Author
Eremin Dmitry Sergeevich
Radiologist (CT)
Doctor
Radiologist
until October 31
Total Body Scan (MRI of the whole body) with a 48% benefit + free consultation with a GC doctor* More details All promotions
MRI
(magnetic resonance imaging) is a modern type of diagnostics that uses a magnetic field and radio waves (rather than ionized radiation, which is used in X-ray machines and computed tomography). Therefore, MRI is safe and can be performed as often as necessary.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly informative diagnostic method, most revealing in the study of soft tissues, which allows obtaining images in the form of tissue sections of a particular organ.
What you need to know about the principle of MRI and the design of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
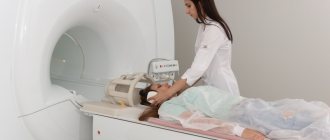
The patient is placed on a movable table that moves through a tunnel-shaped magnet. The magnet creates a powerful magnetic field; Radiofrequency pulses are sent to the examined area of the patient in a magnetic field. As a result of this radio wave exposure, hydrogen atoms resonate in the tissues of the body.
Our body is mostly composed of water and fat, and these substances, in turn, are characterized by a high hydrogen content. The amount of hydrogen varies in different tissues; including in tissues affected by pathological processes, it differs from what is characteristic of healthy tissue of a given organ.
Information about atomic resonance is read by special sensors (coils) and processed using a computer program that reconstructs an image in the form of a slice of the organ under study.
Types of MRI studies
The most popular types of MRI studies are:
- MRI of the spine
. Allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord, cartilage, ligaments and back muscles. Circulatory disorders, consequences of injuries, developmental anomalies, changes in intervertebral discs, etc. are identified. An MRI examination of a specific section or the entire spine may be performed. - MRI of joints
. A specific joint is examined: knee, shoulder, hip. MRI allows you to study in detail the structure of the articular joint, visualize intra-articular (menisci, joint fluid) and periarticular formations (ligaments, muscles). Developmental anomalies, inflammatory and degenerative changes in the joint, and pathologies of periarticular tissues are diagnosed. - MRI of the brain
. MRI examination of the brain is highly sensitive and allows you to visualize both hemispheres of the brain, its stem part, the ventricular system and other structures. Using MRI of the brain, vascular abnormalities, vasodilation, hemorrhages, tumors, foci of inflammation and degeneration, fluid accumulations, etc. can be identified. - MRI of the pituitary gland
. MRI shows the condition of the pituitary gland itself and the sella turcica (anatomical area in which the pituitary gland is located). MRI can detect adenomas and other pituitary lesions. - MRI angiography of the brain
. MRI provides an opportunity to assess the condition of cerebral vessels without the introduction of a contrast agent. This is possible because the method allows one to distinguish a substance in motion (blood) from stationary structures (vascular walls). - MRI cholangiography
– study of the patency of the bile ducts. The intrahepatic ducts, cystic duct and common bile duct are examined, as well as (partial) liver and pancreatic tissue. Allows you to identify stones, polyps, tumors and narrowing of the bile ducts. - MRI of the prostate
. MRI allows you to evaluate in detail the structure of the prostate gland, identify prostate adenoma (benign hyperplasia), foci of inflammation and prostate tumors. - MRI of the pelvic organs
(uterus and ovaries). MRI can detect changes in tissue structure, endometriosis, adhesions, fibroids, polyps, tumors, and helps determine the type of ovarian formation.
Indications
Most often, doctors choose MRI to evaluate:
- conditions of the abdominal organs, including the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, spleen and adrenal glands;
- pelvic organs, such as the bladder and reproductive organs - the prostate gland in men, the uterus and ovaries in women;
- blood vessels of the head and neck, abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- soft tissues;
- joints and intervertebral discs.
MRI is widely used to examine the brain and spinal cord or comprehensive scans of the entire central nervous system. Tomograms will clearly show joint anomalies - injuries, fractures, cracks and sprains, violations of the integrity of cartilage and ligaments. The most common indications for tomographic examination are:
- The need to clarify doubtful or controversial results obtained by other diagnostic methods. For example, an ultrasound showed a small lump similar to a tumor. In order to take a closer look at whether the found formation is a tumor or an abscess, accurately record its size, conduct differential diagnostics, that is, obtain more detailed information about the condition of the affected tissue, the patient is offered tomography.
- To identify congenital anomalies of the brain, abdominal and pelvic organs. Especially as a study of genital abnormalities in children and adolescents, when invasive procedures are undesirable.
- MRI is prescribed if other types of diagnostics are too dangerous in terms of risk for the patient. For example: the patient is allergic to iodine-containing drugs that are used in CT scans, or the patient is a pregnant woman, and X-ray radiation may adversely affect the fetus.
- Before surgery on the brain, spine or joints, to draw up a surgical plan.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment measures, especially for cancer.
- For the diagnosis of cancer.
- MRI is the preferred procedure for examining the brain and blood vessels.
- If it is necessary to evaluate complex cases of ligament and cartilage injuries of the knee joint.
- Diagnosis of intervertebral disc herniation.
Harmlessness of MRI
To date, there have been no cases where the magnetic field or radio waves used in MRI scans have caused harm to a patient. MRI is not done in the first trimester of pregnancy, but this is just a precaution; the facts when an MRI would cause any harm to the fetus are also unknown to medicine.
contraindications for MRI
.
First of all, they are determined by the presence of electronic devices implanted into the body (hearing aids, artificial heart pacemakers), as well as any metal structures and fragments (joint endoprostheses, metal plates, knitting needles, consequences of metal osteosynthesis and gunshot wounds, etc.). Dental implants, vascular stents and umbrella filters produced in the last 5-7 years are usually made from MRI-ready materials. Therefore, for such patients, an MRI examination can be performed after presenting a certificate or confirmation from the medical institution that performed the installation.
MRI is not done if you have a pacemaker (an absolute contraindication).
An MRI cannot be performed if the patient is afraid of confined spaces (suffers from claustrophobia).
Sometimes during the study, a burning sensation or irritation of the skin occurs due to the applied cream, ointment, or certain types of tattoos, in these cases the study must be stopped and, if the cause cannot be eliminated, the study may be stopped.
Breastfeeding, menstruation and the presence of an intrauterine device are not an obstacle to undergoing an MRI.
Types of MRI machines
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
Traditionally, MRI machines are divided by design type into open and closed installations. Closed models consist of a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a circular magnet. Some MRI scanner models are designed in such a way that the magnet does not completely surround them. Such devices are called open-circuit tomographs. Magnetic resonance imaging scanners are also distinguished by the power of the induction field:
- low-floor - 0.2-0.5 Tesla;
- high-field - up to 1.5 Tesla;
- ultra-high-field - 3 Tesla and higher.
The use of one or another type of apparatus depends on the purpose of the examination. For example: MRI examination of a joint, spine, brain, angiography can be carried out on an open or closed tomograph, and the magnetic coils in this case will be located only around the part of the body that is currently being diagnosed. Examination of internal organs is carried out only using high-field MRI. Tomography of the heart, foot or hand is best done on a closed three-tesla unit. The decision about the required power of the MRI machine is usually made by the attending physician and notes this in the direction for tomography.
Preparing for an MRI
No special preparation is required for MRI. The only exception is MRI of the liver and gall bladder, which are performed strictly on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning.
The patient should be prepared for the fact that he will have to spend quite a significant amount of time (from 15 minutes to almost an hour, depending on the type of study) inside the tomograph tunnel. At the same time, the installation produces noticeable noise (this is an inevitable consequence of the technology used). Clothing in which you can undergo an MRI must not contain metal parts (zippers, fasteners, buttons). All accessories (watches, hairpins, hairpins, jewelry, etc.) will need to be removed. It is also necessary to leave electronic magnetic cards and any other magnetic media (flash drives, memory cards, etc.) in a special booth, otherwise all information on them will be erased in the magnetic field.
How is the MRI examination procedure performed?
Magnetic resonance imaging does not require special preparation, with rare exceptions when it is performed using a contrast agent or when examining the pelvic organs and gastrointestinal tract. Before an MRI procedure, the patient must leave all metal and electronic objects, including removable dentures, in a special room. In the diagnostic room, the examinee lies down on the examination table, which slides inside the tomograph. To fix the examination area and amplify the signal, special MRI coils can be used. If a contrast agent needs to be administered, the nurse first injects it through a vein or places a catheter and connects a dosing injector. Depending on the scanning protocol, a series of tomographic images will be taken before and after the injection to compare how the contrast agent has stained the examination area. You should remain still during the procedure unless your doctor asks you to hold your breath or tense your muscles. The lack of movement directly affects the quality of the resulting tomograms and the accuracy of diagnosis. In total, an MRI study includes several sequences during which the device takes pictures. The process of taking pictures is sometimes accompanied by loud sounds, which can be mitigated with special headphones. During an MRI procedure, the patient may feel warming in the area being examined. There is no need to be afraid of this. At the end of the procedure, the radiologist records the results in the form of images on digital media and also issues a written report with recommendations for further actions.
Advantages of MRI at Family Doctor
The “Family Doctor” uses a Brivo MR355 Inspire tomograph, manufactured by GE Healthcare (the medical division of the American company General Electric), to conduct magnetic resonance imaging. Brivo MR355 Inspire is a world-class MR scanner with a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla (the higher this figure, the more detailed the resulting image can be). This tomograph belongs to the class of equipment with high magnetic field power. Thanks to modern technologies, Brivo MR355 Inspire provides high-quality visualization to help make the diagnosis as accurate as possible.
MRI is performed at the Diagnostic Department of the Hospital Center (Baumanskaya metro station). Research is carried out on the orders of Family Doctor doctors, as well as third-party medical organizations.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Relative:
- severe claustrophobia;
- the presence of non-ferromagnetic implants, insulin pumps, heart valve prostheses;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- presence of tattoos containing metallic compounds in the ink;
- heart failure.
Absolute:
- the presence of metallic foreign objects in the patient’s body;
- hematopoietic anemia (with magnetic resonance imaging with contrast);
- use of electronic devices such as pacemakers, etc.