Types of stroke
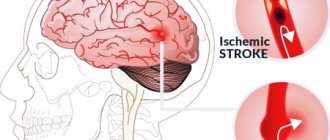
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
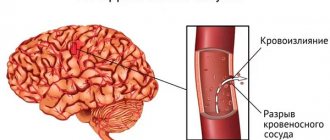
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Complications
The consequences of stroke in the elderly are persistent and are observed in more than half of patients. The severity of complications depends on the location of the injury and the amount of hemorrhage.
Most often, a stroke leads to the following consequences:
• Cerebral edema – develops in the first hours after an attack. To avoid swelling, you need to provide medical attention in a timely manner. • Leg swelling – caused by cardiovascular problems and develops gradually. The patient is prescribed diuretics that help remove excess fluid from the body. • Paresis and paralysis – partial or complete, numbness of the limbs. It is not easy to cure paralysis in an elderly person; treatment takes a lot of time. • Speech disorders: from problems with speaking and tongue movement to understanding spoken and written speech. • Joint problems – due to lack of nutrition. • Disorientation in space, loss of the ability to walk. • Loss of control over urination and bowel movements. • Impaired vision, hearing, swallowing. • Mental problems: depression, mood swings, seizures, development of dementia. Mental problems are usually reversible. • Coma is one of the most severe consequences of a stroke. Occurs due to damage and death of neurons. Expressed in fainting, noisy breathing with wheezing, severe redness of the face, loss of muscle tone, urinary incontinence. In a comatose patient, the blood pressure increases, the pulse becomes rapid, and the pupils do not respond to light.
Some older people recover after a stroke and return to their normal lives, while others remain disabled.
People with left-brain strokes recover faster than people with right-brain strokes. Vascular lesions in the right hemisphere are not accompanied by speech problems. Because of this, it is more difficult to detect, the ambulance arrives later - therefore, a right-sided stroke is more dangerous than a left-sided one. Be attentive to all signs so as not to miss time.
People over 70 years old cannot restore lost functions - problems with the body after a stroke remain for life. If the patient recovers slowly within 3 months after the stroke, a medical examination is carried out, based on the results of which the person’s sick leave is extended or a disability group is assigned.
Patients lose the ability to care for themselves and need helpers. After a stroke, it is difficult for a person to communicate even with loved ones, so the patient is usually limited to a narrow circle of people.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Pre-stroke condition
Advertising:
Is it possible to somehow avoid a serious, often irreversible condition? What to do when the first signs of deterioration in health appear? There are several signs that indicate an imminent stroke. Precursors of acute circulatory disorders in the brain in women after 50 years of age are:
- A one-sided headache that occurs suddenly, sharply and without reason. At the same time it makes me very nauseous.
- Double vision, blurred vision.
- Dizziness affecting coordination of movements and orientation in space. The gait becomes shaky and uncertain.
- High blood pressure that rises suddenly and in a short time.
- Periodic tinnitus.
- Slurred speech.
- Facial redness.
- Problems with short-term memory.
- Increased heart rate.
- Numbness of the arms, legs, tongue, part of the face and torso. A tingling sensation occurs - as if “goosebumps” are running.
- Insomnia, weakness, decreased performance.
- Fainting, loss of consciousness.
The first symptoms appear abruptly, but disappear just as abruptly. They are very individual, so many people brush them aside. And at this time you need to rush to be examined by a neurologist.
The difference between a stroke and a microstroke
Experienced doctors reveal the secret that the term microstroke does not exist in scientific terminology. Experts call this the pre-stroke condition in order to increase the vigilance of patients.
Advertising:
The symptoms of stroke and micro-stroke in women are almost the same. Only a microstroke goes away in a shorter period of time. It is characterized by:
- short-term loss of sensation;
- short-term motor disturbances and dizziness;
- slight changes in speech;
- slight weakness in the hands.
Dizziness usually lasts 10-15 minutes, no more than an hour. But even such short-term phenomena can lead to changes in brain matter. Therefore, the treatment tactics are the same as for stroke.
The difference between a stroke and a migraine
Since the symptoms of apoplexy are very individual, it is often confused with female migraine. To correctly diagnose both pathologies, you need to know the features of migraine:
- it is unlikely to occur for the first time in a woman after 50, as it usually begins in adolescence;
- migraine is often a hereditary disease;
- provocateurs of the disease - hunger, menstruation, stress, weather;
- the pain is strong, but of the same type, without any additional signs.
For more accurate recognition, computer diagnostics are used.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Features and types of disease
A stroke often occurs suddenly, literally within a few minutes. Symptoms can persist for more than a day and can lead to death. According to statistics, the number of deaths from vascular pathologies of the brain is in second place among all cardiovascular diseases. And the percentage of disability is the highest.
In just one year, about 450,000 strokes occur in Russia - it affects one Russian every minute and a half.
Stroke is a broad concept that includes such types as:
- Cerebral infarction, or ischemic stroke. Common in older people who have had heart attacks. It develops when the blood vessels that supply brain cells become clogged. They die without receiving the elements important for life.
- Bleeding in the brain, or hemorrhagic stroke. Usually diagnosed at 45-60 years of age. Its appearance is promoted by hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, hypertension, emotional and physical stress. Hemorrhage occurs after loss of vessel integrity.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. The age of the disease is 30-60 years. Those at risk include smokers, alcoholics, high blood pressure and excess weight. Hemorrhage occurs when a thinned artery ruptures.
Yes, strokes often target older people. But recently it has been diagnosed in young people as well. Although the stroke of a 30-year-old person differs from that of a 60-year-old, mainly in the course of the disease. Because the tissues of older men and women wear out significantly, the brain is affected more quickly in older age. Therefore, the likelihood of fully recovering from a stroke is much less than dying.
Radiculitis in a man is a common occurrence that can put him to bed and prevent him from working for several days. To prevent such a situation, you need to pay close attention to your health, eliminate unfavorable factors, and strengthen your spine. Read more in the article: “lower back pain - causes and treatment.”
The difference between male and female strokes
Advertising:
Does stroke have a gender preference? Both men and women are at risk. Indeed, to a greater extent, the development of the disease is facilitated by an incorrect lifestyle, bad habits and stressful situations.
Bloating and heaviness in the abdomen can occur both when consuming poor-quality food and against the background of various diseases of the stomach and intestines. It is important to carry out treatment in a comprehensive manner - there are a number of effective drugs to eliminate such problems. Read more in the article: “cure for gas and bloating.”
But statistics still indicate a difference in the number of sick men and women:
- between the ages of 18 and 40 years, pathology occurs less frequently in women;
- after 50 and 60 years - on the contrary, more often.
The fact is that until the age of 50, the female body is protected by the hormone estrogen. After menopause, women lose such protection, have a more difficult time surviving the disease and are more likely to die after a stroke.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
First aid for stroke
It is impossible to determine the nature of a stroke in the first hours, therefore it is necessary to normalize vital functions (breathing, blood circulation) and ensure the prevention of possible complications (pneumonia, thromboembolism, bedsores).
The first step is to call an ambulance. It is advisable to reassure the patient and measure blood pressure. If there is vomiting, place the patient on his side and place his hand under his head. Do not bend your neck, because blood flow cannot be impaired. The airways need to be clear. In case of severe respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation must be started.
If breathing is impaired, it is necessary to free the patient from tight clothing. Free the oral cavity from foreign objects, mucus, and vomit. If the patient is indoors, access to fresh air is necessary. If a person is conscious, it is advisable to cheer him up and calm him down.
If you lose consciousness, you need to make sure that the person is not injured or bruised.
There is no need to take medications so as not to worsen the patient’s condition.
If it is not possible to call an ambulance, then you must transport the victim to the hospital yourself.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
How to determine a stroke?
The clinical picture of the disease depends on how much of the brain is affected. What are the most common signs of stroke in women over 50? If it is cerebral, then the following occurs:
- loss of consciousness;
- pulsation of cervical vessels;
- stunned;
- purple face;
- feeling of weakness, lack of energy;
- severe pain in the head;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- loss of spatial and temporal reference;
- feeling of increased temperature, sweating;
- increased heart rate;
- dry mouth.
At the same time, symptoms of brain damage characteristic of the lesion may appear:
Advertising:
- if the motor centers are affected, then lethargy is felt in the limbs, which can turn into paralysis;
- loss of sensation in the limbs, muscle weakness, visual and speech disturbances - if the brain part, which is supplied by the carotid artery, is damaged;
- if the outbreak occurs in the part responsible for coordination, then loss of balance and dizziness appear.
Some stroke symptoms can be called typical for the disease, while others can be called atypical. But for men and women they are almost no different.
Heavy breathing during stroke
There is another symptom characteristic of cerebral hemorrhage. This is periodic Cheyne-Stokes breathing. With oxygen starvation, rare and superficial respiratory movements become more frequent and deeper, but on the fifth to seventh breath they return to their previous intensity. There is a pause - apnea - for 15-75 seconds, after which the cycle repeats.
Cheyne-Stokes breathing is a symptom of stroke, in which more than 80% of patients die within a month.
Similar phenomena are observed both at night and during the day. At this time, the woman’s face turns pale and loses consciousness. The pupils become constricted and do not respond to light. When breathing is restored, patients feel anxious and complain of shortness of breath.
How much is speech impaired?
A disorder of speech skills appears when a stroke affects the corresponding centers of the brain. Moreover, slurred speech is only one type of disorder. A sick elderly woman experiences:
- loss of ability to write and even hold a pen;
- misunderstanding the conversation;
- inability to construct sentences, insert prepositions and put words into the required forms.
The patient loses skills acquired in childhood.
Disease on the face
Advertising:
The face during a stroke is a clear illustration of the disease. You can understand the attack almost immediately. The most common signs are:
- facial asymmetry;
- smoothness of the nasolabial fold.
Numbness of the limbs appears on the same side on which the face is distorted. But this means that the source of the stroke occurred on the opposite side of the brain.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Prognosis after a stroke
A stroke leads to various consequences, doctors do not give guarantees. The first month after a stroke is the most dangerous time. If the patient remains alive after this time, he has a good chance of partial or complete restoration of lost functions. Patient care is of great importance. It determines how quickly the patient will recover and whether a second attack will occur.
Survival statistics for the elderly after a stroke are as follows: in the first month - 35%, in the first year - half of the cases. More women die after their first stroke than men.
A recurrent stroke can occur in 25% of patients within a year, in 30% within 3 years, and in 40% within 5 years.
80% of morbidity cases are ischemic stroke, of which almost half end in death. 20% is hemorrhagic stroke, which is even more dangerous.
To reduce high mortality rates, older people should definitely engage in stroke prevention and immediately seek medical help if warning signs are detected. It is also necessary to educate the population about the disease so that people know how to recognize a stroke and what needs to be done to treat it.
How a stroke will affect the patient’s health depends on various factors: general health, the presence of stress and chronic illnesses, the speed and quality of first aid, the accuracy of diagnosis, the quality of treatment and rehabilitation.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Main symptoms
The following symptoms are typical for women:
- severe headaches (characteristic of migraines);
- decreased intensity of facial expression activity;
- failure of nerve conduction in the facial muscles;
- disturbance of speech and motor activity of the limb on one side;
- visual impairment;
- dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus;
- gag reflex and uncontrollable muscle contractions;
- self-perception disorder;
- sagging corner of the mouth;
- feeling of mental unsettlement.
Symptoms of microstroke in women
A microstroke results in minor necrosis of brain tissue resulting from rupture or thrombosis of small vessels. The visible symptoms of the disease are subtle, and the body recovers relatively quickly. In some cases, microstrokes are not noticed by patients and measures to minimize the consequences and prevent recurrences are not taken. This is the insidiousness of the disease - it always returns, only each return is fraught with more serious consequences.
Hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis, various heart diseases, poor lifestyle and hereditary factors significantly increase the risk of micro-strokes; such patients need to be very carefully monitored even for subtle changes in the condition.
Signs of minor necrosis of brain tissue (ministroke) are:
- short-term numbness of the limbs. Loss of sensation may last from just a few seconds to several minutes;
- sudden pulse headache, short-term dizziness. Such signs indicate rupture or thrombosis of the capillary;
- a sharp increase in pressure. It can appear due to various nervous strains or stress, from fear or after exhausting and prolonged physical labor;
- Coordination of movements is slightly impaired, it is difficult to maintain balance. The symptoms go away on their own, after a short period of time all functions are restored;
- In some patients, vision may deteriorate somewhat, and “spots” appear before the eyes. There is short-term blindness in one eye, a shadow creeps into the field of vision, all this lasts no more than 30 seconds, there is no pain. The syndrome occurs when small plaques already present in the carotid artery begin to fall off and enter the first vessel supplying the eye. In the future, they can rise higher in the bloodstream and affect the brain;
- General weakness occurs, cold sweat appears, the rhythm and fullness of the heartbeat changes.
A microstroke is an indicator of deep-lying changes in the body; if one of the above signs appears, it is imperative to undergo testing in a specialized medical institution. Establishing an accurate diagnosis makes it possible to prevent the development of major strokes of various pathogenesis.
Comprehensive stroke treatment
First of all, doctors need to stop the hemorrhage, relieve swelling, and carry out prophylaxis immediately after the patient’s admission to the hospital, which will prevent a recurrence of the attack. Next, the patient will receive symptomatic treatment based on the individual clinical picture.
Typically, the therapeutic regimen is developed in an interdisciplinary meeting. The commission includes a therapist, cardiologist, pharmacologist and some other specialized specialists. This helps minimize the risk of complications or adverse reactions from the use of certain medications.
The body’s functionality is supported through the following procedures:
- IVL (artificial pulmonary ventilation);
- cleaning the oral cavity from vomit and mucus;
- breathing exercises;
- maintaining blood pressure at the required level;
- droppers that help thin the blood and restore salt balance;
- treatment with anticoagulants;
- if swallowing ability is lost, feeding through a tube.
The success of therapy will depend on the quality of medical care provided and the condition of the patient’s body. Rehabilitation will also play a major role, but it begins only after the 3rd week of continuous treatment of an attack.