—Categories
- car (1)
- audiobooks (1)
- household appliances (1)
- embroidery (46)
- satin stitch, patterned seams (7)
- magazines (2)
- canvas (1)
- we embroider fate on a hoop (2)
- canvas tension (1)
- threads (3)
- amulets (7)
- decoration (4)
- gifts (2)
- useful tips (8)
- machines (1)
- knitting and sewing - tips (49)
- crochet (644)
- pineapples (33)
- collars (2)
- children (33)
- jumpers, pullovers (40)
- jurabs, socks, slippers (7)
- for dogs (1)
- female models 50 (4)
- magazines (33)
- toys (94)
- IR (33)
- border (3)
- leather and hook (5)
- training (122)
- coats, cardigans, blouses, jackets, vests (83)
- dresses (14)
- blankets, rugs, potholders, pillows (34)
- belts, straps (6)
- tablecloths, curtains, napkins (15)
- how much does knitting cost (1)
- bags (12)
- tops, tunics (42)
- patterns (20)
- fillet (12)
- shawls, scarves, stoles, snoods (74)
- hats, headbands (25)
- cords (3)
- skirts (10)
- knitting on a fork (18)
- knitting (960)
- toys (20)
- blankets, rugs, potholders, pillows (14)
- sweaters, pullovers, jumpers (184)
- mittens (6)
- two-color patterns (22)
- children (42)
- for dogs (3)
- jackets, vests, cardigans, coats (196)
- magazines (34)
- border (2)
- men (28)
- socks, slippers (13)
- training (156)
- dresses (9)
- belts, straps (1)
- tablecloths, curtains, napkins (2)
- how much does knitting cost (1)
- bags (5)
- tops, tunics, ponchos (30)
- patterns (52)
- colored knitting (67)
- shawls, scarves, stoles, snoods (173)
- hats, headbands (58)
- skirts (4)
- for children (172)
- paper dolls (15)
- education (56)
- knitted dolls (28)
- exam (2)
- games, coloring books, toys, houses (25)
- tilde dolls (20)
- music (17)
- science and technology (1)
- training - dolls (2)
- songs, poems, riddles (17)
- salt dough (8)
- home economics (47)
- soap (4)
- plastic windows (4)
- repellents for moths, mosquitoes and ticks (2)
- washing, cleaning (36)
- painting (9)
- animals (1)
- cats (1)
- life (4)
- earnings (5)
- internet, computer (76)
- mortgage, purchase and sale of apartment (3)
- how to shop abroad (1)
- quilting (1)
- books, films (2)
- indoor plants (13)
- lemons (1)
- beauty and health (344)
- 2*4 (2)
- acupuncture (22)
- quit smoking (3)
- BF (10)
- hair (20)
- Dizziness (1)
- children (2)
- Gastrointestinal tract (22)
- health (36)
- teeth (4)
- leather (23)
- latina (1)
- lymph (2)
- Lutsenko (3)
- OXY (10)
- oncology (15)
- spine, joints (20)
- weight loss (78)
- colds (7)
- cardiovascular diseases (14)
- sleep (5)
- herbs (16)
- train the brain (3)
- figure exercises (15)
- face and body care (57)
- thyroid (2)
- cooking (530)
- chicken dishes (64)
- vegetable dishes (24)
- baked goods to order (2)
- dumplings, dumplings, dumplings, manti, etc. (12)
- dessert - ice cream, jelly, soufflé, creams, drinks (40)
- homemade dairy products (20)
- snacks (11)
- casseroles (5)
- quality products (4)
- porridge (3)
- beautiful cutting of dough (8)
- Spoon and glass instead of kitchen scales (2)
- pasta (4)
- marinades, pickles, preserves (20)
- mix (1)
- multicooker (3)
- meat (28)
- DRINKS (1)
- savory pastries (45)
- table decoration (13)
- cake decoration (8)
- fried pies, pasties, pancakes, belyashi, brushwood, (33)
- rolls (1)
- fish (17)
- salads (20)
- sweet pastries (163)
- various sauces (6)
- soups, borscht, roast, etc. (8)
- dough (24)
- eggs (11)
- fur (1)
- dream (1)
- House number 1)
- me (5)
- wise thoughts (51)
- music (73)
- classical (28)
- light (25)
- soap making (2)
- mood (58)
- vegetable garden (1)
- vegetable garden on the windowsill (8)
- cards, congratulations, gifts (8)
- vacation (2)
- crafts (7)
- search (2)
- useful little things in everyday life (44)
- holiday (5)
- decoration (2)
- psychology (44)
- religion (22)
- repair (43)
- interior (38)
- plumbing (2)
- wedding (3)
- secrets of success (71)
- style (37)
- poems (51)
- handmade decorations (26)
- dolls (2)
- belts, straps (3)
- lamps, chandeliers (3)
- window decoration, curtains (4)
- flowers, butterflies - ribbons (8)
- watch (1)
- LI.RU lessons - for beginners (63)
- movies (3)
- photo (2)
- flowers (20)
- money tree (2)
- Kalanchoe (1)
- decoration (2)
- peonies (6)
- roses (1)
- sewing (196)
- without patterns (14)
- bedding (8)
- timofeev (6)
- knitwear (5)
- tops (4)
- JUMPER, KNITWEAR (2)
- MITTENS (1)
- trousers (2)
- children (6)
- jeans (7)
- waiting for the stork (11)
- magazines (1)
- toys (2)
- LEATHER (4)
- crash (2)
- fur and knitwear (3)
- training (55)
- dresses (23)
- miscellaneous (20)
- bags (3)
- slippers (4)
- fabric+knitting (8)
- trench coat (1)
- tunics and leggings (5)
- hats, berets (4)
- scarf, French scarf (4)
- sewing machines (2)
- chiffon (9)
- skirts (9)
- denim skirts (2)
- school (46)
- biology (7)
- geography (6)
- history (12)
- literature (9)
- mathematics (7)
- Russia (4)
- speed reading (1)
- physics (2)
- esoterics (41)
- languages (36)
- English (18)
- German (1)
- Russian (15)
-Music
—Search by diary
—Subscription by e-mail
— Regular readers
—Communities
-Statistics
Friday, July 22, 2021 15:03 + to quote book
Brandt-Daroff exercises for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
Brandt-Daroff gymnastics is a set of special exercises for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which the patient does at home independently after the Epley-Hughes rehabilitation maneuver has been performed in the clinic. Methodology:
1. Starting position - sit on the bed and keep your head straight, then lie down on your right side, placing your right arm bent at the elbow under your head, your palm holding your head. 2. Remain in this position for 30 seconds or until the dizziness stops completely. 3. Return to the starting position while sitting. Hands on knees. Sit for 30-40 seconds. 4. Perform the exercise in the opposite direction (see points 1-3).
General principles of physical therapy
Special gymnastics for dizziness is an effective way to normalize the condition
Gymnastics for the vestibular apparatus for dizziness should begin as early as possible. Patients can do exercises after the first signs of improvement. Physical therapy is indicated during drug treatment. The function of the vestibular organ is restored much faster if the patient constantly stimulates it with various movements.
Scientists and doctors have conducted research on the effect of physical exercise on restoring the functioning of the vestibular system. It has been proven that with regular exercise, 50-80% of patients experience positive dynamics. At the same time, in a third of patients the balance apparatus was completely restored.
Exercises should be as varied as possible, since the vestibular apparatus quickly adapts to the load. The patient constantly needs to complicate tasks so that the receptors of the balance apparatus are constantly in good shape. This helps to quickly restore neural connections between the brain and the auditory organ.
The gymnastics complex should be adapted for patients with vestibulopathies. The selection of exercises depends on the severity of the disease. In many patients, the balance apparatus is severely damaged. This increases the risk of falls during exercise. Patients are allowed to train with their eyes open and perform tasks with support. Bedridden patients after a stroke undergo physical therapy (physical therapy) in bed, helping them to rise and sit down.
When performing exercises to train the vestibular apparatus for dizziness, stressful situations and overwork should be excluded. It has been scientifically proven that anxiety and depression slow down rehabilitation measures. Patients with depression show signs of vestibulopathies for a long time, even after a long recovery period.
Drugs for the treatment of dizziness
When prescribing a set of exercises, the effect of medications should be taken into account. Some medications improve the functioning of the balance organ. These drugs include Betaserk, Tanakan. Studies were conducted on the effectiveness of Tanakan in a clinic setting on patients with primary vestibulopathies. The patients took the drug in conjunction with physical exercise. All patients showed positive dynamics.
Drugs that inhibit the restoration of vestibular function are: antipsychotics, sedatives, tranquilizers. During the rehabilitation of vestibulopathies, patients are tried to stop these medications. If you stop taking neurotropic drugs, the effect of treatment is much higher.
Patients should exercise in a well-ventilated area. All sharp objects should be removed. The carpet should not have folds, as this may cause the patient to fall.
There must be mats in practice rooms. Patients should be trained in well-lit areas. If the patient cannot complete the task, then they try to help him. This reduces the likelihood of falling, especially at the initial stage of treatment.
Indications for gymnastics for dizziness:
- Meniere's disease;
- vestibulopathies caused by osteochondrosis, stroke, impaired cerebral blood flow;
- benign positional paroxysmal vertigo;
- vestibular neuronitis;
- vestibular migraine.
Semont maneuver
The Semont maneuver is initially performed with the help of an assistant.
The Semont maneuver is an effective exercise for dizziness, but at the initial stage it is better to perform it with the help of a doctor. Helps get rid of BPPV in cases of damage to the vertical semicircular canals.
Features of execution:
- Starting position – sitting on the couch, feet on the floor.
- The doctor turns the patient’s head 45 degrees and fixes the position.
- The patient lies on his side and stays in this position for at least 2 minutes.
- Return to starting position.
- Repeat the maneuver on the other side.
Perform all movements smoothly and slowly. The method is not suitable for people with decompensated pathologies of the cardiovascular system. With caution - with hypertension, coronary heart disease, elderly people.
After the maneuver, you need to sleep for 2 days on a high pillow, avoid tilting your head. Improvements are noticeable on the third day.
Devices and exercises for patients with vestibulopathies
Biofeedback trainer for balance restoration
Several types of gymnastics have been created for the rehabilitation of patients with balance disorders. To facilitate exercise, as well as to adapt the load of physical exercise, various devices are used.
Computer programs with special feedback platforms are used for patients. The most popular of them is the “Target” program. The patient stands on a special support. A monitor is fixed in front of the patient, on which there is a cursor reflecting the position of the center of gravity. The patient, moving his body, must hit the target. In this case, the patient needs to be prevented from falling if the body is strongly tilted. The doctor who performed this procedure may make the task more difficult by reducing the area of support.
For patients after a stroke, there are special suits that help perform exercises and protect the patient from falling. Costumes consist of several elements: shorts, vest, knee pads, shoes. Equipment for patients after a stroke has 2 categories: for patients who are unable to move independently even on a flat surface, for patients who need support when moving on uneven surfaces (stairs, descents, sharp ascents). Vestibular exercises for vertigo for elderly patients are often performed using suits if the person is not fully capable.
Exercises for vestibulopathies
Exercises for dizziness have basic directions that are used in almost all proprietary methods. Patients are included in exercises for head and body movements, exercises to improve static and dynamic balance, and walking training with eyes closed or open. They actively use breathing exercises, yoga, and Tibetan techniques to improve the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
The Brandt-Daroff technique is actively used. You can do it yourself. The patient should sit down, straighten his back, and place his hands on his knees. After this, lie on your left side, turning your head 45° to the right. You need to stay in this position for half a minute, and then sit down again. After the initial position, the patient lies on his right side and turns his head to the left. The task should be repeated 5 more times. If an attack of dizziness occurs, treatment is stopped until you feel better.
Differential diagnosis
For treatment to be effective, it must be prescribed only after the diagnosis has been made as accurately as possible. There are several diseases that are similar in their manifestations to BPPV or accompany it, creating a misconception about a person's condition.
Benign positional vertigo may resemble a migraine aura (one of the symptoms of osteochondrosis) or an infectious pathology. Differential diagnosis, which is the most detailed and accurate, helps to draw the right conclusions in such cases.
Typical signs of BPPV:
- paroxysmal (dizziness occurs for no apparent reason and ends similarly);
- the duration of the attack is no more than a day;
- there are vegetative symptoms (feeling of nausea, pale skin, hyperhidrosis, fever);
- at the end of the attack, the condition becomes completely normal and quite acceptable;
- The occurrence of tinnitus, deafness and headache is unlikely.
The body’s recovery after overcoming the disease occurs very quickly, and treatment requires no more than 30 days.
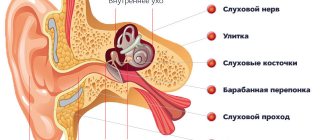
Diagnosis (in case of damage to the posterior semicircular canal)
Canalolithiasis of the posterior semicircular canal can be diagnosed in a patient using a special test. When testing the right labyrinth, the patient is asked to turn his head approximately 45˚ to the left.
After fulfilling the set conditions, the specialist as quickly but carefully places the patient on his right side and waits for 10 seconds of the latent period to pass. Next, the subject experiences dizziness and nystagmus (twitching) directed toward the right ear.
After the symptoms become maximum, their severity will subside. As soon as all discomfort disappears, the patient will be asked to quickly change position and sit down again.
Usually, in this case, signs of the disorder appear again, although with less force, and the nystagmus is directed in the direction opposite to the right ear.
Checking the channel of the left labyrinth is carried out according to a similar principle. This procedure is called the Dix-Hallpike positional vertigo test. In addition to this, you will need to do:
- MRI of the brain;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- CT.
If the horizontal semicircular canals are affected, then the technique for checking the patient’s condition will be slightly different.
Diagnostics (for damage to the horizontal semicircular canal)
This variant of the disease is detected much less frequently, only in 10-20% of cases. In this case, different semicircular canals may be affected on the ears (for example, on the left - horizontal, on the right - vertical), in addition, due to the actions of specialists, they can transform into one another.
If it is the horizontal semicircular canal that is affected, the patient usually feels paroxysmal dizziness when he tilts his head in different directions while lying on his back. This symptom is most noticeable after proper rest and when turning the face towards the sore ear.
Such diagnostics are convenient because they can be carried out independently.
The latent period of BPPV with damage to the horizontal semicircular canal is short (5 seconds), and the attack itself has a long duration. Often the pathology is accompanied by vomiting.
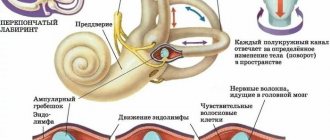
Classification of forms of BPPV
Depending on the location of pathological changes in the ear, several forms of BPPV are distinguished. Particles of the otolithic membrane move freely relative to each other along the structure of the semicircular canal. There is also a classification based on the mechanism of development of the pathology.
Cupulolithiasis
Cupulolithiasis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is rare. It is characterized by the fixation of fragments in the ampoule on the cupule.
The fragments are otoliths that constantly irritate the receptors when the head changes.
Canalolithiasis
More common than cupulolithiasis is BPPV canalolithiasis. In this case, the otoliths in the form of a clot move freely along the endolithm. They also irritate the receptors in the inner ear and cause dizziness.
The anterior canal is affected
Damage occurs in 2% of all cases. This is due to its position, which prevents otoliths from remaining in the anterior canal.
Posterior semicircular canal
In patients with benign paroxysmal vestibulopathy, damage to the posterior canal is more common because the otoliths are fixed there under the influence of gravity.
Canalolithiasis of the left posterior semicircular canal (rarely anterior) occurs in 30-40% of all cases of this disease. This is due to the fact that it is the longest channel - about 20 mm.
Outer form
The external semicircular canal is the shortest, 12-15 mm. Its lumen is wider than the posterior and anterior canals. It forms an angle of 30° with the horizontal plane.
The external canal is more susceptible to inflammation due to infectious diseases.
Causes of dizziness
Benign neoplasm of the brain and other parts of the central nervous system.
In clinical practice, secondary and primary dizziness are distinguished.
The secondary form of vertigo is characterized by the release of excess otoconia from the otoliths. Almost every disease that directly or indirectly affects the inner ear leads to this process.
BPPV often occurs after vestibular neuritis. In this case, it is sometimes confused with recurrent neuritis, characterized by dizziness even at rest.
The “classic” one is post-traumatic BPPV. Dizziness can occur immediately after injury, but most often the event only disrupts the diaphragm and releases the otoconia over several days or weeks. Post-traumatic vertigo often affects both labyrinths at the same time.
BPPV is a common complication of late-phase Meniere's disease, a consequence of recurrent middle ear infections, internal or middle ear surgery, or labyrinthopathy of any other etiology.
However, in 50–70% of cases, no previous damage to the labyrinth is detected, in which case the dizziness is designated as idiopathic (primary). In some patients, this type of disease is associated with calcium metabolic disorder, and studies have shown a correlation with osteoporosis.
The incidence of BPPV is more common in patients with migraine. The occurrence of the primary form is common after 40 years, the number of cases increases with age.
Causes of otolithiasis
Otolithiasis is attack-like (paroxysmal) dizziness. Its characteristic feature is the factor that provokes dizziness - this is a change in the position of the head. Otoliths in the ear, namely the inner ear, irritate the receptors, causing the patient to experience various ailments.
Unidentified causes
In 40-50% of cases, it is not possible to establish the exact cause of dizziness. This is due to the fact that there are many diseases that cause dizziness.
Meniere's disease
It is a non-inflammatory process in the inner ear. It most often occurs in people aged 30-50 years and is unilateral in nature, which usually becomes bilateral.
Dizziness occurs systematically with severe attacks, accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting. If the patient tries to change the position of the body, the condition worsens.
Taking ototoxic antibiotics
Ototoxic antibiotics affect the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and hearing. The destructive property of such drugs is their destructive effect on the cells of the ear and auditory nerve. The disease begins with hearing impairment, and then attacks of dizziness occur.
Viral inflammation of the vestibular apparatus
Viral diseases include vestibular neuronitis, when the vestibular nerve becomes inflamed. It occurs against the background of some previous infection. Inflammation affects the superior branch of the vestibular nerve.
Alcohol intoxication
Alcohol intoxication is a poisoning of the body that affects all its functions. Dizziness appears already in the middle stage of intoxication, when alcohol begins to affect neurological functions and organs. Alcoholic drinks disrupt the transmission of impulses between neurons.
Causes of the disease
BPPV is considered a benign symptom that does not pose any particular threat to the patient. Approximately 17-35% know what it is due to the presence of certain vestibular disorders in the body. However, in parallel with neurological pathology, symptoms can also be caused by other reasons, and treatment depends entirely on the etiology and competence of the doctor.
A neurologist can treat cerebrovascular accidents, a vertebrologist can treat non-existent osteochondrosis, and achieve no success either with gymnastics or prescribed medications.
The occurrence of BPPV can develop for variable reasons, often opposite to those expected, and within the competence of the ENT specialist and neurologist. They can also be hidden in addictions. A classic example of positional vertigo is cerebral circulatory insufficiency, a disorder of the central nervous system - treatment of such conditions is carried out by a neurologist.
Medical statistics also note other reasons for the development of negative syndrome:
- Diseases of the hearing organs - Meniere's disease, which causes disruption of the inner ear, acoustic neuroma, chronic inflammation of the middle ear, otosclerosis. BPPV caused by ear pathologies accounts for almost a third of all reported cases (29%).
- Pathological symptoms can be caused by the consequences of head surgery or trauma in this area.
- Sometimes this picture is caused by cervical osteochondrosis, compression of the arteries and insufficiency of blood flow in the arteries. What it is and how to deal with it is revealed by hardware studies of the vertebrobasilar system, spine, and circulatory system.
It has been noted that in a small percentage, the etiology of benign dizziness lies in the use of antibacterial drugs, diseases of the nervous system, and chronic alcoholism.
But in almost 40%, it is not possible to understand what it is and what causes the alarming symptoms. In this case, the diagnosis of idiopathic BPPV is made. The reasons undoubtedly exist, but at the current level of medical development it is impossible to establish them.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing a disease with such a symptom as dizziness is difficult due to the fact that it occurs in many diseases: osteochondrosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
However, modern diagnostic methods for BPPV make it possible to detect the disease in any form. The need to undergo them is determined only by an otoneurologist.
Instrumental examination
Instrumental examination methods can reveal not only the diagnosis of BPPV. MRI and CT scan of the brain evaluates its condition and reveals the slightest pathologies.
Physical examination
The Dix-Hallpike test allows you to test for benign positional vertigo. The patient is asked to sit on the couch and turn his head in a certain position. Then he is placed on the couch, holding his head.
At this time, the patient reports the moment of dizziness. A positive Hallpike test allows for postural dizziness.
Differential diagnosis of the disease
The differential method identifies diseases of the inner ear. It is performed for pathology of the posterior cranial fossa, multiple sclerosis, and central positional nystagmus.
Non-drug treatment
Dizziness as a symptom of VSD
There are no drugs that have a direct effect on canal/cupolothiasis.
Drugs are used that reduce the excitability of the vestibular system, both selectively and through a general sedative effect. The first include drugs with a vestibulolytic effect - blockers of H1 and H3 histamine receptors, cinnarizine, atarax, first generation antihistamines - diphenhydramine, pipolfen.
Evidence has been obtained in favor of reducing the intensity of dizziness when performing the Epley maneuver simultaneously with taking betahistine 24 mg x 2 times a day for a week.
Sedatives, most commonly benzodiazepine tranquilizers (diazepam), are used in hospital settings for the symptomatic treatment of severe recurrent attacks.
Ten years later, scientists McClure, Hall and Ruby put forward the theory of “canalolithiasis.” According to this theory, particles of statoconia, which move along the canal and excite receptors, provoke the appearance of positional vertigo, but the otoliths are not involved. When the particles reach the lowest point of the channel, the attack disappears.
Scientists of modern medicine criticize the above theories. They say that statoconium particles can come off even when the human body is stationary. They name the following reasons for their rejection, which results in benign dizziness:
- Head injuries.
- Meniere's disease.
- Certain antibacterial drugs (Gentamicin).
- Frequent migraines.
- Incorrect surgical treatment.
This therapy gives a very good effect. It involves the patient performing positional maneuvers (changing the position of the body and head). When performing exercises, an attack of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is possible. It is also worth remembering that some sets of exercises should be performed under the strict supervision of a specialist. The patient performs all maneuvers while sitting on an ottoman with his legs down.
These exercises can be performed independently, the number of repetitions is five times in each direction. Progress:
- Take the starting position.
- Lie on your side (legs slightly bent) and turn your head to the side 45 degrees. Lie like this for 30 seconds.
- Sit down.
- Lie on the opposite side.
- Sit down.
Semont maneuver
This set of exercises should be done under the guidance of a doctor, as nausea and other severe reactions may occur during the process.
To perform the exercises, a person needs to take a certain position. The next step is for the doctor to fix the patient’s head with his own hands; it should be turned to the side by 45 degrees. Next, the patient falls onto his side and remains in this position for a couple of minutes. Then he sits down again and immediately lies down in the same way on the other side for two minutes, after which he needs to sit down. All this time the head remains in the same position.
This set of exercises causes conflicting attitudes among doctors. Some recommend more gentle exercises, while others, on the contrary, consider this complex to be the most effective, even if benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is severe.
This maneuver also requires the presence of a medic. The doctor, holding the patient's head, abruptly places him on his back (his head goes over the edge of the couch). The patient lies like this for about a minute, and then he needs to turn his head in the other direction, gradually turning his torso. So you need to lie down for 30-60 minutes, and then return to the starting position.
In order to alleviate the condition of a patient suffering from benign paroxysmal vertigo, medication treatment can be used. It will help get rid of nausea and other unpleasant symptoms. If attacks recur frequently, the patient must remain in bed.
The goal of treating such dizziness with medications is to improve the general condition of the patient. At the same time, medications may be prescribed that will help normalize blood circulation in the vessels of the brain.
In severe cases, surgery may be performed. It is used to fill the semicircular canal with bone chips. The surgical intervention method is used only in severe cases, as there is a risk of serious complications. There is no specific drug treatment for BPH.
Benign positional vertigo has a favorable prognosis for recovery. BPPV is a safe disease and does not pose a threat to human life.
How to get rid of dizziness?
Dizziness is only a symptom of many diseases. Treatment for BPPV will be effective only after identifying other factors that trigger vertigo and diagnosing BPPV.
Then it will become clear how to treat benign paroxysmal vertigo. Incorrect therapy will aggravate the course of an undetected pathology. Medicine recognizes the high effectiveness of gymnastics treatment.
Positional gymnastics
Benign positional vertigo can be treated with special exercises designed to influence the movement of otoliths. Only in 2% of cases does it not help.
Gymnastics are prescribed by a doctor depending on the location of pathological changes in the ear.
Semont maneuver
It is better to carry out this exercise only in the presence of a specialist. An exceptional feature of the maneuver is the rapid movement of the patient at a certain angle. To avoid nausea or vomiting, take antiemetic medications.
Brandt-Daroff
Brandt Daroff gymnastics is performed several times a day: the first approach is done immediately after waking up. Each of them includes tilts in both directions at a certain angle.
Vestibular gymnastics by Brandt Daroff is always selected individually depending on the nature of the disease. Before starting, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the techniques in the video of the Brandt-Daroff exercises.
Epley exercises (video)
The Epley maneuver is effective for pathology of the posterior semicircular canal. There are quite a lot of nuances in performing the Epley Maneuver exercise, so it should be entrusted to a doctor.
The specialist will turn the patient’s head in a certain direction, depending on the location of the pathology, then change the position of the patient’s body.
Dix-Hallpike gymnastics
Gymnastics is based on different movements of the body, head and eyes. The effectiveness of a gymnastics regimen depends on factors such as age, one- or two-sided pathology, and duration of the disease. Positive changes are already observed in 50-80% of cases.
Lempert method
The method is used for benign paroxysmal vestibulopathy of the horizontal semicircular canal. The head is turned 45 degrees in the horizontal plane towards the pathology.
After which the patient is placed on the couch and the head and body are turned in a certain sequence. The method involves a series of sequential maneuvers, which can be found in the video in Russian.
Drug treatment
Treatment of BPPV with drugs was the mainstay of treatment until about 15 years ago. Today, gymnastics and maneuvers performed by doctors are effective. Medicines should only be used to treat inflammation or relieve symptoms.
Vasodilators
Vasodilators are vasodilators in nature and are prescribed to improve blood circulation. To treat benign paroxysmal vertigo, medications such as:
Vestibulolytic drugs
Drugs in this group affect the pathogenesis of vestibular disorders of vascular etiology and the treatment of otolithiasis. After therapy, blood supply to the brain tissue improves:
Herbal nootropics
Nootropics improve brain activity, increase mental performance, and reduce fatigue. Some believed that treatment with folk remedies, to which they were previously classified, gives a temporary effect, but depending on the duration of treatment, a positive result also appears.
| Bilobil | 1 capsule 3 times a day for adults, course of treatment – at least 3 months |
| Ginko biloba extract | 1-2 capsules 1-2 times a day, course of treatment – 3 months |
| Ginseng | Tincture – 15-25 drops, tablets 0.15-0.3 mg before meals 3 times a day |
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are designed to suppress the effect of the allergen.
Antiemetic drugs
Drugs in this group relieve attacks of nausea and vomiting that occur against the background of postural dizziness.
Treatment
Dizziness after 60 years
Treatment always depends on the cause. Mostly, vestibular rehabilitation, multifunctional psychotherapy, and drug therapy help.
Non-pharmacological treatment
The therapeutic basis is special exercises that can eliminate the problem for benign positional vertigo. In practice, 2 maneuvers are used to displace irritating stones (otoconia) in the inner ear away from the area of receptor cells and into a non-sensitive area. The maneuvers are also suitable for benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood.
Brandt-Daroff maneuver
Balance exercises work on several levels. Their essence is to increase the supply of stimuli to the nerve cells of the central part of the vestibular system located in the brain stem.
Principles of therapeutic exercises:
- While lying down, move your eyes to the sides in horizontal and vertical directions, bringing your eyes closer together (looking at the tip of the approaching finger).
- In the next stage, add slow, gradually accelerating head movements, first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed.
- Add head movements while sitting - turns, bends, again with eyes open and closed.
- Then add throwing the ball from hand to hand, more complex maneuvers (throwing the ball under a raised knee, etc.).
- Gradually try bending your entire body with your eyes open and closed.
- On the next one, sit down and stand up, first with your eyes open, then with your eyes closed. Once you become good at the exercise, add a twist of your torso when standing up.
- Walk with your eyes open on a level surface, then add walking with your eyes closed; walk along the drawn line, add a turn of your head as you walk, again with your eyes open and closed.
Semont maneuver
Although this maneuver is demanding, it is most effective in practice. The method is used to distinguish canal damage. Using a maneuver, the patient can get rid of the problem after the first exercise, but sometimes it needs to be done several times. The maneuver is not used in patients with organic back pain; it is rarely used for dizziness in children (due to the difficulty of performing). The method consists of quickly turning the patient on his side with his head turned 45º. Performed exclusively by a doctor!
Epley and Lempert maneuver
In terms of complexity, the Epley and Lempert maneuvers are similar to the Semont method, however, they are performed for vertigo in children.
The basis is a position on the back with the head turned, after which a turn is carried out on the side, after a few seconds - taking a sitting position. All these movements are performed with open eyes, 2 times a day, 3 times in a row.
If the maneuver is performed correctly and all prescribed rules are followed, the success of the treatment manifests itself quickly. Patients are recommended to sleep in a semi-sitting position for 24 hours after exercise.
Pharmacological treatment
Today, there is no pharmacological therapy for benign positional vertigo. But, if the patient suffered from hearing loss before benign positional vertigo was detected, it is recommended to supplement the exercises with vasodilators
The importance of this therapy is to stop or slow down hearing loss. In pharmacological therapy, drugs containing betahistine hydrochloride are used
This active ingredient increases blood flow in the inner ear. Other effects include reducing the frequency and intensity of dizziness and suppressing tinnitus. In an acute condition, relief of vegetative symptoms is necessary: nausea, vomiting. For this purpose, antiemetics are used, in particular Torekan (Thiethylperazine).
For central and peripheral vertigo, vasoactive (vasodilator) drugs are used:
- Agapurin, Trental, Pentoxifylline (active substance pentoxifylline);
- Duzodril, Enelbin (naftidrofuryl);
- Xanidil (xanthinol);
- Oxyphylline (etophylline);
- Cavinton (vinpocetine).
Surgical methods
Surgical methods for treating dizziness:
- labyrinthomia - used in advanced stages of Meniere's disease;
- ototoxic antibiotics – drop attacks in Meniere’s disease;
- neurovascular decompression – for vestibular paroxysm;
- elimination of canal blockage – with BPPV;
- decompression operations with hydrates – for Meniere’s disease;
- neuroma surgery;
- perilymphatic fistula surgery.
Prevention of cupulolithiasis
There are many reasons for the occurrence of BPPV; without provoking them, you can avoid an unpleasant disease. Dizziness of any etiology is not scary if you follow a healthy lifestyle, do exercises in the morning and hardening. Benign positional vertigo syndrome is more complicated, since the causes of its occurrence are not always clear. However, a general set of actions will help avoid not only DDZ:
- If the patient has already had the disease, then therapeutic maneuvers should be performed several times a week so as not to provoke a relapse.
- Maintaining a daily routine that requires 7-8 hours of sleep.
- Active lifestyle, training to strengthen the body.
- Proper nutrition with a minimum content of salty, fatty, spicy foods.
Treatment
For positional vertigo, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the underlying disease:
- In old age (etiol.: cerebral hypoperfusion) and with dehydration, the appearance of vertigo can be stopped by drinking fluids (rehydration).
- For orthostatic dysregulation, a morning cold shower (stimulating blood circulation), classical Kneipp therapy (physiotherapy: hydrotherapy, movement therapy, herbal medicine designed to strengthen the body as a whole), sports, and morning coffee help to treat. A medicinal method is also possible (taking medications, for example, Etilefrin or Gutron).
Positional gymnastics
For BPPV, treatment is based on the use of relaxing maneuvers (the main one is the Semont maneuver). Paroxysmal vertigo occurs in the form of dizziness that lasts for several seconds or minutes after assuming or changing a lying position. As part of the gymnastics, a specialized ENT examination is carried out, followed by positional exercises. The prognosis is favorable - spontaneous remission. This maneuver can be done either under the supervision of a specialist or independently at home.
Turn your head to the left 45°, from a sitting position in the middle of the bed (with your legs down), lie on your side (on both sides) as quickly as possible, without changing the tilt of your head. Free otoliths, by inertia, penetrate beyond the area where the vestibular apparatus was irritated.
It is recommended to avoid a horizontal position for 24 hours after the maneuver and sleep half-sitting for the first night. Sometimes it is possible to achieve complete correction of symptoms after just 1 maneuver. But more often it is necessary to repeat it several times over the next days.
The exercise is suitable for both adults and children (children's type of BPPV is rare, its correction sometimes occurs on its own, without the help of a doctor or taking medications).
The next version of positional gymnastics is the Brandt-Daroff exercises, training with an effectiveness of up to 95%. One cycle lasts 2 minutes (4x30 seconds - each position is maintained for 30 seconds). Exercises are carried out 5 times in a row (10 minutes) 3 times a day for 2 weeks and 2 times a day for 3 weeks
When lying on your back, it is important that your head is pointing upward at 45º
Meniere's disease
The disease is characterized by endolymphatic edema, leading to mixing of perilymph and endolymph with subsequent loss of vestibular function - balance and hearing. This manifests itself as an attack of rotational vertigo with hearing loss and tinnitus, lasting from several minutes to hours. Spontaneous nystagmus from the affected ear and vomiting are often present.
In accordance with the recommendations of an ENT specialist, the following therapeutic measures are carried out:
- bed rest, taking antiemetics, antivertiginous drugs;
- for severe vomiting - infusion and Betagistidine;
- in case of numerous attacks and resistance to therapy, surgery is recommended: saculotomy, labyrinthine shunting, neurectomy of the vestibular nerve.
Prevention includes popular recommendations: a diet with a low salt and fluid content, prevention of triggers - stress, alcohol and nicotine, preventive use of Betahistidine.
Patient reviews
Anzhelika Rogonova, 35 years old:
Frequent dizziness began and it was impossible to get out of bed. I sinned on the blood vessels, but after Dix Hallpike’s test, the doctor revealed the diagnosis. I’ve been going to physical therapy for a month now and doing exercises for BPP, the Brandt Daroff method, and I feel positive changes.
Alesya Rumyantseva, 28 years old:
She suffered from the flu very badly, and began to have heart problems, which also caused dizziness. But it turned out that it was otolithiasis and inflammation of the inner ear. I do Brandt Daroff vestibular gymnastics, go to the pool, treatment has just started, but I feel like life is easier.
Diagnosis of BPPV
This diagnosis is made in the presence of the above symptoms, as well as in the presence of the following symptoms:
- Attacks last no more than 20-24 hours;
- In addition to dizziness, there are symptoms such as: pale skin, fever, increased sweating;
- BPPV always resolves without headaches, tinnitus or darkening of the eyes;
- The disorder always occurs in attacks (paroxysmal). The attacks come suddenly and do not last long;
- Outside of an attack, the patient feels great;
- BPPV most often occurs between the ages of 50 and 60 and rarely occurs in young people.
The specialist must make a differential diagnosis with diseases such as:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- vertebro-vestibular insufficiency;
- orthostatic hypotension.
The use of therapeutic exercises
Positional vertigo (causes may be related to osteochondrosis) can be successfully treated with gymnastics.
It is recommended to perform the following exercises:
- Tilts the head forward and backward.
- Head tilts in different directions.
- Acute rotation of the head clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Tilt the head forward and backward with a delay in each position for 10 seconds.
Each exercise must be repeated 10 times, pauses between them must be at least 10 seconds. It is better to do gymnastics before bed; it should not cause discomfort or severe pain.
IP – LYING ON YOUR BACK
- Arms extended behind the head, stretching in four counts. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Arms are extended behind the head, without lifting your hands from the floor, raise your head and look at your outstretched socks. Repeat 4-6 times
- “Bicycle” - put your hands under your head, legs bent, 3 sets for a count of 10.
- Legs bent at the knees, straighten your legs up, spread them apart, then connect them and lower them down. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Diaphragmatic breathing: inhale - inflate the stomach, exhale - draw in the stomach, 6-8 times.