Congenital defects, anomalies, defects in brain development
Numerous developmental defects in children arise due to disruption of intrauterine embryogenesis.
Congenital anomalies in the fetus and newborn child are detected immediately by the appearance of the skull or several years after the onset of neurological disorders. Depending on the location, migration disorders of cerebral tissue cause certain clinical symptoms. The acute course of the pathology will allow neurologists to make a diagnosis in a timely manner. Chronic development with cycles of exacerbations and remissions is not a specific sign of nosology.
When and why genetic pathologies of the fetus occur: risks by age
Anomalies in fetal development occur already at the moment of fertilization of an egg by a sperm. For example, a pathology such as triploidy (the presence of three chromosomes in a row of a chain, and not two, as expected), occurs when two sperm penetrate the egg, each of which leaves one chromosome. Naturally, with such a set, a living organism cannot survive, so at a certain stage a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy occurs.
Spontaneous miscarriages occur in 50% of abnormal fertilizations. This is how nature protects humanity from complete degeneration.
In general, chromosomal pathologies are divided into 4 groups:
- Gametopathy.
The pathology is present even before conception in the sperm or egg itself, i.e. This is a genetic disease - a congenital pathology. - Blastopathy
. Anomalies occur in the first week of zygote development. - Embryopathy
. The embryo receives damage from 14 to 75 days after conception. - Fetopathy
. It consists in the formation of pathology of fetal development starting from the 75th day after fertilization.
No one is immune from the birth of a baby with genetic disorders. If previously the risk group included mothers over 35 years of age, diabetics, women with chronic diseases (kidney failure, thyroid problems), today sick children are born to young mothers aged 20 to 30 years.
These statistics lead to gloomy thoughts. Thus, the risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities in 20-year-old women is 1:1667, and in 35-year-old women it is already 1:192. But in reality, this means that in 99.5% of cases, a child of a thirty-five-year-old mother will be born healthy.
Brain dysplasia - what is it?
Limited cerebral damage in a limited area provokes a variety of clinical manifestations. Epileptic seizures are combined with impaired consciousness and cortical disorders.
Initial signs of nosology using electroencephalography. Minor cerebral changes can be treated with anticonvulsants.
Types of focal dysplasia:
- The first type is a local change in cortical architectonics;
- The second type is focal cytoarchitectonic changes;
- The third type is pathology of architectonics in secondary diseases (temporal sclerosis, cerebral malformation, Rasmussen's encephalitis, ischemia).
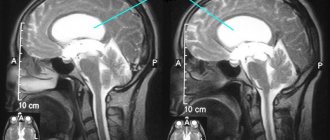
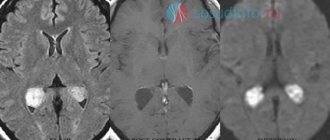
Methods of radiation neuroimaging MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg help verify the stage of nosology.
Polycystic dysplasia of the brain is characterized by the presence of many cystic growths within the cerebral tissue.
To diagnose defects, the results of CT and MRI are compared
Diagnosis
If in doubt, it is recommended to consult the child with specialists such as a neurosurgeon or neurologist. First, simple, almost recreational tests are conducted to check the functions of different parts of the brain. First, the doctor checks the fundus of the eye using an optical instrument called an ophthalmoscope. If there is increased pressure in the brain, there may be swelling where the optic nerve enters the eye.
Special tests may be performed to detect abnormalities in the brain. Below we provide examples.
- X-ray of a child's skull . X-rays reveal changes in the skull caused by the tumor. In addition, if very small calcium deposits (calcifications) are detected in the brain, these may also indicate the presence of a tumor.
- (computed tomography), scanning. This test produces a series of highly detailed images on a television screen and in photographs that show not only the skull, but also the brain itself and any tumor that may be present.
- NMR research (nuclear magnetic resonance). This examination, through a complex electronic mechanism equipped with a powerful magnet, allows the doctor to obtain unusually detailed images of internal organs - in this case, the brain. In any case, this test is a perfect magnetic examination without the danger of radiation.
- EEG (electroencephalogram). This test records minute-by-minute measurements of electrical activity (voltage) on graph paper. It is worth remembering that most common childhood tumors can usually be cured by surgical removal.
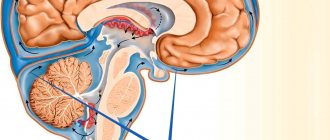
Anomalies of brain stem development - causes
Depending on the morphological changes, groups of brain abnormalities are distinguished:
- Regulations;
- Quantities;
- Size and shape;
- Structures (buildings).
The first group of nosologies arises due to underdevelopment of the rudiment of the cerebral structure or the complete absence of the embryonic rudiment. If the baby is born normal, the prognosis is poor due to the absence of part of the brain.
Positional anomalies include the doubling of an organ, the merging of several parts together at the same time.
Defects in the position of cerebral structures
All nosological forms of the group are determined by three factors:
- Inversion displacement of the organ relative to its own axis, median position;
- Dystopia is an unusual localization of embryonic structures;
- Heterotopia is a pathology of organ anlage.
The degree of displacement is determined by the severity of clinical symptoms and a person’s life expectancy.
Defects in brain size and shape
The list of nosologies in this category is determined by a number of morphological changes:
- Synostosis of several organs;
- Hyperplasia - an increase in the number of tissues and sizes of cerebral tissues;
- Dysplastic hypoplasia – reduction in the size of the structure;
- Simple hypoplasia - no changes in morphology.
Defects in brain structure
The nosology is accompanied by anomalies in the natural formation of the hole and morphological features of the structure. Heteroplasia develops at the stage of intrauterine development. Characterized by atypical tissue formation.
Dysplasia is a pathology of the relationship of articular surfaces.
Hamartria is the abnormal development of tissue structures. Stenotic narrowing of the canal or duct can be congenital or acquired.
A dysontogenetic cyst is accompanied by a significant narrowing of the compensatory capabilities of the organ.
Classification of embryonic developmental defects:
- Fetopathies;
- Embryopathies;
- Blastopathy;
- Gametopathies.
Depending on the time of occurrence of defects in embryonic development, a certain type of disorder occurs.
Based on the extent of damage, the following types of cerebral defects are distinguished:
- Multiple – affects several brain areas at once;
- Systemic – localized within one area;
- Isolated - cause damage to one organ.
Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system can be provoked by infectious agents:
- Toxoplasma;
- Cytomegalovirus;
- Coxsackie virus.
Alcohol abnormalities occur if a pregnant woman drank alcohol during pregnancy. The pathology is provoked by chromosomal aberrations and genetic mutations during the formation of the neural tube (third or fourth week of pregnancy).
Types of ultrasound examinations
Ultrasound diagnostics represents a wide range of studies. There are several types of ultrasound that accurately determine intrauterine malformations of the baby.
Standard ultrasound
. It is usually combined with a biochemical blood test. It is carried out no earlier than 10 weeks of pregnancy. First of all, the thickness of the fetal collar zone is detected, which should not exceed 3 mm, as well as visualization of the nasal bone. In a baby with Down syndrome, the nuchal region is thicker than normal, and the nasal bones are not developed. The following factors also influence the increase in thickness:
- heart disease
- stagnation of blood in the neck veins
- lymphatic drainage disorder
- anemia
- intrauterine infections
Doppler - uh
This is an unusual ultrasound test that evaluates fetal blood flow. The difference between the sent and reflected signal indicates the norm or pathology of the “fetus-placenta-mother” chain.
- 3D ultrasound allows you to see a color image of the baby, see the limbs, the absence of fused fingers, underdeveloped feet, etc. The accuracy of diagnosing the nuchal translucency increases by 30%. The doctor can tell for sure whether there are pathologies in the development of the neural tube.
- 4D ultrasound does not differ in operating principle from simpler options, but has many advantages. The doctor sees a three-dimensional image of the heart and a view of the fetus from different angles. It is 4D diagnostics that finally dots all the i’s, whether there are chromosomal abnormalities or not. It can be stated with 100% accuracy whether there are malformations of the nervous system, skeletal dysplasia, cleft lip or cleft palate.
Main types of brain defects
Defects in shape, size, and location of individual anatomical structures are identified. Let's consider the main types of congenital anomalies of brain development.
What is encephalocele
Penetration of cerebral tissue through skull defects causes various neurological symptoms, depending on the characteristics of the site of prolapse. Mild anencephaly resembles a cephalohematoma, but skull radiography reveals midline cleft and asymmetrical areas.
With the help of surgical intervention, it is possible to eliminate the pathology, but large lesions cannot be eliminated by ectopic protrusion. Encephalocele is verified by radiation neuroimaging methods - MRI and CT.
Features of anencephaly
The pathology is characterized by the absence of individual bones of the skull. The sites of destruction are overgrown with connective tissue, which does not allow optimal regulation of intracranial pressure.
Most nosological forms are incompatible with life. Death occurs immediately after birth, when the lungs open and the supply of oxygen to the cerebral parenchyma begins.
Manifestations of microcephaly
Underdevelopment of cerebral tissue occurs in one child out of five thousand newborns. The nosology is determined by a decrease in the size of the cranium, a violation of the relationship between the brain and the facial part of the skull.
Microcephaly (Giacomini syndrome) develops in utero in women with infections and parasitic diseases.
Causes of primary microcephaly:
- Genetic abnormalities with autosomal recessive transmission;
- Toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus encephalitis, rubella.
Etiological factors of secondary microcephaly:
- Cerebral cysts;
- Calcifications and hemorrhages inside the brain parenchyma.
A decrease in the size of the skull is characterized by about ten percent of oligophrenia. From an early age, the child exhibits developmental delays and closed developmental defects. Mental retardation is accompanied by convulsive syndrome. Muscle twitching is accompanied by improper development of the brain part of the skull.
What is macrocephaly characterized by?
Enlargement of the cranium allows diagnosing pathology. The nosology is characterized by hypertrophy of one hemisphere, disproportionate development of one half. Mental retardation is the most common manifestation. Seizures occur in approximately nine to ten percent of patients.
The clinic of nosology appears during the first years of life, which allows timely verification of pathology. Brain migration disorders are too severe for effective treatment of the disease.
Symptoms of holoprosencephaly
Holoprosencephaly is a disease accompanied by a defect in the development of the hemispheres. The lack of separation between the cerebral halves causes changes in the activity of functional centers.
Severe dysplasia leads to ventricular anomalies, asymmetry of the facial and brain parts. Severe defects lead to necrosis of the cerebral parenchyma with a high probability of death in the first days after the birth of the child.
The formation of a single hemisphere is a congenital defect due to a genetic abnormality of the thirteenth to fifteenth chromosomes. Nosology is often combined with other developmental defects:
- Cyclopia;
- Ethmocephaly;
- Cebocephaly.
The disease is accompanied by stillbirth. The ability to survive is minimal. The prognosis is unfavorable.
Clinic of cerebral cystic dysplasia
Multiple cystic cavities cause migration disorders. Developmental defects are accompanied by abnormalities in the distribution of cerebrospinal fluid. Numerous cysts cannot be removed. Often provoke muscle cramps. Low effectiveness of anticonvulsant treatment leads to progression of symptoms.
Single cysts may not pose a danger. Subclinical symptoms may occur due to increased intracranial hypertension.
How does agyria manifest itself?
Lissencephaly is a defect in the formation of the architectonics of the cerebral cortex. Severe convulsions are caused by underdevelopment of the cerebral convolutions. Nosology shapes motor and mental manifestations. Neurological signs of the disease – Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, Vesta.
The coherence of the brain provokes paralysis, paresis, and polymorphic convulsions. Signs of nosology develop in the first year of life. The baby lives for approximately this period of time.
Clinical signs of pachygyria
The developmental defect is due to the lack of formation of the secondary and tertiary gyri. Straightening the grooves of the second type disrupts the cerebral architecture.
The pathology of the layered structure of the cortex is characterized by heterotopia of nerve cells. MRI shows pachygyria well.
Clinical symptoms of craniostenosis
The disease is characterized by a narrowing of the skull with compression of the brain between the bones. Depending on the progression, decompensated and compensated variants of the nosology are distinguished.
According to the characteristics of the course, stable and progressive forms of the disease are distinguished. More often, the causes are due to early healing of the coronal or sagittal sutures. Pathology without timely treatment leads to death, as brain infringement occurs. Clinical symptoms depend on the predominant localization of the zone of compression of the white matter and parenchyma.
Neurological symptoms are characterized by numerous disorders against the background of increased intracranial pressure.
A child with craniostenosis has a severe headache, so the baby is restless, irritable, and whiny. Memory loss and impaired concentration occur when the condition persists for a long time. The prognosis of the pathology is unfavorable.
Indicators of agenesis of the corpus callosum
Nosology is characterized by underdevelopment of the corpus callosum. Concomitant pathology is underdevelopment of the third ventricle of the brain. Hypoplasia provokes underdevelopment of muscle muscles, paresis and paralysis, muscle cramps.
Manifestations of Aicardi syndrome occur when underdevelopment of the corpus callosum is combined with chorioretinal defects. The clinical picture is complemented by myoclonic convulsions, the formation of numerous lacunar nodes in the retina and optic nerve head. The nosology is characterized by microphthalmia, pendulum-like eye movements.
Some researchers have identified X chromosome defects in men in patients with agenesis of the corpus callosum.
Micropolygyria Clinic
The disease occurs due to the formation of numerous small convolutions. The normal cerebral cortex has six layers. With an anomaly, four layers can be traced. The abnormal structure leads to clinical symptoms:
- Swallowing disorder;
- Pathology of masticatory and facial muscles;
- Oligophrenia;
- Facial paraplegia.
The onset of the disease is observed in the first year of life.
Clinical manifestations of heterotopia
The nosology arises from neuronal migration. The lack of nerve signal transmission occurs due to heterotopions - pathological accumulations in the form of a ribbon or nodular form.
Due to heterotopia, mental retardation, epileptic syndrome, and various muscle cramps appear.
Causes of fetal pathologies: what affects the birth of children with genetic abnormalities
Factors contributing to the birth of children with genetic abnormalities include:
- Genetic predisposition . Genes are information inherited from both parents. Indicators such as height, eye and hair color are determined. In the same way, various deviations are laid down if both or one of the parents has a damaged gene. This is why close relatives are prohibited from marrying. After all, then the likelihood of bearing a fetus with a genetic pathology increases. With a partner who has the opposite genetic makeup, you are more likely to give birth to a healthy baby.
- Age of parents
. The risk group includes mothers over 35 years of age and fathers over 40 years of age. With age, immunity decreases, chronic diseases arise, and a woman’s immune system simply “will not notice” genetically damaged sperm. Conception will occur, and if a young woman’s body itself rejects the defective fetus, the pregnancy of an older mother will proceed more calmly. - Mom's bad habits
. Almost 90% of pathological pregnancies occur with oligohydramnios. In a smoking woman, the fetus suffers from hypoxia; the breakdown products of aldehydes (alcohols) in the early stages of pregnancy lead to mutations and abnormalities. In 46% of cases, alcoholics have children born with genetic pathologies. Alcohol also “breaks” genetic chains in fathers who like to drink. - Infections
. Diseases such as influenza, rubella, and chickenpox are especially dangerous. The fetus is most vulnerable until the 18th week, until the amniotic sac is formed. In some cases, a woman is offered an abortion. - Taking medications
. Even regular chamomile tea is toxic for a pregnant woman. Any medication taken should be accompanied by consultation with a doctor. - Emotional turmoil
. They cause the death of nerve cells, which invariably affects the development of the fetus. - Bad ecology and climate change
. If you become pregnant while on vacation in Thailand, there is a chance that along with your pregnancy you will bring a dangerous infection, which will begin to develop slowly in your native land, affecting the health of the baby.
Diagnosis of congenital brain defects
Most nosological forms are detected initially by clinical manifestations. Mild course, hypotonic muscle contractions provoke convulsive syndrome in children of the first year of life.
Instrumental diagnostic methods - ultrasound, neurosonography, MRI and CT - can exclude hypoxic and traumatological manifestations. The procedures are sufficient to identify developmental anomalies, cysts, and heterotopic areas.
Electroencephalography detects areas of increased cerebral activity in the presence of convulsive muscle twitches. Congenital species require genetic diagnostics to study DNA and determine mutations of the chromosomal apparatus.
Reasons for violations
Monogenic inheritance causes the anomaly in only 1% of cases. Most often, disruptions in intrauterine development are caused by a number of harmful teratogenic factors affecting the body of the mother and child. Exogenous factors include:
- Radioactive exposure;
- Exposure to chemicals;
- Heat;
- Action of high-frequency currents;
- Unfavorable environmental conditions, causing toxic substances to enter the pregnant woman’s body.
In addition, many medications and hormonal drugs that the mother takes in the early stages, without knowing about pregnancy, can be teratogenic. It has been proven that most pharmacological drugs easily cross the placental barrier, entering the child’s circulatory system. Even taking large doses of calcium supplements and vitamin complexes can be dangerous. Immune incompatibility between mother and child is unfavorable for the formation of a healthy fetus. Developmental defects can also be caused by dysmetabolic disorders, viral and intrauterine infections, including asymptomatic ones. Very dangerous:
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Diabetes;
- Metabolic pathologies;
- Syphilis;
- Cytomegaly;
- Rubella;
- Listeriosis;
- Toxoplasmosis.
The lifestyle of the pregnant woman has a huge impact on the successful course of pregnancy. Teratogenic effects are exerted by:
- Addiction;
- Alcoholism;
- Smoking.
Diagnostic methods
In case of severe anomalies, diagnosis can be made by visual examination. Indications for additional examination may include:
- Muscle hypotonia during the neonatal period;
- The appearance of convulsive syndrome;
- Impaired mental function.
Diagnostic methods are:
- Screening and obstetric ultrasound during pregnancy;
- Neurosonography through the fontanel in the first 1-1.5 years of life;
- EEG and EEG video monitoring make it possible to determine the presence of convulsive syndrome and select effective anticonvulsant therapy;
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which is the most informative method that allows you to visualize pathologies, their structure, shape, size and location.
To detect concomitant somatic defects, ultrasound of the kidneys, heart, and abdominal cavity is indicated. In addition, genetic counseling may be required.
Cerebral anomalies must be distinguished from fetal asphyxia or hypoxia and neonatal injuries.