Symptomatic epilepsy
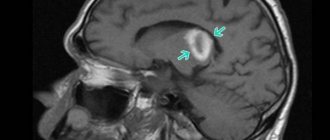
Associated with the characteristics of genetic defects in brain formation or congenital changes in the brain. Often the risk of epilepsy arises due to a traumatic brain injury, a stroke, or an infectious lesion of the nervous system, for example, after meningitis. 5 years after illness is the maximum risk. In older people or in patients with a brain tumor, cavernoma, vascular aneurysm, parasitic cysts, the incidence of epilepsy is very likely. In childhood, the risk of epilepsy is diagnosed with cerebral palsy.