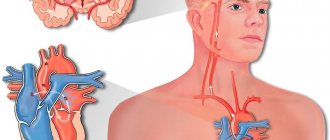
Stroke is a common problem. Cerebrovascular accident can occur in a woman at any age, but the most dangerous age is after 55-60 years. Most often, signs of stroke in older people are the reason for visiting a neurologist. With a brain stroke, the patient’s life depends on the actions of relatives and doctors. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital save the lives of patients and help them overcome the difficulties that arise during recovery and adaptation to life. The neurology clinic has created conditions for a comfortable stay for patients and provides round-the-clock supervision by experienced doctors.
Types of stroke
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Statistics on stroke in old age
Stroke is the second most common cause of premature death. According to WHO, 5–6 million people worldwide have a stroke every year, and 450 thousand in the Russian Federation. It occurs in people regardless of gender and age, but most often affects the elderly. After reaching 60 years of age, the likelihood of occurrence increases sharply and doubles after every 10 years. 75% of the total number of recorded cases of stroke occur in patients 65 years of age and older.
According to statistics, stroke affects men 11.25 times more often than women. Women are susceptible to stroke at a later age, which is why women's mortality from the pathology exceeds men's. A genetic predisposition has also been proven if the parents had a stroke. This is explained by the inheritance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism disorders, hypertension.
The spinal type is the least common - 1% of the total number of cases.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Consequences and complications of left hemisphere stroke
Even with all of the above rules, sometimes the patient experiences consequences and complications after a left hemisphere stroke. This:
- Slower speech, problems connecting words. This can be corrected by studying with a speech therapist, but treatment does not always restore speech completely.
- Epilepsy is a process during which a person experiences unexpected seizures.
- Occasional difficulty eating due to problems swallowing.
- Changes in a person’s character and behavior. The patient may experience irritation, unjustified anger, or, conversely, sadness.
- The emergence of mental disorders. For example, the appearance of uncontrollable laughter and crying for no reason.
- Retardation of movements.
The older the patient, the more complications he may experience. Complications such as fever, frequent convulsions, and vomiting can significantly complicate the rehabilitation process.
Sometimes recovery is complicated by the behavior of the patient himself. There are also cases when he does not agree to stay in a special center and undergo rehabilitation, believing that after a course of procedures and treatment he is absolutely healthy. However, ignoring the consequences of a left hemisphere stroke cannot lead to anything good. Often, after some time, the patient is forced to see a doctor again and still undergo treatment at the center.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Treatment of stroke in Moscow in elderly women
Symptoms of stroke in older women arise as a result of the acquisition of cardiovascular pathology after menopause. After vascular accidents in the brain, about 20% of women can move only with the help of crutches or other devices; this disorder can be eliminated with proper rehabilitation and the desire of the patient.
To prevent the consequences of a stroke, it is important to promptly recognize the disease by the first signs and hospitalize the patient. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital in the neurology clinic treat stroke patients, even with severe manifestations of the disease. The clinic's diagnostic equipment allows you to quickly assess your condition and make a diagnosis. A team of professors and doctors of the highest category uses modern equipment and accumulated knowledge to save the lives of patients.
At the Yusupov Hospital, for the convenience of patients and their families, comprehensive rehabilitation programs have been created, which include step-by-step treatment of the disease, a wide range of services and the ability to add services and treatment. The patient’s recovery after a stroke takes place with the participation of doctors of various specializations: rehabilitation specialists, neurologists, speech therapists, occupational therapists, neuropsychologists. You can make an appointment with a neurologist in Moscow, and also ask questions by phone.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Which older women are at risk?
Most women, approaching the age of 50, have various diseases that can trigger a stroke. Most often it is caused by atherosclerosis. Therefore, older people mainly face the ischemic type.
Although this type of stroke is less dangerous, medical prognosis for elderly patients is not very encouraging. This is caused by the age of patients and changes occurring in the body:
- Brain tissue is affected at a high rate, increasing the likelihood of death. Statistics show the death of 90% of patients who experience a stroke after 65 years of age.
- The recovery of older people is much more difficult, which affects their rehabilitation after an attack. In addition, most elderly patients refuse to receive full treatment.
- People under 60 years of age are more likely to experience the most severe type of the disease - the hemorrhagic type.
- Stroke in elderly women 80 years of age and older is fatal in 95% of cases. No more than 5% of patients survive the attack, but their full recovery is no longer possible.
- Women are more likely to suffer major strokes in old age than men.
Read the material on the topic: How to prevent a stroke
The first symptoms of an impending attack can be noticed several days before it. We are talking about micro-strokes, which are usually left unattended. If the first symptoms are not recognized in time, or a late visit to the doctor will lead to a major attack. The causes of stroke in older women can be different. The risk group is represented by patients suffering from:
- rheumatic diseases;
- vasculitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- cerebral aneurysm;
- hematological diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- endocrine diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- heart disease;
- acute infections.
In addition, a sedentary lifestyle, nervous shock and anxiety contribute to the development of stroke. Most older people are characterized by increased emotionality caused by hormonal changes and age-related characteristics. Any little thing that would previously have gone unnoticed can contribute to imbalance. Statistics indicate more frequent cases of stroke resulting from emotional stress in lonely old people and in people living separately from children and feeling lonely.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Treatment of stroke in an old person
If there are signs of a stroke, you should consult a cardiologist. After collecting the necessary information from relatives and the patient himself, the attending physician prescribes blood tests and conducts:
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiogram;
- magnetic resonance (computer) tomography;
- ultrasonography.
All this will allow us to identify the pathology, the location of the lesion, and determine the type of stroke.
The patient also needs examinations by a neurosurgeon and an ophthalmologist, which can identify other affected areas in the body.
It is quite difficult to determine the pathology of hemorrhagic stroke in patients over 75 years of age. Typically, such patients have mild changes in the blood test or they may also indicate other diseases. In such cases, doctors conduct additional examinations, such as electroencephalography and angiography.
Treatment should only take place in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. A specialist can prohibit transporting a patient to a hospital only in the case of a severe coma with severe impairment of vital functions.
In order for treatment to benefit an elderly patient, he must follow the sequence of procedures, complete their full course and subsequent rehabilitation measures. Only under such conditions will an old person be able to quickly recover from an attack.
The main goal of treatment after a stroke is to restore the functioning of the cardiovascular system and protect the remaining brain cells. After the patient is recovered from a serious condition, he is prescribed medication and physical therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of stroke in an elderly person are available only by prescription. Among them:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Medicines aimed at reducing blood pressure by reducing vascular tone. A very large group of medications does not affect the presence of cholesterol and does not affect atherosclerosis.
- Class 2 receptor blockers. They have a long period of action, consistently reduce blood pressure, and have virtually no side effects. In conventional therapy, they are often prescribed for chronic hypertension.
- Diuretics. They are used if the first groups of drugs are contraindicated for the patient due to various, most often age-related, reasons.
- Beta blockers. Designed to dilate peripheral blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and help fight arrhythmia.
- Calcium antagonists. As a rule, they are used to treat stroke in old age in the presence of concomitant angina and other heart rhythm disorders. Often prescribed together with ACE inhibitors.
- Adrenergic receptor blockers. Used to reduce blood pressure. Can be used for renal failure and diabetes.
- Centrally acting drugs. With a pronounced effect, contractions of arrhythmias can also lower blood pressure. Used for comprehensive healing of the heart muscle.
- Vascular drugs. In case of a stroke in an old person, they are administered as injections to restore nerve cells and blood vessels in the brain.
- Nootropics. Indispensable during the rehabilitation period of elderly patients for the restoration of brain cells.
- Antihypoxants. Preventative drugs. Prescribed if there is a risk of developing oxygen deficiency.
- Thrombolytics thin the blood, prevent the formation of blood clots and plaques, and are used to restore blood composition.
During the rehabilitation period, various natural supplements and vitamins are included in the patient’s diet.
What treatment does the doctor prescribe depending on the type of stroke?
1. In case of hemorrhagic form, the patient is given intramuscular injections of calcium gluconate, and intravenous injections of calcium chloride. For treatment, Rutin, Vikasop, Dicynon, ascorbic acid with gelatin, Rutamin, and aminocaproic acid are used. If necessary, the lateral hematoma is removed by surgery. In emergency cases, other surgical procedures may be used.
2. For ischemic stroke, vasodilators and nicotinic acid are used. The patient is recommended to use “Trental”, “Stugeron”, “Heparin”, “Phenilin”, “Aspirin”, “Prodectin”, “Complamin”, solutions of diethyphene and cocarboxylase.
We recommend
“Vitamins for elderly people over 70: which ones are needed first” Read more
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.
What does a stroke mean for older people?
Almost all older people over the age of 80 suffer from one or another chronic disease. Accordingly, when stroke occurs in such patients, treatment and recovery measures are complicated. At this age, surgery is usually prohibited if an aneurysm is detected in a patient, which also negatively affects the course of the pathology. What other reasons complicate the treatment of stroke in an old person?
- Due to the fact that elderly patients do not tolerate anesthesia well, and operations due to concomitant pathologies are often accompanied by hemorrhages and other side effects, surgical intervention is rarely used for people over 70–75 years of age.
- Extensive atherosclerosis in elderly patients becomes permanent, pronounced and difficult to treat. You can only slightly lower the level of cholesterol in the blood, but it is very difficult to rid the blood vessels of fatty plaques.
- Treatment of stroke is complicated by the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
- Susceptibility to infectious diseases that weaken the body of an old person, impair blood clotting, lead to oxygen starvation and other adverse consequences.
- The need to take a variety of medications to keep the body normal. Forced reduction in drug dosages.
- The risk of recurrent stroke if the course of rehabilitation is not completed, the required diet and other medical recommendations are not followed.
- The impossibility of restoring the brain of an elderly person after a coma resulting from a hemorrhagic stroke.
An old person who has had a stroke has neurological impairment. Almost 100% of patients over 80 years of age become disabled after an attack. Relatives need to be prepared for the need for constant care for the patient, as well as for the following consequences of the illness:
- complete or partial lack of movement (paralysis) of the body;
- paresis (impaired motor functions) of the limbs;
- loss of orientation in space;
- impaired speech;
- loss of swallowing function;
- complete or partial deafness;
- lack of urinary and bowel control;
- changes in mental and emotional state.
We recommend
“The main problems of older people and ways to solve them” Read more