The year 1915 can be considered the beginning of the European and American approach to this topic.
We recommend
“Nutrition for a healthy lifestyle: healthy foods, life hacks, menus” Read more
However, our compatriots found themselves on the same topic in the same years, and at the Military Medical Academy in St. Petersburg, Professor Korenchevsky in 1913 already described the adaptation syndrome and said that it is not a pathological, but a physiological reaction to cell damage, tissues, damage to some external environment.
The Austrian doctor Hans Selye graduated from the Medical University of Prague. Having moved to Canada, he studied the effects of the secretions of hormonal glands, which he obtained by crushing organs isolated from animals and injecting them into mice (not hormones at that time, because they were not isolated in their pure form).
He noticed a very interesting thing: no matter what hormone extract he injected into the mice, the reaction was very similar. There is a legend that one day he made some kind of technological mistake and forgot to untie his experimental mice and left them overnight.
And those mice that were injected with substances the day before and those that were not injected gave the same reaction in the form of ulceration of the gastric mucosa. The next day, some of the experimental subjects even died. And that’s when he first spoke about the general adaptation syndrome. Actually, this was the beginning of the story of stress.
Selye made very interesting conclusions that in fact only the intensity of the need for restructuring or adaptation matters. And the stimulus itself and the changes that led to the formation of this adaptation syndrome practically do not matter. The second conclusion that Selye made is that adaptive energy is available in limited quantities, given from birth.
Later, the American researcher Goldstone in 1952 entered into a debate with Selye and began to say that adaptive energy can be produced regardless of how much of it was given to the body at birth. It, of course, decreases in old age, but can remain in the form of adaptation capital.
Gradually, this topic began to develop from the organismic and cellular concepts, with which Selye began, into the social concept. From one experiment on mice, entire directions in biology, medicine, sociology and even politics related to the topic of stress have developed.
4. Treatment of the disease
Typically, people who develop ARDS are already in a fairly serious condition and are most often treated in a hospital. And, as a rule, acute respiratory distress syndrome requires resuscitation measures
.
There is actually no specific treatment for ARDS. The goal is to support the patient's respiratory function
and allow the lungs to recover.
This may involve the use of ventilators
or
oxygen injection into the lungs
. Currently, scientists are developing new methods of maintaining the lives of patients with ARDS. And, for example, it was found that the operation of conventional mechanical ventilators, which creates air flow, reduces the mortality rate of patients with ARDS and allows them to begin breathing on their own faster and abandon ventilators.
In addition to maintaining breathing, treatment for ARDS includes combating the underlying cause of the pathology.
. For example, if a patient is diagnosed with a bacterial infection, antibiotics are usually prescribed. Because patients are usually unable to feed themselves during therapy, fluids and nutrients are administered to the body through IVs and tubes.
Outlook for patients with ARDS.
As already mentioned, ARDS is a life-threatening condition. It is worth noting that the survival rate of people with ARDS has increased in recent years. While some recover completely from the disease, others experience long-term breathing problems and chronic lung damage.
Usually bad forecasts
associated with some unfavorable factors:
- Progressive cancer;
- Advanced age of the patient;
- Sepsis (bacterial blood infection);
- Long-term alcohol abuse;
- Chronic liver diseases;
- HIV infection;
- Multiple organ damage;
- Organ transplantation.
Full recovery from ARDS can take several months or even years. Pulmonary rehabilitation
is an important part of the recovery program. A good pulmonologist will definitely tell you how to restore normal lung function. And, of course, periodic examinations by a pulmonologist are necessary to assess the condition of the lungs and adjust the course of rehabilitation.
Psychological causes of stress
Stress can have a number of causes: biological, chemical, physical and, of course, psychological. With the latter, things are not easy. The psychological causes of stress are so diverse that it is simply impossible to list them all. Each person is unique: his way of thinking and habitual patterns of behavior together give a unique picture of his personality and a set of probable reactions to stressful situations. There are a lot of such reactions.
Stress is caused by internal and external problems
. External are various life situations that a person has the ability to control. These could be financial difficulties, relocation, difficulties at work or in your personal life, etc. Internal causes of stress arise in the depths of the human mind and often have nothing to do with reality; the person himself invents them. This may be due to constant blues, a pessimistic attitude, unfulfilled desires, lack of self-love, self-esteem, and self-rejection.
Psychology identifies eight causes of stress, which are the most significant for a person and have the greatest impact on him.
- Death
. When a loved one passes away, few people can maintain their presence of mind and continue to live a normal life. This is the most powerful psychological cause of stress. Anticipation of death (for example, of a sick relative) is also a cause of powerful emotional stress.
- Finance
. For a huge number of people, financial difficulties are the main cause of stress.
- Lack of self-expression
. Most people strive to express their own “I,” but not everyone can do this.
- Lack of control over the situation
. This can concern both your own life and the lives of loved ones. The inability to control everything weighs on some people and plunges them into a state of stress.
- Disease and insecurity
. Fear of getting sick, experiencing pain, fear of death - all this leads to a loss of peace of mind, a person ceases to feel safe.
- Job
. For a huge number of people, work is a powerful source of stress. Difficult responsibilities, management pressure, difficult clients - all this keeps you in suspense, forces you to constantly think, analyze, and make plans.
- Friends and loved ones
. Communication with loved ones, relatives, and friends is always emotionally charged, which means it can provoke stressful situations.
- Family
. If things are not going smoothly in relationships with family, a person is unlikely to feel comfortable.
We recommend
“Physiology of stress and ways out of it” Read more
Any event can serve as a starting point for stress. Both women and men can become hostage to their psychological difficulties. It is important to remember that the primary task in a situation of constant emotional stress is to find out the cause of the uncomfortable state. By eliminating it or looking at the situation from a different angle, a person begins to feel much better. Without this, life can turn into a constant battle with windmills.
Symptoms of stress
How to assess a person’s condition when maladjustment has already set in, and when you need to start worrying and give some recommendations? It is important to understand whether stress has set in or not yet. Let's talk about diagnostic methods.
- By appearance
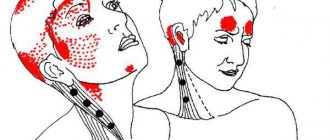
The person has puffiness, watery eyes, slightly bulging eyes, may be sweating, may have sweat on their face, and may be malnourished or overweight in what is known as chronic distress. The presence of these criteria may indicate that a person is in the first phase of stress.
- For somatic complaints
A person complains about his health. He can talk about high blood pressure, which increased suddenly after some event or experience. He may complain of a sudden rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, constipation, a feeling of bloating, pain in the middle under the ribs, or a sharp increase in appetite, a feeling of insatiability - “I can’t get enough, I eat, I eat, but I feel like I’m not getting enough.”
Signs of stress can also include frequent respiratory viral infections, the urge to urinate, episodes of urinary incontinence that suddenly begin to occur after events or experiences, decreased erectile function in men or sexual desire in women, pain in muscles and joints.
- By behavior
Based on behavior, we will notice some desire to reduce the area of support; the contact area is a manifestation of post-traumatic stress disorder.
“You-statement” is very typical for a person who is in a situation of stress and physical trauma as well.
- Family history
In the family system, a person who has asked for help may find out that there are suicidal people - people who have committed suicide. Perhaps a person will say that he was not breastfed at all or that his mother gave up breastfeeding early. This is a family history factor that leads a person to tend to react with distress to external circumstances. This is prematurity - the more severe a person's history of prematurity, the more prone he is to distress reactions.
A sign of stress may be the presence of a dysfunctional family in which violence is practiced, alcoholics and drug addicts, people who have been in prison. These are panic disorders in the client or his family members.
- Predisposing personality traits
This is hyper-responsibility, pedantry, so-called perfectionism - the desire to do some action perfectly, this is some kind of mental rigidity - an unwillingness to adapt to circumstances, a desire to do it your own way, to insist on your own. This is alexithymia - the inability to understand, express feelings and basic anxiety.
- Mental complaints
This is a changeable mood - from irritability and anger to complete apathy, the feeling that nothing interests me.
These are insomnia, impaired memory, attention, anxiety higher than in usual conditions, the appearance of panic attacks, asthenia, when you don’t have enough strength for some basic actions, you don’t want to get up, drink water, brush your teeth, or go to work. This is hyperinhibition, when a person suddenly slows down and stops reacting in the usual way to familiar situations. And these are psychotic breakdowns, when suddenly a person begins to get offended, cry, scream, swear, which was not typical for him.
- Events
In general terms, these are events associated with changes in life. Here it is important to understand what is important for a person and what is not so important, what kind of event can throw him out of balance so much as to cause stress.
3. Diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome
There are no specific tests to diagnose acute respiratory distress syndrome. The doctor usually performs a general examination
and listens to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope.
characteristic breathing
will be heard - wheezing, with crackling sounds.
When there is low oxygen in the blood, the skin and lips may take on a bluish tint. An arterial blood test can be done to check your blood oxygen levels.
.
In some cases where ARDS is suspected, general tests
:
- Chest X-ray
, which will help ensure that there is no fluid in the air spaces of the lungs; - Complete blood count
and other blood tests to detect signs of infection; - Sputum testing
to detect the presence of bacteria or fungus in mucus released from the lungs when coughing; - Computed tomography (CT) scan to look for fluid in the lungs, signs of pneumonia, or to diagnose other lung problems.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!