Disease Information
Alzheimer's disease gets its name from the German psychiatrist who first described its symptoms in 1901. Moreover, the first mentions of the loss of reason were found in ancient treatises. Currently, there are three theories of the development of the disease:
- cholinergic: degeneration is associated with a decrease in the synthesis of acetylcholine, which is responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses;
- amyloid: disruption of the nervous system occurs against the background of deposition of pathological amyloid protein;
- tau hypothesis: the development of the disease is provoked by a change in the structure of the tau protein, which is responsible for the proper functioning of neurons.
To date, the most likely theory for the development of Alzheimer's disease is amyloid, but research is ongoing.
Make an appointment
Spasticity
Gavrilkina Oksana Sergeevna Chief rehabilitation doctor, physical therapy and sports medicine doctor,
More about the doctor
Spasticity or muscle hypertonicity as a syndrome signals the progression of central nervous system diseases. It can occur in older people in response to the death of motor neurons or as a consequence of a cerebral stroke, spinal stroke, head or spinal injury . Different severity of spasms can either not interfere with the patient’s life at all or lead to disability. It is noteworthy that at the initial stages of rehabilitation after a stroke, muscle spasticity indicates the possibility of complete restoration of motor activity of the limbs.
Factors causing spasticity
Mildly expressed cramps and spasms are often diagnosed in the elderly due to age-related changes in the nervous regulation of muscles and tendons. This is also facilitated by wearing tight shoes and clothes, frequent hypothermia, bad habits, excess weight, constant stress, and some chronic diseases. Since neurodegenerative diseases develop in genetically predisposed patients, muscle spasticity , which develops due to pathologies of the central nervous system, can also be considered as a syndrome that is inherited. In addition, spasticity occurs against the background of such diseases:
- brain stroke;
- inflammation of the meninges (meningitis);
- varicose veins;
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- brain and/or spinal cord injuries.
Spasticity often develops against the background of Parkinson's disease , Alzheimer's disease , and senile dementia . Cramps and increased muscle tone can be triggered by any inflammatory diseases, constipation, or infections of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms of spasticity in the elderly
The first thing a specialist pays attention to when diagnosing spasticity is increased muscle tone. In this case, the patient complains of spontaneous cramps, especially at night and after physical activity, pain when flexing/extending the limb. Deformations in the joints are also observed, and posture changes. The reflex response increases. The pathology is aggravated by concomitant inflammatory processes in the joints, and the intensity of pain increases.
Diagnosis and treatment of spasticity in the elderly
When assessing the severity of pathology neurologically, the Ashworth scale . In it, the severity of the disease is divided according to the severity of muscle hypertonicity. The maximum degree of damage is 4, in which the limb under study practically does not bend/extend. Using CT or MRI, the presence of any disorders in the central nervous system or spinal injuries that can cause spasticity is determined.
Treatment is conservative, comprehensive, and includes both the use of medications and physical therapy. Self-medication is contraindicated; all drugs used to treat spasticity are available with a doctor's prescription. Their action is aimed at reducing muscle tone by inhibiting interneurons and blocking nerve impulses. An overdose leads to hallucinations, respiratory arrest, and death.
Local anesthetics may be used to relieve pain. Convulsions can be controlled with magnesium supplements. It is mandatory to take B vitamins to improve the functioning of neurons, activate trophism and blood circulation, and relieve inflammation.
Physiotherapy consists of the use of electrophoresis , acupuncture , therapeutic massage , and exercise therapy .
In case of injuries, tumors, or deforming changes in the joints, surgical intervention may be required. The operation consists of truncation of nerve roots that cause muscle hypertonicity. For the treatment of mild and moderate spasticity in elderly and senile people, surgical intervention is not recommended.
Causes
The exact causes of Alzheimer's disease have not yet been clarified. It has been proven that the risk of disease increases significantly:
- with a hereditary predisposition (the disease has been proven to be associated with certain gene mutations);
- for acute and chronic disorders of the blood supply to the brain (stroke, transient ischemic attacks, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, etc.);
- against the background of concussions or brain contusions;
- for benign and malignant brain tumors;
- in people suffering from depression, as well as those who have suffered severe psychological trauma;
- against the background of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), as well as acute or chronic intoxication;
- with low intellectual activity throughout life.
Age is one of the main predisposing factors: the older the person, the higher the risk of developing pathology. In addition, women get sick more often than men.
What causes Alzheimer's disease
This disease has been known about for more than a century, but scientists have still not been able to establish the exact cause of its occurrence. Thus, two different people who have similar habits and lead approximately the same lifestyle are likely to experience old age in completely different ways. Some will retain mental clarity until their last days, while others will be destined to face Alzheimer's disease.
Experts call the main risk factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- advanced age - the risk of developing dementia increases after 65 years of age;
- presence of head injuries, including those sustained in youth;
- hypertension, stroke, atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases;
- encephalitis, herpes and other infections that affect the nervous system.
The factors mentioned above lead to the death of neurons, which causes dysfunction of the brain. Researchers also found that the disease is more common in women over 60 years of age than in men.
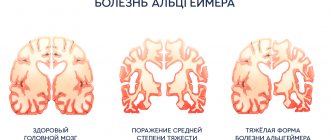
Stages and symptoms
Alzheimer's disease has a long course. It develops gradually and practically does not manifest itself for a long time. As pathological changes increase, symptoms become more noticeable. Doctors distinguish four stages of development of the disease, each of which has its own symptoms.
Predementia
This is the initial stage of Alzheimer's disease, characterized by mild symptoms. Most of them can only be identified through special testing. Over time, the patient and his relatives note:
- deterioration of short-term memory: a person poorly remembers events that happened the day before, while older facts are reproduced perfectly;
- problems with acquiring new knowledge and skills;
- decreased ability to concentrate work;
- difficulty remembering individual words, which does not cause significant discomfort during a conversation;
- general slowness of speech;
- slight deterioration in motor coordination.
Simultaneously with cognitive impairment, apathy begins to develop, which accompanies a person at all stages of Alzheimer's disease.
Since the symptoms are mild, most people are in no hurry to see a doctor, attributing problems to the natural aging process. The stage lasts 7-8 years.
Early dementia
At this stage, short-term memory disorders become clearly visible, and it becomes impossible to attribute them to normal aging. At the same time, the person perfectly remembers events from his youth, any learned facts, and applies old skills. Many patients also develop:
- apraxia: a disorder in performing sequential actions, for example, unbuttoning and fastening buttons, sewing, drawing, etc.;
- agnosia: impaired recognition of objects, can be visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory or sensitive (tactile), as well as total;
- speech disorders: decreased tempo, poor vocabulary, problems expressing specific thoughts.
The patient can perform simple self-care actions, but complex tasks are no longer possible for him.
Moderate dementia
At this stage of Alzheimer's disease, the patient loses the ability to live independently. He has:
- pronounced agnosia and apraxia;
- paraphasia: speech becomes meaningless because the person chooses words incorrectly;
- dysgraphia and dyslexia: loss of writing and reading skills.
As a result, a person stops performing daily tasks: eating, hygiene procedures, changing clothes. Memory disorders continue to progress, the patient does not remember and does not even recognize close people. Psychiatric symptoms develop:
- emotional instability;
- aggressiveness or tearfulness;
- refusal to accept help;
- vagrancy;
- rave.
The patient at this stage requires constant supervision from relatives, since he may cause harm to himself or others.
Severe dementia
The last stage of Alzheimer's disease inevitably turns a person into a helpless disabled person:
- speech ceases to be coherent, the patient communicates in separate words or short phrases;
- severe apathy develops, at times turning into aggression;
- the ability to perform simple actions is lost;
- control over physiological functions disappears.
Ultimately, the person becomes bedridden, resulting in loss of muscle mass, pneumonia, and bedsores.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and determination of its stage are carried out by doctors from the Neurology Department and psychiatrists. The set of examinations includes:
- survey and collection of complaints;
- studying the history of the disease (when the first problems appeared, how quickly they grew, etc.);
- assessment of life history: previous and existing diseases, injuries, hereditary factors;
- detailed neurological examination;
- laboratory diagnostics: general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test: glucose level, lipid spectrum, coagulation indicators, etc.;
- examination of cerebrospinal fluid to detect beta-amyloid (one of the specific signs of Alzheimer's disease);
- electroencephalography;
One of the main methods for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease is neuropsychological tests to assess cognitive impairment:
- name the objects shown in the picture;
- remember 5 unrelated words, repeat them immediately and after 3 minutes;
- distribute words into categories (food, animals, furniture, etc.);
- perform simple arithmetic operations;
- draw a clock showing a specific time;
- draw a picture or write a sentence from dictation.
If necessary, additional consultations and examinations are prescribed.
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Treatment is aimed at slowing the progression of the pathology. Doctors use drugs from various groups to improve the functioning of the central nervous system and relieve the main symptoms:
- anticholinesterase drugs aimed at improving memory (donepezil, reminil and others);
- memantine, which slows the progression of dystrophy and reduces the severity of symptoms (the only drug approved by WHO for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease);
- drugs to improve metabolism in brain cells (mexidol, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline);
- nootropics (Cerebrolysin, Actovegin) to stimulate the formation of additional connections between nerve cells;
- symptomatic drugs: antidepressants, antipsychotics, anxiolytics, etc.
The combination of drugs, their dosage, frequency and duration of administration is selected by the doctor on an individual basis. Often, the drug regimen is adjusted during treatment to achieve an optimal result with a minimum number of side effects.
Various psychotherapeutic techniques are used as a complement to drug treatment. They help reduce aggression and anxiety, improve the quality of thinking and stimulate memory. A good effect is provided by:
- art therapy: improves the emotional state of the patient, reduces the level of anxiety and depression, reduces aggression;
- sensory room activities and sensory integration;
- reminiscence therapy (used for severe dementia, helps to set the patient in a positive mood).
Simultaneously with the therapy, relatives are trained in the rules of behavior with the patient and caring for him. To maintain a stable patient's condition it is necessary:
- organize a clear and unchanging daily routine;
- try to maintain a person’s autonomy and independence;
- do not discuss medical problems among themselves in the presence of the patient;
- maintain a friendly atmosphere in the family;
- avoid conflicts and disputes.
If necessary, family members also work with a psychologist, since constant communication with the patient requires significant mental stress.
Make an appointment
Folk remedies for Alzheimer's disease
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease using alternative medicine methods involves taking medicinal herbs, natural juices and bee products, which can reduce the frequency of seizures, slow down the progression of the disease, calm the nervous system, and strengthen the immune system in general. To enhance the effect of folk remedies, it is recommended to adjust your lifestyle: completely give up alcohol, do simple physical exercises, walk a lot, stick to a daily routine, and eat right.
Traditional methods can enhance the effect of medications, so they are recommended to be combined with traditional treatment.
Medicinal herbs for Alzheimer's disease
To treat this disease of the central nervous system, herbs are used - antidepressants, which improve blood flow and normalize brain nutrition:
- common motherwort . For medicinal purposes, take motherwort tincture, which normalizes blood pressure, reduces increased excitability, aggression, and calms the nervous system;
- Schisandra chinensis combined with ginseng root . The plant components are mixed in equal proportions, take 10 g of the mixture, pour a liter of boiling water and cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Drink small portions throughout the day;
- acai berries . Stimulates brain activity and increases endurance.
- Goji berries . Protects against neurodegenerative disorders
- ginkgo biloba . Improves blood circulation in the brain, thereby improving memory. To prepare ginkgo biloba extract, take 50 g of dried leaves of the plant, add 500 ml of vodka, leave for 2 weeks;
- heather, St. John's wort . Plants with strong antidepressant properties. Herbal teas from St. John's wort and heather have practically no contraindications, they can be drunk every day;
- chicory _ It has antioxidant properties, thereby reducing the effects of oxidative stress and reducing neuroinflammation in microglia and brain cells;
- wormwood, dandelion, calamus, elecampane . These herbs stimulate the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. 2 tbsp. Pour the plant mixture into a thermos with 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave overnight. Drink a third of a glass three times a day;
- Eleutherococcus, Echinacea purpurea, Aralia, Leuzea . Stimulate the immune system, increase body tone;
- Dioscorea Caucasica . Stimulates blood circulation in the brain, prevents blood clots, resulting in improved mental performance, memory, spatial orientation, speech becomes more meaningful and understandable, dizziness and headaches are eliminated, noise and ringing in the ears go away. For treatment, an alcohol infusion is used: 100 g of crushed dioscorea roots are poured with vodka (1 l), infused for 2 weeks, filtered. Drink 1 tsp. tinctures before meals 3 times a day;
- turmeric _ This delicious seasoning has a very powerful antioxidant effect. When consumed regularly, turmeric blocks the production of lipofuscin, a substance that causes atrophy of cells and organs.
Bee products
Honey and other bee products have an anti-sclerotic effect, so they are a very effective way to improve memory. In addition, this product helps improve the thinking processes of the brain.
The daily norm for an adult is 3 tsp. honey
Nutrition for Alzheimer's disease
In addition to using medicinal decoctions and tinctures, to support the body with Alzheimer's disease, you need to eat right. The patient's diet should contain a sufficient amount of fish, vegetable fats, vegetables, and fruits. The following products are especially useful: tomatoes, spinach, garlic, onions, broccoli, black currants, oranges. It is also necessary to eat foods rich in natural antioxidants: cabbage, carrots, sprouts of grains and legumes, lemon, dried fruits.
Regular (1-2 times a day) consumption of black or green tea will be a good stimulation of the nervous system. It is only advisable to sweeten it not with sugar, but with natural honey, and replace cookies and sweets with dried fruits.
It is recommended to drink a sufficient amount of liquid (6 - 8 glasses), mainly clean water or fresh compotes. Dehydration negatively affects the condition of nerve cells, which is especially harmful after 50 years.
Daily regime
The patient should move a lot, engage in physical exercises and mental activity, and do breathing exercises. The older the person, the simpler and easier the exercises should be; in some cases, walking in the fresh air is enough.
In order for the brain to always work, it is necessary to regularly learn poetry, solve crosswords and puzzles, and be interested in world news. It is very useful to start an interesting hobby and improve your skills in this direction.
Prevention
A set of measures to prevent Alzheimer's disease is relevant for all people. It reduces the risk of developing the disease in healthy people and reduces the rate of its progression in patients. Doctors recommend:
- observe the work and rest schedule, avoid chronic stress and overwork;
- avoid physical inactivity, regularly give the body moderate physical activity (hiking, swimming, cycling);
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking;
- keep blood pressure, blood glucose, cholesterol levels under control;
- eat right: the diet should contain a sufficient amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as microelements; It is advisable that the menu regularly include fatty sea fish, olives and olive oil, whole grain bread, nuts, spinach, and fruits;
- provide a load for the brain: solve crosswords, learn poetry, read classical literature, play chess, etc.;
- be regularly examined by a doctor.
Features of caring for older people with Alzheimer's
It should be remembered that there is no cure for the disease, and your task is to alleviate the patient’s suffering. This difficult work can take up to 50 hours a week. The syndrome also requires large material costs: medications, diet, minor rehabilitation products, hyena products and diapers, smart watches, etc. Your elderly relative will be helped by:
- A daily routine with clearly defined routines is the basis of Alzheimer's care. The patient should know that waking up, eating, walking and going to bed are scheduled at the same time.
- “Training the mind” by solving crossword puzzles and logical problems. If the patient had a hobby, you need to constantly remind him of his hobby.
- Communication. The opinion that a person who is losing his adequacy needs to be hidden from friends is wrong. The ability to dialogue is preserved only at the first stage of the disease; an elderly person should not be deprived of this opportunity.
- Tactile interactions, touching, hugging. Continue to see an older relative as the person you know and love.
- Your peace of mind. You cannot respond with insult to insult and insults to insults. Moreover, it is forbidden to argue with the patient and “pull” him out of the fictional reality.
- Physical therapy designed specifically for older people. Movements should not be difficult, energy-consuming or uncomfortable.
- Diet. It is necessary to increase the fat content in the patient's diet at the expense of carbohydrates. Nuts, sea fish, fruits, vegetables and herbs will help you. Salty, fried and fatty foods are prohibited. Vegetables are prepared by boiling, meat by steaming.
- Comfortable conditions, safety of living space, assistance in everyday routines.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If your relative begins to suffer from memory impairment, do not blame everything on age. Doctors at the Health Energy clinic will evaluate his condition and conduct all the necessary examinations to identify signs of Alzheimer's disease. Modern treatment methods are at your service:
- drug therapy in accordance with WHO recommendations and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body;
- work with a psychologist and psychotherapist;
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- training relatives in the rules of caring for the sick;
- comprehensive recommendations on preventive measures, nutritional and lifestyle corrections;
- organization of consultations with foreign specialists and sanatorium-resort treatment if indicated.
Advantages of the clinic
The modern multidisciplinary medical facility is equipped in accordance with international standards. We offer each patient:
- screening and targeted diagnostic programs to assess health status and identify hidden pathologies;
- detailed diagnostics in accordance with complaints;
- consultations with qualified specialists;
- modern treatment methods, including drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage;
- help from psychotherapists;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment;
- own day hospital for course treatment.
Don't wait until Alzheimer's changes the lives of everyone in your family. Sign up for the Energy of Health clinic for diagnosis and selection of treatment at the first alarming signs, or come to check-up screening programs.