Cognitive processes
There are three types of cognitive impairment after a stroke:
- Damage to one of the cognitive functions: memory (amnesia), the ability to perform any actions (apraxia), impairment of visual, auditory, tactile perception (agnosia).
- Violation of several functions that generally do not affect social adaptation.
- Multiple injuries that lead to social maladaptation: impaired attention, memory, volitional processes. In this case, post-stroke dementia is diagnosed. In older people with dementia, household activity decreases and self-care skills are lost. This category of patients is at risk of recurrent stroke.
The first and second variants of the disorder can be corrected due to the plasticity of the brain: damaged functions are compensated by functions that remain intact.
Rehabilitation of older people with post-stroke dementia includes sessions with psychologists. With the help of special exercises, patients develop auditory and visual memory, the ability to concentrate, and solve logical problems. The recovery process is accompanied by drug therapy.
Rehabilitation after a stroke at home
After overcoming the acute period in the hospital, a rehabilitation period begins for a pensioner with a stroke. Relatives need to decide where it is better for an elderly person to undergo a recovery course: at home or in a rehabilitation center.
You may also be interested in the article: How to obtain patronage for an elderly person
If the family has decided to independently care for the patient after a stroke, they need to follow the recommendations of the attending physician and maintain constant contact with specialized specialists: a psychologist, a neurologist, a speech therapist.
At home, a separate place is assigned to a bedridden patient after a stroke. The bed is equipped with an anti-decubitus mattress. A small table is placed nearby, on which essential items are placed: a bottle of water, care products, a table lamp.
Specialists can come to the home 1-2 times a week, work with the patient and teach home methods of conducting developmental activities. The rest of the time, family members carry out the recommended exercises with the pensioner for 10-20 minutes several times a day. During weekly visits, specialists monitor the dynamics of changes, make additions and adjustments.
Motor abilities are restored using a complex of therapeutic exercises. Before performing the exercises, it is advisable for the patient to take a shower or bath to warm up the body. If there are contraindications to taking a bath or other difficulties, the affected areas are warmed with a heating pad. The muscles will be more flexible and there will be no pain.
Examples of gymnastic exercises:
- pulling up while lying on your back, holding the headboard of the bed;
- eye movements left and right, up and down with closed and open eyelids;
- alternately raising the right and left arms and legs;
- bending the knee and grabbing the shin with the hand;
- joint movements of healthy and motionless limbs to the right and left with a rubber ring put on them.
When carrying out therapeutic exercises, the pensioner’s condition is closely monitored. He shouldn't get tired. If such signs are observed, it means that the amount of stress does not correspond to the physical strength of the patient. We need to make an adjustment: reduce the pace and number of exercises.
Speech is restored by memorizing poetry and tongue twisters. At the initial stage, simple children's poems are chosen, which are easier for a pensioner to recite after a stroke. Gradually more complex material is selected.
Looking at family photographs can activate the process of remembering, since it is easier for the patient to recall the past in his memory. An elderly person remembers acquaintances and friends in the images, then the events associated with them. He tries to pronounce the names of the places he has visited, the objects he sees in the images.
Scientists believe that singing has a beneficial effect on people who have suffered a stroke. If they hear singing, sing together with loved ones, speech activity will be restored faster.
For rehabilitation to be successful, an elderly person should not be in a social “vacuum”: you constantly need to communicate with him, talk, ask questions, even if at first he cannot answer them. In this way, the patient’s desire to speak is stimulated, he remembers words and their meaning.
Chess, checkers, and dominoes are used to develop thinking abilities. In a family, even a small child can take part in restoring the health of a grandfather or grandmother by putting together puzzles, mosaics, or playing a board game.
A separate issue is the organization of nutrition for an elderly person after a stroke.
Excluded from use:
- alcoholic drinks;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- coffee, strong tea;
- sweets.
It is advisable to add to the diet:
- drink liquid of at least 1.5 liters. per day;
- increase consumption of fruits and vegetables;
- eat whole grains;
- replace sweets with dried fruits.
Food should consist of useful substances and be easily digestible so that the body is not overloaded.
It is useful to cook boiled vegetables, dishes from lean fish and meat, and porridge with low-fat milk. If there are paresis and problems with swallowing, the patient is fed through a tube with ready-made nutritional mixtures. As soon as the opportunity arises, you need to take the patient for a walk. Staying in the fresh air is good for brain activity, the body receives oxygen and vitamin D, and appetite appears.
You may also be interested in the article: How to choose a private facility for the elderly
The moral atmosphere in the house is of great importance. Patients who receive family support recover faster. If they experience hostility from others or rudeness, the healing process is slowed down. There is no need to criticize and laugh at clumsiness and awkwardness. Only with encouragement will an elderly person develop a strong desire to overcome the disease.
3-type-stroke Deathstroke
Stroke is one of the most common causes of premature death. In Russia, about 200 thousand people die from it every year. Approximately another 200 thousand become disabled. Of these, only 8% return to normal life.
Stroke is a non-infectious disease and means damage to blood vessels in the brain. For a long time it was defined by the word “apoplexy” - translated from Latin as “strike”. In fact, this is a blow to the blood vessels of the brain.
If you do not take strokes resulting from injuries or provoked by any congenital diseases or genetic abnormalities, they can be divided into three groups - ischemic, hemorrhagic and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage is less common, but this type of stroke is the most dangerous - almost 50% of cases are fatal. And even with early diagnosis and timely adequate treatment, a person is more likely to remain severely disabled for the rest of his life. The main symptom is an acute sharp headache like a “blow to the head,” often with pulsation in the occipital region; there are also vomiting, convulsions, and consciousness.
Hemorrhagic stroke, or bleeding in the brain, leads to death in 40% of cases. Symptoms - fever, headache, blurred vision - may not even have time to be noticed, because... A stroke develops quickly, usually during the daytime. Its causes can be either banal overexertion or hypertension, atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases, and at a young age – cocaine addiction.
Ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, is the most common. To recognize it, it is enough to remember the word “asymmetry”, because the area of the brain responsible for the motor function of the right or left part of the body is affected. A person cannot raise both arms and legs at the same time or smiles from one corner of his mouth. In addition, he may have confused speech, or he may lose the ability to respond to calls to him.
Risk factors leading to the development of ischemic stroke before old age include arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, smoking and diabetes mellitus. All these factors often depend on the person himself: to prevent them, you need to not smoke, eat right and be physically active. What does it mean to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Recovery in a boarding house
Rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke at home requires the full-time employment of one of the relatives for the next six months. While the patient is bedridden, he cannot be left at home alone for two reasons: he is helpless and it is necessary to deal with him several times a day. The volume of care is so large and multidirectional that soon the caregiver himself will need support and replacement.
In boarding houses for the elderly, professionals are involved in the rehabilitation of patients. Special equipment is used for treatment. An individual program is developed for each patient. Restoration methods that have been developed over the years produce positive results within a month.
What is a stroke?
A cerebral stroke is most often caused by a blockage (thrombosis) of a brain vessel or bleeding into surrounding tissue. As a result, nerve cells die and cease to perform their functions, that is, to regulate the vital functions of the body. This is a serious illness that requires urgent medical attention. After hospital treatment, most patients require a course of rehabilitation to restore lost brain functions.
At the age of 55–60 years, the disease occurs more often in men, and in older age – in women.
The disease can be accompanied by symptoms of varying severity - from slight difficulty speaking to paralysis and death of the patient. The use of modern medical technologies can improve the prognosis.
Diagnosis of stroke and first aid
The time from the onset of its development to the receipt of medical care is of utmost importance in the successful treatment of the disease. Therefore, if facial asymmetry, weakness in the arms or legs and speech impairments appear, you need to call an ambulance. First aid for stroke:
- lay the patient down, calm him down;
- provide access to fresh air, unfasten tight clothing;
- measure pressure;
- put a cold compress on your forehead.
It is also necessary to prepare existing medical documents, personal hygiene items and the patient’s clothing for hospitalization, and also, very importantly, to remember or prepare all the medications that the patient is taking.
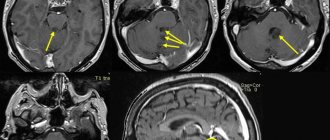
In a hospital setting, diagnosis includes a full examination, neurological examination, blood tests, CT or MRI of the brain, and ECG. The patient is placed in the intensive care unit.
After transfer to the department, the patient is prescribed drugs that improve cerebral circulation, nootropics, and vitamins. Rehabilitation after a stroke begins - first small movements, then light exercises. It is useful for the patient to read aloud, talk to him, good care is very important.
The consequences of a stroke can be different - from almost complete recovery to paresis and severe paralysis, loss of speech, vision, conscious urination and defecation. Therefore, the rehabilitation program is compiled individually. It is important that at the outpatient stage of treatment the patient is observed by a qualified neurologist who monitors the implementation of all its points.
Causes
Long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages causes microdamage to the vascular walls, during the restoration of which connective tissue grows and microaneurysms form, thereby reducing elasticity. Increased blood pressure and increased heart rate cause an increase in the volume of blood passed through. Damaged vessel walls are not able to adequately respond to stretching, so rupture and local hemorrhage occur. The surrounding tissues suffer from hypoxia, and massive death of neurons in the affected area occurs. The formed hematoma puts pressure on neighboring structures, causing even greater damage.
There are two pathological types of acute cerebral circulatory disorders:
- hemorrhagic, occurring as a result of rupture of the vascular wall;
- ischemic, occurring due to blockage of a vessel or severe vasospasm, as a result of which the flow of blood to any part of the brain stops.
The condition is preceded by TIA (transient ischemic attacks) - short-term disturbances in brain nutrition, often the first signs of a stroke after heavy drinking. With prolonged toxic effects of alcohol, the body's compensatory capabilities are reduced. The condition after an alcoholic stroke is much more severe than in patients who did not drink alcohol.
Classification of hemorrhagic stroke
Despite the general symptoms, the course of treatment and prognosis depend on the location of the brain lesion. Divided into:
Parenchymatous
, which is the most severe type, since the blood enters directly into the gray matter. Depending on the location of the hemorrhage, it is divided into:
- hemispheric;
- cerebellar;
- stem;
- pavement;
- subcortical.
Subarachnoid
. With this type of pathology, the subarachnoid membrane suffers from hemorrhage. It is divided into basal and convexital types, i.e. blood enters the lower surface of the hemispheres or convex areas, respectively.
Subdural
involves blood entering the area located above the dura mater.
Epidural
when hemorrhage occurs under the dura mater.
Ventricular
, it is also called ventricular because blood enters the cerebral ventricles.
Mixed
.
Hemorrhagic stroke can be caused by primary or secondary causes. Accounts for 80% of the total number of attacks. Among these causes are increased blood pressure and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Secondary ones are much less common - only 15–20%, these include:
- the presence of an aneurysm, vascular structural disorders, liver cirrhosis, eclampsia;
- taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, narcotic drugs;
- problems with blood clotting;
- intracranial neoplasms of various types;
- vasculitis.
Based on statistics, the most common causes of an attack are:
- arterial hypertension (70% of the total);
- arterial aneurysm/malformation (20%);
- atherosclerosis (8–10%).
Prognosis and prevention of stroke
Improvement in health depends on the severity and location of the stroke, as well as on the complications that have developed (pneumonia, bedsores, convulsions, etc.). During the first year, up to 20% of patients who have had this disease die.
Stroke prevention:
- maintaining normal levels of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar;
- to give up smoking;
- taking all necessary medications for coronary heart disease or hypertension;
- elimination of stenosis of the carotid arteries caused by atherosclerosis, including surgically;
- therapy for atrial fibrillation - rhythm restoration, pacemaker implantation, anticoagulants.