Rehabilitation after a stroke at home in Krasnodar and the Krasnodar region will help a person restore all lost skills. But the whole process needs to be was carried out under the supervision of qualified specialists using a personal approach. The brain is an extremely important human organ, so in case of any disease it is necessary to take timely measures. Otherwise, this will lead to risks of deterioration in the performance of the entire body.
During the development of the disease, any part of the brain or several at once is affected. And this leads to loss of speech, cognitive, motor functions or a number of others.
A well-designed and compiled rehabilitation program at home helps to cope with all the negative consequences and restore lost functions. It is necessary to be in constant contact with specialists, strictly follow their recommendations, take care of the patient, and provide all possible support and assistance.
And also be sure to evaluate all possible risks and understand whether it is possible to opt for rehabilitation in an inpatient boarding house under round-the-clock supervision of doctors. In Krasnodar and the Krasnodar Territory, such a reliable option is the private boarding house for the elderly “Harmony”.
What should you expect when you return home?
When you are discharged from the rehabilitation center, you will be given a discharge summary. It will cover all the necessary guidelines for caring for you at home, as well as the necessary equipment and supplies you may need. Returning home can be initially scary. You may not fully recover and will need to continue rehabilitation on an outpatient basis. You may also have many questions about how you can continue living a full life after a stroke.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing a recurrent major stroke, you must follow the preventive recommendations:
- Monitor blood pressure levels daily;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- control weight;
- adhere to the principles of rational and balanced nutrition;
- carry out planned surgical correction in the presence of congenital aneurysms.
Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of stroke. This symptom affects most people who have had a stroke, regardless of its severity, and is usually most noticeable when they return home from the hospital.
This type of fatigue is different from the usual and usual fatigue for us, and it does not depend on your activity or activity. Each of us sometimes feels tired, but this feeling often goes away after rest. However, after a stroke, the fatigue you feel may make you feel like you don't have the energy to do anything. Often you may feel that the feeling of fatigue comes completely unexpectedly and at this moment the only thing you can do is rest until this feeling passes.
Sometimes it takes months or even years for this symptom to go away. Many people after a stroke say they have good days and bad days - days when they feel they can do more things and days when they need to rest more because they feel tired. During the recovery process, good days tend to increase and bad days decrease. Often this fatigue is invisible to other people, so it can be difficult for them to understand what you are feeling. Despite this, you can help yourself in various ways. The key to success is to realize that it is not your fault and it is not your fault. You need to accept the fact that it takes a long time to overcome this symptom of fatigue.
Main types of stroke
First of all, understand what type of apoplexy the patient has and the further process of recovery depends on this. Thus, the ischemic variant has a more superficial nature of vascular damage and the rehabilitation period will be shorter. But with the hemorrhagic type, the rehabilitation period is longer, but the negative consequences are the least pronounced.
To do this, it is important to identify the main stages of a stroke attack:
- The most acute is the beginning of the blow itself with damage to the nerve endings. Lasts from several hours to a day.
- Acute - occurs in the first minutes after a disruption of nerve connections has already occurred with a pronounced manifestation of dangerous symptoms.
- Subacute. At this stage, specialists have already helped to cope with the attack, prevented the development of death, and stabilized the person’s condition. On average, this stage lasts 3 days and requires mandatory round-the-clock supervision by doctors, reliable care, and following all the prescriptions of specialists to prevent the recurrence of the stroke.
Then a rehabilitation program is carried out, which is divided into early and late . Early occurs within the first few weeks of the client's hospital stay. And late rehabilitation after a stroke at home in Krasnodar is carried out after discharge . It is important to analyze in more detail the features of rehabilitation in specific areas and identify their features.
Daily routine
A daily home routine can be helpful. Your day will be less monotonous and this will allow you to learn to listen to yourself and determine when you feel active and do some housework accordingly. The daily routine is based on your needs and the needs of your loved ones. Think about what chores you need to do every day, what you can do on your own, what you need help with, and what you will need to learn to do again. Think about how much time you will need to complete all this work. If you feel yourself getting tired, try to perform the most difficult and tiring tasks that require more energy during the day or week when you feel more energized, making sure to take time to rest. It is very important to be as active as possible. Try to continue your hobbies, social activities and other activities as much as possible. And if you can, try to breathe fresh air every day!
Consequences of damage to the cerebral hemispheres
Based on the developing symptoms of a stroke, one can assume the localization of the damage. With a major stroke, the blood supply to one of the hemispheres is often disrupted, which makes it possible to predict possible consequences. The left hemisphere is responsible for analytical and logical functions, verbal communication. After damage to this area of the brain, problems with speech and pronunciation are likely to develop, loss of the ability to analyze events, loss of visual memory, decreased sensitivity of the right half of the body, psycho-emotional disorders, aggression, apathy, and reluctance to live. According to studies, it turned out that damage to the left hemisphere is less life-threatening, and the chances of recovery are quite high if you provide timely assistance and undergo full rehabilitation.
The right hemisphere is responsible for the perception of surrounding information and thinking, therefore, when it is damaged, the following complications develop: memory impairment (up to loss of short-term memory), motor disorders of the left half of the body, mental disorders, aggressiveness, increased excitability, disorders of the perception of space and time. Rehabilitation for such disorders can last several years, and the likelihood of returning even a small proportion of lost functions is low.
Stay active and keep in touch with friends and acquaintances
Many people feel weak, have difficulty speaking, or have any other problems after a stroke. This leads to them losing interest in the outside world and not wanting to communicate with friends and acquaintances. An important step in rehabilitation after a stroke is socialization. You may find it difficult to go to places you used to go to before your stroke because of your mobility problems, or you may be worried that you will not be able to cope with your problems outside the home. You may find it easier to stay home, but this can lead to isolation, loneliness and low mood. There is always a solution to problems, you can take the help of others or use a stroller to move around. Try to keep in touch with your close friends, invite them to visit or travel with them. It will help if your friends know your capabilities, what you can and cannot do. Meeting new people may be intimidating at first, but it is likely that meeting new people can be especially beneficial for you. Often people make new friends with people who have also had a stroke, and this helps them share their experiences. A positive mood, an active life and maintaining relationships with friends and acquaintances are the key to your recovery.
Kinds
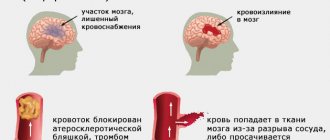
Acute cerebrovascular accidents are divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. In the first case, the lumen of the artery closes, in the second, blood escapes from the damaged vessel. Various reasons lead to the development of these types of stroke. In addition, they differ in pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical presentation. Extensive stroke is divided into the following types:
- Hemodynamic. Vasospasm provokes a decrease in the amount of oxygen that reaches the brain tissue. The cause of this condition is often hypotension.
- Microocclusion. A stroke develops due to a local disturbance in blood flow.
- Lacunar. In the brain, due to increased pressure in the vessel, a cavity is formed. It is filled with liquid.
- Cardioembolic. Arrhythmias lead to the detachment of a blood clot. As a result of uneven contraction of the myocardium, blood turbulence occurs. The detached blood clot enters the brain vessel, causing the development of a stroke.
- Atherothrombotic. The cause of acute cerebrovascular accident is the blocking of the artery lumen by an atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis is formed due to changes in the lipid composition of the blood.
Emotional state after a stroke
You will need time to understand what is happening to you, and understanding this is an important step in your recovery. It is important to remember that recovery and recovery time varies from patient to patient.
Try to share your feelings and sensations with people you trust. People often experience a variety of feelings after a stroke, such as:
- Fears and concerns are a natural shock, mistrust and feelings of loss can affect you and your family. You may be worried about partial memory loss or may be afraid of having another stroke.
- Anger and frustration – You may be angry about something that happened to you or you may be frustrated that you can't do the things you used to do, especially if you have difficulty speaking. Sometimes you may be irritated by other people around you, you may have changes in mood, this is something that can affect you and your family.
- Depression and Anxiety – You will probably experience feelings of anxiety and worry and this is quite normal. Depression is a natural process that occurs after a stroke, so if you are often depressed, you may want to talk to your doctor and start taking antidepressants.
- Tension in relationships – irritability and increased emotional state can lead to tension in relationships with people who are close to you. You may find yourself directing your anger, anger, and frustration towards those close to you. Remember that your family and your friends are trying to understand you and how you feel.
- Loss of self-confidence – Feelings of self-doubt and low self-esteem are common after a stroke, but you should focus on becoming as independent as possible and should take as many opportunities as possible to improve your self-esteem. Making the right decisions about how to care for you, learning new skills, and setting realistic, achievable goals can help you do this.
- Lack of incentive – Recovery from a stroke usually occurs gradually with small but important goals and achievements. If you feel tired and in a low mood, this can affect your motivation to heal and recover. You can set small and achievable goals, and this may feel strange at first, but it will help you stay in a good mood and help you stay motivated and eager to recover. It is vital to stay in a good mood. Remember that it is quite normal if everything works out for you one day, but not the next. There are limits to what you can achieve and do!
Symptoms, clinical picture
Precursors of a stroke may appear weeks and even months before an acute cerebrovascular accident. Among the obvious first symptoms of a stroke are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- darkening of the eyes with sudden movements;
- episodic global memory loss (amnesia);
- sudden short-term disorientation.
The main signs of a major stroke appear several hours before an acute cerebrovascular accident or directly during an attack. Depending on the type of stroke, within a day the patient experiences pronounced symptoms of brain damage:
- drowsiness followed by excitement;
- stunned;
- loss of consciousness;
- increasing sharp headache;
- nausea and vomiting.
Patients are concerned about pain in the eyeballs, a feeling of heat, sweating, increased heartbeat, dry mouth, and convulsive syndrome develops. One of the most common symptoms of a major stroke is coma. It indicates significant and deep damage to brain structures. After treatment and rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital, 37% of patients who suffered a stroke live a full life, 25% regain consciousness, but there remain residual disturbances in speech and motor functions, which are also gradually corrected in the rehabilitation clinic.
General cerebral symptoms of a major stroke include:
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- stunned state;
- sopor;
- rarely coma;
- pale skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- convulsive syndrome;
- hyperthermia.
Focal symptoms depend on the location of the pathological focus. When the right hemisphere is damaged, motor and sensory disorders occur in the left half of the body, and vice versa. Among the main symptoms are:
- violation of superficial and deep sensitivity;
- inability to independently flex and straighten limbs;
- drooping corner of the mouth;
- inability to smile;
- impaired speech and swallowing;
- deviation of the tongue towards the affected side;
- memory loss;
- mental disorder;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dry mouth.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital pay special attention to the symptoms of a major stroke. The clinical picture, together with the diagnosis, allows us to determine the type of cerebrovascular accident and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Relationship
A stroke does not only affect you, but also those around you. Your relationships with others may become difficult and may be affected by how you feel. Your family and friends will try to understand how you feel and you should be honest with them. By telling them about your feelings and trying to understand what they feel, you can help yourself. Adapting to life after a stroke will lead to some changes in your life and in the life of your spouse, and this can then lead to stress in your relationship. Emotional changes, changes in your body and difficulties in relationships can also affect your sex life.
Together but apart
I realized a very important thing for myself: it is necessary to always be there, but at the same time, my participation in rehabilitation should also be as inconspicuous as possible. Standing over your soul is a hopeless matter. We have to resort to tricks. To make sure my husband doesn’t get bored doing his exercises, I do gymnastics at the same time (wonderful motivation, by the way). In order not to remind him every time of the need to do this and that, I made a list of activities recommended by experts - and I try to distance myself from it. My husband learned to read in early childhood, and he’ll manage somehow. Against each point there are numbers - ones and twos. “2” means that two people need to do the exercise. We try to postpone these until the second half of the day, when I finish work.
Driving
A stroke can affect your ability to drive safely in a variety of ways, such as your physical condition, visual impairment, or difficulty concentrating for long periods of time. In the first months, even after a mini-stroke, you are not allowed to drive. After some months, you will need to visit your doctor, who will give you advice and recommendations regarding driving and will tell you whether you can start driving again. They will likely refer you to have your driving abilities reassessed. It is important to tell your insurance company that you have had a stroke.
What's next?
Last year’s text ended with a story about how we climbed the mountain above the Montenegrin city of Kotor. This year we broke the record, rising even higher, but the mountain is big, there is room for improvement. When you look from below, you can’t see the top, even though you throw your head back so high that it starts to spin. The higher you go, the clearer it becomes: new spaces open up, new paths open up, some of which lead to nowhere, while others lead down. To know that a path is wrong, you have to try it. In any case, a walk will be useful: movement is life.
Returning to work
A stroke will be a real challenge for you if you have previously worked. It can leave a big imprint on your life and change your role in the family and society. Many people do not look at the situation realistically and try to do many things in a short period of time. Fatigue, cognitive complications such as memory loss, and difficulty concentrating may mean you will not be able to return to work. It is important to have an honest conversation with your employer so that you can consider on-the-job adaptation. Part-time work and a reduced workload may be a viable option. Don't be too hard on yourself if things don't work out or aren't going as well as they did before you had your stroke. A lot of people are returning to work. Many see this as an opportunity to try something new, such as working from home or taking on new responsibilities.
Mechanism of hemorrhagic stroke
Among the main causes of hemorrhagic stroke are:
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- excessively thin blood;
- congenital deformations of the vascular wall.
Rupture of blood vessels with subsequent leakage of blood into the brain cavity most often provokes a sharp rise in blood pressure. In addition to the listed etiological factors, aneurysm, traumatic brain injury, physical or emotional stress can cause hemorrhagic stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by a sudden and rapid onset. Symptoms include severe headache, rapid breathing, confusion, and possible development of coma. The skin becomes cold to the touch, the corner of the mouth droops, and blood pressure rises. Against the background of hemorrhage in the brain, the tone of the muscles of the limbs decreases, strabismus may appear, the pupils dilate, and swallowing is impaired. Hemorrhagic stroke has a less favorable course and is often accompanied by complications.
There are 2 types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- intracerebral. Occurs due to thinning of the arterial walls and a sharp jump in pressure. The risk group includes persons aged 45 to 60 years;
- subarachnoid. Occurs when a cerebral artery aneurysm ruptures and blood escapes under the arachnoid membrane of the brain. The risk group consists of people aged 30-60 years, abusing alcohol and smoking, and having excess body weight.
REDUCING THE CHANCE OF REPEATED STROKE
Is there a risk of another stroke?
If you have had a stroke, you are at risk of having another stroke. However, there are several things that can reduce the risk of a second stroke:
- Taking the medications you have been prescribed
- Control and maintain blood pressure within normal limits
- Control and maintain blood cholesterol levels within normal limits
- Diabetes control (if necessary)
- Adapting to a new way of life to reduce danger
Changes in your life may include:
- Stop smoking
- Healthy and varied diet
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight
- Staying physically active
- Reducing alcohol consumption
What measures help prevent stroke?
Prevention comes down to eliminating or minimizing the impact of all those factors that increase the risk of cerebrovascular accident. The recommendations are simple:
- Eat healthy.
- Maintain a normal weight.
- Try to completely give up smoking and other bad habits.
- Monitor your blood pressure. It is good to have a home blood pressure monitor and take measurements daily.
There are screening studies that help assess the condition of cerebral vessels and risks. Seeing the results of studies and analyses, neurologists can give recommendations that will help prolong the active life of your loved one and prevent the development of vascular crisis in the future.
According to statistics, up to 80% of strokes can be prevented. In addition to a healthy lifestyle, it is important for people from high-risk groups to visit a doctor on time, undergo examinations, and follow the recommendations of a neurologist.