29 Jun 2021 at 12:16 MRI of the head in Tushino 7409
If you often find yourself forgetting things and becoming too suspicious of others, you may need medical advice. Dementia is often perceived as analogous to memory loss. However, this disease, even in its acute form, is a common symptom of age-related dementia, the development of which can be stopped.
Dementia in older people and its forms can be divided into three main stages:
- Early.
- Moderate.
- Late.
It should be taken into account that the progression of dementia in pensioners occurs in stages and may not make itself felt for some time . Moreover, treatment of this disease, as a rule, is most effective in the early stages of development. Therefore, it is so important to systematically undergo examination and diagnostic procedures in specialized institutions.
Early stage dementia
Patients are practically no different from healthy people at this stage of development of the disease . Only minor manifestations may be noticed, which are usually associated with the natural aging process. An elderly person does not have significant negative changes in spatio-temporal orientation, he can take care of himself and demonstrates adequacy in behavior.
Symptoms of the onset of the disease:
- Slightly reduced performance.
- Some loss of interest in your hobbies and social circle.
- Strict adherence to traditions progresses, excessive importance is attached to the past and everything new is denied.
- Deviations in memory functioning.
- Decreased alertness or excessive concentration.
- Attacks of irritability, aggressiveness, touchiness and self-isolation appear.
- Physical activity decreases somewhat.
Types of senile dementia
For each type of senile dementia, there are different signs of its manifestation:
Vascular dementia.
Initially, a decrease in attention and concentration appears. Then the patient quickly gets tired and gets irritated. He may be bothered by pain in the head and neck area. Insomnia or, conversely, excessive sleepiness appears. A person can sleep either 4–5 hours or the whole day.
Memory impairments are still not clearly expressed. But you should pay attention to the manifestation of emotions. Sick older people are subject to rapid changes in mood. They are indifferent to surrounding events and suffer from hallucinations. Epilepsy attacks may occur. The mobility of the limbs and gesturing decreases. Facial expressions become less pronounced. Dysuric disorders occur. Such people are unkempt and indifferent to daily self-care.
Atrophic senile dementia.
The main signal of this stage is a process that is accompanied by the inability to save, accumulate and use the information received. Simply put, memory impairment. In mild cases, this results in forgetting the events that just happened. The severe form is characterized by the inability to remember the events of several past years and loss of space. The vocabulary becomes impoverished and attention wanders. But with this form of senile dementia, glimpses of consciousness are possible, when the patient understands the severity of his illness and can somehow mask his illness.
Doctors divide forms of atrophic dementia according to the following criteria:
- Partial dementia. Expressed in memory deterioration, loss of strength, lethargy. Often the patient is depressed.
- Epileptic dementia. Clear signs appear over time. A sick person is characterized by attacks of aggression, anger, and rancor. They can perform actions carefully, consistently, often with diligent repetition. Speech inhibition is observed, interest in what is happening around disappears.
- Schizophrenic dementia. This condition requires constant supervision of the patient, preferably in a specialized institution. This form is characterized by deep withdrawal into oneself, loss of emotionality and activity.
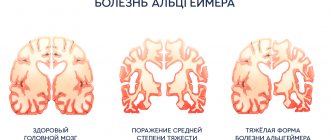
- Alzheimer's disease. It is worth taking into account that this disease can be inherited. The onset of painful processes is possible before the age of 60, but often the likelihood increases sharply by the age of 65–75.
Initially there is memory deterioration. Distracted attention, forgetting any things or events do not bother a person at first. An alarming signal is when the patient systematically cannot remember episodes that occurred recently. However, older people remember events that happened ten years or more ago very well and in detail. But over time they are also forgotten.
The patient cannot recall in memory the data that he needs at a certain moment. The information just received is also not perceived. There is disorientation in place and time. An elderly person cannot remember the date of today, where he is now and does not even recognize himself, his family, or his friends. Along with this, vision and hearing decrease, and sensitivity decreases.
Next, the person ceases to identify himself with the outside world. The knowledge and skills associated with his profession decrease and then disappear altogether. The situation gets worse when the patient cannot cope with personal needs, the vocabulary becomes poorer, and diction is impaired.
In the early stages, older people still understand that an illness is emerging and make attempts to resist it. But with the progression of senile dementia, the critical assessment of one’s own condition decreases. Interest in his hobbies and events around him disappears, the patient withdraws and withdraws into himself.
- Pick's disease. The same applies to atrophic senile dementia, only more global. Women are often susceptible to this type of dementia.
Appears as a result of destruction and death of the cerebral cortex in the frontal and sometimes temporal lobes. Disease processes affect the emotional sphere. A person's critical self-esteem disappears. He ceases to control himself and falls into opposite emotional states (apathy, euphoria). Swears with obscene words, makes scandals for no reason.
Patients with this diagnosis are characterized by lustful behavior and the inability to control feelings of lust. A person changes before our eyes and can behave antisocially. There are no speech impairments; on the contrary, it is fast and with many words, but there is a problem with the correct use of terms and expressions. Thought processes are preserved, but the patient cannot analyze or draw correct conclusions based on the information received.
The acquired skills in counting, writing, and those related to professional activities remain for a long time. Memory does not deteriorate as much as in Alzheimer's disease, that is, the patient does not fall into an unconscious state.
Mixed dementia.
This type of senile dementia occurs as a result of destructive, destructive actions associated with the use of drugs, substances that change the human psyche. This question is relevant for those people who have been taking psychotropic drugs prescribed by psychiatrists for several years. These substances must be taken in courses. Long-term use leads to acute poisoning of the body, which can develop into dementia.
In addition to the state of causeless inspiration and enthusiasm, a persistent attachment to these substances appears. Their accumulation in the body leads to serious disorders of mental processes. With addiction comes emotionally unstable states, frequent mood swings, and blues. All this is aggravated by loss of strength, weakness, lethargy and insomnia. As a result, a severe mental disorder on the verge of insanity occurs, the person ceases to perceive the reality around him.
Reality is not a stimulus to action. The use of poisonous drugs and isolation from reality accelerate the degradation of personality. But such patients have a much higher chance of recovery and adaptation to normal living conditions than patients with Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia.
We recommend
“Causes of itching in older people and ways to combat the disease” Read more
Moderate stage of dementia
Symptoms of the disease:
- The ability to care for oneself is lost: a person has difficulty getting dressed and using household appliances.
- There is an irresponsible attitude towards personal hygiene.
- Memory deteriorates: the patient may forget recent events, the names of loved ones, and may not recognize himself in the reflection of the mirror.
- Sleep disorders.
- Difficulties arise with orientation in space, so a person should not be left alone on the street.
- Personal qualities change, and with them character.
- There is a process of degradation of intellectual abilities.
- The physical condition changes: an unsteady gait, the patient may mince, muscle tissue weakens, tremors of the limbs and muscle stiffness appear.
Diagnosing dementia
A qualified doctor must study the patient’s condition, his clinical picture along with the medical history, and interview relatives. To accurately diagnose dementia, a questionnaire is used using a specific neuropsychological scale.
The following number of factors need to be taken into account:
- Symptoms appear for at least six months.
- Problems with emotions: unstable behavior, attacks of apathy and irritability.
- Impaired cognitive functions.
- Medical meanings of deviations and how they affect a person’s quality of life.
To obtain the most complete picture of the disease, additional brain examinations, blood samples for hormonal studies, and MRI may be prescribed.
Dementia - how to behave with a person?
First of all, have a positive attitude when communicating with your sick relative. Speak only in a polite, pleasant tone, but at the same time clearly and confidently. When starting a conversation, attract the patient's attention with his name. Always formulate your thoughts clearly, expressing them clearly in simple words. Always speak slowly and in an encouraging tone. Clearly ask simple questions that require clear answers: yes, no.
For difficult questions, give a hint. Be patient with the patient, give him the opportunity to think. Repeat the question if necessary. Try to help your relative remember a specific date, time, and names of relatives. It is very difficult to be understanding. Do not react to reproaches and reproaches. Praise the patient, take care of the consistency of his daily routine. Break down any activity into steps. Reminisce about the good old days with the patient. It's calming. Good nutrition, drinking regimen, and regular movement are important.
Treatment of dementia in older people
The treatment program for this disease should include a course of medication, certain rules and psychotherapy.
Drug treatment for dementia
Dementia can be classified as a mental illness, but therapy is somewhat different. Treatment uses methods of influencing the head vessels, and this requires paying attention to the cardiovascular system, and only then considering the manifestations of disorders.
Prevention of stroke and heart attack requires the use of ACE inhibitors, diuretics, perindopril and lisinopril. Cerebrolysin, various tranquilizers or nootropics may also be prescribed for treatment.
The prescription of psychotropic drugs occurs only in cases where a person is observed to have depression, anxiety and problems with sleep patterns.
Drug treatment
Since aggression often occurs due to illness, pain, or physical discomfort, a patient with dementia should regularly visit doctors in order to prevent chronic diseases. If caregivers cannot independently understand what triggers the attack, they should consult a psychiatrist.
The main drugs used to treat aggression in dementia are risperidone and aripiprazole.
The use of antipsychotics to relieve attacks of aggression in dementia
| Characteristics of the drug | Risperidone | Aripiprazole |
| Pharmacological group | antipsychotic | antipsychotic |
| Dosage | sublingually, 2 mg/day | sublingually, 10-15 mg/day |
| Contraindications |
|
|
| Side effects from the nervous system | sleep disturbances, fatigue, excitability, increased anxiety, headaches, extrapyramidal disorders, seizures, increased risk of stroke, impaired thermoregulation | sleep disturbances, headaches, dizziness, extrapyramidal syndrome, hostility, depression, nervousness, mania, obsessions, suicidal thoughts, cognitive disorders, increased risk of stroke |
Senile dementia and aggression require attention and care from others. Drug treatment is not always the best way out of this situation, since sedatives solve the consequences, but not the problem, and often affect the patient’s consciousness, aggravating other symptoms. You should resort to pharmacological therapy only if all other methods of correcting aggressive behavior have already been exhausted. But even in this case, it is necessary to constantly monitor the development of dementia and, if possible, use more gentle methods.
High-quality treatment of the underlying disease reduces the risk of psychosis. Treatment of aggression in dementia with antipsychotics worsens the course of dementia, especially cognitive status. Among people using antipsychotics, the mortality rate is a quarter higher than among patients using other drugs.
Treating dementia at home
An extremely important factor in home treatment is the environment in which he lives, as well as his activities and lifestyle.
Recommendations for older people with dementia
- Follow the regime . It is necessary to strictly follow the diet, rest and activity regimes. It will be useful to do moderate work, but it is not recommended to overwork yourself. It is better to eat a little food up to 6 times a day.
- Train and exercise . You need to support both your brain and your body. Moderate physical activity in the form of helping around the house, walking and therapeutic exercises will be useful. You can also use yoga classes.
- Effective treatment requires mental development . Reading printed publications, poems, crosswords, memory tests - everything can bring significant benefits. Creative activities have proven themselves to be excellent: hobbies, embroidery and knitting.
- A person with dementia should be provided with love and pleasure . Pets, communicating with family members, looking through family photo albums, listening to beautiful music, etc. can help with this.
Treatment of dementia with psychotherapy for older people
Psychotherapy plays a significant role in rehabilitation and proper socialization . Specialists will help you restore faith in your strength and spirit for a decent future life, as well as a positive recovery outcome. Psychologists help the patient change his views on situations and pay more attention to the positive aspects of life.
Recommendations for the patient's relatives
An elderly patient with dementia should be provided with constant care, care and control. The responsibilities of loved ones include caring for the patient. For quality assistance, it is possible to use the services of professional nurses who work in private boarding houses, such as Eden.
It is also important to understand all the intricacies and nature of the illness of an elderly relative and be prepared for predicted events. A person can be determined to have a disability and be assigned guardianship.
The process of communicating with the patient should be as simple as possible . It is worth speaking with utmost clarity and clarity, with simple turns of phrase. You need to prepare to repeat and remind the patient many times, and also, if possible, not to rush him or get irritated. To do this, you need to remember that such behavior is not his whims, but manifestations of dementia.
It is necessary to create the most calm conditions surrounding the patient and facilitate his daily activities . Comfortable furniture, good lighting, and avoidance of noise – all this will contribute to treatment.
Monitoring the patient's condition is mandatory . It is necessary to teach him to control his regime, personal hygiene and the use of medications.
Support any of his activities: let him participate in the cleaning process, walks, communication and hobbies. You should not force a person by force: such coercion will only increase the manifestations of depression and apathy.
People caring for older people with dementia need social and emotional support. Caregivers are 20% more likely to develop the disease than others. Don’t neglect yourself for the sake of care – take care of yourself too.
Reasons for aggression
Long before the first manifestations of aggression, symptoms of inappropriate behavior arise:
- ordinary frugality turns into stinginess, the patient hides money, can destroy it, not trust loved ones and at the same time easily succumb to the deception of scammers;
- suspicion, the formation of obsessions and delusions;
- fear, fear of intrigue, conspiracies of others aimed at causing harm to the health and life of the patient, which is often accompanied by refusal to take medications and food (fear of poisoning);
- excessive and inappropriate sexual activity.
From a medical point of view, aggressiveness in dementia develops due to the massive death of neurons, the loss of neuronal connections, leading to a gradual change and disintegration of the personality. Individual character traits are erased, fear and negativism appear, accompanied by emotional outbursts.
The frequency of manifestation of a particular psychotic disorder often depends on the type of dementia. Atherosclerotic cerebrovascular disease and psychosis, for example, are considered related. One of the pathologies in which aggression occurs most often is Alzheimer's disease.
Aggression in the structure of psychotic disorders in Alzheimer's disease
| Type of psychotic disorder | Prevalence among patients, % | Time before/after diagnosis, months. |
| Aggression | 40 | After 22-24 months. |
| Paranoia | 21 | In 16-17 months. before |
| Anxiety | 26 | In 6-7 months. before |
| Accusations from others | 15 | Shortly before diagnosis |
| Irritability | 46 | Several months. later |
| Restless behavior | 79 | After 11-13 months. after diagnosis |
| Depression | 48 | In 24 months before |
| Mood swings | 22 | Shortly before diagnosis |
| Antisocial behavior | 17 | In the first six months after diagnosis of the disease |
Aggression in dementia can take a verbal form: swearing, cursing, threats, raising the voice up to the point of screaming, and can be expressed physically - an increased tendency to get into fights, biting, scratching, etc. With dementia, even previously calm and not prone to aggression people show aggressive behavior. The reason for this is unmet needs or unsuccessful attempts to express one’s thoughts and desires. Patients with dementia, along with healthy members of society, need emotional communication and comfort.
Aggressive dementia can occur for biological, social, and psychological reasons. The first include:
- pain syndrome;
- disease;
- physical discomfort (hunger, constipation, forced posture);
- the appearance of external sound and visual stimuli (noise, light);
- taking certain medications, side effects of therapy;
- hallucinations, delusions requiring an aggressive response;
- visual and auditory disturbances, loss of spatial orientation, when a person is unable to independently realize his desires.
The second group includes forced loneliness, cessation of social connections, inaction, attempts to hide symptoms from others, lack of trust in loved ones, and sensory deprivation.
Psychological factors that provoke aggression include ignoring the patient’s opinion, violation of his rights, incorrect assessment on the part of the patient of the actions of caregivers, the threat of invasion of personal space (help from strangers in performing hygiene procedures). Strangers and unknown environments also provoke aggression. Attacks of aggression during dementia can also appear because a person lives in his own reality: he believes that he must perform certain actions (pick up a child from kindergarten, take a walk in the park, make tea), but they try to interfere with him or do the work for him.
Dementia, depression and psychosis are also inextricably linked. Feelings of loneliness and abandonment often push the patient to act aggressively.
Preventing dementia in older people
During the natural aging process, as you approach age 50, it is worth considering dementia prevention . The tips described below will significantly reduce the risk of the onset and progression of dementia, as well as remain healthy, happy and full of strength in old age.
- Maintain interaction with pleasant friends . It’s worth communicating more with your loved ones, meeting like-minded people, taking part in interest groups, etc. You shouldn’t be alone for a long time.
- Move . Any type of systematic activity that is enjoyable and not stressful will play a positive role in the prevention of dementia. Walking in the fresh air, swimming and cycling have significant benefits.
- Maintain proper nutrition . It is worth eliminating any junk food from your diet. You should eat small amounts several times a day. You can also include vitamin complexes in your diet.
- Don't stop learning new things and training your memory . The development of intellectual activity, mental exercises, etc. will help maintain brain function at the proper level.
- Completely give up harmful addictions . It is worth eliminating the use of alcohol and tobacco from your life, as they negatively affect the condition of blood vessels in the brain and health in general.
- Learn to react calmly . Methods of relaxation, meditation, yoga and psychotherapy help maintain physical and psycho-emotional health.
- Get treatment in a timely manner . It is worth timely treatment for various possible diseases, especially infections and problems in the cardiovascular system.
We hope that after reading this article you have a more complete picture of the disease such as dementia in older people. If you use all the material provided, you can prevent the disease, or learn to maintain a good standard of living when the diagnosis has already been made.
Additional measures and patient care
All treatment for senile dementia is to prolong life and stop the development of the disease. The task of doctors is to stop progressive pathologies, reduce symptoms, and increase mental abilities. Therefore, complex treatment is carried out, which includes the following elements:
- Sociotherapy. It consists of qualified assistance, good care, activation of the patient’s mental processes and providing a comfortable environment.
- Psychotherapy. Aimed at interacting with both patients and their relatives. Includes physiotherapy, massages, classes with specialists in maintaining and correcting speech.
- Psychopharmacology - treatment with antidepressants.
- Individual therapy aimed at reducing the content of harmful substances in the body.
Close people should behave correctly with patients. Ignoring the disease can make the situation worse. Of course, it’s unpleasant to see a loved one deteriorate. But the patient’s life expectancy and its conditions depend on proper care, treatment, assistance, care, and attention.
You shouldn’t drive away thoughts of illness, you need to accept this fact. Try to understand how the elderly person feels when you help him. There is no need to mechanically carry out your duties of caring for the patient, otherwise he may become something for you that requires constant care.
Talk to an older person. Often, patients hear and even understand what is being said to them, but simply cannot take part in the conversation due to cognitive impairment. Don't swear, don't get annoyed, don't criticize.
Ask simple questions that require yes or no answers. It may be necessary to repeat them several times, changing the words so that the patient understands the meaning.
Dementia involves the patient being unable to remember events that just happened. But the memories of ten years or more ago are very vivid and distinct. Discuss these situations with the person, listen to his stories.
To develop everyday skills, come up with a system of sequential actions and follow the patient’s daily routine.
It is also worth giving an elderly person small tasks, so he will feel needed.
Provide safety around the patient. Remove objects that could cause injury and clear the room of unnecessary furniture. Make special devices in the bathtub that you can hold on to. A place to sleep and rest should be comfortable.
Do therapeutic exercises with an elderly person without heavy loads.
All of the above measures are aimed at increasing the effectiveness of dementia treatment.