Consultation with a neurologist – RUB 1,750.
- What is encephalopathy?
- Types of acquired encephalopathy
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of encephalopathy
- Popular questions
Encephalopathy
is a general term used to describe non-inflammatory diseases of the brain.
Characterized by a decrease in the volume of nervous tissue and impaired brain function. Encephalopathy of the brain can be congenital
or
acquired
. Congenital encephalopathy occurs due to genetic disorders or abnormal development of the brain during fetal development, or damage to the brain during childbirth.
Acquired encephalopathy is divided into several types.
Types of acquired encephalopathy
Depending on the cause of the disease, the following types of acquired encephalopathy are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy
- develops as a result of traumatic brain injury. It is often detected in athletes. It happens that signs of the disease appear long after the head injury. - Toxic encephalopathy
is caused by long-term negative effects on the brain of toxic substances, for example, alcohol, certain medications, heavy metals, and poisons. - Discirculatory encephalopathy
- occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the brain. - Residual encephalopathy
occurs due to the death of cells of the central nervous system. - Hepatic and uremic encephalopathy
- caused by severe diseases of the liver and kidneys. - Pancreatic encephalopathy
- occurs with diseases of the pancreas. - Hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic encephalopathy
- occurs in diabetes mellitus. - Radiation encephalopathy
– occurs due to radiation damage. - Vascular encephalopathies
- occur with chronic disruption of the blood supply to the brain. They develop as a result of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, hypertension, etc.
Treatment of speech delay (SRR, ZPRR) in the center of Dr. Leviticus
In the clinic of Dr. Lev Levit, a safe proprietary method of craniocerebral stimulation (from the Latin cranium - skull, cerebrum - brain) is used to treat speech delay. This method is aimed at improving biochemical processes in the brain lobes responsible for speech activity and communication.
The traditional approach to the treatment of delayed speech and psycho-speech development includes:
- speech therapy classes
- massage for motor development, speech therapy massage
- electroreflexotherapy
- drug treatment (nootropics, stimulants, neurotransmitters, etc.)
Drug treatment is not used at the center. Correction, speech training and speech therapy sessions with the child are not carried out during the course. However, after a course of treatment, children themselves begin to make progress in their speech, because the procedures affect the root cause of the delay in speech development.
With subsequent speech therapy correction and activities with the child, such children quickly overcome delayed speech development and are no different from their peers.
The technique of craniocerebral stimulation is aimed at improving the functioning of those parts of the brain that do not function well enough. In the case of mental retardation, the child’s speech activity improves.
The method circulates cerebrospinal fluid and, as a result, metabolism also improves in children with speech problems and general retardation.
Diagnosis of encephalography
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a number of methods:
- Rheoencephalography (REG)
is a non-invasive examination method that allows you to obtain information about the condition of the walls of blood vessels in the brain. - Doppler ultrasound (USD)
is a safe and highly informative method for diagnosing vascular disorders that lead to the development of encephalopathy. - MRI
- MRI of the vessels of the brain, head and neck, pituitary gland, and eyeball is performed.
For some types of encephalopathies (for example, dyscirculatory encephalopathy), the following are used as diagnostics: Source: Kadykov A.S. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy: algorithm for diagnosis and treatment in patients with arterial hypertension / A.S. Kadykov, N.V. Shakhparonova // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - pp. 12-17.
- neuropsychological research with special attention to the state of memory, attention and intelligence;
- ECG and dynamic blood pressure measurement, if necessary, echocardiography, Holter monitoring, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring;
- study of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Danilova Olga Andreevna
neurologist
Encephalopathy is a group of diseases, the main manifestation of which is the gradual degeneration of brain tissue. To treat the disease, it is important to eliminate the main factor that is gradually destroying the brain. This may be insufficiency of liver or kidney function, atherosclerosis, previous traumatic brain injury, diabetes mellitus and many other reasons. At SM-Clinic we carry out a full diagnosis to determine the cause of encephalopathy, and only after that we begin treatment.
Signs of speech delay
By carefully observing a child, you can notice symptoms of speech disorders at a very early age. Thus, a baby with pathologies of the speech apparatus will already suck weaker in the first month than other infants. Later he may have problems chewing food. It is very important to diagnose speech development delay as early as possible, then with effective treatment the child will quickly catch up with his peers.
Below are some early signs of delayed speech development in children under two years of age.
1. At three months, the child does not grow and does not react to the presence of adults. From a certain time, from about 4-6 months, the humming disappears, this is the norm, it is replaced by baby babble;
2. A baby under 5 months does not walk, does not pronounce the consonants g, x, k, and vowels y, s;
2. From 6 months, the child practically does not babble (ma-ma, ba-ba);
3. At 8-9 months the child does not babble
4. By the age of 1, the child’s vocabulary includes less than 5 words such as “ma-ma”, “ba-ba”, “nya-nya” “give”, etc. Speech activity is minimal, speaks little in “his own language”
5. Closer to one and a half years, the baby does not say the words “dad” and “mom” addressed to his parents. Does not understand his name or the names of surrounding objects
6. At one and a half years old, the child does not understand speech addressed to him and does not respond to the requests of his parents;
7. At 2 years old, a child cannot construct simple sentences. Pediatrics allows a delay in speech development of 4-5 months for boys, and 2-3 months for girls. That is, if a boy does not babble for a year, this is also a variant of the norm for speech development.
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment methods for encephalopathy directly depend on the disease that caused the brain damage.
The most common treatment methods are:
Drug treatment
— a wide range of different groups of drugs are used, which are selected depending on the cause of the disease, possible concomitant diseases, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Drugs that optimize cerebral circulation, neuroprotectors, vasodilators, diuretics, nootropics, amino acids and other drugs are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
— for non-drug treatment of encephalopathy
magnetic therapy
, electromagnetic stimulation,
electrophoresis
,
ultraviolet irradiation of blood , ozone therapy
,
acupuncture
, and plasmapheresis are used.
Surgery
— most often, operations are performed on blood vessels necessary to normalize blood flow in the brain. Surgical treatment is used for brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, congenital anomalies of cerebral vessels
Lifestyle correction
— in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to lose excess weight, eliminate saturated fats, salt, alcohol from the diet, move more, stop smoking and taking drugs.
If symptoms of encephalopathy occur, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. If you delay the start of treatment, there is a risk of depression of brain function and even disability.
Timely treatment, in turn, can not only slow down the development of the pathology, but also completely get rid of the negative consequences of the disease.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Electrophoresis (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| UHF therapy (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| Magnetotherapy category I difficulty | from 550 | — |
| MRI of the brain | 4 200 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Speech delay in children
Content:
Causes of delayed speech development
Speech delay or other disorder?
Signs of speech delay
Treatment of speech development delay (SRD, ZPRD) in the center of Dr. Leviticus
Every year the problem of delayed speech development in children becomes more and more urgent. Modern parents can be divided into two groups. For the former, a delay in speech development is comparable to a natural disaster; they fall into despair if their child cannot remember a nursery rhyme or does not pronounce certain sounds. The latter, on the contrary, turn to specialists for help when it is too late to completely rehabilitate the child.
Doctors, as a rule, reassure overly worried parents. The fact is that delayed speech development in children does not have a clear definition, therefore, even if the baby pronounces fewer words than expected for a certain age, you should not worry too much.
The lack of speech, or even “baby language”, babbling may be an individual characteristic of the child, and he will quickly catch up with his peers in the future. In addition, some boys begin to pronounce words much later than girls.
However, if alarming symptoms of a true delay in speech development appear in a child over the age of one and a half years, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
It should be taken into account that certain factors increase the risk of serious developmental disorders in children.
Results
Residual encephalopathy is a serious disease that requires comprehensive study in neurology. Usually, it is not possible to establish the presence of a disease without numerous consultations with different specialists. The pathology can remain undetected for a long period of time, as it is often confused with other complications due to head injuries, ischemia, vaccinations and other phenomena. Sometimes encephalopathy is a sign of a hereditary disease that was not noticed at the time. Then the disease will manifest itself in full not after birth, but during puberty. It is important to identify the pathology in a timely manner, since irreversible changes in the brain occur over time. Only an integrated approach to this problem gives a person a chance for recovery.
Symptoms
Residual organic encephalopathy is manifested by persistent neurological deficit caused by disease or adverse external influences. EC is often combined with other syndromes and diseases of the nervous system, which makes it difficult to make a differentiated diagnosis. Symptoms of residual encephalopathy in adults:
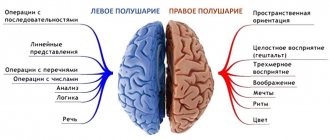
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities (memory, mental activity).
- Pain in the head area.
- Dizziness, difficulty maintaining balance.
- Depressive, neurotic disorders.
- Irritability, emotional lability.
- Increased fatigue.
Signs of residual encephalopathy include pyramidal insufficiency of the reflex type (impairment of complex, fine voluntary movements), paresis, confusion, vegetative-vascular dystonia (pain in the heart, a feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, paresthesia in the extremities, sleep disturbance, fainting) .
RE can manifest itself as convulsive seizures of the myoclonic type - generalized seizures, often short-term, characterized by short, involuntary twitching, muscle contractions in the area of the whole body or its parts (limbs, head). Residual encephalopathy is often accompanied by hydrocephalic, hypertension syndrome and immunological disorders. The main syndromes that are observed with EC in children:
- Epileptic.
- Psychovegetative.
- Focal neurological symptoms.
The pathology often manifests itself with general cerebral symptoms, which in children include pain in the head area, dizziness, nausea, accompanied by bouts of vomiting. Cephalgia in the initial stages of the disease is paroxysmal in nature, later it is permanent. Cephalgia is most often localized in the frontal, frontotemporal, frontoparietal, and occipital zones.
Nausea and vomiting often occur at the peak of a hypertensive-hydrocephalic crisis. Attacks of vomiting in some cases bring relief to the patient, in others they are repeated without signs of improvement in well-being. Dizziness may be accompanied by tinnitus and spontaneous nystagmus (frequent, involuntary, oscillatory movements of the eyeballs). Neurasthenic disorders:
Frequent mood changes. Inability to concentrate. Narrowing the range of interests. Apathy, indifference to the surrounding reality.
Residual encephalopathy is a pathology that in the acute period can manifest itself with mild meningeal signs (stiff neck, Kernig and Brudzinski symptoms), which indicates irritation of the meninges. Focal symptoms:
- Stem. Paresis of the third oculomotor nerve, impaired visual perception (color and twilight vision), nystagmus.
- Cerebellar. Impaired motor coordination - unsteadiness of gait, adiadochokinesis (inability to alternately perform movements opposite in direction at a fast pace), instability of the body in the Romberg position, asynergia (impaired ability to perform combined movements).
- Hemispheric. Pyramidal insufficiency (asymmetry of tendon reflexes, pathological foot and hand reflexes - Jacobson-Lask, Hoffman, Babinsky, Oppenheim, convulsive syndrome accompanied by impaired perception and disorder of automatic motor activity), cranial nerve paresis (VII-facial, XII-hyoid), visual , auditory dysfunction.
Damage to the nerve endings innervating the speech apparatus leads to disruption of speech formation, which indicates residual encephalopathy with hemispheric focal symptoms.
TBI is one of the common causes of disability, death and the development of post-traumatic EC. Neurological symptoms are caused by atrophic, scarring, degenerative changes that have occurred in the medulla as a result of injury. Symptoms include cerebrovascular disorders. A decrease in cerebral blood flow leads to an imbalance between the brain's needs and the amount of oxygen supplied, which provokes the development of oxidative stress. Other signs:
- Asthenia (weakness, decreased performance).
- Post-traumatic epilepsy.
- Disorder of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
- Mental and behavioral disorders.
Intoxication with neurotoxicants is manifested by disturbances in sensory, motor, and higher cortical functions, as well as changes in emotional status. Neurotoxicants primarily affect the activity of neurotransmitters and synaptic transmission of nerve impulses.
Symptoms and main syndromes of residual encephalopathy
The stage of the disease and the area of brain damage can be diagnosed by the following characteristic symptoms:
- Mood changes that appear suddenly and without cause, regardless of provoking factors.
- Seemingly causeless headaches, which are similar in symptoms to severe migraine attacks, appear suddenly and are not relieved by painkillers.
- Violation of the regime of wakefulness and sleep - a person suffers from nighttime insomnia, while during the daytime he experiences fatigue, lethargy, and a desire to sleep.
- Memory impairment—short-term lapses and confusion.
- The occurrence of visual and auditory disorders.
- Impaired speech and swallowing reflex.
- Decreased coordination and thinking abilities.
- Limb spasms.
At the first stage, residual encephalopathy manifests itself in the form of mild symptoms characteristic of most neurological and vascular diseases. Ignoring the symptoms leads to the fact that the rate of death of brain cells increases and the disease moves to a late stage. The patient experiences significant disturbances in brain activity, resulting in a risk of developing the following syndromes:
- Parkinson's syndrome - due to the massive death of neurons, the patient develops a complex of neurological disorders that cannot be treated.
- Hypertensive syndrome – provokes a significant increase in pressure, both arterial and intracranial.
- Pseudobulbar syndrome - occurs due to the destruction of the nuclei located in the medulla oblongata and disruption of the interaction between them, while brain functions may be partially preserved.
- Epileptic syndrome - manifests itself in the form of sudden attacks of epilepsy.
The last stage of the disease in the absence of treatment and supportive care is the person falling into a coma, followed by death.