To begin with, let's divide all seizures into generalized, when the whole body is subject to a convulsive attack, and local, when only one area is affected - for example, the calf muscle.
There are also tonic and clonic seizures. The first ones are more like not a cramp, but a spasm, in which the body seems to be frozen in one position. A classic example of a tonic seizure is opisthotonus in tetanus. Such seizures are rare and are always caused by a serious illness: tetanus, neuroinfection, brain tumors.
The second option is clonic convulsions, in which the body makes frequent chaotic movements, that is, it beats in a typical convulsive seizure, as most of us imagine it.
This option can be encountered much more often in life - these include febrile convulsions when the temperature rises in young children, and epileptic seizures in people of any age. If your leg is cramped or your biceps is constantly twitching, this is unpleasant, but not dangerous.
If we are talking about generalized seizures, a person needs quick medical attention. Although neurologists like to repeat that a seizure is not as terrible as it looks from the outside.
Febrile seizures
The content of the article
This is a fairly common occurrence when it comes to children under 6 years of age. It is believed that every tenth child responds to a rise in temperature at least once in his life with a generalized convulsive seizure.
Typically the temperature is required to rise above 38.5 degrees. Then, in the still imperfect child’s brain, foci of pathological excitation arise, triggering many false signals to the muscles.
It looks scary, but in reality everything is not so dangerous: usually the seizure goes away within 2-3 minutes, but it can last 15, after which it ends as suddenly as it began.
And what is important - without causing any harm to the baby. Only seizures lasting more than half an hour require hospitalization and observation. You should also call a doctor if a child over 6 years of age, a teenager, or an adult develops seizures in response to a fever.
What to do? The only way you can and should help a child is to be close to him and make sure he doesn’t get hurt. Just in case, be prepared to turn your head to the side if vomiting begins. Forget about sticking spoons in your mouth.
In attempts to unclench your teeth and pull your tongue out of your mouth, you will only injure yourself and the child. Epilepsy subsequently develops in only 3% of children who have had febrile seizures, but it is still worth doing an electroencephalogram after recovery.
Local tonic convulsions
Muscle spasm in response to excessive physical activity or prolonged uncomfortable position is a common phenomenon. Professional athletes know this more than others, but even for ordinary fitness enthusiasts, sudden muscle pain causes many unpleasant emotions.
A cramped muscle is tense and hard to the touch, and the spasm is accompanied by severe pain. In addition to the calf muscles, convulsive spasms affect the muscles of the neck, and sometimes the muscles of the thigh and forearm can be affected. Usually, local tonic convulsions go away on their own within 5-10 minutes, but it’s still better not to endure the pain.
There is a simple scheme of actions that will help return the muscle to its normal state.
What to do? The most basic cause of spasm is a lack of microelements (primarily magnesium), excessive stress on an insufficiently warmed muscle, or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (this is what causes muscle spasms during sleep).
Therefore, people involved in physical exercise are recommended to take additional vitamin and mineral complexes, eat dried apricots before training, avoid dehydration, and most importantly, devote enough time and effort to warming up to “warm up” the muscles.
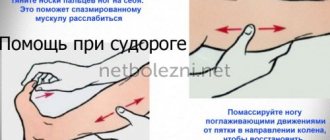
If a spasm does occur, there are techniques for local impact on the muscle. For example, if you have a spasm in the calf muscles, you need to stretch your leg forward as much as possible and strongly pull your foot towards you.
Calf muscle cramp - what to do
The most difficult problem that the victim faces is the sleepy state. Even if you know by heart how to combat spasms, it is difficult to remember them in the middle of the night and reproduce them correctly, especially when severe pain is tormented. And yet it’s worth talking about this and setting yourself up for the fact that providing self-help will allow your leg to get out of hell as quickly as possible.
Simple and effective actions when your calf muscles cramp at night:
- Stretch your heel as far as possible, while grasping your toes and pulling them towards you.
- Pinch the leg and prick the surface of the hard muscle with your nails.
- Give a massage - stroke the muscle, then massage it with the pads of your thumbs, and then beat it with your fist or the side of your palm.
- If you have a Kuznetsov applicator, you can put your foot on it.
- Apply a cool compress to the affected area for 10-15 minutes.
To avoid getting confused at night, it’s better to practice, and you can do it right now!
Treatment recommendations
Having discovered cramps in the calf muscles and toes, the patient should not self-medicate in the first place. These recommendations are designed to alleviate the intensity of the symptom as much as possible and no longer suffer from lack of sleep due to severe pain.
- A visit to the doctor is mandatory. To begin with, a general practitioner who will prescribe the necessary tests for the patient and refer him to specialists. To establish the cause of night cramps, consultation with a phlebologist, endocrinologist and orthopedist is required.
- It is advisable to reduce stress on your legs during the day. Before establishing the cause of the symptom and prescribing a course of treatment, you should ease your daily activity: take the elevator more often, temporarily give up shoes with heels, do not exhaust yourself with sports, resorting only to light physical exercise.
- Next, you should analyze your diet for the purpose of correction. In some cases, you will have to contact a nutritionist for additional recommendations. Drink more water. Proper nutrition, including lean meat and coarse fiber, as well as plenty of water (at least 1.5 liters per day) will have a positive effect on the functioning of blood vessels, which will ease cramps and reduce their frequency.
- In addition, it is necessary to get rid of bad habits - alcohol and smoking (read what happens after quitting smoking here), since these factors also lead to sudden spasms of the calf muscle during sleep.
- Take vitamins. If during the examination a vitamin deficiency is detected in the patient, take a course of necessary vitamins. Pay attention to foods such as: fatty fish, moderate amounts of cheese, dairy products and nuts.
A cramp in the calf muscle at night during pregnancy may indicate low hemoglobin. This is undesirable and in some cases even dangerous for the child. The expectant mother is recommended to take a finger prick blood test to find out if she has anemia. If hemoglobin is low, the doctor prescribes special medications to help bring the level back to normal.
Folk remedies
Some patients effectively treat calf muscle cramps with folk remedies. For example, apply tincture of thyme, walnut, dill or chamomile to the affected area of the leg. Naturally, this should be done only after the doctor’s permission.
Local clonic seizures
The reasons for periodic twitching of a particular muscle may be the most unexpected. For example, strong emotional experiences, stress, due to which excitation in our body begins to prevail over inhibition, various neuroses arise.
Or heredity, due to which we inherited easily excitable muscles. If your grandmother or mother often complained of local convulsions, this is from them. An unhealthy diet lacking essential micronutrients (crash diet) can also cause these symptoms. On the one hand, they do not cause serious concern, but they are not easy to get rid of.
What to do? The problem of muscle fasciculations becomes significant for the doctor and the patient when twitching occurs too often and really interferes with life. In this case, you should contact a neurologist. The course of treatment may take some time and include taking vitamins and minerals, medications that affect the nervous system (including sleeping pills and antidepressants), physiotherapy and massage.
Why do leg cramps occur?
Contractions of muscle fibers that cause characteristic leg spasms always occur suddenly:
- the muscles are cramped by a sharp squeezing pain;
- legs go numb and become “stone”;
- after a few minutes the attack subsides and sensitivity returns;
Convulsions can “cover” in a series of several consecutive attacks. Sometimes muscle contraction is interspersed with convulsive twitching that lasts several seconds. The calf muscles are most often affected. Less commonly, similar painful symptoms occur in the feet and toes or in the thighs. The pain may only bother you at night or during times of greatest muscle tension. It can cramp one leg or both at once.
Immediate causes of cramps: vascular spasms, causing disruption of blood flow in the legs. Signals from the brain to relax muscle structures in such conditions do not reach the affected areas. The main provoking factors for spasms:
- Hypomitamism and deficiency of minerals: group B, ascorbic acid, potassium, calcium and magnesium. This unfavorable condition is caused by poor nutrition, impaired absorption of essential substances, and their increased consumption in the body.
- Heavy physical activity. Monotonous, long-term movements that involve the same muscle groups are especially harmful. For example, excessive passion for cycling, gardening.
- Sharp thermal effects. Cramps often occur when leaving a warm house into the cold, or when immersing a hot body in cool water. The vessels react by immediately constricting, and blood flow in the lower extremities is blocked. A sudden drop in ambient temperature by more than 10C is a powerful provoking factor.
- Severe stress. In emotional people exposed to difficult experiences, the autonomic nervous system suffers. The mechanism of flexion and extension of active muscle groups is disrupted first.
- VSD. A complex symptom complex affects the activity of blood vessels in the legs. Regular attacks of the disease are associated with exposure to cold, psycho-emotional stress, or existing chronic disorders.
- Dehydration. Imbalances in the balance of electrolyte salts and water lead to disruptions in the mechanism of muscle innervation. Normally, the body should consume up to 2–2.5 liters of clean water per day. Excessive sweating, increased urination, or the habit of replacing water with other drinks cause active leaching of potassium salts from the blood. And their deficiency leads to seizures.
- Diseases: central nervous system, musculoskeletal system, varicose veins, endocrine, atherisclerotic changes, diabetes mellitus. With the development of pathologies, convulsive syndrome is part of the characteristic symptoms.
- Acute or chronic intoxication: some biological and chemical poisons affect the functions of the nervous system, causing dehydration and leg cramps.
- Immaturity of the central nervous system in childhood and adolescence. Neurons and blood vessels often cannot keep up with actively growing skeletal muscles, which is manifested by various negative signs of the body’s development, including leg cramps.
- Pregnancy. Spasms in this case are provoked by a deficiency of minerals, an increase in the load of the growing belly on the vessels and nerve endings.
For some people, leg cramps are an occupational illness. It affects dancers, climbers, swimmers, weightlifters, football players, sales assistants, hairdressers, and drivers. Physical inactivity, tight uncomfortable shoes, prolonged forced stay in one position are additional negative factors for the appearance of painful symptoms.
Epileptic seizure
A seizure in epilepsy, or, as it is also called, status epilepticus, is perhaps the most striking example of what the average person imagines when they mention seizures.
The man suddenly pushes, his body contracts chaotically, incoherent wheezing is heard, foam comes out of the mouth. The picture is terrible, and the situation requires quick medical intervention. Surprisingly, just one intravenous injection quickly brings a person back to life.
What to do? The main task of a witness of status epilepticus is to ensure the safety of the unfortunate person so that he does not accidentally injure himself on surrounding objects. If possible, it is recommended to lay him on a soft surface and turn his head to the side so that vomit and foam do not enter the respiratory tract. Call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
If an attack occurs for the first time, it is very important to undergo a full examination as soon as possible. This may be the onset of one of the neurological diseases or a brain tumor.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter