Why does nervousness increase during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, as mentioned above, the hormonal background of the expectant mother changes greatly. Hormonal changes occur in any organism in which a new life is born, so any woman in one way or another becomes vulnerable psychologically. During the period of bearing a baby, people around you, and especially relatives and friends, need to be very sensitive towards the woman.
Already at the moment of fertilization, the value of the hormone gonadotropin jumps sharply. Its indicator reaches its maximum at 7-10 weeks. Increased concentration greatly affects a woman’s physical condition and changes her psychological background, making her mood changeable. Many people feel nauseous and their taste preferences change.
Reference! The hormone progesterone has a great influence on the mood of the expectant mother. Its level fluctuates from low to high at high speed, which dramatically affects mood. An important role is played by estriol, a natural antioxidant produced throughout the entire period of gestation.
What happens to a woman during pregnancy?
24.07.2020
The polite one suddenly becomes aggressive, the calm and reasonable one becomes nervous and whiny.
Being and Consciousness
Metamorphoses are not accidental. The body of pregnant women undergoes complex hormonal changes. The level of progesterone increases: this hormone not only relaxes the uterus , preventing it from contracting excessively, but also affects the emotional background. The woman becomes a little inhibited and more sensitive.
Little things that were not touched at all before are painfully touched; as soon as there are tears.
An increase in estrogen levels awakens hitherto dormant instincts, such as the protection of offspring. The baby has not yet been born, but his mother is already protecting him. Often pregnant women are aggressive, preventing a possible threat from others, experience irritation when touched by strangers, and feel anxiety in the crowd.
The body also produces a new hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin. It changes the psyche in accordance with the upcoming event, making you either fly with happiness or indulge in despondency.
Emotions monthly
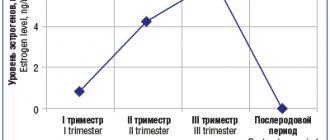
The first trimester of pregnancy is the most stressful. Joy and euphoria are interspersed with excitement and even fear. Increased irritability and excitability are observed, emotions become more superficial, laughter or tears are possible for no reason.
In the second trimester, anxiety decreases and a positive mood prevails. The hormonal background, changes in which caused problems in the first months, stabilizes, emotions stop overflowing. Nausea disappear , ailments become less acute. The expectant mother begins to feel her pregnancy more realistically; she feels the first movements and tremors of the baby, during an ultrasound examination she sees his arms, legs, head, and hears his heart beating.
But in the third trimester, anxiety appears again, which is now associated with the upcoming birth . It's not just the fear of pain. A woman is afraid of the changes that will happen in her life after the child is born: a new regime, responsibilities, responsibility for the baby. Questions torment me: What will I do with it? Can I handle it? What if I can’t become a good mother to him?
Baby sensations
Scientists say that a mother's emotions significantly influence the condition of the unborn baby. Observations made during an ultrasound examination show that the baby behaves differently depending on the woman's mood. When she is nervous, he becomes restless and sometimes has hiccups. When the mother is in a good mood, the baby is peaceful, and on a 3D ultrasound you can see his smile.
If we explain the relationship between mother and baby from the point of view of biochemistry, then at the moment of manifestation of strong negative emotions, the level of adrenaline in the blood . vessels narrow , fetoplacental (uterine) blood circulation worsens. The baby in the womb does not have enough oxygen, it becomes cramped and uncomfortable. The mother’s positive emotions, on the contrary, give the baby endorphins, hormones of joy. And even in the perinatal period, the child develops what psychologists call basic trust in the world.
The relationship also occurs at the cellular level: different emotional states correspond to a certain structure of intracellular components. Changes in it are perceived by the child either negatively - as anxiety, threat, lack of resources, or positively - as pleasure, joy, a sense of security.
Published in Pregnancy and pregnancy management Premium Clinic
Causes of increased irritability:
- in the 1st trimester
In the first trimester of pregnancy, women are the most whiny and irritable. This is due to a sharp jump in hormonal levels and adjusting it to the most acceptable one. Frequent predetermining factors of bad mood during this period include:
- Peculiarities of the woman's psyche. If the expectant mother, before the period of conception, had a tendency to unexpected changes in mood, then she will bring this state into her beginning pregnancy. The psyche of such young ladies is quite resistant to stress, therefore it is not so dangerous for emotional health in general.
- Previous bad pregnancy experience. If a woman has previously experienced miscarriage, then the stress received during this period automatically turns into a new pregnancy. In this case, coping with the emotional fear of loss becomes very difficult. A woman listens to her body every minute in order to avoid previous sensations.
- Unexpected pregnancy. If conception occurs unplanned, then upon learning about this, the woman experiences stress, either joy or panic. It’s good if the baby is long-awaited. In this case, the emotional background quickly returns to normal and the stress disappears. But if the child is unexpected, then a storm of emotions simply covers the confused mother. Here you need to quickly decide to accept the situation, otherwise you can cause irreparable harm to the child.
- The role of a strong personality. If a woman is accustomed to hard work and solving independent problems, then the understanding that she will have to wait a while causes her a slight psychological shock. To cope with emotions, you should get used to the idea of motherhood and your feminine essence: softness and weakness.
- in the 2nd trimester
By mid-pregnancy, women tend to calm down a little. They are already fully aware of the role of the expectant mother and their psyche returns to normal. However, in the second trimester of pregnancy there are very frequent emotional breakdowns, which are accompanied by irritability on the part of the expectant mother.
Attention! A woman may begin to be offended by everyone around her. She is literally hurt to the core by the words of her colleagues that she is absent-minded or has put her coffee cup in the wrong place. Even if there was no reproach, the woman will still find a hint of resentment in the advice or hint.
Sounds and smells can suddenly begin to irritate, and even quiet noises cause great bewilderment, even to the point of hysteria. If in the second trimester a woman continues to be bothered by toxicosis, then irritability intensifies against this background. At the same time, vomiting can lead to a constant feeling of hunger, which mom tries to eat with something tasty and satisfying. In turn, an addiction to sweets and starchy foods significantly adds pounds to the scale, which also adversely affects a woman’s well-being and her emotional background.
- in the 3rd trimester
The third trimester is quite a difficult test for a woman. Her weight noticeably increases, and her stomach begins to pull down, it becomes difficult to stand on her feet for a long time, and she feels the urge to lie down more. It is precisely because of excess body weight and the enormous load on the legs that a woman experiences severe discomfort and leads to irritation.
Quite severe swelling is inevitable, especially in cases where a woman is forced to spend time at sedentary work, and there is no opportunity for physical exercise. At the same time, after work, a pregnant woman is burdened with household responsibilities (cleaning, cooking), which put emotional pressure on the psyche and provoke reasonable nervous breakdowns. It is important for men to support their loved one, help her with household chores, and even transfer some functions onto their shoulders.
An early meeting with the baby adds a note of apprehension to the mother’s mood: she is worried about the normal process of childbirth and the successful birth of the child. Every day, worries accumulate, and the closer the period of childbirth comes, the more stress and worries a mother has in her head.
Stages of fetal development
The calendar gestation period is just over 9 months. However, there are 28 days in an obstetric month, so the obstetric gestational age is 10 months or 40 weeks.
The 2nd trimester of pregnancy lasts from 13 to 26-27 weeks of pregnancy. By the time it begins, the unborn baby’s main organs have already been formed, and their weight and height are rapidly increasing. Let's look at how intrauterine development of the fetus occurs week by week in the 2nd trimester.
Week 13
At this stage, cartilage tissue is formed, which protects internal organs from adverse effects. The digestive system is actively developing. Peristalsis occurs in the intestines - a wave-like contraction of the muscle layer of the walls of the organ. A fold of the laryngeal mucosa appears, consisting of the strip ligament and vocal muscle.
The tooth buds separate from the epithelial plate and begin to develop and mineralize. First, dentin is formed - the hard and basic part of the tooth. After this, enamel is formed - the protective shell of the crown. By the fifth month of gestation, the formation of the enamel of the front teeth is completed, and by the end of the second trimester - the chewing teeth.
Intensive development of the placenta is observed: it produces estrogen and progesterone, which support the normal course of pregnancy.
Week 14
Lanugo, a thin layer of hair that performs a protective function, is formed on the fetal body. The body of the unborn child synthesizes a gray waxy substance that covers the skin. This substance has antibacterial and antifungal properties. Thanks to lanugo, lubricant lingers on the skin and reliably protects it from pathogenic organisms and the effects of amniotic fluid.
The formation of protective hair is completed by the 28th week of pregnancy. The hairs disappear by the end of the third trimester or a few weeks after giving birth.
At the same time, active development of muscle tissue occurs. The fetus is able to move its head, mouth, and limbs. By the end of the 14th week, its size is about 10 cm and its weight is 40-43 g.
Week 15
The musculoskeletal system develops, the density of cartilage and bone tissue increases. The gallbladder begins to fulfill its functions: to accumulate and remove bile. The size of the unborn baby increases by 1-2 cm, and weight - up to 70 g.
Facial muscles and skin are well developed, salivary and sweat glands are formed. The heart works in active mode and pumps about 500 ml of blood per day.
Week 16
The formation of the placenta, which provides the unborn baby with oxygen, nutrients, hormones, vitamins, and microelements, is completely completed. The brain, spinal cord and urinary system are actively developing.
The formation of nail folds and the appearance of a primary (false) nail plate occur. Full nails will form only by the end of the third trimester of pregnancy.
Week 17
The fruit is proportionally complex, its size is 13 cm, and its weight is 150 g. The formation of cellular immunity begins. Single lymphoid nodules appear that prevent foreign particles, foreign proteins and bacteria from entering the blood. Adipose tissue is formed, which protects the body from heat loss and forms an energy depot.
Week 18
The temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres, in which the auditory centers are located, are actively developing. Bone density increases. The future baby's need for iron increases significantly.
Week 19
Brain neurons are formed that are responsible for processing and transmitting information. The skin is covered with a viscous substance - a protective lubricant. The left or right hand begins to dominate. Meconium, the first feces, forms and accumulates in the intestines.
The fetus learns to swallow amniotic fluid, which contains oxygen, salts, fats, glucose, and hormones. The digestive tract is “trained” to digest nutrients. The unnecessary part of the fluid is excreted through the urinary tract and returns to the amnion.
20-21 weeks
The skin becomes denser, bones and muscles are strengthened, the fetus is actively growing and gaining weight. He regularly uses amniotic fluid for food and drink. The intestines are able to absorb glucose and other nutrients.
The bone marrow begins to perform a hematopoietic function: it creates new blood cells to replace dying ones. Additional hematopoietic organs are the spleen and liver.
22-23 weeks
The reproductive system develops: the genitals move down from the abdominal cavity. The fetus begins to perceive sound signals well. The lungs develop: they produce special substances that prevent the walls of the alveoli from sticking together.
24-25 weeks
The endocrine system is improved. The adrenal glands synthesize glucocorticoids, which are involved in the process of hematopoiesis, affect metabolism, and interact with other hormones. The pituitary gland produces the hormone corticotropin, which regulates the functioning of the adrenal glands.
26-27 weeks
By the end of the 2nd trimester, the size of the fetus is about 33 cm, weight - 900 g. He can move, smile, suck his finger while sleeping. The unborn baby's eyelids open, and the sensitivity of the organs of vision to light increases. Thus, the fetus gradually turns into an active little person.
What to do if a pregnant woman is irritable?
With severe irritation, a woman’s mood changes, fussiness and panic appear, sleep is disturbed and tears appear in her eyes. It is urgent to deal with the symptoms that have overtaken mommy in order to avoid consequences. Experts recommend adhering to the following rules of conduct:
- Relax. You need to take a comfortable position and distract yourself from all thoughts. To do this, you can turn on an interesting film with a positive orientation, go for several sessions of a relaxing massage, take a walk in a nearby park or public garden, and turn on soothing music. You can simply take a warm shower or sit in a bath with your favorite scent of foam.
- Do what you love. This could be a trip to the store or beauty salon. Returning to your hobby can also be considered a useful activity. It is important to find something you like that will completely relax both body and soul, give you harmony and peace.
- Talk it out. It is very important for a woman to tell people around her about all her accumulated fears and assumptions, especially her partner. A man should listen carefully to his wife, without necessarily saying anything in response. It will be enough to nod or console the worried woman. This method works flawlessly. Not a single girl can resist the understanding and attentiveness of her chosen one.
- Try to remember the funniest and most exciting moments from your life. When there is no one to talk to, and melancholy simply fills everything inside, you need to try to take out from your memories the most amazing moments that can immediately correct the “plight.” Sometimes 10 minutes of this process is enough for mommy to calm down and all the functions of her body to return to normal.
- Protect yourself from negative information. Try to react as little as possible to the surrounding space. You cannot watch TV with sad news, or listen to sad music on the radio. It is best to sit in peace and quiet, it is better to turn on videos about animals, birds, small children.
Pregnancy management program in the 2nd trimester
The pregnancy management program in the 2nd trimester includes control examinations by an obstetrician-gynecologist (at terms: 14, 17, 20, 23, 25, 28 weeks), a cardiologist, and an ENT doctor. Before consulting an obstetrician-gynecologist leading the pregnancy, the expectant mother takes tests (blood, urine). At the appointment, the obstetrician-gynecologist measures weight, blood pressure, abdominal circumference and gives recommendations necessary for the healthy development of the baby (nutrition and acceptable healthy sources of vitamins, exercise, regimen). At 18-20 weeks of pregnancy, the second stage of screening prenatal diagnostics with ultrasound is performed, which makes it possible to exclude pathologies of fetal development and assess the condition of internal organs (including the placenta). At this stage, the doctor also listens to the fetal heartbeat.
The pregnancy management program in the 2nd trimester includes:
- Appointments with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
- Appointment with a therapist with an ECG.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound of the fetus) at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Laboratory tests of blood, urine, smears, cultures.
- Examination by an ENT specialist: analysis of discharge from the pharynx and nose.
- Biochemical screening (hCG level, ACE, risk assessment, etc.)
- Coagulogram (extended).
More information about the program and cost of pregnancy management in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimesters can be found here.