Parkinson's disease is a severe brain pathology associated with a disorder in the metabolism of dopamine, which regulates the conduction of nerve impulses. With its deficiency, motor activity suffers: muscle tone increases, they begin to contract slowly and with difficulty, and the person is not able to move at the usual pace. In such situations, drug therapy for Parkinson's disease is supplemented with physical therapy for all muscle groups.
Features of the treatment of Parkinson's disease with physical exercises
Against the background of constant muscle tension, a patient with parkinsonian disorders changes his posture, his gait becomes shuffling, his movements are slow, tremors in the limbs and balance problems appear. In the final stages of the disease, the patient becomes completely immobilized due to impaired functional activity of the muscles.
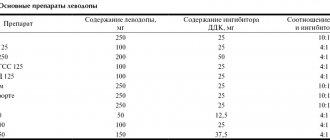
Treatment of patients with parkinsonism includes drugs based on levodopa, which replenish dopamine deficiency, as well as elements of physical and breathing exercises, exercise therapy in combination with medications act as follows:
- Reduces tone in tense muscles (this also reduces trembling);
- Restore mobility in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine;
- Regulate coordination of movements;
- Normalize motor skills and gait;
- Increased thoracic kyphosis is leveled;
- Increase range of movements;
- Improves mood and general condition.
Recommendations for performing gymnastics
When performing exercises, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Exercise must be done daily.
- The number of daily exercises should be discussed with a specialist, who can be either a neurologist or a physical therapy methodologist.
- After each exercise performed, the patient should definitely feel slightly tired. At the same time, it is not allowed to overstrain the body with exhausting and grueling activities. After a correctly performed exercise, the patient should feel comfortable in the muscles and pleasant fatigue.
- It is necessary to select such sets of exercises that will involve all the muscles of the body. A special exercise is selected for each muscle group.
- The exercise therapy complex should include exercises that help practice those movements that were most difficult for the patient.
- Before you start exercising, it is recommended to do a short warm-up to prepare and warm up your muscles.
- Each exercise should be completed smoothly and slowly.
- Having mastered this or that exercise, you need to gradually increase the load on it : perform the exercise more times, or choose heavier dumbbells.
- When eating food, it is recommended to chew it as thoroughly as possible , thus affecting the jaw muscles.
- If the patient loved to sing before illness , then to develop the muscles of the jaws and throat, you can include singing in a set of daily exercises.
- Under no circumstances should you exercise on slippery floors or in poorly lit rooms. When choosing a place for training, preference should be given to those rooms where there are carpets that do not allow the patient to slip.
- If the patient does not feel well enough to perform exercises such as squatting or walking, then the first time exercise therapy is recommended to be performed in bed or on a special training mat.
Experienced specialists recommend that each patient choose his own hobby, for example, swimming, dancing, yoga, etc. It is important that the patient really likes the chosen activity and does it with great pleasure. As practice shows, such patients achieve significantly better results compared to others.
A set of exercises useful for Parkinson's disease
Each lesson should last at least 10 minutes and include the following elements:
- Power loads;
- Stretching tasks;
- Dynamic joint training;
- Mimic gymnastics;
- Breathing techniques.
Note!
The number of classes per day is determined individually by the physical therapy doctor and depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the form of the disease.
It is recommended to do an average of 10-12 approaches.
Exercises to improve posture
- In a sitting position, we try to straighten our back as much as possible, resting our palms on the lumbosacral region.
- Still sitting, place your feet shoulder-width apart and place your palms on your waist. We lean back and forth. You can complete the task while holding the back of a chair.
- From a similar position, we tilt the body left and right.
- Lean against the wall so that only the occipital protuberance, shoulder blades, sacrum and heel bone are in contact with it. Press firmly with the interscapular area on the vertical surface.
Abdominal exercises
- Stretch out on the floor with your arms outstretched at right angles to your torso, palms up. Twist your body to the right, covering your left palm with your right, and vice versa.
- Lie on your back, pull your feet towards your buttocks. Raise your upper torso towards your hips. You can help yourself with your hands, hugging your knees with them and pulling your body forward.
- Lie flat, arms at your sides, feet facing you. Raise your head and shoulders, trying to see your toes.
- If possible, pump your abs in the classic way, with your hands behind the back of your head. In this case, an assistant can fix your legs in the area of the knees and shins.
Exercises for the neck and shoulder muscles
- We consistently bow our heads to one shoulder girdle and to the opposite one.
- We tilt the head to the chest and throw it back to improve mobility in the cervical vertebrae.
- We slowly turn our heads in one direction or the other, trying to examine the surface of the shoulder blades. In this case, there is no need to rush, so as not to provoke dizziness.
- We smoothly make circular movements with our heads, first pressing the chin to the chest, then the ear to the shoulder, the back of the head to the spine, the second ear to the shoulder girdle and back.
Exercises for the muscles of the shoulder girdle
- As you exhale, raise your shoulders up, and as you inhale, lower them. Significant tension in the muscles of the upper shoulder girdle should be felt.
- We place the fingertips on the shoulder joints and carry out rotational movements in them alternately anteriorly and posteriorly.
- We place our arms perpendicular to the body, bend them at the elbows, bringing our hands to the front surface of the shoulder joints. As you inhale, we try to connect the shoulder blades as much as possible; as you exhale, you should relax and take the starting position.
- Take a gymnastic stick in your hands, extend it in front of you parallel to the floor and pretend that you are working with an oar while rowing with one or the other hand.
Hand exercises
- We approach the wall at the length of an outstretched arm, rest our palms on it and smoothly lean forward, shifting our body weight onto our hands. We do not stick out our buttocks. Then we push off the wall with our hands and straighten up.
- We sit down at the table, placing our forearms on the tabletop with our palms down. We rhythmically turn the hands, either palmally or with the back surface up, moving faster and faster.
- We clench our fingers into fists and rotate our wrists, first inward, then outward.
- We take turns connecting the pads of our thumbs with all the others, gradually increasing the pace.
Exercises for the muscles of the lower limbs
- Lie down on the floor. Bend your left knee without lifting your sole off the floor. Place your right hand on your knee joint and pull it to the right for 10 seconds. Repeat with the other leg.
- Turn over face down, resting on your forearms. Bend your legs alternately at the knee joints, trying to touch your heel to the buttock area.
- We sit on the floor, stretch our legs forward. Rotate your feet first inward, then outward.
- We squeeze and straighten our toes.
Exercises to improve knee movement
- Sitting on a stool or on the edge of the bed, we straighten and bend our legs at the knee joints in turn.
- In the starting position from the previous exercise, stretch out the right leg and place it on a low stool. Sliding our hands along the front surface of the leg, we stretch as far as possible, touching the foot if possible. We freeze in this position for 10 seconds and straighten up. Repeat with the left leg.
- Sit on the floor, stretching your legs and resting your straightened arms on the floor slightly behind your back. Bend your legs at the knee joints, pulling your feet towards your pelvis, and return to their original position.
- Lie down on a horizontal surface and do the classic version of the “bicycle” exercise, simulating pressing the pedals.
Tension and relaxation of the thigh and calf muscles
- Leaning on the back of a chair on one side, we lunge forward alternately with one and then the other leg. We try to get down as close to the floor as possible and hold in this position for 15-20 seconds.
- Still holding onto the chair, we first stand on our tiptoes, stretching the calf muscles, and then again on the full sole, relaxing.
- We perform regular or half squats at a support.
- We lie on our backs straight and alternately raise our straightened legs up as far as possible.
Examples of exercises
To fully restore the patient’s motor activity, it is necessary to perform complex exercises, which should affect all muscle groups, as well as joints.
Each set of exercises is designed to develop a specific muscle group. In this case, the main emphasis when performing exercises should be on developing those movements with the help of which the patient can restore impaired motor activity.
It is easiest to perform motor exercises while listening to rhythmic music that the patient likes, or counting “in the head” or out loud.
Exercise for knee joints
Sitting on a chair, straighten your right leg at the knee, and then bend it again, returning the limb to its previous position. Perform the same movements with your left leg.
In a sitting position, raise your leg and place it on a low chair. Then you should put both hands on the knee of this leg and try to stretch forward as much as possible. Count to 10, remove your leg from the chair and repeat the exercise with the other leg.
For the muscles of the thighs and legs
Turn sideways to a chair with a high back and rest your hand on it. Move one leg 50 cm forward and the other the same distance back. Then bend the leg that is in front at the knee and slowly lower, trying to transfer the weight of the body to the bent leg.
In this case, the muscles of the leg located behind should tense and stretch as much as possible. Hold this position for 20 seconds, then switch legs and repeat the exercise.
For the calf muscles
The patient stands right next to a chair with a high back and rests his hands on it. Then you should rise on your toes and return to your previous position.
Hand exercises
The arm muscles can be stimulated using a special expander. This method is considered the most acceptable and convenient for Parkinson's patients.
The patient stands in the corner of the room, facing the wall, and fixes his palms on the walls. Bending your elbows, you need to slowly lean towards the corner until a feeling of tension appears in the arm muscles.
Exercises to restore facial muscles
To perform the exercise, you need to prepare a mirror. Looking into it, the patient depicts various emotions: sadness, surprise, joy, etc. Then he should compress his lips, stretch them as wide as possible and say “cheese” with some tension.
In this case, each movement must be delayed for 3-5 seconds. Afterwards, you need to raise and lower your eyebrows, take out your tongue and slowly move its tip sideways, right and left, and then rotate in a circle to the right and left.
Exercises for the cervical spine
Sitting on a chair, tilt your head to the right and left, trying to reach your shoulders, while the patient's gaze should be directed straight ahead. After 10 turns in both directions, a slight tension should appear in the neck muscles.
Sitting on a chair, slowly turn your head to the right and left. Every time you turn your head, you need to direct your gaze to your shoulder so that you can see its back. Keeping your head in this position, count to five, then turn your head in the other direction.
Walking
Each patient should try to walk at the rhythm, pace and speed that is most suitable for him.
When doing exercises, you should try to walk as long as possible, carefully monitoring the quality of your walking. One of the goals of walking is to overcome the “shuffling” gait.
Exercises to restore balance
To practice measures to ensure balance when walking, it is necessary to conduct training in special equipment - parallel bars. Any difficulties that accompanied the patient when walking, especially on stairs or uneven roads, must be overcome through diligent and long-term training.
Exercises to restore speech
The exercise therapy complex also includes exercises aimed at restoring speech. To do this, the patient should read aloud an interesting book every day. When the TV is on in the house, you can try to reproduce the speaker’s speech.
It is also recommended to write down the most commonly used phrases in a notebook and carefully rehearse them, so that later you can easily pronounce them in a store, at a post office or in any other public place.
Exercises for facial muscles
In Parkinson's disease, not only skeletal muscles suffer: facial muscles also become less mobile, “waxy”. With the help of a special complex of physical therapy, the patient is able to get rid of the mask-like, amicable face and again actively express emotions. To better control the correct execution, you should practice in front of a mirror.
- Alternately portray surprise, joy, and anger on your face. Hold each expression for 3-5 seconds.
- Consistently raise your brow ridges, frown, and close your eyes tightly.
- Stretch and purse your lips tightly, then open them slightly and say “cheese.”
- First, at a slow and then at the fastest pace, stretch your lips, and then pull them out with a tube.
- Inflate and deflate your cheeks.
- Stick out your tongue and move it alternately left and right, up and down.
- “Draw” circles with the tip of your tongue, first clockwise and then counterclockwise.
Perform each exercise at least 10 times.
Important information!
Tongue exercises are necessary to prevent swallowing disorders. These disorders occur in the later stages of the disease and cause serious complications in the respiratory tract when food gets into them.
Differences between exercise therapy and other physiotherapeutic procedures
Important distinctive features of exercise therapy are its versatile effects on the body and ease of implementation. In the process of performing exercises, a person’s breathing, digestion, and heart function are normalized.
Exercise for Parkinson's disease is quite simple, which allows you to do it without much effort. Patients in later stages of the disease may require supportive assistance from a physical therapy trainer or someone close to them.
The disease is manifested by trembling at rest and muscle stiffness. Exercising brings the muscles out of a resting state.
What disability group is given for Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is considered chronic and usually occurs in old age.
When the patient is able to master the skill of muscle relaxation, the symptoms of muscle stiffness will decrease. With prolonged absence of movement, stagnation of the joints occurs, which leads to an increase in the limitation of range of motion. As a result, painful sensations appear in the muscles and joints, and thanks to exercise therapy, such disorders are gradually normalized.
The degree of movement impairment depends on the duration of the pathology. If the patient has recently fallen ill, and before that he was engaged in any types of vigorous activity - swimming, tennis, skiing or hiking, then it is advisable to continue to engage in favorite activities further.
Properly selected drug treatment in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures and a healthy lifestyle makes it possible to prolong the patient’s physical activity for several decades.
If the patient did not lead an active lifestyle until the disappointing diagnosis was made, then he needs to immediately start exercising.
Systematic exercise therapy helps to significantly improve the patient’s psychological state and feel more confident in everyday life.
Breathing exercises
The function of the respiratory muscles in Parkinson's disease also suffers: the depth and efficiency of inspiration decreases. This is also facilitated by changes in posture and the formation of stoop. To restore the normal biomechanism of inhalation and exhalation, the following exercises are recommended:
- Sit on a stool or the edge of the bed and place your palms on the front abdominal wall. Inhale deeply, feeling your stomach inflate. Exhale slowly through pursed lips.
- Go to the wall and press your back against it so that your spine touches it along its entire length: from the lower cervical region to the sacrum. As you inhale, extend your arms upward, also along the wall. As you exhale, cross them over your chest.
- As you inhale, stand on your tiptoes, raise your arms up and stretch, while exhaling, stand on your full foot, bend down so that your arms hang freely.
Each time you need to do 10 breathing movements.
Deep breathing
Goal:
to achieve deeper breathing through exercise.
In a sitting position. Place your hands on your stomach. Take a slow, deep breath through your nose, feel how your chest expands and your stomach “inflates.” Then slowly, counting to 5, exhale through your mouth, as if blowing out a candle. Repeat 10 times. In a standing position. Go to the wall. Stand so that your entire back and lower back feel the wall or other vertical surface: closet, door, etc. Raise your hands up and, touching the wall with them, take a deep breath; As you exhale, lower your arms down and cross them in front of your chest and stomach so that your right hand grabs the elbow of your left hand and vice versa. Repeat 10 times.
Additional tips and tricks
When performing any exercise, you need to follow the rules to achieve the greatest effectiveness from your workout:
- You should exercise regularly, in accordance with the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
- It is advisable to start training after taking medications, when the symptoms of the disease are less pronounced, it becomes easier to move, and the patient’s physical activity increases.
- Before training, it is advisable to perform a light muscle massage to improve local blood flow and reduce spasm.
- You need to move slowly at first, then gradually increase the pace.
- Rhythm is very important, so it is better to practice with appropriate music or a loud score.
- You should not bring yourself to excessive fatigue. Normally, half an hour after finishing classes, your strength should be fully restored and your energy should appear.
- After completing the main gymnastic complex, time is allocated for breathing training.
Recommendations from experts!
In the early stages of Parkinson's disease, neurologists recommend not only classical exercise therapy, but also activities such as walking, skiing, swimming, cycling, playing volleyball, badminton, and golf. Patients should overcome a shuffling gait through regular long walks; through swimming, they should restore their usual posture; dynamic games help improve balance and posture.
Exercise therapy for Parkinson's disease is necessary primarily to maintain normal motor activity and the ability to move. With adequate drug therapy, physical activity slows down the progression of the process and makes the course of the disease easier, preventing the development of complications.
The effectiveness of exercise therapy
The main task of exercise therapy is to solve motor problems. Special gymnastics helps:
- Stretch muscles that are constrained by stiffness syndrome.
- Develop joints and increase their mobility.
- Improve the quality of movements.
When regularly performing gymnastic exercises, patients lose the constant feeling of stiffness, their posture straightens and coordination of movements improves. Also, exercises allow you to restore your gait to a natural level.
The treatment of Parkinson's disease necessarily includes a set of exercises for the whole body, including gymnastics for the facial muscles.
This complex includes walking, exercises for the spine, arms, legs, balance training, as well as speech therapy exercises to restore speech.
To achieve tangible results, patients must do exercises according to the recommendations of the attending physician, observing a certain frequency. It is important to remember that with too much physical activity, no less unpleasant symptoms can occur than with its lack.
Exercise therapy should be carried out during the maximum effect of antiparkinsonian drugs.
Dance classes and Chinese tai chi gymnastics have a beneficial effect. When performing complex exercises to coordinate movements, new neuronal circuits are formed in the brain, and the patient’s motor activity increases.
Neurologist
Pershina Natalia Sergeevna
8 years of experience
Patients with Parkinsonism are characterized by chronic depression, and constant exercise helps to change their psychological state: satisfaction with the quality of their life and health increases.