Causes of pain in the neck and back of the head
Pain in the occipital part of the head and neck can be caused by inflammatory processes and injuries. They also occur when blood vessels and nerves leading to the brain are damaged, pinched or compressed. These symptoms periodically appear in a healthy person, against the background of fatigue and stress, physical activity and other factors. However, if the head in the neck and back of the head hurts frequently, it is necessary to seek timely medical help.
Migraine
Migraine is a type of headache that occurs in attacks and often affects one half of the head. According to various experts, it is associated with vascular disorders and can be transmitted genetically. In this regard, the disease is considered familial, and its presence in the anamnesis of relatives is taken into account when making a diagnosis. Classic migraine occurs with an aura - a period of poor health that manifests itself several hours before a headache attack. It includes a number of typical symptoms:
- dizziness, possible fainting;
- blurred vision, the appearance of circles and spots before the eyes;
- various types of hallucinations (visual, auditory, tactile);
- heightened reaction to bright light, loud sounds and other irritants.
Migraine attacks can occur spontaneously, but more often they are associated with certain external factors. Patients who have long suffered from this disease can trace the relationship between headaches and the conditions under which they occur. Thus, attacks can be triggered by changes in weather conditions, stress and fatigue, consumption of fatty foods and alcoholic beverages. Their duration ranges from several hours to several days.
To treat migraines, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment regimen - painkillers are often ineffective. To relieve headaches, analgesics may be needed in combination with antidepressants, calcium channel blockers, beta-adrenergic blockers, as well as muscle relaxants and other drugs.
Diseases of the cervical spine
Pain in the back of the neck and head is often caused by various diseases of the cervical spine. The cervical vertebrae form a protective canal through which the vertebral artery passes, and the roots of the spinal nerves are also located here. Blood and nerve impulses are sent to the brain and maintain its normal functioning. Neck diseases cause inflammation, mechanical compression of nerves, ischemia (oxygen starvation) of the brain, as well as other dangerous processes.
- Osteochondrosis is one of the reasons why the back of the head, closer to the neck, hurts. This is a chronic disease in which there is a deterioration in the nutrition of the intervertebral discs and their thinning. As a result, depreciation between adjacent vertebrae during movement decreases, and bone spines and growths form. Osteochondrosis is one of the common causes of cervical migraine.
- Spondylitis is an inflammation of the vertebral bodies. The process is often caused by an infectious pathogen; tuberculosis bacteria can be detected. The disease is manifested by acute pain in the neck, stiffness of movement, and increased body temperature. Prolonged inflammation can lead to spinal deformation, compression of nerves and blood vessels.
- Spondylosis is the fusion of adjacent vertebrae, which affects the mobility of the affected area of the neck. This may be due to the formation of bone growths as a result of osteochondrosis or other diseases, as well as the deposition of salts in the tissues of the long ligament running along the anterior edge of the vertebrae. Pain and discomfort are felt constantly, intensifying when throwing the head back.
Diseases of the cervical spine are one of the common causes of chronic headaches. A complete diagnosis necessarily includes an MRI of the neck, as a result of which any pathologies of the vertebrae and soft tissues can be determined. Treatment is selected individually, but pain in the back of the head and neck goes away only after their underlying cause is eliminated.
Hypertension
Chronic hypertension – increased blood pressure. Normally, in an adult, this figure is 120/80 mm. Hg Art., but individual characteristics should be taken into account. Pressure changes at rest, since physiological hypertension is observed after exercise and emotional stress. It is not associated with pathological processes and goes away after some time.
Acute or chronic hypertension, which develops as a result of vascular pathologies, poses a danger to human health. It manifests itself in attacks and causes a sharp deterioration in well-being. One of its causes is atherosclerosis, a chronic disease in which the walls of the arteries become weak and inelastic, and deposits and plaques appear on the inner surface of their walls. In addition, hypertension can be the result of heart defects and disorders acquired as a result of excessive physical activity, poor diet and excess weight, as well as a sedentary lifestyle.
Hypertension most of the time manifests itself asymptomatically, but during periods of exacerbation it is accompanied by acute headaches in the back of the head and neck. Attacks can be triggered by sudden changes in weather and atmospheric pressure, head injuries, stress or intense physical activity. Increased blood pressure can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- sharp, throbbing pain that spreads to the neck and back of the head;
- blurred vision, blurred vision, visual hallucinations in the form of dark circles and spots;
- hearing loss, tinnitus;
- redness of the skin of the face and mucous membranes, minor hemorrhages are possible due to damage to the capillaries under pressure;
- nausea, digestive tract dysfunction.
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend monitoring blood pressure readings, even if there are no complaints about your health. For some people, they are normally more or less than the average value, and this makes diagnosis difficult. If chronic hypertension is detected, a course of drugs is prescribed to correct this indicator. They must be taken constantly and not wait for the next attack, as well as adjust your diet.
Increased intracranial pressure
Another reason why the back of the head and neck hurts is an increase in intracranial pressure. This is an independent quantity that is not necessarily proportional to the blood pressure in the arteries. It consists of several components: the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid of the ventricles, blood in the cerebral vessels, as well as the substance of the brain itself. When intracranial pressure increases, brain cells experience a lack of oxygen, which can lead to dangerous disruption of many functions. Chronic ischemia in children can cause mental retardation and therefore requires drug correction.
Intracranial hypertension is diagnosed based on clinical signs. Patients complain of a number of characteristic symptoms:
- headache in the back of the head and neck;
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- involuntary muscle contractions, tremors or tics;
- fainting with a sharp increase in blood pressure.
It is impossible to measure intracranial pressure at home. The indicator is determined indirectly, using additional equipment. Thus, swelling of the fundus is considered one of the typical signs of intracranial hypertension. In rare cases, a puncture of cerebrospinal fluid is prescribed, which is obtained by puncturing the membranes of the spinal cord. This is an invasive, painful procedure, so it is carried out strictly according to indications. Most patients are diagnosed based on the clinical picture and the results of indirect examinations. Magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the head are also informative.
Neck muscle diseases
One of the reasons why the back of the head closer to the neck hurts is muscle tissue diseases. Painful sensations are associated with limited mobility of the cervical spine and impaired blood circulation to brain cells. Treatment depends on the cause and nature of the pathological process.
Myositis
Myositis is inflammation of muscle tissue. The process may be of infectious origin, but in some patients it is associated with hypothermia, injuries, and prolonged stay in a forced, uncomfortable position. Inflammatory changes cause pain and swelling in the muscle fibers, spasm and limited mobility of the neck. The muscles compress the vessels and nerves located in this area. There are several types of myositis, depending on the reasons for its occurrence and the nature of its course:
- infectious – develops against the background of viral diseases, including may be a complication of influenza or ARVI;
- purulent - the most dangerous form, which manifests itself under the influence of bacteria;
- ossifying - a disease in which inflamed muscles lose their elasticity and dense connective tissue grows in their thickness;
- dermatomyositis - the process affects the muscles and skin, is autoimmune in nature;
- neuromyositis is a dangerous disease that spreads not only to muscle fibers, but also to nerves in the neck.
To treat myositis, local preparations based on anti-inflammatory and analgesic components are used. In the first few days of inflammation, ointments with a cooling effect are useful - they cause vasoconstriction and reduce swelling. Next, warming ointments are prescribed, which will help improve blood circulation and quickly relieve pain. For infectious myositis, a course of antibiotics is selected to prevent purulent complications.
Myogelosis
The disease is caused by insufficient blood supply to muscle tissue. As a result, painful lumps form in the thickness of the muscles, which increase over time. Myogelosis can be one of the long-term consequences of injuries, and can also occur as a result of hypothermia. It often occurs in athletes and people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. The nodules may be located close to the nerves and cause constant pain that worsens during movement. However, in some cases they can only be detected by palpation (feeling) of the problem area of the neck.
Typical symptoms include:
- pain in the neck and back of the head, which intensifies when bending and turning the head;
- stiffness, spasm of the neck muscles;
- constant tension, decreased range of motion of the cervical spine.
The danger of myogelosis is that at the initial stage it is difficult to diagnose it by symptoms. The pain is not concentrated in a specific area, but spreads to the head, back or arms. Then the nodes begin to be felt under the skin, which makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis. Treatment must begin with eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. Muscle relaxants, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, anticonvulsants and vitamins are also prescribed.
Occipital neuralgia
Another cause of pain in the back of the head and neck is occipital neuralgia. It is pain caused by inflammation or damage. This nerve originates in the cervical spine, then travels through the thickness of the muscles, passes under the base of the skull and follows to the scalp. Often chronic headaches are caused by damage to the occipital nerve.
Causes of the disease include:
- chronic diseases of the cervical spine, which lead to compression of nerve fibers;
- injuries and their consequences, including the formation of calluses after fractures of the bodies and processes of the cervical vertebrae;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- diseases of the muscles of the cervical spine;
- incorrect posture, stooping in the neck, curvature of this section;
- prolonged stay in a forced immobile position, especially during the recovery period after injuries.
During diagnosis, acute pain is detected upon palpation of the occipital nerve in the places where it passes. You can also note a decrease or increase in sensitivity of the scalp, in the back of the head. Anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and antispasmodics are used to treat this disease. However, to relieve pain, it is important to eliminate the causes that lead to compression or damage to the nerve fibers. To relieve acute pain, which persists not only during movement, but also at rest, an occipital nerve block is performed.
Other reasons
Pain in the neck and back of the head is the result of a huge number of diseases and conditions that lead to spasms of muscles and blood vessels, increased or decreased pressure, and inflammatory processes. Even a healthy person periodically experiences headaches associated with fatigue, stress, and physical exertion. In addition, the condition can be triggered by the following factors:
- Tension headaches (tension headaches) – occur after prolonged stress on the muscles of the neck and back of the head, as well as as a result of physical or mental activity;
- arteritis – inflammation of the arteries, which can be idiopathic;
- long-term use of certain groups of drugs, as well as the period of their withdrawal after a long course of treatment;
- polluted air, high gas levels;
- congenital or acquired anomalies in the structure of the cervical vertebrae and the vessels that pass in this area.
If the back of the head hurts closer to the neck, this disorder can have many causes. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain recommend not to self-medicate, since many diseases pose a danger to the patient’s health and do not go away at home. However, you should pay attention to headache prevention methods yourself.
Neck injury
Sign up for a consultation by phone
Or fill out the form online
Make an appointment
Injuries to the cervical spine and spinal cord are among the most severe injuries leading to human disability, i.e. to permanent loss of performance.
Damage to the spine can occur either as a result of a direct blow to the neck area or as a result of extreme flexion or extension movement of the head. The latter mechanism is called "whiplash" in car accidents or "diver's injury" when the head hits the bottom during a shallow dive.
This type of injury is often accompanied by damage to the spinal cord and can be fatal.
Most often, the fourth, fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae undergo fractures of the cervical vertebrae.
Fractures of the first and second cervical vertebrae are considered the most severe.
Acute injury to the neck and cervico-occipital junction occurs when falling or colliding with another moving or stationary object or person.
Chronic injury to the neck and cervico-occipital junction is formed by static load from monotonous efforts over a long period of time (sedentary work).
At the same time, for some time a person experiences discomfort in the neck and back of the head.
Against the background of injury and pain, irritation of the vertebral arteries occurs, which pass in the transverse sections of the cervical vertebrae.
In addition to pain in the neck and head (back of the head, temples, crown, forehead), patients may also experience vestibular disorders. Vestibular disorders as a result of irritation of the vertebral arteries, which are expressed by dizziness and unsteadiness when walking, nausea and vomiting. Sometimes the clinical manifestations of cervicocranial syndrome lead some doctors to misdiagnose a concussion.
With cervicocranial syndrome, there may also be complaints of noise or ringing in the ears and head, numbness of the skin of the face, the back of the head, in the ear area, and the mucous membrane of the tongue. Fatigue occurs quickly. In the morning after sleep there is no feeling that you managed to get enough sleep. Sometimes insomnia may occur against this background. General performance and attention decrease, and irritability occurs.
To diagnose a neck injury and cervicocranial syndrome, you should consult a doctor for a neurological examination, during which the biomechanics of the cervical spine should be assessed. Based on the results of the examination, a clinical diagnosis can be made and treatment can be suggested. In case of an unclear diagnosis, additional diagnostic tests may be prescribed.
Benefits of the service
Convenient work schedule
We work until late in the evening to make it convenient for you to take care of your health after work
No queues
The patient registration system has been debugged over many years of work and works in such a way that you will be seen exactly at the chosen time
Cozy interior
It is important to us that patients feel comfortable within the walls of the clinic, and we have done everything to make you feel comfortable
Attention to the patient
At your service there are attentive staff who will answer any question and help you navigate
Examination methods
The most correct decision on what to do if you have a headache, back of the head and neck is to contact for a full diagnosis. Even an experienced specialist will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis based only on an initial examination, so additional examinations are prescribed to understand the overall picture of the disease. They may include a number of specific techniques aimed at studying the condition of the vertebrae, muscles and blood vessels:
- rheoencephalography - study of cerebral vessels;
- MRI is the most informative way to examine the neck and head, especially if tumors and injuries are suspected;
- X-ray – used to exclude injuries to the cervical spine.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a complete examination, which will determine the cause of persistent headaches. Accurate, modern equipment is located here, thanks to which all examinations are carried out within the center. Experienced specialists will be able to decipher the indicators and prescribe an effective treatment regimen.
Classification of subaxial injuries of the cervical spine
Clinical classification of subaxial ( C3 - C7 vertebrae) injuries of the cervical spine includes the following types of injuries:
- compression fracture,
- burst fracture,
- flexion-distraction injury of the neck,
- dislocation of the articular processes (unilateral or bilateral),
- fracture of the articular processes.
There is also a classification by Allen and Ferguson for injuries of the cervical spine, which is used in specialized literature and in scientific research. This classification of subaxial ( C3 - C7 vertebrae) injuries of the cervical spine is based on radiographic data and the mechanism of injury:
- flexion-compression,
- vertical compression,
- flexion-distraction: subluxation of the articular process,
- unilateral dislocation of the articular processes,
- bilateral dislocation of the articular processes with 50% displacement,
- complete dislocation (100% displacement),
Treatment of pain in the neck and back of the head
The course of treatment is selected individually, depending on the causes and nature of the disease. To relieve pain at home, rest and pain medications are recommended. The complete treatment regimen will include several stages that complement each other and affect the causes and symptoms of the disease:
- drug treatment - anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, muscle relaxants and antispasmodics may be required, as well as drugs to improve blood supply to the brain;
- massage – prescribed by a doctor, prohibited for inflammatory muscle diseases;
- physiotherapy - a set of techniques to accelerate metabolism at the cellular level, stimulate blood circulation in the affected area;
- Surgical treatment is rarely required when bone growths and injuries appear in the cervical spine, as well as to remove tumors.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as pain in the neck and back of the head. For most patients, it is enough to take the medications at home, but a course of treatments may also be necessary. Be sure to visit them on schedule to consolidate the effect.
Diagnosis of neck injury and cervicocranial syndrome
To diagnose injury and bruise of the neck (cervical spine) and cervicocranial syndrome, you should consult a doctor for a neurological examination, during which the biomechanics of the cervical spine should be assessed (range of motion, muscle tone and strength, the presence of fibromyalgia in the neck muscles, etc.). d.).
A neurological examination of a patient with a neck injury may reveal:
- symptoms of monoradiculopathy,
- symptoms of spinal cord compression.
Monoradiculopathy occurs in patients with unilateral dislocation. Unilateral dislocation of the articular processes at the level of the C5 - C6 vertebrae usually manifests itself in the form of radiculopathy C6 root. In this case, the patient complains of muscle weakness when extending the hand, numbness and tingling in the fingers.
The pattern of segmental innervation on the surface of the human body helps to clarify the localization of the level of radiculopathy and spinal cord compression.
Unilateral dislocation of the articular processes at the level of the C6 - C7 vertebrae usually manifests as radiculopathy C7 root. In this case, the patient complains of muscle weakness when extending the arm at the elbow (triceps), when bending the hand, as well as numbness and tingling on the index and middle fingers.
Neurological symptoms of spinal cord compression occur with bilateral dislocations of the cervical vertebrae, which may worsen as the subluxation increases.
Based on the results of the examination, a clinical diagnosis can be made and treatment can be suggested. In case of an unspecified diagnosis, additional diagnostic appointments may be given:
- REG, USDG of vessels of the neck and brain
- X-ray of the cervical spine with functional tests
- cervical spine
- MRI of the cervical spine
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spine (lateral view) helps diagnose disc damage and determine the position of the cervical vertebrae when they are displaced.
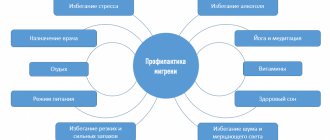
Prevention methods
Headache and the diseases it signals can occur even in a previously healthy person. However, if you follow simple recommendations from doctors and pay attention to prevention, they can be avoided. At home, you can take the following measures to prevent headaches:
- monitor your posture both when walking and while working in a sitting position;
- give up bad habits, smoking and drinking alcohol;
- devote time to physical education every day, perform simple exercises in the fresh air;
- eat right, try to get enough vitamins.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individual programs for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as pain in the neck and back of the head. It is important not to tolerate discomfort, as it may indicate the beginning of dangerous processes in the body. If you pay attention to the first symptoms and receive competent medical care in a timely manner, you can prevent further development of diseases and dangerous consequences.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 12 votes
Share article on social networks