Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of a concussion are quite variable and include the following:
- Headache.
- Unsystematic dizziness.
- General weakness.
- Nausea and vomiting once or twice during the first time after injury.
- Loss of consciousness for a short time at the time of injury.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Mood swings.
Signs of a concussion should also include an improvement in general condition on the first or second day after the injury. This is sometimes associated with such undesirable phenomena as the desire to stop treatment in a hospital setting.
What to do if symptoms appear?
The cause of a mild concussion can be even a small contusion of the head, and therefore the patient should be immediately given first aid and sent for examination . If the patient can move independently, then it is enough to simply walk him to the hospital or take him by car.
If it is difficult for the patient to move, then before starting self-treatment for a mild concussion, you should call an ambulance team and take some measures before the doctors arrive, namely:
- It is necessary to lay the patient on his side, raising his head slightly; this must be done so that in case of sudden vomiting, the vomit does not enter the respiratory tract.
- Ensure complete silence in the room or house and curtain the windows. With a concussion, bright daylight can be irritating to the patient, so it is better for him to be in a dimly lit room.
- With a concussion, the patient may feel thirsty. What can you drink? You can offer him hot black tea with sugar.
- Under no circumstances should the patient sleep until the doctors arrive, so you need to constantly be with him and distract him.
- It is very important to monitor the patient’s pulse, as well as how the patient breathes and the condition of the pupils.
Important! Only a specialist will be able to immediately determine the presence of a pathological condition, and therefore, if you receive an injury, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
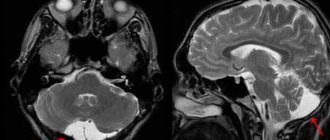
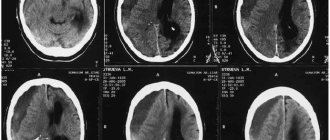
The diagnosis of concussion is rather a diagnosis of exclusion (it is necessary to exclude subarachnoid and subdural hemorrhage, brain contusion, diffuse axonal damage, etc.). To reliably make this diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct an examination (MSCT or MRI) to exclude violations of the integrity of bone structures, hemorrhages, and focal changes.
Diagnostic criteria also include the absence of severe symptoms, the presence (or absence) of mild cerebral symptoms, and diffuse organic symptoms. The fact of loss of consciousness after injury or the presence of severe nausea and one or two vomiting is also very important.
Concussion or not? Severe symptoms, pronounced neurological manifestations, the fact of prolonged loss of consciousness and repeated vomiting, amnesia after injury, even without structural changes in the brain, the fact of a violation of the integrity of the skull bones, persistent symptoms without dynamics against the background of prescribed treatment for 4-5 days, the slightest suspicion of focal lesions favor a more severe diagnosis.
Read also
Facial paralysis (Bell's palsy/facial neuritis)
Facial paralysis is spontaneous weakness of ½ of the face.
The cause is swelling of the facial nerve, as a result of its compression inside the temporal bone or in the outlet from it. Most often this leads to... Read more
Weakness and numbness in the arm and leg
The appearance of general muscle weakness and numbness in the body, arm or leg is a very serious syndrome, and if it occurs, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Connected…
More details
Vertebral artery syndrome
The main vascular highways carrying blood to the brain pass in the neck - these are two carotid and two vertebral arteries. A decrease in blood flow through the vertebral arteries will lead to the development of acute...
More details
Restless legs syndrome
Restless legs syndrome - manifests itself as unpleasant sensations in the lower extremities, mainly in the evening and at night, forcing you to make relief movements with your legs, which leads to…
More details
Neuropathy
In the human body, the work of internal organs and systems is regulated by the brain, namely by nerve impulses emanating from it. These impulses travel along nerve fibers. Damage to them can damage this...
More details
Treatment
In order to answer the question of how to treat a concussion, you should turn to the manifestations, because treatment is most often symptomatic. Treatment of this pathology is carried out in a neurosurgical hospital for a period of 9 to 12 days, followed by outpatient rehabilitation if necessary. A certificate of incapacity for work is usually issued for two weeks in a hospital setting and only if necessary is extended for a longer period, especially for certain work factors that require concentration and quick psychomotor reactions. It is necessary to prescribe semi-bed rest for a period of one to two weeks.
Drug treatment of concussion is reduced to the prescription of general restorative and symptomatic drugs. For severe headaches, analgesics are prescribed (paracetamol, analgin, baralgin, etc.); for dizziness, it is sometimes advisable to prescribe betahistine, cavinton. In all cases, it is permissible to prescribe neuroprotective therapy; phenotropil, vitamin therapy, and glycine are often used. As a rule, all manifestations disappear completely within the first month after the injury.
Causes of concussion
A concussion can be caused by bruises, blows, or sudden movement (either acceleration or deceleration). The most common cause of concussion is road traffic accidents, work-related, sports or household injuries.
Criminal circumstances can also play a negative role.
Mechanical causes of traumatic brain injury
The axial load on the brain produced by the spinal column during an insufficiently cushioned jump or a sudden fall on the buttocks can, just like a direct impact on the bones of the skull, lead to a traumatic effect on the brain.
Having an understanding of the mechanisms of brain injury, it is possible to predict the consequences of even the most minor forms of concussion in various age categories.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which fills the closed space between the brain and the bones of the skull, protects the brain “floating” in it from serious physical influences. During a sudden impact, the brain continues to move in the opposite direction by inertia for some time. The pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid between the inner shell of the skull and the brain at this moment increases many times. As a result, the brain receives a mechanical or hydraulic shock.
A counter-impact on the side opposite to the area of high pressure creates an impact of the same force with a minus sign. Forced vibrations produced by the brain “floating” in the cerebrospinal fluid expose it to repeated damage. In addition, the brain receives additional trauma as a result of its rotational displacements around its axis, as a result of which it hits the protrusions of the skull. There is a directly proportional relationship - the more sudden and strong the mechanical impact, the more significant damage to the brain.
Biological causes of traumatic brain injury
The vessels of the brain do not receive significant damage during this injury, but the concussion triggers a mechanism of inadequate reactions of the vessels themselves, nerve cells of the brain and intracranial nerve pathways. Studies conducted with animals, after modeling a concussion in them, showed the following results: when examining brain tissue under a microscope, displacements of the nuclei of nerve cells, damage to their elements - membranes, mitochondria, as well as pathologically altered space between them, an increase in the size of axons (nerves) were discovered. fibers).
Such damage indicates that a traumatic brain disease is occurring.
Symptoms of traumatic disease:
- Pathological dilatation of cerebral vessels, which occurs after their initial spasm, leads to impaired cerebral circulation. It is quickly restored with a mild concussion, but this recovery occurs unevenly in different parts. Complications of this process include slowing blood flow, vascular congestion, and intracellular edema.
- Changes in the metabolism of brain structures, colloidal balance, chemical and physical properties of the brain matter, resulting from changes in intracranial pressure at the time of traumatic exposure. Studies conducted with experimental animals have documented increased vulnerability of nerve cells in rodents, disruption of extracellular and intracellular ion metabolism, and an imbalance between the energy supply from blood cells and the need for it.
- A short-term disruption of axonal conductivity, expressed in the loss of relationships between nerve cells and the centers regulating their vital functions. At the same time, the structure of the nerve tissue maintains its physical integrity.
- Impaired coordination between important functional centers of the cerebral hemispheres (breathing, thermoregulation, cardiovascular activity) due to a breakdown in connections between them and the rest of the brain due to rotational displacement.
Analysis of the mechanism of concussion makes it possible to adequately assess the symptoms of injury and first aid tactics.
A sleepless night is tantamount to a concussion
According to a study conducted by Swedish scientists, a night without sleep, regardless of the reason for it (insomnia, night shifts, entertainment), is equivalent in its consequences to a concussion. A sleepless night has a negative impact on a person’s health, performance and mood.
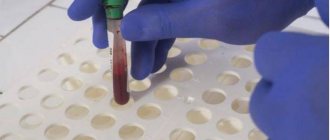
Their findings were confirmed by an experiment conducted at Uppsala University with 15 volunteers in excellent health. The results of blood samples taken from participants after a sleepless night were analyzed. Brain damage was indicated by 20% increased levels of calcium binding protein (S-100B) and neuron-specific enolase (NSE). This is a dangerous sign, since the indicators differ from the norm, but are close to similar indicators in patients after a concussion.
During a sleepless night, the tissues of the human body do not cleanse the tissues of the human body at the cellular level from toxins received while awake. Disruption of this physiological process leads to an increase in the concentration of markers in the biochemical parameters of the blood, similar to the same results after a concussion. The symptoms experienced by those forced to spend the night without sleep are similar to those of a concussion: headache, noise in the head, impaired memory and attention, nausea.
Toxins tend to accumulate in the body, so several sleepless nights in a row are comparable in severity to physical trauma to the brain.
Complications of concussion
The list of complications possible after a traumatic brain injury is very diverse. The most common is the so-called “post-concussion syndrome.” After some time - and this can be days, months, and sometimes even years - a person begins to experience headaches. These pains can be excruciating—a headache-like sensation, so to speak. A person is bothered by anxious thoughts, he gets irritated, and cannot concentrate on something specific. Sleep is disturbed and it becomes very difficult to do work.
In such a situation, it is necessary to begin treatment with medications. Seeing a psychotherapist does not bring relief. When prescribing narcotic painkillers, it is important to remember the negative consequences of drug addiction.
For treatment, it is very important to maintain rest and strict bed rest. There should be no bright light in the room to avoid pain. Medications used include sedatives, hypnotics and painkillers. Elderly people are treated for multiple sclerosis and accompanying diseases.
In order to avoid complications after a traumatic brain injury, it is necessary to undergo clinical observation for one year by a neurologist in a clinic at the place of residence.
In people who practice boxing, “boxer's encephalopathy” may occur as a complication. Its symptoms are as follows: imbalance, mental changes and trembling of the limbs.