Plexitis is a very dangerous disease caused by inflammation of the nerves of the brachial plexus. This disease brings great discomfort to the patient and also entails disability. The fact is that as a result of the disease, a person’s performance decreases. The patient is unable to perform the simplest everyday movements, for example, washing his face, brushing his teeth or combing his hair.
This disease is considered serious, causing inconvenience to a person. The most interesting thing is that the disease leads to the fact that in the affected area is exactly the hand with which the person works most. Right-handed people find it difficult to perform actions with their right hand, and left-handed people find it difficult to perform actions with their left hand. In order to correct the situation and restore the functionality of the hand, the patient will have to spend a lot of time and effort on appropriate treatment.
Patients with this disease are forced to endure severe and very unpleasant pain, which occurs due to inflammation of the brachial nerves. It is mainly felt by the patient at night, as well as when the person moves the affected arm. In addition, the pain becomes stronger at those moments when the patient raises his arm up or moves it behind his back.
The patient's situation worsens when he brushes his teeth or frequently moves his hand while working with a toothbrush. The pain also increases when a person fills a cup with water and brings it to his mouth to drink from it. It becomes very difficult for the patient to get down and tie his sneakers, or start the car with the key. In severe forms of plexitis, when the situation can be called advanced, the patient completely loses sensitivity in the hand. As a result, muscle atrophy, paresis and paralysis develop.
The consequences of the disease can be different. Everything will depend on the form of development of the disease.
Plexite is distinguished:
- Upper,
- Lower,
- Total.
Often, patients visit the clinic and complain to the doctor about plexitis of the working hand. It is difficult for right-handers to work with their right hand, since the joints of the right shoulder are affected, and for left-handers it is difficult for them to work with their left hand.
There are two stages of development of the disease:
- Neuralgic,
- Paralytic.
Each stage is characterized by its own clinical manifestations. The first is due to pain. In the second stage, the pain is accompanied by reduced muscle strength in the shoulders.
Forms of plexite
Certain forms of development of plexitis are identified. These include:
- Traumatic. It is detected as a result of injury to the nerve plexus,
- Compression-ischemic. Can occur with prolonged compression of the plexus. Leads to impaired nutrition of nervous tissue,
- Infectious. The disease is associated with infection in the nerve ending,
- Infectious-allergic. Occurs due to an unusual allergic reaction of nerve endings due to the introduction of a vaccine. This is accompanied by excessive inflammation in the plexus,
- Toxic. May develop as a result of poisoning,
- Dysmetabolic. This form of plexitis is associated with impaired metabolism in the body due to poor nutrition.
Signs of pathology
The first symptom of the disease is severe pain in the affected area, transmitted from the center of the plexus to the peripheral zones. The pain may spread throughout the arm and shoulder. It occurs spontaneously, has a cutting, shooting nature, some patients complain of aching limbs. The pain syndrome tends to intensify during increasing force load, when trying to lift, rotate, or bend the arm at the joints. Next comes muscle weakness.
With varying degrees of impairment, the patient experiences difficulties either in broad motor skills (lifting weights) or in fine motor skills (up to the inability to independently fasten buttons, hold cutlery, etc.). The reflex responses of the tendon apparatus are lost. Partial or total paralysis of a limb occurs.
At subsequent stages of disease progression, trophic manifestations appear:
- discoloration of the skin in the affected area;
- increased sweating or its complete absence (anhidrosis);
- thinning of the epidermis, vascular network on the surface of the hand, decreased elasticity, dryness;
- excessive hardening, brittleness of the nail plates.
Due to loss of elasticity, the skin is easily injured, even small scratches bleed for a long time.
Causes of plexitis
The most common causes of this disease include:
- Dislocation of the shoulder joint,
- Compression of the nerves of the shoulder,
- After a collarbone fracture,
- After osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic region,
- After vibration exposure in the shoulder area,
- Due to birth plexitis,
- In case of metabolic disorders,
- Due to pathological processes of the lymph nodes in the armpit area,
- After suffering injuries to the shoulder, neck, shoulder girdle,
- When squeezing blood vessels in the costal area.
How to treat post-traumatic plexitis of the shoulder joint
Post-traumatic brachial plexitis is a fairly common disease that can occur after a ligament and tendon sprain, clavicle fracture, shoulder dislocation, etc. Post-traumatic plexitis often occurs with constant use of crutches. Representatives of certain professions are susceptible to microscopic injuries: builders, painters, finishers, hairdressers, etc.
Before brachial plexitis is treated, a diagnostic examination must be performed. Then, after the diagnosis is made, it is necessary to exclude the continuation of traumatic exposure. If the patient detects the presence of scar tissue in the area of injury, then measures must be taken to remove it. This can be done surgically. But it is safer to remove scar changes using manual therapy and laser techniques.
Plexitis of the shoulder joint can be treated effectively and safely using several methods: conservatively, surgically, pharmacologically. The most effective methods of influence are manual, physiotherapeutic and kinesiotherapy. The first stage of therapy is to restore nutrition and position of the brachial nerve plexus. Then measures are taken aimed at restoring the lost functionality of the soft tissues of the upper limb.
Symptoms of plexitis
Brachial plexitis is very easy to identify, as it has clear and pronounced clinical symptoms. The pain syndrome worsens to a greater extent at night or at the time of movement.
When this disease develops, the patient has a very difficult time moving the shoulder or arm in general. In this case, fine motor skills are impaired. If a severe form of plexitis develops, the patient completely loses sensitivity in the hand and muscle atrophy develops. In addition, muscle strength is significantly reduced, even to the point of disability. Examining the hand, one immediately notices its pallor, sweating, and impaired nail development.
When superior plexitis is detected in a patient, the sensitivity of the hand decreases. It is very difficult for the patient to work with it, to bend the elbow, and also to rotate the shoulder.
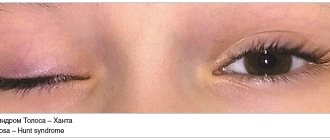
When diagnosed with inferior plexitis, impaired motor skills of the fingers are detected, pain is felt in the shoulder and forearm. At this stage of the disease, the patient is quite likely to experience Horner’s symptom: the pupil narrows, the eyelid droops, and the eyeball sinks.
Depending on the extent of the disease detected as a result of medical examinations, the doctor will determine the treatment. Accordingly, it will differ noticeably.
To carry out effective therapy, it is very important to find out what the mechanism of disease development is.
Birth injury to the brachial plexus
Birth injury to the brachial plexus, or “obstetric palsy” as it is often called, is paralysis of the upper limb resulting from birth injury to the brachial plexus or the nerve roots that form it. Often this is facilitated by difficult and difficult childbirth, discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the birth canal, pathological presentation of the fetus, and the use of various methods of obstetric intervention. It should be noted that the cause is not always the incorrect provision of medical care, since some factors cannot be corrected in advance.
Currently, there are three forms of obstetric paralysis and paresis. This division is necessary to determine treatment tactics and make a prognosis for the future, since the clinical picture, depending on the form, will be different:
- lesions of the upper part of the brachial plexus - the Erb-Duchenne form - are most common (from 60% of cases). In this case, the muscles in the area of the scapula and shoulder joint suffer, and flexion of the arm at the elbow joint is difficult or completely absent. The arm hangs passively, movements are maintained only in the hand, the arm is usually pressed to the body and turned inward;
- damage to the lower part of the brachial plexus - Dejerine-Klumpke form - a rather rare form of paralysis (up to 10% of cases), with this form of movement in the shoulder joint is preserved, and movements in the hand and fingers are significantly difficult or completely absent;
- damage to the upper and lower parts of the brachial plexus - a mixed form of obstetric paralysis - (about 30% of cases), the most severe form, in which movement along the entire limb - from the hand to the shoulder - is significantly limited or completely absent.
In the first days and even weeks of life, it is not always possible to determine the severity of the damaged brachial plexus, since the entire arm is completely immobile. Only by 3-4 weeks of age does it become clear which part of the brachial plexus is most affected.
The course of paresis depends on the severity of the lesion. In mild cases, motor functions of the hand are restored within 1-3 months. If complete recovery does not occur during this period, the impairment of motor function will remain forever, but the severity of this impairment, the degree of limitation in everyday life, the degree of visibility of the problem to others can be completely different, and this already depends on the treatment.
For lesions of mild to moderate severity, early, comprehensive and regular complex treatment helps to achieve good compensation.
With severe lesions , the limitation of movements in the hand will be pronounced, but the range of movements and muscle strength can be increased quite noticeably.
Active early treatment must begin in the first weeks of life with orthopedic correction in the form of special hand placements, as well as therapeutic massage, physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
The most effective work with a child is in the first year of life, especially in the first 3-6 months, since the most active restoration of functions occurs during this period.
It should be noted that in the absence of treatment, radiographic changes in the form of osteoporosis are revealed in the affected limb, and ossification processes slow down already at 5-7 months of life. By the age of one, the process of lag in the development of the humerus, forearm and hand bones on the affected side becomes more obvious and sometimes irreversible, the development of the elbow joint is disrupted, and persistent contractures are formed. The severity of these changes depends on the severity of damage to the neuromuscular system, activity and adequacy of treatment.
Therefore, courses of massage and physical therapy must be repeated every 1.5 - 2 months. Physiotherapeutic procedures include laser therapy on the area of projection of the brachial plexus. Very early, from 3 to 4 months of age, electrical stimulation of muscles is used. At the same age, reflexology is also performed. This comprehensive approach brings tangible results.
Closer to one year of life, more active work with contractures is often necessary. Even mild contractures in the shoulder and elbow joints can be very persistent, significantly limit movement, fix the arm in a pathological position and are difficult to treat. During this period, thermal procedures are prescribed, the massage therapist and kinesiotherapist pay a lot of attention to the development of joints.
To summarize, we note that complex treatment of birth injury to the shoulder joint necessarily includes, along with drug treatment, therapeutic massage, physical therapy, electrical muscle stimulation, and reflexology.
Complex treatment in the form of regular courses should continue throughout the child’s growth period. Most often in early childhood and preschool period. In the future, depending on growth activity, i.e. During the period of growth spurts (stretching), rehabilitation courses are carried out more often.
Even with severe lesions of the brachial plexus, with timely and ongoing treatment, it is possible to increase the range of movements, “raise” the arm to a horizontal level and higher, reduce or even completely prevent the development of contractures in the joints, slow down or stop the growth retardation of the affected arm. This requires patience and regular hard work of parents and children.
Unfortunately, with irregular, insufficient treatment, there will inevitably be an increase in the severity of contractures, a decrease in muscle strength, a decrease in the active range of movements, and the deformation of the skeletal system will be more severe: shortening of the limb, scoliotic deformity of the spine.
I would like to emphasize once again that the basis for successful treatment is the earliest possible start of therapy (in the first 2 weeks of life) and regular, comprehensive, highly professional and consistent treatment in the future.
At the Pain Treatment Center of RAM Clinics, we, using the extensive experience of our specialists in treating children with birth injuries of the brachial plexus, will consult your child, draw up a treatment plan for the near future, issue detailed recommendations, and also offer the services of our Treatment and Rehabilitation Center.
Treatment of plexitis
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor only after examination and identification of the stage of the disease. If the patient complains of severe unbearable pain, doctors prescribe painkillers. In treatment, it is extremely necessary to ensure conduction along the nerve fiber, restore microcirculation, and prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease and its form, a specific method of administering medications is prescribed. In severe cases of plexitis, blockade is possible.
If the cause of the disease is an infectious process in the body, then the doctor prescribes antibacterial therapy.
Physiotherapy is very important during the treatment process. This method is considered to be the most effective and also reduces pain syndromes. For such purposes, doctors prescribe reflexology, massage, manual therapy, laser treatment, phonophoresis, and physical therapy. It becomes extremely important in treatment to normalize the functioning of the shoulder joint, gradually restoring motor mode. The joint can be fixed using certain orthopedic devices.
Treatment for plexitis should be selected individually for each patient. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe surgical treatment. Surgeries are performed only when a tumor is detected, serious injuries to the shoulder, or an aneurysm of the subclavian artery.
It is better to carry out treatment in specialized clinics where modern diagnostic equipment is available. This will allow for accurate, prompt diagnosis and identification of treatment methods. Only an experienced doctor can achieve one hundred percent and good results using combined, individually formulated therapy for the patient. The tasks of an experienced specialist include not only eliminating pain, but also eliminating the cause of the development of plexitis.
The most important thing is timely rehabilitation of the patient. This will help restore shoulder motor function.
Those diagnosed with this disease should not be exposed to hypothermia or physical exertion. Patients should try not to interact with toxic substances. Upon completion of the course of treatment, they are prescribed preventive measures, which are extremely necessary.
To identify a typical disease, doctors perform laboratory tests. To prevent the disease, the following methods are used:
- Antibiotic therapy,
- Treatment with antiviral drugs,
- Immobilization of the injured shoulder joint,
- Removal of a tumor or hematoma,
- Detoxification,
- Correction of metabolic disorders.
Vasoactive and metabolic therapy is very effective, which ensures normal, improved nutrition and rapid recovery of the body.
When treating plexitis, doctors prescribe pentoxifylline, complex preparations of B vitamins, and nicotinic acid.
It is no less advisable to carry out thermal procedures and mud treatment. Symptomatic therapy plays an important role. The doctor prescribes diclofenac, metamizole, and sodium to the patient. A therapeutic blockade is carried out using novocaine, UHF, and reflexology.
To normalize blood circulation in the affected area of the body, it is recommended to carry out a complex of physical therapy and hand massage. If necessary, the massage course is re-prescribed, as well as exercise therapy with increasing load. For the most part, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Inpatient treatment is not excluded. Only a qualified specialist can help the patient by prescribing correct and effective treatment. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment takes place on an outpatient basis, in severe situations - in a hospital. For plexopathy, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, painkillers, dehydrating drugs are used, and physiotherapeutic procedures are also prescribed. After the pain subsides, special exercises, massage, and a complex of vitamins are prescribed.
In more severe situations, surgical treatment is prescribed to eliminate the compression and restore the functionality of the plexus branches.
Prevention of plexitis
After completing the course of treatment, the patient should follow preventive measures. They should also be performed by those who have not encountered this disease for prevention purposes. Swimming is very beneficial. It is this activity that helps stimulate and keep all muscles toned and prevents the development of the disease.
Swimming is an excellent remedy against the occurrence of arthritis, arthrosis, and other negative symptoms. It is worth combining physical activity with this hobby to warm up your joints. This will prevent ossification, increase the body’s performance, as well as its resistance to various diseases.
For prevention purposes, it is very important for the patient to wear warm clothes in winter. Don't forget about proper, balanced nutrition. You need to include foods high in fiber in your diet. Such products include vegetables, fruits, and herbs. You should avoid canned, fried, spicy and hot foods. You should eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day. It is important not to spread infectious diseases. Their timely treatment with the use of antibacterial and antiviral agents is the key to good health and prevention of the typical disease of plexitis.
For the purpose of prevention, the patient is also prescribed sanitary and resort treatment in health resorts. Basically, this option for restoring health can be prescribed as a result of identifying a chronic form of the disease. It is very important for a patient with this diagnosis to rest more and not overexert. You should try to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eliminating bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
In order to prevent the recurrence of the disease in the future, it is necessary to initially identify the source of infection, preventing its spread.
In many sanatoriums, the following methods of restoring health are used for plexitis:
- Conditions for complete rest are provided,
- Therapeutic baths,
- Restoring the health of the soul,
- Mud treatment
- Thermotherapy,
- Massage course,
- Physiotherapy,
- Acupuncture,
- Proper, balanced nutrition is provided.
A special role is given to a proper diet rich in B vitamins.
What is shoulder plexitis, how to recognize and treat it
Very often, along with the shoulder, plexitis also affects the cervical region, since it is located in close proximity to the shoulder. At the first noticeable problem in the shoulder and arm area, for example, pain when moving a limb, after waking up there is a prolonged feeling of numbness.
Plexitis occurs on the right or left side, but is often referred to as bilateral plexitis. The disease can be the result of a large list of reasons, including injuries, infections, allergies and others.
How does the disease progress?
The course of the disease is divided into two stages:
- Neuralgia
Here the symptoms manifest themselves as pain in the muscles and joints, aggravated by movement.
- Paralysis
Here the pain turns into muscle weakness, which ends in atrophy, which, in turn, ends in paralysis.
Symptoms of plexitis
- Shoulder pain that gets worse with the slightest movement of the arm. It can be of the nature of attacks, and radiate to the collarbone and arm.
- Atrophy is swelling and pallor of the skin at the site of the lesion, the nails of the affected hand become brittle, and the palms sweat profusely.
- The sensitivity of the hand decreases, which indicates paralysis.
- The muscles of the arm are so weakened that they do not allow performing basic tasks.
Additional symptoms
- Breathing problems.
- Intense hiccups.
- Constriction of the pupils.
- Recession of the eyeballs on the side affected by the disease.
The disease can be localized in various areas of the shoulder joint and can be divided into:
- Upper – pain is focused in the supraclavicular region.
- Lower – pain is concentrated in the area of the elbow, hand and forearm.
- Total - pain spreads throughout the shoulder and arm.
Methods for diagnosing plexitis
- Examination by a doctor and medical history.
- Neuromyography.
- Electromyography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasonography.
- X-ray.
- Laboratory blood tests.
Work with plexitis and its diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist, who often involves doctors from other fields of medicine, for example, a gynecologist, urologist, and traumatologist. An x-ray of the entire spinal column and an ultrasound of the internal organs may also be prescribed.
Treatment of brachial plexitis
Nowadays, only conservative therapy methods are used to treat the disease, and usually the injured arm is fixed with a splint in order to avoid its mobility.
To begin with, drug treatment of plexitis is prescribed in order to relieve nerve inflammation:
- Painkillers are of various types that will quickly and effectively relieve pain.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - they act locally on the sore spot.
- Multivitamin complexes with a predominance of vitamins of groups B, A, E.
- Anticholinesterase drugs (improves the transmission of nerve impulses).
- Decongestants.
- Medicines that increase tissue nutrition.
- Products that improve blood microcirculation.
After the main pain has subsided, a course of rehabilitation therapy begins, among which much attention is paid to manual and physical therapy. The most common recovery methods are:
- Acupuncture.
- Therapy with leeches.
- Massage course.
- Various therapeutic and physical training complexes.
The most commonly used physiotherapeutic methods are: cryotherapy, magnetic therapy, dynamic currents, ozokerite, balneotherapy and other methods of physiotherapy.
Treatment of plexitis usually takes place in combination with the use of traditional medicine methods, since only a complex effect on the disease can bring tangible and significant results.
In the event that plexitis is a consequence of an injury received by the baby during childbirth, then treatment is usually started immediately. Typically, treatment methods include massage, exercise therapy, special nutrition, and medications that improve the level of immunity.
The main thing is to consult a doctor in time so that treatment of the disease can begin in a timely manner.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Possible complications and consequences
Complications may include a persistent neurological defect, paralysis, weakness in the limbs, and impaired sensitivity.
Among the possible consequences, a violation of labor adaptation as a result of a neurological defect is identified. Due to severe muscle weakness, it is impossible to perform certain types of work. It becomes extremely important to follow the correct regimen, perform physical therapy and start eating right.
It happens that when this disease develops, the patient has to move with the help of crutches. In this situation, it is important to choose them correctly, as well as to know how to use them, so as not to provoke increased pain in the shoulder area.
You can buy an omron compressor nebulizer from us inexpensively.
Causes
These nerves can be damaged by stretching, pressure, or cutting. A strain can occur when the head and neck are forced away from the shoulder, such as during a fall from a motorcycle or sometimes a car accident. In more severe cases, the nerves may become torn from the spinal cord. Pressure can occur when the brachial plexus between the collarbone and the first rib is damaged, which can occur during a fracture or dislocation. Swelling in the area from excessive bleeding or damaged soft tissue can also lead to injury.