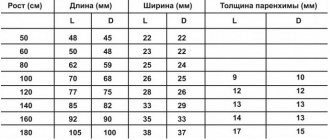
Among neuroimaging diagnostic methods, electromagnetic screening has the highest level of information content and reliability. MRI of the brain is a medical method that helps doctors carefully examine all the structures of the organ, the ventricular section, the substance present, the cavities where there is cerebrospinal fluid. You can find a clinic where you can undergo an MRI of the brain with a contrast reagent or in the usual mode at mrt-v-spb.ru. Call the hotline for a free consultation and get a discount on examination up to 1,000 rubles.
Brief information about the central nervous system
The central nervous system is responsible for the stable functioning of the entire body. When any disorder develops in it, a person experiences painful symptoms, leading to harmful consequences. Factors indicating the progression of abnormalities affecting the performance of the brain are considered: painful sensations, neurological signs (visual, motor, auditory disturbances), fainting, etc.
Non-invasive techniques are used to diagnose lesions in this organ. MRI of the brain produces clear, three-dimensional images that can be zoomed in and out to closely examine the structure of the region. The screening programs installed in the device allow you to visualize cerebral vessels. The results of tomography allow the doctor to determine the cause of the disease, its location, as well as establish a diagnosis and create an acceptable treatment regimen.
What is an MRI of the brain?
During tomographic screening, doctors can install different diagnostic programs. This helps in targeted testing of different areas of the brain. The main protocols are:
- MRI of the brain - the purpose of the procedure is to evaluate the white and gray matter, as well as the ventricles along with the membranes.
- MR angiography - visualizes the vessels of the organ.
- MRI of the nasal sinuses - the procedure shows the anatomical structure and pathologies in the nose.
- MRI of the eye - the method is aimed at studying the condition of the eyeball along with the optic nerve and orbit.
- MRI of the pituitary gland - diagnosis of the sella turcica area.
The choice of protocol depends on the symptoms, objectives of the study and the goals of the doctor.
What brain lesions and tumors look like on MRI
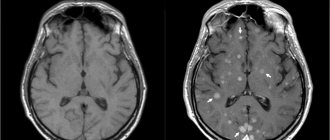
Focal brain damage is characteristic of multiple sclerosis, some parasitic, viral, bacterial diseases, and age-related changes in nervous tissue. On the tomogram it is visualized as a small area, differing in its characteristics from the surrounding structures. The lesions can be single or multiple, scattered throughout all hemispheres or located within the boundaries of a particular region. They lead to displacement and changes in other areas of the brain that are not involved in the pathological process.
Metastases and brain tumor on MRI
The tumor is a single formation that compresses the surrounding structures. Benign neoplasias have clear contours, grow slowly, but still gradually compress the brain in the confined space of the skull. Malignant neoplasms are characterized by rapid growth rates, irregular shape, and lack of clear outlines. Assessment of the vascular bed, which is present in each tumor, also allows us to judge the size and boundaries of the latter.
Another type of neoplasm - cysts - is a fluid-filled cavity surrounded by a capsule. They form at the site of hemorrhages and abscesses. Cysts do not have their own vessels. Sometimes they begin to grow due to an increase in the fluid they contain, which will also lead to compression of the brain.
What is shown on the results of an MRI of the brain?
The head diagnostic program includes monitoring of the following departments:
- ventricles of the brain;
- white matter of the subcortical plan, located in the frontal lobe;
- chiasmal area;
- middle sections;
- cerebellar tonsils.
Additionally, during the procedure, the radiologist evaluates the pituitary gland along with the paranasal sinuses.
What does an MRI of the brain show?
A study using electromagnetic equipment makes it possible to visualize the following abnormal conditions in a patient:
- infectious diseases;
- lesions of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis;
- failures in the structure of the pituitary gland;
- malformations of the brain;
- bleeding from traumatic head injuries;
- malfunctions of the vascular system;
- dementia of a senile nature;
- sources of malfunction of the visual and auditory organs.
What can an MRI of brain vessels show in multiple sclerosis?
It is characterized by the formation of zones of white matter - nerve fibers that lose their myelin (outer) layer. The tomogram shows focal formations that accumulate contrast differently depending on the stage of the disease. The lesions appear as light areas and can be located in all parts of the white matter. Their number can vary greatly: from one to dozens. In the initial stage of the disease, if only one lesion is detected, it can be mistaken for a small space-occupying formation. Unlike cancer, lesions in multiple sclerosis do not deform surrounding structures.
Hydrocephalus (dropsy). Normal and hydrocephalus Dilation of the cavities of the ventricles, subarachnoid, perivascular space. Severe forms may be accompanied by compression and atrophy of the cortex and subcortical formations of the brain.
Congenital developmental anomalies Serious anomalies in brain development, as a rule, are detected in the prenatal period or in the first months of a child’s life. If the anomaly does not cause a significant loss of any body function, then it can only be detected by chance, during an MRI, which is planned for another purpose. Just as no two people are identical, different people cannot have two absolutely identical tomograms. Therefore, only a specialist with sufficient experience and qualifications can evaluate the MRI result. You should not look for abnormalities in the images yourself, since not even all doctors know how to do this correctly. Also, you should not independently analyze the description of the study, since many different abnormalities can be detected in a healthy person, but such findings are not clinically significant.
When should you get an MRI of the brain?
The main symptoms that become the reason for undergoing research are called:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- double vision;
- epilepsy attacks;
- memory problems;
- high pressure readings.
Other manifestations of unknown origin for which MRI of the brain is prescribed include:
- feeling of weakness in the limbs;
- problems with coordination;
- chaotic thinking;
- neoplasms of various origins;
- pathologies of vascular development;
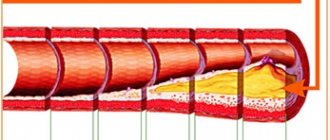
- vascular lesions such as stroke and their consequences;
- demyelinating disorders; degenerative abnormalities; inflammatory lesions;
- encephalitis, including in patients with HIV status, abscess; congenital developmental anomalies;
- arachnoid type cysts; hydrocephalus; Arnold-Chiari pathology;
- defective development of the corpus callosum; neurocutaneous syndrome; Acute TBI; hematomas.
The doctor recommends undergoing an electromagnetic brain procedure to monitor the radicality of the removal of the tumor body and to exclude its further growth in patients after surgery.
When MRI is less effective or ineffective
MRI is a very reliable diagnostic method, but there are specific indications for it, to determine which it is advisable to contact a knowledgeable specialist. Otherwise, performing the procedure may bring little or no benefit.
For example, MRI diagnostics are poorly suited for determining lung diseases, therefore, if it is unreasonably prescribed to a patient with respiratory diseases, he will have to confirm the results with other, more suitable methods. Similarly, tomography is not suitable for examining the intestine, and is not good for detecting bone disease.
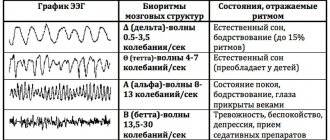
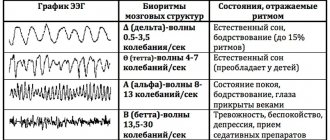
She cannot determine some indicators at all. For example, MRI does not make it possible to evaluate the color of mucous membranes, like endoscopic methods, does not allow us to judge bioelectrical changes in the brain, like electroencephalography, etc. Therefore, before turning to MRI, it is worth assessing its real capabilities and the feasibility of the procedure.
When is it prohibited to do an MRI of the brain?
Despite the high level of information content of the procedure, the method is not suitable for everyone. The main contraindications apply to people who suffer from asthma and chronic kidney disease. Pregnant women should be treated with special caution when considering MRI of the brain. Despite the long-term use of tomographic equipment in practice and the absence of adverse effects in pregnant women or newborn children after the examination, patients need to inform the attending physician and radiologist about the current situation.
Relative restriction is called claustrophobia. If the patient is afraid of a closed space (where he will be during the diagnosis), you should choose a clinic with open-type tomographs. Typically, the procedure occurs without consequences for patients with titanium implants.
However, people who have structures made of other types of metal and electronic devices (insulin pump or defibrillator) in their bodies should not undergo MRI of the brain. The presence of such objects in the body can distort the results of the study, disable the device, as well as the devices themselves implanted into the body.
Where can I do it in Russia?
There are a large number of MRI diagnostic centers in the Russian Federation. Most city medical institutions are ready to provide such a service. The largest private clinics:
- "Invitro". Over 20 years of operation, this private laboratory has gained the trust of doctors and patients. Now it has 700 offices open not only in Russia, but also in other CIS countries.
- "Hemotest". This laboratory has been operating since 2003.
- "Skliflab". This laboratory is subordinate to the Research Institute named after. Sklifosovsky.
- SM Clinic, part of a holding company founded in 2002.
- "Capital". There are four Moscow ones. These are 4 diagnostic centers that specialize specifically in MRI. Their specialty is 24/7 operation.
- "Medsi". This network is the largest in Russia. It includes clinics in Moscow and the regions, including children's clinics, diagnostic centers, and sanatoriums.
Do you need to prepare for an MRI of the brain?
No special preparatory actions are required from the patient. There is no need to stop taking previously prescribed medications or change your lifestyle. To undergo an MRI of the brain, you will need to request an appointment in advance. You can do this quickly and without problems at mrt-v-spb.ru, where dozens of medical centers in the city are presented with a brief description, current prices and technical criteria for equipment.
If the person being examined has built-in metal implants in the body, you will need to notify the doctors of the clinic where you are going to be examined in advance. The patient will need to take with him a document for the design or electronic device, which contains a column about compatibility with research equipment.
When planning to undergo an MRI of the brain with contrast, you should have a light snack 40 minutes before the session. This will help reduce or completely eliminate the patient from vegetative processes when the dye is administered. It is better to come to the procedure in loose and loose clothing without metal fittings, in which you will be comfortable lying.
On the day of the MRI, it is best to leave jewelry at home. Women are not recommended to wear makeup as some cosmetics contain traces of metals. Before the diagnosis, the patient will need to leave electronic devices in a safe. It will not be possible to enter the office with a smartphone, watch, player, hearing aid or other devices. If you are concerned about the safety of things, it is better to leave them at home.
Examination of pathologies using MRI involves checking the head. Problems appear in people with metal structures located in the mouth. Braces or dental implants can create artifacts that can distort the image and make it difficult to interpret the data.
Having studied the properties of the material from which the structure was created, the radiologist can change the tomograph settings or recommend an alternative diagnostic method to the patient. If there is an urgent need for an MRI, you will probably need to remove the orthodontic device for a while.
Interesting but true
Endoprostheses can degrade the quality of the resulting images. Metal can seriously distort the image. It is also important to remove all metal objects from your pockets and remove jewelry.
Interestingly, even a tattoo can negatively affect the study. There may be metal particles in the paint. Therefore, a tattoo is a contraindication for MRI. Its owners will not only receive incorrect results, but will also suffer from severe pain during the procedure.
The picture will be ruined by braces. You must notify a specialist about their presence. They must be removed during examination.
Brain MRI technology
The electromagnetic scanning method is carried out as follows:
- The patient fills out documents at the reception desk at the clinic, where you can make an appointment through. You will need to provide results of past examinations and tests related to your current medical condition, as well as a referral from a doctor (if you have one).
- The subject goes to the diagnostician’s office for consultation, clarification of the absence of restrictions and instructions on the norms of behavior inside the scanner;
- The patient goes into the diagnostic room, lies down on a mobile table, taking a comfortable position.
- The technician may secure the limbs and heads with fasteners to prevent accidental uncontrolled movements during the session.
- During the screening, the entire medical staff leaves the diagnostic room and monitors the process through a glass barrier in the next room.
- When an MRI with contrast is prescribed, an additional enhancer is administered intravenously to the patient before starting the device.
- After completing the examination, the doctor will help the patient get up, take him to the locker room and hand over personal belongings.
Test results can be waited in the break room for 15 to 60 minutes or collected the next day. The patient can also ask the doctor to send the answers by email.
Interpretation of brain MRI results
A radiologist is responsible for compiling a description of the diagnostic procedure performed. After an MRI, a series of informative images are obtained, which helps the physician to carefully examine the anatomical structure of the intracranial areas. During the study, the main criteria and detected signs of anomalies are noted. The radiologist deciphers in detail all existing foci of a pathological nature and indicates their volume. At the conclusion of the diagnosis, a conclusion is drawn up about the structure of the organ.
If necessary, the doctor makes recommendations regarding additional procedures or a follow-up examination after some time. The diagnostician may advise the patient to consult with specialized doctors. MRI information is used to make a correct diagnosis, draw up an adequate treatment regimen, and also when planning surgery.
Is it safe to have an MRI of the brain?
An examination based on the electromagnetic method does not harm the patient’s health in any way. It does not involve an ionizing load on the body, which means that the safety of MRI can be compared with ultrasound screening. But the accuracy and information content of tomographic testing is many times higher than that of ultrasound. You are allowed to undergo MRI an unlimited number of times without a long recovery period. The examination can be combined with any other types of hardware or instrumental screening on the same day.
Which is better: CT or MRI of the brain?
The computer monitoring method is based on exposure to radiological radiation. The advantages of the study are the speed of implementation, high levels of information content regarding bones and blood vessels (with contrast). The disadvantages of diagnostics are related only to the radiation exposure to the patient’s body, so there are restrictions on the number of permissible sessions. CT scanning is not performed during pregnancy or children.
It is impossible to determine whether it is better to do an electromagnetic or computer test. CT and MRI of the brain are complementary studies, each of which can be more relevant in a certain clinical situation. Computer scanning is prescribed for:
- damage;
- likelihood of parasitic infection;
- bleeding;
- signs of complications of acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- detection of areas of calcification.
MRI of the head is recommended by doctors to identify ischemic processes, neoplastic lesions and inflammation. The method helps in visualizing vascular diseases that do not cause ruptures in the walls of arteries and veins. For in-depth research, angiographic diagnostic mode or contrast is used.
In some cases, the results of MRI alone are sometimes not enough to make a diagnosis. Therefore, doctors prescribe directions to the patient for two procedures at once in order to collect as much information as possible about the lesion and reduce the chance of an erroneous medical conclusion to a minimum.
MRI: stroke or multiple sclerosis
It is almost impossible to distinguish MRI images of stroke and multiple sclerosis from each other. Because stroke is a sudden disorder, multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune “sluggish” disease that affects brain tissue for years (people live with lesions of multiple sclerosis in the brain for more than 40 years after discovery).
What do pathological changes look like on the pictures? In the picture it looks like a lighter, asymmetrical spot with jagged edges (since the picture is a negative, doctors call it a darkening). The formation can deform and displace other structures (ventricles, subcortical centers). Tumor growth, as a rule, is accompanied by the rapid development of additional vessels in the affected area, so contrast is used to analyze volumetric processes.
With the development of an ischemic stroke, a zone of brain hypoxia appears; on an MRI of the head it will appear lighter in color, but unlike a tumor, the spot will correspond to the area of innervation of one of the cerebral arteries. With contrast, blood supply to the stroke area will be reduced. The smoothness of the furrows and convolutions above the affected area can be determined.
Where can I get an MRI of the brain?
Using our search service you can select top-rated and reliable clinics in the city. You will find verified information about each organization: a brief description, current prices, promotions, information about the medical team and technical indicators of tomographs, work schedule, as well as reviews from visitors.
Users are provided with a clear search system for medical institutions for MRI, which can be found near the metro or in a specific area. Additionally, there is an online map with verified addresses and a panel for sorting clinics by price and rating. Registration for diagnostics is carried out remotely.
To make an application to see a doctor at a convenient time and date, call the hotline. Operators provide free consultations and record daily from 8 am to 12 midnight. Call now to get a discount of up to 1,000 rubles on an MRI of the brain.
List of sources used:
- Kornienko V.N., Pronin I.N., Golanov A.V. and others. Diffusion-weighted images in the diagnosis of brain gliomas // Medical visualization. - 2000. - No. 1.
- Konovalov A.N., Kornienko V.N., Pronin I.N. Magnetic resonance imaging in neurosurgery. - M.: Vidar, 1997.
- Antonova O.G. Brain stem strokes as an object of magnetic resonance imaging / Materials of the All-Russian Scientific Forum “Achievements and Prospects of Modern Radiation Diagnostics” M. 2004.
- Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B. et al, Acute human stroke studied by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging // Ann Neurol, - 1995 - Vol 37.
- Bigler ED, Kerr B, Victoroff J. el al. White matter lesions, quantitative magnetic resonance imaging, and dementia H Alzheimer, Dis, Assoc. Disord, 2002, No. 3 (16).
- Dolgushin, M.B. 3D diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body in patients with metastatic brain lesions / M.B. Dolgushin, L.M. Fadeeva, A.Yu. Zaitseva // Neurovisualization: selected articles / ed. V.N. Kornienko, I.N. Pronina. - M.: TM Andreeva, 2008.
- Belichenko O.I., Dadvani S.A., Abramova N.N., Ternovoy S.K. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases. M.: Vidar, 1998.
- Barber PA Identification of Major Ischemic Change: Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Versus Computed Tomography. // Stroke 1999; 30:2059–2065.
- Kornienko V.N. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of intracranial hematomas: Abstract. report All-Union Symposium on Computational Tomography / V.N. Kornienko, A.M. Turkin. Tashkent, 1989.
- Clinical application of new MRI techniques / Yu.N. Belenkov, O.I. Belichenko, V.E. Sinitsyn and others. Medical radiology. - 1990. - No. 3.
Who needs to be able to interpret MRI results?
When deciphering MRI images, the indicators of a particular study are compared with normal sections of a healthy brain.
Different fabrics in the pictures have different degrees of staining. The lightest is the white substance. The gray looks a little darker. The bones will be the darkest. An experienced specialized doctor or radiologist specializing in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging images can correctly interpret the MRI results.
To do this, he must have in-depth knowledge of the structure of the brain, understand all its components, know their sizes, and understand what tissue they are made of. The specialist must have knowledge of physiology and pathological anatomy.
The patient himself will not be able to cope with such a complex task; in most cases, it is not worth even trying to decipher an MRI image on his own. Moreover, the diagnosis is often made jointly by the radiologist and the attending physician.
Decryption is carried out in a certain sequence:
- The tomograph sends the results to the computer. The brain is examined in 4 projections.
- The photographs are printed.
- The specialist mounts the photographs on a special backlit stand.
- The doctor examines the images in detail and also compares them with the norm.
- The radiologist writes a report, which is given to the patient. It indicates the state of all brain tissues and their shape. There must be a conclusion about whether there are pathologies.
It is extremely important to ask your doctor questions. If there are certain changes, he should tell as fully as possible what brain structures they affected, what they could lead to, and what they are connected with.
It is possible that the study will need to be completed several times. This way the doctor will be able to observe the dynamics of the process, the speed of progress of changes. In this way, it is possible to evaluate the benignity or malignancy of changes, the results of treatment of blood vessels, and their condition.