Intervertebral disc herniation is characterized by a violation of the strength of the fibers of the fibrous ring of the disc, resulting in protrusion of the pulpous fragment. Every year, for every 100 thousand inhabitants, approximately 150 patients are diagnosed with a herniated disc. And in 80% of cases, this disease is a complication of long-standing osteochondrosis. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 40-55 years, however, vertebral hernias at 25-40 years are by no means uncommon. Of the total number of patients, approximately 20% of people require surgery.
The lumbosacral region is most often affected; it has the highest mobility and is the supporting region for the upper and central segments of the spinal column. The discs at the neck level are much less damaged, and in very isolated cases the thoracic intervertebral elements are affected.
Men are more likely than women to face a similar problem, since the connective tissues of the male body have a slightly lower degree of firmness and elasticity. Another explanation is that the male sex is more involved in heavy physical labor. Regular physical activity, incommensurate with the physiological capabilities of the musculoskeletal system, is the leading cause that stimulates degenerative changes in the spine and, as a consequence, leads to the development of unfavorable pathology.
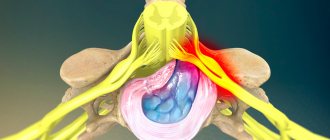
The disease begins with protrusion - a slight deformation of the intervertebral layer, while the internal fibers of the fibrous ring are damaged, but the integrity of its external structures is preserved. In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathogenesis progresses to the stage of a true hernia - prolapse. In the later stages of the disease, the ring ruptures and part of the nucleus falls out beyond the boundaries of the vertebrae, putting compression on the spinal canal and neurovascular structures. In the most severe case, sequestration occurs - separation of the nucleus from the disc and its entry into the spinal canal. Complicated options pose a huge danger to the patient, as they are fraught with complete or partial paralysis of the limbs.
basic information
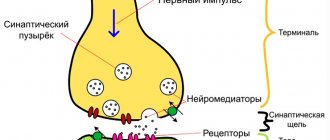
Between the vertebral bodies there are layers of cartilage - these are intervertebral discs. They consist of a ring-shaped element (annulus fibrosus), inside of which there is a jelly-like substance (nucleus pulposus), which has good elasticity. Intervertebral discs are the main shock absorbers of the spine. When walking, running, and even while standing, they help soften the vertical pressure (axial load) on the spinal column and dampen vibrations when the body moves.
Under unfavorable factors that worsen metabolism in the osteochondral components of the spinal system, degenerative and dystrophic processes in the structure-forming units of the shock-absorbing layer are activated, due to which the fibrous ring is destroyed and torn. The gelatinous substance, in turn, begins to put pressure on the damaged area, which leads to protrusion of the disc from a certain side. Since the protruding part is usually located in close proximity to the spinal nerve formations, irritation occurs of these nerves with which the pathological protrusion comes into contact. Thus, a person begins to experience painful symptoms in the affected area of the back or neck, often radiating to the leg or arm.
Pathology
A herniated disc is one of the most common causes of back pain, mainly affecting the lower part of the spine. An intervertebral disc is a cushion-like structure located between the vertebrae to absorb stress on the spine and facilitate movement.
The disc contains a fibrous outer ring, interstitial fibrosis, and a jelly-like material filling the center of the disc, the nucleus pulposus.
The initial stage of the condition involves herniation of the nucleus pulposus towards fibrosis of the anulus. Fibrosis of the annular space may present with one or more ruptures or a complete rupture causing complete or partial release of the nucleus pulposus into the external space. This can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots. A herniated disc causes local inflammation and possible nerve damage, leading to significant pain, clinically known as radiculopathy, and in some cases, severe neurological symptoms such as foot drop.
Symptoms
Symptoms of herniated intervertebral discs depend on the location, size of the developed protrusion, and the degree of involvement of spinal structures in the pathological process. Below we present the main symptoms that are observed with this disease:
- local pain syndrome (aching, pulling, deep or shooting) in a specific spinal segment, which, as a rule, increases when performing any movements;
- radiating pain that radiates to any part of the upper or lower limb, buttocks, foot, shoulder area or chest;
- impaired sensitivity (hyperesthesia or hypoesthesia) of the limb;
- muscle weakness of the leg or arm (depending on the location of the lesion);
- stiffness in a certain part of the spine;
- frequent headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, blood pressure surges, insomnia, unsteadiness of gait and other neurological disorders;
- dysfunction of the intestines and genitourinary system (spontaneous defecation, urinary incontinence, failure of reproductive functions).
This is how pain zones are distributed depending on the location of the hernia.
Attention! The first sign that should alert you and motivate you to immediately visit a doctor is pain in the back or neck of any intensity in a certain area.
Complications and consequences of intervertebral hernia
Untimely treatment of a dangerous pathology leads to dysfunction of the pelvic organs, muscle atrophy, and progression of neurological disorders.
Prolonged pinching of the intervertebral hernia leads to tissue necrosis. The pain increases to an unbearable state. The sensitivity and reflexes of the lower half of the body are significantly weakened. Paralysis, reproductive dysfunction, impotence in men, and infertility are possible. Complete recovery of a long-ignored condition is impossible even after an operative procedure.
Reasons for development
The fundamental factor provoking the pathology is osteochondrosis. A complex of degenerative-dystrophic disorders observed in the cartilaginous tissues of the spine. If it is not treated, which for some reason is considered quite normal for many people, a seemingly harmless diagnosis can develop into a serious problem - a hernia between the vertebrae. Pay attention to the photos; from them you can better understand what the intervertebral layer looks like in a healthy and pathologically altered state. The following reasons contribute to the occurrence of such degenerations in the discs:
- traumatic lesions of the musculoskeletal system;
- excess body weight;
- deficit of motor activity;
- excessive physical activity (playing strenuous sports, lifting weights, etc.);
- congenital and acquired weakness of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus;
- impaired metabolism in the body;
- autoimmune diseases, hormonal imbalances;
- various curvatures of the spine;
- prolonged sitting (often occurs among drivers and office workers);
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unfavorable heredity and age-related aging of the body.
Correct technique of body position during physical work.
A disc herniation not only suppresses motor functions at the local level, but also inhibits the transport branch of the nervous system, giving rise to a whole chain of neurological disorders and quite dangerous damage to the central nervous system, ending in immobility of the limbs. In its neglected state, it leads to severe disorders of the pelvic organs, brain, cardiovascular system and other vital functional components of the body that are adjacent to the area of damage to the spinal column.
Causes of spina bifida in adults
Spina bifida can be congenital or acquired.
Acquired spinal hernia is characterized by slow development, which is not accompanied by any particular discomfort. However, at some point the hernial protrusion makes itself felt.
Spina bifida in adults can occur due to the following reasons:
- lack of treatment for osteochondrosis;
- previous spinal injuries;
- carrying unbearable weights;
- uncomfortable working postures;
- strength training;
- making sudden movements;
- excess weight.
The development of a hernial protrusion may be associated with incorrect posture, an imbalance of substances in the tissues adjacent to the pathological focus, and spinal infections.
Diagnostics
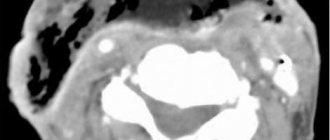
Conventional x-rays have low information content regarding the recognition of vertebral hernias, because they visualize bone structures well, in our case the vertebrae. Based on the X-ray image showing the distorted relative position of the vertebral bodies (angular displacement, narrowing of the space between them, etc.) and the presence of dystrophic signs (osteophytes, etc.), we can only assume that there is a disc protrusion. However, magnetic resonance imaging has the ability to clearly visualize precisely soft tissues (disc structures, spinal cord, nerve endings). Computed tomography is an average method in terms of information content - better than x-rays, but worse than MRI.
Hernia between the 3rd and 4th segments.
However, visit any thematic forum, where you will learn that patients who complain of pain in the back first undergo an x-ray. Hence the question: why not immediately send for highly informative diagnostics? Initially, specialists issue a referral for radiography, and only after receiving primary information about the condition of the ridge, do they decide whether the person needs to further undergo a diagnostic examination using MRI or CT.
Dynamics from the initial to the last stage of the disease.
Many other pathologies that are completely unrelated to damage to this organ manifest themselves with similar signs, for example, true diseases of the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. With multiple sclerosis, numbness of the limbs occurs, which is often observed with an intervertebral hernia. Therefore, it is important to correctly differentiate the problem. Perhaps an x-ray will show the ideal condition of the spine, then further diagnostic measures will be of a completely different plan.
Diagnosis of lumbar hernia
To prescribe the correct treatment, the patient needs to undergo an examination and establish a final diagnosis. For this purpose, the doctor examines the patient and prescribes the following instrumental studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an ideal method for identifying lumbar hernia, allowing you to see soft tissues - discs;
- Computed tomography (CT) – allows you to examine the condition of the bone tissues of the spine and, based on indirect signs, determine the presence of a hernial protrusion;
- X-ray of the spine in two projections - a hernia can be detected only by indirect signs.
Without an examination, it is impossible to diagnose an intervertebral hernia and prescribe full treatment. You should not sit at home and wait for complications; consult a doctor as early as possible.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
Which doctor treats you?
Which doctor should I contact if I feel painful discomfort in the lower back, thoracic and cervical vertebrae? Initially, you should visit a therapist, he will listen to your complaints, examine you and send you for x-rays, and also issue forms for urine and stool tests. Next, based on the primary diagnostic data received, the general practitioner will refer you to the right specialist.
Neurosurgeon.
There are two main doctors who specialize in the treatment of intervertebral disc herniations: an orthopedist and a neurologist. If we are talking about surgical intervention, the spine is operated by a neurosurgeon. In addition to the main specialists, physiotherapists and exercise therapy instructors will work with you. Conservative therapy takes place on an outpatient basis and partly at home, surgery and rehabilitation after it take place in a hospital setting.
Treatment of intervertebral hernia in Moscow
In the well-known clinic of Dr. Dlin (Moscow), patients are offered effective and safe modern treatment for spinal diseases, of which a significant part are intervertebral hernias, using comprehensive programs combining traditional and innovative medical technologies. To identify the causes of pain in the spinal column, high-quality diagnostics are carried out using modern equipment of the latest generation. After an accurate diagnosis is established, professional recommendations for effective treatment of the disease are offered.
The clinic’s specialists, with a long history of successful work, undergo regular advanced training in the world’s leading centers - leaders in the treatment of painful symptoms of any origin. From the first sessions, patients experience pain relief and a full quality of life is restored.
Offers for patients:
- effective treatment at an international level using innovative technologies;
- use of modern diagnostic and treatment equipment and the latest safe medications;
- services of experienced doctors;
- elimination of negative manifestations from the first therapy sessions;
- attentive staff and comfortable environment.
To make an appointment and clarify any questions you may have, call the contact numbers listed on the website!
Pregnancy and hernia
If there is a pregnancy, an experienced specialist recommends gentle conservative therapy that does not negatively affect the fetus and the well-being of the expectant mother. Pregnant women will require treatment according to a specific regimen, since its absence can lead to very bad consequences, including disability. The operation is postponed until the postpartum period. Typically, during pregnancy, wearing a bandage, light exercise, swimming, and the use of non-aggressive medications and folk remedies to relieve pain are recommended.
Main principles of treatment
Disc protrusions measuring less than 6 mm are generally treated with symptomatic and supportive therapy. Symptoms in mild forms are most amenable to conservative treatment. Non-surgical tactics make it possible to stop the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life by increasing blood and lymph flow in the paravertebral structures and limbs, normalizing muscle tone, and beneficial load distribution. The standard therapeutic regimen includes:
- creating temporary rest for the affected part and wearing special orthopedic devices (corset, bandage, collar);
- physical therapy exercises (they develop the spine, increase the endurance of the musculoskeletal corset without overloading the problem area);
- visiting physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, electrophoresis, ultrasound with Karipain, etc.;
- conducting massage sessions, manual therapy, kinesitherapy, horizontal or vertical traction (help relieve pressure from the hernia from the nerve roots, improve local blood circulation and tissue nutrition);
- drug treatment, namely the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, vitamin-mineral complexes, etc.;
- following a special diet.
When a conservative approach does not bring relief, and the size of the hernia does not exceed 6-7 mm, then it is advisable to perform a non-traumatic and painless procedure called nucleoplasty. It comes in various types: laser, cold plasma, electric wave. For large sizes (from 8 mm or more), complex surgical intervention is used: discectomy (a traumatic and rarely used tactic) or microdiscectomy (a common technique).
Most often the center is located at the level l5 S1; treatment for the pathogenesis of such localization is important to begin as early as possible, even at the stage of protrusion. A damaged disc element with a prolapsed nucleus pulposus, located between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae, poses a real threat to the performance of the legs, the functioning of the intestines and the urinary system. Immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis, immediately begin responsibly implementing all medical prescriptions. Never self-medicate, a highly qualified doctor will tell you how to treat a l5 S1 hernia in your case, but only after you have undergone a full examination.
If we take into account the frequency of lesions in the cervical region, then in the C5 C6 segment the disease is most often detected. Despite the fact that only 8% of hernias are detected in the cervical intervertebral cartilage, any of them is considered dangerous, as important vessels, nerves, and arteries responsible for the functionality of the brain pass nearby. Large formations can compress the vertebral artery supplying the brain and cause an early stroke, or damage the conductive function of nerve impulses and lead to partial or complete paralysis of the upper limbs.
Any surgery near the head, where the spinal cord connects to the brain, carries the greatest risks. Therefore, in the area C5 C6, treatment (5 mm is already a lot) is tried in every possible way to limit it to intensive conservative methods. However, unfortunately, lesion volumes of even 5-6 mm are considered large, which sometimes forces emergency surgery.
Complications of herniated disc
Each type of intervertebral hernia has typical symptoms. However, during complications, additional signs may appear. Symptoms of complications often carry many dangers and can cause a variety of ailments. A hernia of the spine formed in the cervical region is almost always complicated by constant pain in the neck (cervicalgia) , limited mobility, and inability to turn or lower the head . In addition, a common complication of a hernia in the cervical spine is cervicobrachialgia - pain in the neck combined with pain in the arm, numbness , and tingling in the fingers . The most dangerous complication of cervical disc herniation is compression of the vertebral artery, which impairs blood circulation to the brain . This is fraught with frequent and intense headaches (even migraines), sleep disturbances, frequent fatigue, irritability, weakness, and inability to concentrate. In addition, a cervical hernia can cause hearing and vision impairment, as well as cause a stroke.
An intervertebral hernia in the thoracic spine can cause complications in the form of constant chest pain (thoracalgia) , as well as acute shooting pain in the ribs. A hernia of the lower thoracic region is complicated by pain in the abdomen and discomfort in the intestines. In addition, it can cause bladder dysfunction ( incontinence , retention , discomfort ), decreased sexual desire , and frigidity . As the most common type of disc herniation, lumbar disc herniation is rife with possible complications. As a symptom of a complication, a dull, aching pain in the lower back (lumbodynia) may occur, which can be replaced by a sharp and constraining movement (lumbago). Also, lumbar pain can affect the sciatic nerve and leg (lumboischialgia). Complications of a lumbar hernia include its effect on internal organs: intestinal disorders, deterioration of the bladder (incontinence or urinary retention, pain when urinating), impotence, gynecological diseases. Such symptoms can be especially observed with cauda equina syndrome - compression of the last segments of the spinal cord. The most dangerous complication of an intervertebral hernia is compression of the spinal cord, which, if sudden movement or physical activity is unsuccessful, can lead to complete paralysis.
Operation
Surgical intervention is primarily indicated if conservative therapy for 2-3 months has not produced any results. Surgery can be performed at any stage if significant complications arise. With severe compression of the spinal cord, spinal nerves and blood vessels, which caused the cauda equina syndrome, inability to flex and extend the feet, muscle atrophy and paresis of the arm or leg, serious impairment of blood supply and oxygen starvation of the brain, etc. The stage of sequestration, at the time of which a herniation occurs from the disc, requiring immediate surgical attention.
Position of the patient during surgery.
Microdiscectomy involves performing corrective and anti-compression manipulations through a small surgical incision (maximum up to 3 cm) under the control of an endoscope or microscope, without damage to muscle and ligamentous tissues. Only the prolapsed element of the disc, in fact, what we call a hernia, can be removed. And the disk itself is preserved to the maximum. This minimally invasive technology is easily tolerated, but in the future, despite the minimal invasiveness, high-quality rehabilitation of the patient must follow. With an impeccably performed microdiscectomy and ideally organized restorative therapy, you can confidently count on a favorable prognosis.
In the early stages, if persistent symptoms make it impossible to live a normal life, gentle surgical treatment using one of the methods of nucleoplasty is permissible. Reconstruction of the disc occurs by exposing the displaced central nucleus to cold plasma or laser. Cold plasma or laser energy is supplied to the pulpous element through an electrode placed in a thin conductor probe. The probe is inserted into the nucleus under X-ray control and the specialist begins to expose it to the appropriate type of radiation. Thus, it is compressed and the sagging mass is pulled into place, and at the same time the normal shape of the disc is restored. Rehabilitation is quick and hospitalization is not required.
How does a hernia appear?
The formation of protrusion occurs in several stages:
- Protrusion. The beginning of pathological changes. The fibrous ring becomes less elastic and can shift and become deformed.
- Partial loss of a section of the disc. This is the second stage in which tissue destruction can occur. This process is inevitably followed by displacement of the gel-like core of the disc.
- Prolapse. The nucleus emerges from the disc ring and begins to influence the nerve endings located nearby.
- Sequestration. The process by which a semi-liquid substance from the nucleus penetrates the cavity of the spinal column. This is accompanied by allergic reactions, nerve connections and blood flow in the tissues are disrupted. Due to constant pressure in an area that is not designed for it, there is a loss of sensitivity and the threat of paralysis.
If help is sought in a timely manner, when the process does not involve the nerves and spinal cord, conservative treatment is used and the patient can be completely cured.
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine
The main treatment, as we have previously witnessed, is possible in two options: without surgery and with the use of surgical tactics. The choice of which approach is appropriate in a given situation is made by the doctor. Everything is taken into account: symptoms, severity and generalization of pathomorphological signs, direction of protrusion, individual characteristics of the patient (weight, age, professional activity, etc.), concomitant pathologies, etc. The main symptoms in the presence of a lumbar herniated intervertebral disc are as follows:
- the appearance of pain in the lumbar region, gluteal area, thigh and lower leg, foot;
- pain syndrome, usually radiating to one of the legs;
- feeling of numbness, tingling, tingling, coldness or crawling in the lower limb, in the perineum;
- atrophic syndrome (weakness) of the leg muscles;
- feeling of a “hoop” in the lower back;
- a very common phenomenon is when the foot loses its ability to support itself and when walking it drags;
- disturbances in the functioning of organs located in the pelvic cavity (rectum, bladder, ovaries);
- reduced potency in men, infertility in women, problems with the menstrual cycle.
All points relate mainly to moderate and severe degrees. It’s sad, but it is at these stages that a person most often begins to experience severe discomfort, which forces him to visit a doctor. Treatment is always prescribed, regardless of the severity of the manifestations. The forum is not the place to look for remedies to solve your problem; you should urgently seek highly specialized help from a medical institution. Otherwise, irreparable consequences may occur in which surgery will not help. A fatal outcome when hernial fragmentation occurs is also not excluded.
A highly specialized specialist will instruct you on how to treat a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation correctly. Not only is he directly familiar with the real clinical picture of your problem area, he knows all the subtleties and pitfalls of the anatomy of the spine, and measures for its safe and effective treatment.
| Lumbar hernia size | Characteristic | Therapeutic approach |
| from 1 mm to 5 mm | slight protrusion | outpatient therapy and treatment at home (physical therapy, exercise therapy, spinal traction, taking chondroprotectors, etc.) |
| from 6 mm to 8 mm | moderately expressed lesion | conservative methods are still valid if there is no progression of the disease |
| from 9 mm to 1.2 cm | very large protrusion | surgical intervention is generally required |
| more than 1.2 cm | critical stage, dangerous due to sequestration | emergency surgery is performed |
Spinal cord herniation in newborns
A spinal cord defect occurs around the 9th week of pregnancy and is characterized by incomplete closure of the neural tube in an insufficiently mature spinal cord. The pathology also extends to bone structures - the vertebrae above the open area are also underdeveloped. They do not have a tight connection in the area of the spinous processes, forming a gap and a hernial sac into which the spinal cord itself or nerve roots can fall out.
The most common treatment is for a hernia of the lumbosacral spine, since the formation of the cauda equina (a bundle of nerve fibers that innervates the lower back and legs) and the closure of the spinal canal in this area occurs last. However, hernial protrusion can also form in other segments.
The severity of the anomaly and the possibility of a child’s recovery are determined by the size of the unprotected areas of the spinal cord and nerve fibers, as well as the localization of the process. It is possible to diagnose fetal pathology even during intrauterine development using ultrasound scanning and take all possible measures so that the newborn child can grow and develop normally.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the formation of spina bifida during embryonic development have not been fully established, but an important factor affecting the fetus is considered to be insufficient supply of vitamins (in particular folic acid) through the placenta, the age of the pregnant woman, dioxin poisoning, viral infections (rubella, influenza, measles, etc.) .), as well as maternal smoking and alcohol abuse. Folic acid, as well as its derivatives, is necessary for the body for the growth and development of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems.
Such an anomaly is not a genetic heredity, but is considered a congenital defect. Therefore, if spina bifida is detected in the early stages of embryonic development of the fetus, then, with the consent of both parents, an operation to terminate the pregnancy is performed. Repeated pregnancies, provided the woman receives all the necessary vitamins and a sufficient dose of folic acid, have every chance of being resolved successfully without such defects.
Types of spina bifida
Hidden spina bifida (spina bifida occulta). With this pathology, the spinal cord, the structure of the nerve fibers and the bone tissue of the spine are fully developed and have virtually no defects. The anomaly is expressed only in a small gap between the vertebral bodies that make up the spinal column.
In this form, the disease is so moderately expressed that it practically does not cause any concern to the patient. In some cases, patients do not even suspect that they have such a defect, but find out about it by chance after taking x-rays. Very rarely, clefting is accompanied by bladder and/or bowel dysfunction, chronic low back pain, leg muscle weakness, and treatment for scoliosis or other postural problems.
Meningocele. A more severe form of the disease in which the vertebral bones do not completely cover the spinal cord. The brain itself and nerve roots are developed normally or with slight deviations. The hernia looks like a sac containing liquor fluid, into which the spinal membranes protrude. Under the skin there are three layers: the hard spinal layer, the arachnoid membrane and the soft layer. Treatment of this type of spinal hernia requires surgery.
Myelomeningocele. One of the most severe disorders of the central nervous system and it accounts for approximately 75% of all cases of spina bifida. In this form, part or all of the spinal cord falls out through a defect in the spine. In some cases, the hernia may be covered by skin; in some cases, exposed brain tissue and nerve roots come out.
Neurological disorders directly depend on the location of the anomaly and the degree of development of the spinal cord. When the terminal sections of the spinal cord are involved in pathology, the patient is diagnosed with early disability, as it manifests itself in the form of paralysis of the legs with complete disruption of the acts of urination and defecation. Such patients cannot care for themselves. In addition, there is a high risk of myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord) and spread of infection by cerebrospinal fluid to the brain and throughout the body.
Symptoms of the disease
A herniated cord in newborns may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- developmental defects of the lower extremities (clubfoot, hip dysplasia, abnormal placement of the feet, underdeveloped limbs, etc.);
- paresis or paralysis of the lower extremities, complete or partial loss of sensation;
- Quite often accompanied by hydrocephalus (swelling of the brain);
- depression of intestinal functions, uncontrolled process of bowel movement;
- bladder dysfunction, urinary incontinence and/or incomplete emptying.
Diagnosis and treatment
Spina bifida anomalies can be diagnosed during fetal development. A blood test for the content of germinal protein (alpha-fetoprotein), carried out at 15-20 weeks of pregnancy, may alert doctors. Early ultrasound will help identify pathologies in the development of the spine, spinal cord and nerve endings. Amniocentesis (puncture of amniotic fluid) will detect signs of open neural tube defects.
Newborn children with spina bifida undergo a CT or MRI examination, ultrasound of the internal organs and the spinal column. Consultation with a neurologist, neurosurgeon, vertebrologist, orthopedist, and urologist is required. But we can fully say that spinal cord herniation is precisely the disease that must be prevented even before the birth of a child, so as not to condemn him to lifelong disability.
Non-surgical hernia treatment (classical conservative) brings results only with hidden spina bifida. Massages, exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures are aimed at strengthening and uniform development of the back muscles, and improving the general health of the child.
Physiotherapy (laser, electromagnetic, etc.), medications (neurotrophics, nootropic substances, groups of vitamins) are not able to cure the patient, but they alleviate his suffering, improve blood circulation in the lower extremities, and help at least partially restore the sensitivity of nerve fibers. In most cases, a child with spina bifida needs a wheelchair and parents need to learn to follow certain hygiene rules (special diet, prevention of bedsores, urological procedures, etc.).
Surgery. As a rule, surgery is planned before the baby is born. To avoid further injury to the hernia during childbirth, a cesarean section is strongly recommended. If the baby’s condition is good or satisfactory, plastic surgery is performed in the first days of his life (non-viable nerve fibers are removed and defects in the vertebral arches are eliminated with their further stabilization).
Abroad, operations to eliminate anatomical anomalies in the development of fetal vertebrae in the womb have recently become widely used. In this way, it is possible to avoid further damage to the spinal membranes and nerve roots, but it is not possible to completely compensate for the defects. This way, the sensitivity of the lower extremities is almost never restored, and in most cases the paralysis does not go away.
After removal of the hernia, comprehensive treatment of associated defects and a long period of rehabilitation with mandatory psychoneurological therapy are carried out.
Particular attention should be paid to developing the patient's reflexes to empty the bladder and bowels at certain times of the day. In general, children with spina bifida are constantly under the supervision of their attending physician. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine
In the cervical region, hernias are the most insidious in terms of danger. Do not delay treatment and do not ignore preventive measures if you have cervical osteochondrosis, because it is this that becomes the provocateur of threatening pathogenesis. You most likely know how its symptoms can manifest themselves. But still, let us remind you:
- crunching, grinding with various movements of the neck;
- burning sensation between the shoulder blades;
- limited mobility of the head in a certain direction (tilting to one side, turning to the side, lowering to the chest);
- neck muscle tension;
- recurrent or constant headaches, sleep disturbances;
- impaired coordination of movements when walking;
- absent-mindedness, memory loss, deterioration of visual acuity and hearing;
- unpleasant sensations in the hands and head (tingling, numbness, goosebumps, etc.).
Cervical region.
The progression of degenerative-dystrophic reactions, if appropriate measures have not been taken for a long time, contributes to the development of a hernia. Depending on where it is concentrated, certain symptoms appear. Let's consider the symptoms of the disease with localization C5-C6, where a bundle of nerve fibers lies, which, by the way, is responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the shoulder and elbow joints, and the thumb:
- tremor of the hands, loss of sensation in the hands;
- weakness in the wrist, biceps brachii;
- difficulty in raising and bending the elbow, the limb hangs like a whip;
- along the back of the forearm, a feeling of numbness, crawling, burning or tingling;
- local painful phenomena, including those that “hit” from the shoulder to the thumb;
- a sharp drop in vision, spots before the eyes.
As for the size, if there is a hernia of 1-5 mm, mandatory outpatient treatment is recommended: therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy and immobilization of the neck for some time using a cervical collar are the basic principles. 6 mm or more is an absolute reason for surgery.
Mechanism of formation of intervertebral hernia
The spine is designed to withstand loads. It supports and stabilizes the body in a standing position, providing complete freedom of movement. When lifting weights, uncomfortable positioning of the body, strong and stressful loads, it takes on the main effort. The load is especially severe when lifting heavy objects with outstretched arms. The heaviest load and, accordingly, wear falls on the lumbar region. When age-related or pathological changes begin in the body, tissues change structure and can no longer fully perform shock absorption functions. Under force, they can become deformed and crumble, which disrupts the functions of the spine and can disrupt the functioning of the entire body.
Intervertebral hernia of the thoracic spine
This zone is less likely to suffer from such pathogenesis. However, it is impossible not to inform people what symptoms are characteristic of intervertebral hernias that appear in a certain area of the thoracic region. The most commonly observed signs are:
- sharp, dull, aching, shooting pain in the upper back (the most common complaint);
- pain in the chest (many perceive it as pain in the heart), ribs, upper abdominal area, axillary area, arms (from the armpits to the palm);
- pancreatic enzyme deficiency, dyspepsia, intestinal dyskinesia;
- various kinds of skin paresthesia (numbness, crawling, tingling, etc.), which are felt in the upper extremities along the inner surface, in the epigastric part of the abdomen, on the front side of the chest;
- pain and feeling of weakness in the glenohumeral region;
- difficulty breathing, night snoring, shortness of breath.
If the damage is not limited to the nerve roots and damage to the spinal cord has also occurred, then unpleasant symptoms can spread to the legs, bladder and rectal cavity. A dramatic crisis in the form of paralysis can occur in the entire part of the body located below the damaged segment.
Manifestations depending on the location of the hernia
The characteristics of a hernia are determined by its location. In this area, the nerve roots are pinched and a characteristic clinical picture occurs. The nerve that is pinched during the formation of the lumbar protrusion of the spine runs along the inner surface of the leg from the hip to the ankle. The pain is not necessarily localized along the entire length; it can be reflected in the leg, foot, buttock, or outer side of the thigh. The lower back may also hurt at one point. As the situation develops, the pain may move lower - to the lower leg, heel and toes. In intensity, it can be a constant aching pain or lumbago that occurs when moving.
Basically, the pain becomes more intense with prolonged walking, standing, turning the body, and bending. It is also painful to lift your leg, do a number of exercises, and also drive on uneven roads.
At the beginning of the development of a hernia, pain can be relieved by lying down, bending one leg at the chest. This will help relieve tension and pressure on the nerve endings. In a more complex situation, this method will not help. Movements are constrained, their amplitude is greatly reduced, and the leg gets tired.
Basically, the patient feels compression of the spinal cord as tingling, burning, and numbness. It dulls the pain. The main symptom that the specialist will pay attention to during the examination is muscle tension on the side of the back, painful when pressed.
Dorsal hernia l5 S1
This is one of the most common and dangerous types of protrusion, and mostly occurs in the lumbosacral link l5-S1. This form can also occur in the neck, mainly involving the C5 C6 disc. The word “dorsal” means a hernia in which the displacement is concentrated directly towards the spinal canal (posterior location). That is, if the hernial protrusion is directed into the intervertebral lumen of the spinal canal, it will be called dorsal. Such a hernia, in turn, can be median (central) and paramedian (at an angle). As we said, this is the most typical form of the disease, but central protrusions are more severe because they prolapse into the spinal canal just along the midline.
Education at level I5 S1.
Since it is here that the central nervous system (spinal cord) and the adjacent abundance of nerve plexuses are localized, the appearance of this type of deformation is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms and a more sophisticated set of neurological signs. And in the absence of adequate treatment - blocking the lumen of the canal and paralysis of the limbs. The reasons for its development are the same as for all other hernias.
Foraminal type and disc protrusion
Foraminal hernia and protrusion are disc bulges facing the aperture where the nerve roots emerge. In other words, the lesion migrates to the narrowest opening in the spine, which in Latin is called “foramen” (intervertebral foramen). This compartment is formed by the posterior arches of two adjacent vertebral bodies. The spinal nerves are freely located in it. When a foreign body appears, especially a larger one, it becomes oppressed, irritated, inflamed, and compressed.
Protrusion.
This is also one of the alarming diagnoses, which differs from others in its rapid progression. It causes the so-called neurocompression syndrome, namely, compression of the roots, which makes itself felt by sharply occurring, pronounced, local attacks of pain, which forces a person to take a forced adaptive posture. When changing position, the pain only intensifies. Analgesics and NSAIDs provide a short-term and insignificant effect.
Surgery relieves persistent excruciating pain that cannot be relieved. Such a fatal stage as sequestration occurs within a fairly short time after the formation of protrusion. Fortunately, this classification of the disease is diagnosed quite rarely; of the total number of all possible variations of protrusion, it accounts for 7%.
Therapeutic drug blockades in the form of hormonal injections, which are given directly to the diseased area, cannot be performed on yourself! This is too complex a manipulation that requires high precision needle insertion and excellent professionalism. Local corticosteroids are indicated in the most extreme situations, if there are debilitating pain symptoms that do not go away after the use of NSAIDs. And remember, hormones do not resolve the hernia, but only relieve local swelling, thereby reducing pressure on the nerve endings.
Localization feature l4 l5
A designation such as l4 l5 means that between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae the integrity of the cartilage lining is broken. This object affects the L4 nerve, which is part of the structure of one large nerve - the sciatic. If we take into account the corresponding part of the spinal column, such damage to the l4 l5 disc (treatment is urgently necessary!) occurs in 46% of cases. In 48% - between the fifth lumbar body and S1 (first sacral), which is not much more common.
Zone l4 l5, the focus is indicated by arrows.
A flat subligamentous hernia l4-l5, known in medicine as hernial sequestration, is the final stage of the disease. With such unfavorable development, the contents of the disc (nucleus pulposus) begin to flow in parts into the cavity of the spinal canal, which is fraught with the complete disappearance of voluntary movements in the limb. When the subligamentous process has begun, even sneezing and coughing cause incredible pain to a person in the form of a terrible lumbago in the lower back, not to mention performing physical tasks. In 80% of cases, the final stage ends in disability. If you undergo emergency surgical treatment, and after it are well rehabilitated, you can hope for 70-80% of the restoration of supporting and locomotor functions as close as possible to normal.
Clinically, the disease in this place manifests itself in a special way, so it is not difficult to distinguish it from a problem, for example, with the cervical area C4 C5. Firstly, there is local hyperalgesia (shooting, aching, pulling in the lower back), and there is also pain radiating to the right or left leg. In addition, the patient complains that the leg is numb, especially in the area of the lower leg and foot, and also that the knee bends insufficiently or muscle-ligamentous weakness is felt in the ankle area. Additionally, increased sweating, marbling of the skin, and curvature of the spine may occur.
Do not sleep on a hard bed or lie down or sit on a cool surface. In case of intervertebral hernia, as orthopedic specialists warn, this is strictly contraindicated.
Approach to the treatment of the disease in the Moscow clinic "Paramita"
Our clinic uses all known methods of treating lumbar hernias. The peculiarity of our specialists’ approach to the treatment of these diseases is the combination of standard and latest Western techniques with traditional Eastern techniques proven over thousands of years, aimed at restoring balance in all organs and systems, which leads to the elimination of pathology.
We make sure to carefully examine our patients using oriental techniques and modern instrumental studies. We do not have a standard treatment plan; the doctor selects an individual combination of various techniques for each patient.
The specialists at the Paramita clinic know how to treat a hernia of the lumbar spine. All our patients get rid of pain in the shortest possible time, and then return to the clinic for regular maintenance treatment and forget about their problems forever. Detailed information about treatment can be found on our website.
ICD 10 classification
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, or ICD for short, is a normative document that includes all known human diseases, each of which is assigned its own alphanumeric code. By converting the verbal formulation of the diagnosis into a code value, the convenience of collecting, archiving, retrieving, analyzing, and exchanging data in an international format about a particular disease is ensured. The ICD allows for adherence to uniform standardization in relation to diagnosis and methodological principles in the treatment of a particular pathology. Simply put, it is a referral network that is intended for medical and healthcare professionals.
Patients may encounter an incomprehensible abbreviation, for example, in medical documentation regarding disability. Well, so that you are not puzzled when you see incomprehensible letters and numbers in the statement, we will try to inform you on this issue. So, according to the international classifier, the ICD code for vertebral hernia is assigned strictly taking into account the type and location of the lesion.
- Since the disease belongs to the group “Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue”, to which the Latin letter “M” is assigned, it will begin the code.
- Next comes a certain two-digit number from the “Dorsopathy” category, where 50 are lesions of the cervical spine, 51 are lesions of the thoracic, lumbar and sacral spine.
- Then a dot is placed, and after it another number from the range 0-9 is entered, which will clarify the clinical picture.
For the cervical region, including the cervicothoracic region, for example, 0 is a hernia with myelopathy, 1 is with radiculopathy, etc. For the thoracic/lumbar/sacral zones: 0 and 1 – similar clarifications; 2 – displacement of a different nature (Lumbago); 3 – formation occurring without neurological signs (the same with the neck); 4 – placed for Schmorl’s hernias, known to everyone, and so on. To make it clearer, we give an example of a complete diagnosis in an abbreviated version of a Schmorl’s nodule: M51.4. If the diagnosis is not specified, an additional clarifying examination is required, then M50.9 or M51.9. Although you don’t need ICD codes in principle, a superficial idea of what they are will be enough.
FAQ
Is it possible to give birth?
A lumbar hernia is not an absolute contraindication for pregnancy. But it all depends on its type, size and existing complications. In any case, a woman must first undergo treatment and then plan a pregnancy.
Is it possible to do yoga?
Yes, with the permission of your doctor, you need to start doing the exercises under the supervision of an instructor.
How to sleep with a herniated lumbar spine?
You need to sleep on a hard surface with an orthopedic pillow, which allows you to relieve the spine during sleep. You can sleep on your back with a pillow under your knees, or on your side with a pillow under your back to maintain your chosen position.
Is it possible to run with a lumbar disc herniation?
Running is shaking, which is undesirable with a hernia. It's better to go swimming.
A herniated lumbar spine is not a death sentence. With regular maintenance treatment, you can lead an active life with this disease and forget about pain. Clinic "Paramita" is waiting for its patients!
Literature:
- Tsivyan Ya.L., Burukhin A.A.: Pathology of the degenerating intervertebral disc. Novosibirsk: Science. Sib. department, 1988.
- Technique and principles of surgical treatment of diseases and injuries of the spine / A.V. Baskov, I.A. Borshchenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 136 p. : ill.
- Kambin P. (Editor) Arthroscopic and Endoscopic Spinal Surgery Text and Atlas, Second Edition, Humana Press, Totowa, NJ.
- Regan J editors. Endoscopic Spine Surgery and Instrumentation. New York: Thieme Medical Publisher; 2004. p. 48-55.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 07/29/2020 Date of update: 03/16/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.75 / 5 (4)
Paramedian hernia T6 T7
The disc, which forms a shock-absorbing “cushion” at the T6-T7 level, which corresponds to the thoracic area, is almost never damaged. This is due to the fact that it is in this part that the spinal structure is very securely fixed by a muscle corset. However, destruction of the T6 T7 disc with all the ensuing consequences cannot be 100% ruled out. It may be a tiny percentage, but it is there. Therefore, if you feel some painful discomfort between the shoulder blades and/or in the hypochondrium, a high-quality differential diagnosis is necessary to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms:
- pneumonia and pleurisy;
- abscess pneumonia;
- heart attack;
- angina pectoris;
- pericarditis, myocarditis;
- inflammation of the esophagus, pancreas, gastric mucosa, etc.
When it is confirmed that the disturbing signs are associated with paramedian protrusion, prolapse of the thoracic intervertebral plate, you need to start fighting it. After all, complications can be terrible - paresis and paralysis of all parts of the body that are located below the focal point.
Army service
We cannot help but touch upon the issue of the army, because the male sex often suffers from this disease. Therefore, we want to immediately inform you about whether they will be recruited into the army if the young man’s medical history includes a herniated disc. In most cases, the conscript is given an exemption.
The pathology we are considering does not allow intense physical training, and is also often accompanied by quite serious complications. A person is shown a special way of life: constant medical supervision, immobilization, proportionate gentle loads and strict adherence to a treatment and prophylactic course.
But it is worth considering that the medical commission considers each case individually, based on the complexity of the specific problem. Uncomplicated, asymptomatic and mild forms of the disease are not an absolute contraindication for enlistment in the military.
To obtain an exemption from the army, you must provide a medical commission with medical information. documentation (together with photographs) from the main place of treatment confirming the diagnosis. Based on the severity of the clinical picture, a verdict will be made: service with restrictions; stock; deferment, when the recruit must recover before the next conscription campaign; complete exemption from conscription (unfit).