Types of sclerosis
Clinicians distinguish several types of pathology:
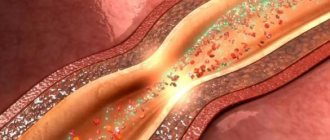
- Atherosclerosis. The disease is characterized by the presence of “cholesterol plaques” on the walls of blood vessels.
- Multiple sclerosis. It occurs quite often in people over 70 years of age. It manifests itself as a violation of neural communication between organs, tissues and brain cells.
- Thrombosclerosis. Characterized by the occurrence of blood clots, adhesions, and hematomas.
- Senile sclerosis. This type is caused by changes occurring in the structure of the brain.
- Pneumosclerosis. It is rare and develops as a result of damage to the nerve cells of the lungs.
- Autoimmune sclerosis. It develops against the background of damage to the myelin sheath of the nerve fibers of the spinal cord and brain.
Despite the wide variety and complex course of the pathology, medicine has modern means of diagnosing it.
Multiple sclerosis: stages and types
Features of the course of the disease make it possible to classify it into types and stages. The following forms occur in multiple sclerosis:
- Remitting is a pathology with rare exacerbations, when the onset of remission gives the body the opportunity to recover.
- Primary progressive - multiple sclerosis develops slowly, gradually. The worsening of symptoms in this type of multiple sclerosis is unhurried, but there is no chance of restoring body functions.
- Secondary progressive - exacerbations with such multiple sclerosis are rare, symptoms increase, there are more of them.
- Progressive-remitting form of multiple sclerosis - at first the disease develops slowly, but then the symptoms become more numerous and pronounced.
The following stages are attributed to multiple sclerosis in women and men:
- Acute stage - the first 14 days after the rapid development of symptoms.
- Subacute - multiple sclerosis develops in the first 2 months from the onset of exacerbation.
- Stabilization - patients with multiple sclerosis note the absence of symptoms for 3 months or more.
Causes
The main causes of senile sclerosis:
- Biochemical processes that negatively affect brain cells. As the body ages, the transmission of impulses between neurons decreases.
- Cerebrovascular accident. With age, the permeability of the bloodstream and the elasticity of blood vessels decrease, which contributes to the death of neurons.
- Slowing down neuronal cell regeneration. Negatively affects the functioning of the central nervous system and overall health.
In some cases, the development of the disease is due to a genetic predisposition. However, in most cases, the occurrence of pathology is facilitated by processes associated with age-related changes occurring in the body of older people.
Age-related memory decline: when, why, how to identify, how to help?
Currently, experts clearly observe a demographic trend towards an aging population. Thus, the number of elderly people today constitutes approximately 20% of the total population of our country [1]. Increased forgetfulness is one of the most common complaints in elderly patients [2]. According to research:
- mild cognitive impairment syndrome (MCI) occurs in 3–25% of older adults [3–5];
- MCI is present in 44% of elderly people who sought neurological help [3, 4];
- within 5 years, dementia develops in 50–70% of patients with MCI; in the rest, cognitive impairment is either at a stable level or regresses [3, 6–8];
- decline in cognitive functions begins as early as 45–50 years of age and progresses with aging [3, 9, 10].
Physiological age-related changes are based on hormonal changes and energy deficiency in the body as a whole, which leads to regional ischemia with symptoms of oxidative stress [11, 12]. Such changes contribute to age-dependent tissue damage, local inflammation and, consequently, aging.
In addition, the causes of memory and attention disorders in old age are nutritional disorders, intoxication, as well as dysmetabolic disorders due to somatic or endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, liver failure, chronic hypoxemia as a result of respiratory failure or sleep apnea), deficiency of cyanocobalamin and folic acid, often occurring in the elderly, as well as with the abuse of alcohol and psychotropic drugs [11, 13, 14].
Diagnosis of memory disorders in the elderly [11]
Step 1
Find out what medications the patient is taking and in what doses, and, if possible, discontinue those that may cause memory impairment.
Step 2
Conduct a biochemical blood screening (to determine dysmetabolic disorders): analyze the level of glucose, uric acid, ammonia, creatinine, carbon dioxide and calcium, folic acid, homocysteine, the content of B vitamins, the concentration of thyroid hormones.
Step 3
Prescribe neuroimaging studies (computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging - MRI), necessary for suspected brain tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, degenerative and vascular lesions of the brain, since memory impairment is often the only signal of these diseases in the early stages. MRI of the brain is indicated for all patients with memory disorders.
Step 4
Assess the patient's mental status for anxiety or depression. It is not always possible to fully examine the patient in an outpatient setting, so in some situations a trial treatment with antidepressants is prescribed.
Step 5
Directly identify cognitive impairment using special techniques that stimulate attention at the memorization stage. Clinicians use several neuropsychological tests: the Mini-Mental Status Scale (MMS), the Mattis Dementia Scale, the Frontal Dysfunction Battery, and the Clock Drawing Test.
Correction options
Practitioners often believe that memory impairment is an age-related feature and inevitable, and therefore does not require correction. However, it is precisely at the stage of mild cognitive impairment that pathogenetic therapy has the greatest chance of success!
Considering the high effectiveness of neuropeptide complexes in the treatment of various diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), accompanied by a decrease in cognitive functions, you can pay attention to the dietary supplement Memoprov® (EVER Neuro Pharma GmbH, Austria) [1].
Memoprov® is a peptide complex produced in accordance with international pharmaceutical standards from purified nerve cell proteins, containing amino acids and bioactive peptides [1]:
- has a number of neurochemical and neurophysiological effects, many of which are similar to the effects of nerve tissue growth factor and other neurotrophic factors [1];
- the possibility of oral administration (modern production processes, together with the chemical nature of the peptides, prevent their untimely enzymatic destruction in the gastrointestinal tract) [1, 15];
- entry into the central nervous system within 40–60 minutes after administration, with high concentrations of protective neuropeptides in the frontal cortex, hypothalamus and medulla oblongata [1, 15];
- absence of significant side effects [1].
Evidence base
- Studies by XA Alvarez et al., which analyzed data from healthy older adults with age-related memory changes, confirmed that Memoprov® can effectively support brain function, leading to significant improvements in cognitive performance and increased bioelectrical activity of the brain [1, 16].
- In a controlled randomized clinical trial, TH Crook et al. in 54 healthy elderly people with age-related decline in memory functioning, taking the Memoprov® complex for 30 days statistically significantly improved memory (assessment on the ADAS-cog scale - Alzheimer disease assessment scale cognitive - cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer's disease assessment scale) with no differences at all on the occurrence of any side effects in comparison with the placebo group [1, 17].
- An observational study by D. Volc et al. showed an improvement in cognitive functions while taking Memoprov® [1, 18].
These data make it possible to place Memoprov® among the drugs prescribed for the correction of age-related memory loss.
Literature
- Shishkova V.N., Adasheva T.V. New opportunities for improving cognitive functions in elderly patients in the practice of a therapist. Nervous diseases. 2021; 1.
- Damulin I.V. Vascular cognitive impairment in the elderly. Russian medical journal. 2009; 17 (11): 721–25.
- Titarenko A.V., Shishkin S.V., Shcherbakova L.V. and others. Dynamics of cognitive functions during aging and their relationship with the level of education. Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. 2018; 10 (4): 46–51.
Symptoms
Sclerosis negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of an elderly person and often leads to prolonged depression. The pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Extreme touchiness.
- The assessment of current events is exclusively negative.
- Progressive forgetfulness.
- Joint pain.
- Migraine.
- Increased blood pressure and, as a result, the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases.
If these symptoms appear frequently, this is a reason to consult a specialist, since only early diagnosis and timely treatment will help slow down the destruction of brain cells.
When the disease is diagnosed at a late stage, the prognosis for improvement is unfavorable. This is due to the occurrence of an irreversible process of destruction of brain neurons. In this case, an elderly person experiences the following symptoms:
- Dementia.
- Disorientation.
- Aggressiveness.
- Inability to perceive information.
- Anxiety, causeless anxiety.
- Apathy, depression, increased drowsiness.
- Senile egoism.
- Inability to reason logically.
The appearance of these signs indicates the presence of deep senile sclerosis in an elderly person. At this stage of the disease, neuron cells die off quite rapidly, which precedes such mental manifestations as hallucinations and delusions. In some cases, a person may lose control of himself.
Symptoms of senile sclerosis
The disease begins to manifest itself gradually. The first alarming symptom that you should pay attention to is a negative attitude towards your environment. Next appear:
- acute reaction to minor troubles,
- tendency to exaggerate troubles,
- anger,
- indifference to loved ones,
- withdrawal into oneself and one's problems.
Patients feel loneliness, uselessness, and unappreciation of their merits and personality. Sleep is disturbed and appetite disappears. A depressed mood prevails. This condition leads to pain in the heart, possible seizures, and unpleasant sensations throughout the body.
Signs appear against the background of loss of memory and cognitive functions. The patient first forgets small periods of time and events that happened several hours ago. Then these gaps become larger. The patient does not remember where he was going or how he got to a certain place.
The process develops in leaps and bounds. A monthly lull can give way to a sharp deterioration in two to three weeks. Treatment of sclerosis is difficult and not always effective. Our goal is to make the life of your family and your loved one diagnosed with senile sclerosis as easy as possible.
Diagnostics
Correct treatment of the pathology is possible only after the following diagnostic measures:
- MRI and CT of the brain.
- Complete blood test (sugar, creatinine, blood electrolytes, vitamin B1 level).
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
In addition, a neurologist examines the medical history and collects information about a possible genetic predisposition to the development of this pathology.
Causes
Now there are a lot of means of maintaining the body in normal condition until old age. This is the level of development of medicine, and a lot of all kinds of health practices, benefits on proper nutrition, etc. Not everyone faces old age with completely destroyed health. A lot depends on the person himself. If you take proper care of your body, you can be vigorous and intellectually active even at 80 years old. Old age is not a disease, but just one of the stages of life's journey. There are many examples where people in very old age remain active, have hobbies, are interested in everything that happens in the world, and babysit their grandchildren.
At the same time, it is important to be aware of what happens to the nervous system at the age of 60 or more. The main features are:
- Deterioration of blood supply to the brain. The more years we live, the more worn out our blood vessels become. They lose elasticity and normal permeability. Cholesterol plaques and blood clots cause the brain to literally begin to “suffocate.” This is fraught with the death of neurons, and then sclerosis is just around the corner.
- Slowing down cell regeneration. In a young body, cells are formed very quickly and tissues are constantly renewed. With old age, this process slows down several times. Such “inhibition” has a bad effect on both the physical condition and the functioning of the central nervous system.
- Decreased biochemical activity of the brain. Impulses between neurons are transmitted using specific substances - neurotransmitters (dopamine, adrenaline, etc.). As a person ages, less and less of them are produced.
With a lack of neurotransmitters, impulses between cells weaken and brain function changes. This affects intellectual and physical activity. Now medical science is working to find out the exact causes of these processes. When all the answers are found, it will definitely lead to a breakthrough in the treatment of senile sclerosis and other diseases of old age.
Treatment
Treatment of senile sclerosis requires an integrated approach. Therapy is quite long and is often accompanied by the participation of a cardiologist, neurologist and psychotherapist. Only in this case is there a high probability of stopping the destruction of brain neurons.
Before prescribing treatment, the specialist finds out the cause of the degradation of brain cells. Therapy for senile sclerosis includes the use of medications, effective folk remedies, psychotherapist sessions, dietary nutrition, physical activity and normalization of the daily routine.
Drug treatment
For senile sclerosis, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Psychostimulants. In most cases, therapy is based on taking psychostimulants. Drugs in this group have a stimulating effect on parts of the brain.
- Nootropics. These drugs have a positive effect on the integrative functions of the brain, suppressing aggressive manifestations.
- Tranquilizers. Medicines in this group help reduce excessive emotional excitability and anxiety.
In addition to drug therapy, psychotherapeutic treatment is recommended for an elderly person suffering from sclerosis. Sessions with a neuropsychiatrist promote positive thinking and help prepare for long-term treatment.
Folk remedies
Effective folk remedies can be used as part of the complex treatment of senile sclerosis. Tinctures from rowan bark, elecampane, clover, heather decoction, garlic oil, onions with honey have a beneficial effect.
Before using such products, you should consult your doctor.
Other methods
Positive dynamics in treatment depends not only on the timely use of medications and folk remedies. Factors such as:
- Interest in life. The involvement of an elderly person in society and family affairs has a beneficial effect on his psycho-emotional state.
- Elimination of stress. To avoid exacerbations of sclerosis, it is necessary to protect the elderly from worries and stress, since this significantly impairs memory.
- Memory training. Reading is one of the most effective ways to train memory at any age. After reading a book or article, it is necessary to analyze what you read and highlight the most important episodes.
- Planning. Thought processes in any manifestation effectively affect the functioning of the brain in old age. Daily brain training can include making a plan for several days. This could be a trip to the store, household chores, hobbies, etc.
- Concentration of attention. Mastering computer literacy, foreign languages, learning poems and songs will help activate your memory. When absorbing significant volumes, it is necessary to take a break of at least two hours. This will allow you to better assimilate new information.
Treatment of senile sclerosis is a long process, so relatives must support the elderly person. This requires providing not only emotional support, but also monitoring the intake of medications and compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician.
The essence of the disease
The word “sclerosis” is often used in everyday life. It is usually used when people complain about memory problems. However, senile sclerosis is a slightly different medical field. This disease is closely related to cerebral atherosclerosis. In young people who are far from senile dementia, difficulties in remembering some information may be associated with nervous strain, stress, and finally, impaired blood circulation in the brain due to injuries or illnesses.
Older people suffer from sclerosis due to the gradual death of brain neurons. This is a process caused by age-related changes, but it happens at different speeds for everyone. Cell death increases if a person:
- does not eat properly;
- prone to bad habits;
- moves little;
- has “bad” heredity (there were/are relatives in the family with similar problems).
The disease is indeed strongly genetically determined. DNA encodes information about all processes, including the rate of cell death. This process is purely individual. And yet, an incorrect lifestyle greatly undermines the body’s resources and reduces the number of years lived in “sober memory.” If a person is subject to physical inactivity, smokes or is addicted to alcohol, the blood vessels do not supply the brain with the amount of oxygen it needs. Because of this, neurons gradually die and sclerosis develops.
Prevention
You can avoid the occurrence of senile sclerosis if you follow the following recommendations:
- Active lifestyle. A daily walk in the fresh air is a must in an elderly person’s daily routine.
- Positive thinking. Positive emotions are as essential to brain function as oxygen.
- Maintaining a daily routine. An important condition for active brain function in old age is sleep for at least 8 hours.
- Memory training. Watching educational programs, learning a foreign language, memorizing poetry, etc.
- Compliance with drinking regime. Drinking 1.5-2 liters of water per day helps cleanse blood vessels.
- Diet. In old age, it is important that the diet consists of foods rich in protein, fiber and Omega-3. It is also necessary to enrich the diet with vegetables and fruits.
Compliance with these rules promotes the active functioning of brain cells and helps preserve memory for many years.
How to slow down the progression of the disease?
The first symptoms of senile sclerosis may appear long before the onset of obvious problems with memory and skills. It is important to understand that the patient's condition will not improve on its own, but you have time to delay the development of the disease. In the fight for a clear consciousness of a loved one, the following will help:
- active and healthy lifestyle;
- proper nutrition, especially the consumption of foods that promote cerebral vascular health;
- memory training;
- good sleep;
- help in controlling your own thoughts;
- formation of love for yourself and the world around you.
Explain to a newly diagnosed relative that he or she can cope with the disease. To do this you need:
- Accustom yourself to think positively and believe in the success of any endeavor;
- remain calm and do not give in to stress;
- be interested in life and perceive current events positively;
- plan your day;
- read more literature, analyze what you read, ask questions and look for answers in books;
- discuss remembered information with friends and family;
- learn poems and songs, perhaps even foreign languages.
Compliance with these recommendations reduces the chance of rapid development of senile sclerosis. It can be difficult to convince a mature person to learn new things, so it is important to help the patient with his studies and support him in this work. The staff of our boarding houses, including qualified doctors and psychologists, regularly work with guests, trying to prolong the first stage of the disease as long as possible.
Causes of development of vascular sclerosis
The causes of sclerosis depend on risk factors. They can be modifiable, that is, we can influence them - lifestyle and laboratory parameters, or non-modifiable - age, gender and genetic predisposition.
Non-modifiable ones include:
- gender - men suffer more often, this is explained by the fact that in women estrogen has an angioprotective function;
- age - men over 45, women > 50 or with early menopause;
- cases of atherosclerosis in relatives.
Modifiable are:
- smoking;
- drinking excessive amounts of alcohol;
- lack of plant foods in the diet;
- low physical activity;
- stress;
- overweight;
- dyslipidemia;
- diabetes;
- arterial hypertension.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels most often occurs in the following places:
- brachiocephalic trunk;
- carotid artery (common and external carotid);
- cerebral arteries (anterior, posterior and middle);
- vertebral artery and other small vessels.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Vladimirovich Vasiliev
Neurologist, Head of the Research Center for Motor Neuron Disease/ALS, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is an insidious disease that is diagnosed in patients over 45 years of age. The initial stage proceeds almost unnoticed, so patients seek help in an advanced state. People who have relatives with atherosclerosis are susceptible to the disease, so they are recommended to undergo regular diagnostics to detect the disease at an early stage.
The disease occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques. Most often, BMS sclerosis is diagnosed in people who lead an inactive lifestyle, consume tobacco and alcohol, abuse fried foods and are overweight.
The disease develops in several stages. The initial stage is asymptomatic and very difficult to recognize. However, all stages are accompanied by various symptoms:
- Initial. Headaches and dizziness occur, which are most often attributed to overwork. It is worth considering that after sleep the symptoms disappear.
- Progressive. It is characterized by increased symptoms of the previous stage, the patient experiences emotional instability, and the person becomes depressed.
- Decompensation. It is the most complex form of the disease, in which stroke or paralysis occurs. The patient has memory loss and requires constant care.
The disease is most acutely tolerated by a person, as complications appear that end in complete loss of capacity or, even worse, death of the patient.