General characteristics of the drug
Ceraxon is a nootropic drug that has a beneficial effect on the cognitive functions of the brain. Its spectrum of action is wide:
- improvement of memory and thought processes;
- increasing the brain’s resistance to adverse effects (trauma, hypoxia, infections, intoxication);
- preventing the death of damaged brain cells;
- reduction of cerebral edema;
- restoration of self-care skills and volitional qualities after severe diseases of the nervous system
For adults, the medication is indicated during the recovery period after a stroke, traumatic brain injury, and for vascular and degenerative pathologies of the brain.
Use of the drug Ceraxon
The solution for oral use in adults is prescribed 200 mg (2 ml) orally 3 times a day. For children, the drug can be prescribed orally from the moment of birth - 100 mg (1 ml) 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the brain damage. The minimum recommended period is 45 days. The dose of the drug and the duration of treatment can be changed by the doctor. The drug, pre-mixed with a small amount of water, is taken using a dosing syringe. It is necessary to rinse the dosing syringe with water after each use. IV or IM administration In acute and emergency conditions, the maximum therapeutic effect is achieved when the drug is administered in the first 24 hours. IV is administered slowly (injection duration - 5 minutes) or drip (infusion rate - 40-60 drops per minute) . Treatment begins with prescribing the drug for the first 2 weeks, 500–1000 mg (depending on the patient’s condition) 2 times a day intravenously. Then - 500–1000 mg 2 times a day IM. The maximum daily dose is 2000 mg. If necessary, treatment is continued with the drug in the form of an oral solution. The recommended duration of treatment, at which the maximum therapeutic effect is noted, is 12 weeks. It is recommended for children to prescribe Ceraxon in the form of a solution for oral use.
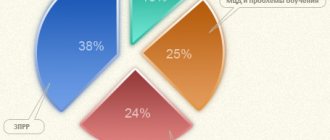
Does Cerakson help with RRR in children?
For children, the drug is indicated for:
- perinatal encephalopathy (traumatic, toxic effects in utero, during childbirth, in the first year of life);
- delayed psychophysical development;
- emotional disorders;
- speech development delay (SDD).
In case of delayed speech development caused by psychogenic disorders - separation from mother, placement of the child in a boarding school, 24-hour kindergarten, long-term illness - the help of a psychologist is necessary.
If RRR is caused by encephalopathy, vascular disorders of the brain, the effectiveness of the drug is undeniable. It activates speech centers in the cerebral cortex and improves auditory perception. The medication has a beneficial effect on the development of cognitive functions (memory, attention, thinking), which indirectly contribute to the development of speech.
Mechanism of action of Cerakson in ZRR
In case of RRD of organic origin (caused by brain damage due to toxic and/or traumatic effects on the fetus during pregnancy, childbirth or on the brain of the newborn), the nootropic effect of the drug is expressed in:
- restoration of damaged neurocytes;
- improving the transmission of impulses in brain tissue;
- preventing the formation of free radicals, leading to additional intoxication of the brain, the development of vascular and degenerative pathologies;
- suppression of the action of phospholipase enzymes involved in the process of cell damage.
Is Cerakson allowed for children under one year of age?
Research in recent years has shown that the medicine can be safely prescribed to babies up to one year old. For children, there is now a special release form of Ceraxon - in the form of a strawberry-flavored syrup. For infants, the medicine is indicated for:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- hypoxia during childbirth, caused by obstruction of the birth canal and delayed first breath;
- premature
The results of using the medication in children under one year of age revealed a significant improvement in the psycho-emotional state and normalization of psychophysical development.
Ceraxon: instructions for use for children
Doses of the drug depend on the severity of the damage to the central nervous system, the stage of delayed speech development, age, body weight, degree of prematurity of the child, characteristics of the nervous system, and individual response to the drug. Only the doctor selects the dosage for each small patient! Approximate treatment regimen:
Up to
a year .
It is preferable to administer in the form of syrup, but in some cases intramuscular injections are also used. The required dose of syrup is measured with a special syringe located in the package and mixed with a small amount of breast milk or artificial formula. Give 30 minutes to 1 hour after feeding. The course of treatment is 3 months. If necessary, after 3-6 months. the course is repeated. The duration of the course is determined only by the attending physician! Dosages by month for babies under one year of age are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Dosages of Ceraxon for babies under one year old
| Release form | ||
| Age (months) | Syrup | Injections |
| 2-4 | 1 ml 2 times a day | 100 mg 2 times a day |
| 5-6 | 1.5-2 ml 2 times a day | 150-200 mg 2 times a day |
| 7 | 2 ml 2 times a day | 200 mg 2 times a day |
| 8-9 | 2-3 ml 2 times a day | 200-300 mg 2 times a day |
| 10-12 | 3 ml 2 times a day | 300 mg 2 times a day |
After
a year,
the drug is used in the form of syrup, tablets, suspension, injections. The form of use, dose, frequency and duration of treatment is determined only by a doctor! Table 2 shows approximate doses of the medication for children 1 year old – 14 years old.
Table 2. Doses of Ceraxon for children of different ages
| Release form | ||||
| Age (years) | Suspension | Syrup | Pills | Injections |
| 1-2 | 1-2 ml 2 times a day | 1-2 ml 2 times a day | – | – |
| 3 | 2 ml 2 times a day | 2 ml 2 times a day | 1/4 tablet 1-2 times a day | 200 mg 2 times a day |
| 4 | 2-3 ml 2 times a day | 2-3 ml 2 times a day | 1/4 tablet 1 time per day | 200-300 mg 2 times a day |
| 5 | 3 ml 2 times a day | 3 ml 2 times a day | 1/2 tablet 1-2 times a day | 300 mg 2 times a day |
| 6-10 | 4 ml 2 times a day | 4 ml 2 times a day | 1/2 tablet 2 times a day | 400 mg 2 times a day |
| 11-14 | 5 ml 2 times a day | 5 ml 2 times a day | 1 tablet 1 time per day | 500 mg 2 times a day |
Side effects in children
As practice shows, adverse reactions in children occur extremely rarely. There may be individual intolerance to syrup components (for example, fructose). In this case, it is necessary to change the form of the drug - give injections or give suspensions. After three years, you can use the tablet form.
Cerakson is not prescribed to children with a predominance of the parasympathetic type of the central nervous system: it can provoke nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, shortness of breath, redness of the skin, tremor, and swelling. Sometimes hallucinations are possible.
All symptoms are quickly relieved by symptomatic therapy. But you can’t do anything on your own! If such phenomena occur, you should immediately consult a doctor!
The drug is not recommended to be prescribed simultaneously with other nootropics, in particular with Meclofenoxate. Ceraxon also enhances the effect of the antiparkinsonian drug Levodopa.
Reviews from parents about Tserakson
Numerous reviews from parents prove the high effectiveness of the use of Ceraxon for cervical cancer.
Anna: We live in a small town, we don’t have the opportunity to visit a psychologist or speech therapist. The doctor prescribed Ceraxon. Drank for 6 months. Before treatment, the child was silent and did not utter a single sound. Six months later he speaks entire sentences!
Vadim: We took the drug for 1.5 months. The child began to answer questions, so far only “yes” and “no”, we hope for further progress. Does not cause allergies, is well tolerated.
Lena: We’ve been taking the medicine for 5 months. In addition to the fact that the child started talking, he became interested in what was happening, he began to dress himself, eat, and tries to draw something. My daughter drinks with pleasure. The drug has a pleasant taste.
Marina: My son is 4 months old. Born with hypoxia. We take Ceraxon for a month. Before him, my son cried all the time, was very restless, and did not latch on to the breast. Now he is smiling, calm, sleeps well, and walks.
Among the disadvantages of the drug, parents note only the high price and rare adverse reactions.
Thus, Cerakson can be safely prescribed to children of any age with gastrointestinal development of organic origin. Important !
It should be remembered that the treatment must be completely carried out by a specialist! Independently selecting, changing the dose, method of administration, setting the regimen and duration of the course of treatment is strictly prohibited!
Alina Veyts, psychoneurologist, candidate of psychological sciences, especially for Mirmam.pro
International Neurological Journal 3(13) 2007
Currently, perinatal hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system in newborns and their consequences represent an important medical and social problem, since in the future they can lead to neurological disorders of varying manifestations and severity: from mild delays in psychomotor development to severe deviations, cerebral palsy, leading to child to disability [2, 13]. The use of actively developing new perinatal technologies makes it possible to overcome infertility, but at the same time is associated with an increase in the incidence of congenital malformations during high-risk pregnancies and the survival of premature infants with severe somatic and infectious diseases. Intensive care and resuscitation used in the care of premature infants with low birth weight (LBW), allowing to save the lives of very premature and severely injured children, can be considered not only as a positive phenomenon, but also as a source of neurological organic diseases in children, and and subsequently disability [1, 2]. That is why the problem of early, timely, effective treatment and rehabilitation of children with perinatal CNS damage is so important. Time should not be wasted; it is necessary to take full advantage of the high neuroplasticity of the developing brain and actively promote the restoration of damaged structures and functions of the central nervous system [1, 4]. This has become all the more important in connection with Ukraine’s transition to registering newborns according to WHO criteria: a fetus weighing 500.0 g and a gestational age of 22 weeks is considered viable. One of the main criteria for vitality and quality of health is birth weight. The lower the MTP, the higher the perinatal mortality and the level of cerebral congenital and hereditary pathologies [1, 4, 13]. Structural changes in the brain of newborns determine the further development of the child. Modern examination methods make it possible to accurately determine the nature of these disorders and their location. However, the clinical picture does not always correlate with the detected changes. This is due to the structural and functional immaturity of the brain, since at this time the associative connections that are responsible for the clinical implementation of a particular defect have not yet been formed [2]. Along with the active processes of maturation of the nervous system, structural defects in the brain (discovered during the neonatal period) begin to manifest themselves as fundamentally new neurological symptoms. Not only the brain undergoes evolution, but also pathological symptoms, which at a new stage of development have qualitatively new clinical manifestations. This gives the impression of an ongoing process in the nervous system, but this picture is false. It is not the defect that progresses, but the symptoms [1]. Considering the increase in the number of children with perinatal pathology, the birth of premature babies with low weight, immature children, the increase in the number of congenital anomalies of brain development, in our region there was an urgent need for a department where comprehensive rehabilitation of children under 1 year of age was carried out. In 2004, at the Donetsk Regional Clinical Center for Neurorehabilitation, for the first time in Ukraine, 10 beds were deployed in the structure of the inpatient department for the rehabilitation of children aged 3 months to 1 year. The department is located in a separate block, has semi-boxes with all amenities for 1-2 children with the mother staying together. Children receive the necessary nutrition according to their age, including from the dairy kitchen, and are under the supervision of a pediatrician, who identifies concomitant somatic pathologies, prescribes the necessary examination and treatment. The rehabilitation complex includes special physiotherapeutic techniques (developed at ONPCR, adapted for such children): massage, exercise therapy using special techniques (soft, adapted manual therapy) (O.S. Evtushenko, 1999) [9], MRI, orthopedic correction, electrical stimulation , reflexology, as well as drug therapy [3, 7, 10]. The rehabilitation carried out is aimed not only at restoring various dysfunctions of the body, but also at preventing the development of pathological processes [3, 4]. When planning treatment tactics for children with delayed motor skills, indicators of motor development are taken into account, the degree of spasticity at rest and when attempting to move is revealed, in which positions it is more pronounced, the presence of general muscle hypotonia, and the level of mental and speech development [3, 5, 6]. The objectives of treatment include: normalization of muscle tone, prevention of the formation of pathological postures, abnormal muscle tone and movements, the development of contractures and deformities, training parents in methods of therapeutic care and available therapeutic and corrective measures. When training motor functions, the principle of ontogenetic sequence was observed [5, 6, 8]. The creation of a method for the rehabilitation of young children was accompanied by difficulties due to the lack of proven treatment regimens, the choice of drugs and their dosages, the presence of a huge number of neuropharmacological drugs on the Ukrainian pharmaceutical market (piracetam, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Pantogam, glycine, Cavinton, cinnarizine, Tanakan, Mexidol, actovegin, neuromidin, cerebrocurin, etc.). Most modern neuropharmacological drugs have a neurotransmitter or vasomotor type of action with an indirect effect on the structural and functional characteristics of neuronal membranes, ion transport, energy metabolism processes, etc. An exception is a number of nootropic drugs that combine neurotransmitter, neurometabolic and vasotropic effects in their spectrum of action. This also applies to popular drugs - piracetam, Cerebrolysin, thiocetam, which do not have a targeted effect on specific links in pathogenesis and are means of nonspecific nootropic therapy. Today, a drug that has a targeted effect on the key links of neurodegeneration of various etiologies is Cerakson (), the effectiveness of which has been proven by numerous clinical studies and publications. Thanks to its pharmacological properties and clinical capabilities, Ceraxon is a unique drug - a neuroprotector used in the treatment of diseases accompanied by ischemic, traumatic or degenerative damage to neurons. The active substance citicoline (cytidine-5-diphosphocholine) is an organic substance that belongs to the group of nucleotides and is an essential precursor of phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) - the main structural component of all cell membranes, including neuronal membranes [12]. CDP-choline is a nucleotide and plays an important role in cellular metabolism. It consists of ribose, pyrophosphate, cytosine (a nitrogenous base) and choline. Citicoline showed positive results in models of CNS injury: it preserved cardiolipin and sphingomyelin (in membranes); reduced the release of arachidonic acid; stimulated glutathione synthesis and glutathione reductase activity; weakened lipid peroxidation; restored Na+/K+-ATPase activity. These effects partly explain the ability of citicoline to reduce phospholipase A2 activity. In addition, citicoline is also a choline donor for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, stimulates the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase and promotes the release of dopamine. Ceraxon has a bioavailability of up to 99%; elimination from the body is carried out mainly through exhaled air and urine. Peak plasma levels are biphasic: the first at 1 hour after oral administration and the second at 24 hours [12]. The Donetsk Center has completed a year-long program of clinical testing of the drug Cerakson () with its inclusion in the complex of rehabilitation of children aged 2 months to 1 year with the consequences of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system, with early delay in statomotor and pre-speech development, cognitive impairment, and with the threat of development cerebral palsy, children with developmental anomalies of the central nervous system and precerebral vessels, incl. premature, immature children born with low weight and gestational age. 60 children aged from 2 months to 1 year completed a rehabilitation course with inclusion in the Cerakson complex. Cerakson was prescribed to children aged 2 months and older, 100 mg (1 ml suspension) 2-3 times a day. Ceraxon has a convenient form of administration - an oral solution, which is important for use in young children. The dose was selected individually depending on the child’s response to the drug, his weight, degree of prematurity and immaturity. For very premature infants with low birth weight, Ceraxon was prescribed at a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day; with good tolerability and no side effects, the dosage was increased to 100 mg 2 times a day. It was recommended to take it in the morning and daytime, the last dose of the drug no later than 17:00. Before taking the drug, the drug was diluted with water according to the instructions for use. The course of treatment was 1.5–3 months, up to 2 weeks in the conditions of the ONPCR department, then on an outpatient basis. The study revealed that the optimal period of taking Ceraxon is 12 weeks. The children were distributed by age categories as follows: from 3 to 6 months - 35 people; from 6 months to 1 year - 25 people (33 boys and 27 girls). The children were distributed according to nosological groups as follows: 1. Consequences of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system, with the syndrome of early delayed motor and pre-speech development - 35 people aged from 3 months to 1 year (of which 5 people with convulsive syndrome), with the syndrome increased neuro-reflex excitability against the background of perinatal damage to the central nervous system - 5 children; age category from 3 months to 1 year. 2. Early forms of cirrhosis (diplegic, hemiparetic, double hemiplegic) due to perinatal hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system (including those developed against the background of severe prematurity, with periventricular leukomalacia according to neurosonography (NSG) and MRI) - 17 people per aged from 6 months to 1 year. 3. Congenital anomaly of the development of the brain and precerebral vessels, malformations of cerebral vessels, congenital hydrocephalus, Dandy-Walker syndrome, Arnold-Chiari syndrome with convulsive syndrome - 8 people, age - from 6 months to 1 year. In the clinical picture, despite the fact that the children had organic lesions of the central nervous system that varied in topic and etiology, a delay in psycho-speechmotor development of varying severity, motor disturbances in the form of increased or decreased muscle tone, and paresis of varying severity prevailed. Dynamic neurological status data were assessed in all children; when assessing the therapeutic effect of complex rehabilitation, attention was paid to the timing of the development of static and motor skills, the dynamics of movement disorders, the reduction in the frequency or absence of convulsive conditions [3, 5, 6]. Assessment of the neuropsychic pre-speech development of young children with perinatal pathology was carried out using the CAT/CLAMS scale [12]. It was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics and is a compilation of all common scales, as unified and simplified as possible. Also, the motor and neuropsychic development of children was assessed in accordance with the development indicators of young children according to N.M. Aksarina et al. [1], using a formalized map of the study of psychoneurological functions in children of the first 7 years of life according to E.T. Lil'in, E.N. Krutyakova et al. [14]. The results of treatment with the inclusion of the Cerakson complex were assessed on the scale of the effectiveness of rehabilitation of children under 1 year according to O.S. Yevtushenko (2002), including various parameters, such as the patient’s behavior, the state of speech function, the instinct of self-preservation, the development of motor skills, muscle tone, movement functions, the presence of hyperkinesis and episyndrome, etc. [2]. The effectiveness of treatment was assessed by the difference between the sum of scores of all parameters before treatment and at its end. Statistical processing of the research results was carried out on a computer using Microsoft Excel. The average values, their errors, Student's coefficient and the reliability of statistical indicators (p) were assessed. A complex of clinical and instrumental examinations, which were carried out for children before and after a course of rehabilitation with the inclusion of Cerakson, was represented by Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck (Logidop-4 device), electroencephalic mapping (DXNT-32 complex), ultrasound diagnostics (NSG, ultrasound of internal organs, device LOGIQ-200 PRO Series). If necessary, children underwent MRI (Gyroscan Intera, Philips) at the Children's Children's Center. Cerakson was prescribed to children with neurological deficits of varying severity and with various organic lesions of the central nervous system: gross anomalies of brain development, functional disorders of the central nervous system, consequences of periventricular leukomalacia in premature infants at various stages of organization. Positive dynamics were observed in children of all groups, which confirms the action of Ceraxon as a broad-spectrum neuroprotector, its pathogenetic orientation, and the provision of complex neuroprotection. More pronounced progress was observed in the cognitive sphere in all children with disorders in the psycho-emotional, pre-speech and speech spheres. Before the course of treatment in the pre-speech period, these disorders manifested themselves in the form of a reduced response to the voice, lack of oral attention, poverty of the sound components of humming and babbling, delay in the development of speech, and the pronunciation of individual simple words. There was a delay in the “revival” complex, visual concentration on faces, on toys, recognition of loved ones and strangers, emotional lability, and motor disinhibition. At an older age, a decrease in concentration was detected; children did not follow simple instructions. After carrying out comprehensive rehabilitation with the inclusion of Cerakson in the course, a pronounced improvement was noted in the psycho-emotional sphere: the children became more sociable, emotional, and made contact more actively. Concentration improved, some showed interest in toys and others increased. Pre-speech production increased - humming, babbling, the formation of speech and the accumulation of vocabulary accelerated. Improvement in fine motor skills was noted. In the motor sphere, positive dynamics were also revealed in terms of indicators of motor development: head control, turning, sitting, standing, walking, and hand manipulations improved. There was a tendency towards normalization of muscle tone in the limbs, and the volume of spontaneous motor activity increased. However, the most pronounced positive effect was observed in very premature infants and young children, both in the motor and psycho-emotional pre-speech spheres. The children of this group underwent dynamic NSG, and positive dynamics were reliably noted: a decrease and severity of infiltration in the periventricular areas, as well as a subsequent decrease in the volume of cystic degenerations in these areas, which gave hope for recovery and a decrease in the severity of neurological deficit in the future. Ceraxon was used as part of a treatment complex in children with convulsive and epileptic syndromes while taking anticonvulsants. A positive effect was also noted in this group of patients. According to EEG data after treatment, an improvement in cortical dynamics, a decrease in the asymmetry of bioelectrical activity, and a leveling of cortical immaturity were noted. In no cases in children with epileptic and convulsive syndromes (receiving a combination of valproate and Cerakson) activation of epileptic activity was registered. Also, based on the data obtained during the study, one can note an improvement in blood flow indicators in the form of an increase in its linear velocity in the anterior and middle cerebral arteries, a decrease in its deficiency and asymmetry, and manifestations of intracranial hypertension. Positive dynamics of the above-described indicators were observed in children with signs of blood flow deficiency in the cerebral arteries, increased intracranial pressure, and impaired venous outflow before the course of treatment. There were no intolerances or side effects when taking Ceraxon. There were isolated cases of disturbances in falling asleep and sleeping when taking the drug in the evening; when the dose was corrected (in the daytime), these disturbances disappeared. There was also a case of increased neuro-reflex excitability in a young child when taking the drug; when the dose was reduced, the described processes were stopped. Before treatment, the average score on the scale of the effectiveness of rehabilitation of children under 1 year old according to O.S. Yevtushenko’s score was 14.1 ± 1.0, at the end of it - 16.5 ± 0.7 points. Thus, the difference in the amount of points before and after treatment was 2.5 points (p <0.01). The conclusions in this way, summarizing the data obtained during the program, we can say that Corahkson is an effective and safe drug for the treatment of children of the first year of life with the consequences of perinatal lesion of the central nervous system in the form of a delay in the pace of motor and psycho -regional development, as well as children with a threat of cerebral development paralysis, with organic lesions of the central nervous system. No side effects were revealed when using curakson, which confirms its good safety profile, also prolonged use of curakson was not accompanied by toxic effects. A more pronounced effect in therapy was noted when the treatment began at an earlier age - up to 3 months, including in deeply premature children with a low body weight at birth, which made it possible to significantly reduce the neurological deficiency in this group of patients. I would like to note the pronounced influence of Coraxon on the cognitive and speech spheres. As a result of the therapy, a significant improvement was noted - speech products were activated, auditory perception, the establishment of emotional contact with the child, and cognitive activity improved. Fine motor skills have improved. Positive dynamics was also noted from the formation of the functions of motion and statics. The inclusion in the complex of early rehabilitation of Curakson, a new generation neuroprotector, which has no analogues among neurotropic agents, made it possible to increase the effectiveness of treatment, reduced speech, cognitive and motor disorders, thereby improved the quality of life of the child and its social adaptation.