Pain in the back of the head is a fairly common problem. And she has many reasons. Therefore, it is important to find their problems in order to feel relief. Let's find out together with a specialist how to do this.
Headaches in the back of the head can have several different causes. For example, it may only be muscle damage due to a minor injury, or it may be a secondary symptom of other pathologies. The type and location of pain can play a critical role in diagnosing the cause. If the pain is severe and repeated, be sure to consult a doctor.
Causes of pain in the back of the head in an adult
“Pain in the back of the head itself does not indicate the cause of this pain,” explains neurologist Elena Gaivoronskaya.
– The doctor assesses the frequency of pain, its intensity, duration, nature (pulsating, pressing, stabbing), associated symptoms. Only on the basis of all this data can a diagnosis be made. There are a number of reasons why headaches may occur predominantly in the back of the head.
headaches .
This is the most common cause of pain in the back of the head. Such pain can last from 30 minutes to 7 days. Such pain can be caused by severe stress, overwork, lack of sleep, malnutrition, poor posture or not drinking enough water.
Patients with this problem usually feel tension in the back or front of the head. The pain can range from dull to severe.
Migraine.
Another common type of headache that often appears in childhood and gets worse with age. Migraines are most common in women. Its symptoms include severe pain on one side of the head with nausea, vomiting and blurred vision. Patients are usually sensitive to light, noise, or smell. Physical activity may increase pain. It can last from several hours to several days.
Causes of migraines include emotional or physical stress, environmental and dietary changes. Sometimes medications (such as birth control pills) can also cause migraines.
Overuse of medications or recurring headaches.
These headaches can develop if a person takes too many painkillers. They are very strong and are often accompanied by nausea, anxiety, irritability, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, memory loss and even depression.
Occipital neuralgia.
A rare but severe headache that usually begins at the base of the neck and spreads to the back of the head and then behind the ears. Often occurs when the occipital nerves, which run up the back of the neck to the base of the skull, are damaged or irritated. The pain is accompanied by a burning or shooting sensation and persists on one side of the head, but often intensifies with movement of the neck. The patient is usually sensitive to light.
Possible causes include spinal injury, tumors, nerve damage caused by diabetes, swollen blood vessels, and rarely infection.
Headaches during physical activity.
They occur as a result of stressful activities and often occur after physical exercise. This pain resembles palpitations and can last from 5 minutes to 2 days.
Often occurs after heavy weight exercise or running. But sometimes they happen after sexual intercourse or pushing in the toilet.
Headache due to arthritis.
It appears in the back of the head and intensifies with movement. May be the result of arthritis of the first, second or third vertebra. Either it is associated with changes in the bone structure of the neck or inflammation of the blood vessels in the head.
In addition, the cause of a headache in the back of the head can be:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- high blood pressure;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- stress;
- brain tumors;
- brain aneurysm;
- subarachnoid cerebral hemorrhage;
- cervical spine injuries and traumatic brain injuries;
- meningitis.
Diagnostics
First of all, you should contact a therapist and describe the disturbing symptoms. The doctor will immediately be able to:
- measure blood pressure, because such complaints may be the cause of the onset of a hypertensive crisis;
- determine the pulse rate and decide to take an electrocardiogram to exclude cardiac arrhythmias;
- palpate paravertebral points and spinous processes, identifying painful sensations in the spine.
If pressure and heart rate are within normal limits, and changes are detected in the spine, further diagnostic measures are necessary and consultation with a neurologist is necessary.
In the absence of signs of cardiovascular disorders, to accurately determine the causes of a headache in the back of the head and select effective remedies to eliminate it, you need to consult a neurologist. A doctor’s appointment includes clarification of the complaint, collection of a history of the development of the disease, as well as clarification of the presence of a hereditary predisposition to certain disorders. At the first consultation, the neurologist will set the level of pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS), check pain points in the paravertebral areas and along the peripheral nerve trunks. A detailed neurological examination is also required, during which the following is assessed:
- patient position;
- level of consciousness;
- presence of signs of injury;
- breathing rhythm;
- eye movement and pupil size;
- muscle tone of the face, tongue, pharynx;
- hearing level;
- stiff neck;
- the amount of muscle tone on both sides of the body;
- presence of limited active and passive movements;
- tendon reflexes;
- coordination of movements;
- presence of sensory disturbances.
The examination will allow us to make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe those research methods that will most help establish the final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
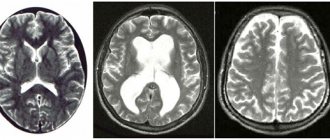
Despite the fact that the main cause of headaches in the back of the head is diseases of the spine, changes in the brain itself cannot be ruled out. Therefore, electroencephalography (EEG) and even MRI of the brain are sometimes indicated.
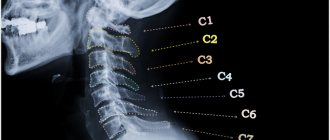
X-ray of the cervical spine
X-ray of the cervical spine is a routine diagnostic procedure and does not require a long time. As a rule, the study itself lasts no more than 3-5 minutes.
X-rays of the cervical spine are taken in an upright position with the patient sitting or standing. This is necessary to obtain images under natural physiological stress.
A functional x-ray examination of the spine is often indicated. It allows you to register disturbances in the motor function of intervertebral discs at earlier stages of pathological processes, and to identify forward or backward displacement of the vertebrae. The essence of the study is to take radiographs of the cervical spine with maximum lateral tilt in the direct projection or maximum flexion and extension in the lateral projection.
Displacement of the vertebrae indicates a loss of the fixation ability of the disc, that is, the initial manifestations of osteochondrosis.
MRI
MRI diagnostics are carried out in specially organized rooms. No special preparation is required to carry it out. However, the research procedure itself will take more time than, for example, x-ray diagnostics. To do this, you will need to set aside about an hour in your schedule.
This study has become widespread due to its high information content and the possibility of making a diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. When examining the cervical spine, it is possible to assess the condition of the cervical vertebrae, intervertebral discs, adjacent soft tissues, nerves, blood vessels and the spinal cord. The area of study can be examined down to a millimeter, which helps identify pathology in the early stages. The changes revealed by this diagnostic method coincide with the X-ray ones: a decrease in the height of the vertebra and intervertebral foramina, changes in the intervertebral discs, protrusion and hernia.
Ultrasound of head and neck vessels
Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck is a common diagnostic method that does not require special preparation. It takes about 20 minutes and the result is given by the ultrasound doctor immediately after the procedure.
The method allows you to assess the condition of the inner wall of the vessel, the speed of blood flow and makes it possible to conduct functional tests. Most often it is used to identify developmental anomalies, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques leading to narrowing of their lumen, the presence of external compression, including intervertebral hernias or deformed vertebrae. Ultrasound results complement MRI.
Modern methods of treatment
Treatment methods depend on the diagnosis.
Tension headaches.
They are usually treated with painkillers, massage and sometimes meditation. However, frequent tension headaches require medical supervision.
Migraine.
Treatment for this disease includes painkillers and rest in a darkened room. Doctors often recommend lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, and anti-migraine medications such as triptans to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines.
Returning pain.
The best treatment for this type of pain is to stop taking painkillers. Yes, at first the headaches get worse, but they go away quickly.
In severe cases, you should consult a doctor - physical or behavioral therapy may be required to break the habit of using analgesics.
Occipital neuralgia.
It can be treated with heat compresses, rest, massage, physical therapy or painkillers. Severe pain may require oral muscle relaxants, nerve blocks, steroid injections, or local anesthesia. In rare cases, surgery is necessary to relieve pressure on the nerves or block pain impulses to that part of the body.
Pain during physical activity.
Taking painkillers before exercise can solve this problem. In addition, it is important to avoid stress, eat right and get enough sleep.
Pentalgin
"Pentalgin" is also a complex medicine that has anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and antipyretic effects. "Pentalgin" slows down the production of hormones that cause pain. Usually, taking one tablet is enough to relieve a headache. It is recommended not to exceed a dose of three Pentalgin tablets per day; you can be treated with this drug for no more than five days.
Pentalgin
OJSC Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia
— pain syndrome of various origins, incl.
pain in joints, muscles, radiculitis, algodismenorrhea, neuralgia, toothache, headache (including those caused by cerebral vasospasm); — pain syndrome associated with spasm of smooth muscles, incl. for chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, renal colic; — post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome, incl. accompanied by inflammation; - colds accompanied by febrile syndrome (as symptomatic therapy). from 57
822
- Like
- Write a review
Popular questions and answers
We asked neurologists to answer questions related to headaches in the back of the head.
When can a headache in the back of your head be dangerous?
“Such symptoms,” says neurologist Olga Zincheva, “can include:
- concomitant increase in body temperature;
- weakness, awkwardness;
- numbness and tingling in the limbs or one limb;
- prolonged increase in pressure, difficult to reduce;
- severe headaches;
- headaches are accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- double vision, impaired consciousness.
When to see a doctor for a headache in the back of the head?
“There are signs,” explains Olga Zincheva, “that require medical attention:
- you have a headache for the first time for no apparent reason;
- pain lasts several days;
- there are concomitant diseases.
“You need to go to the hospital immediately,” adds colleague Elena Gaivoronskaya, “if the headache occurs suddenly, it is very intense, there was no such pain before, or if the pain is accompanied by weakness in the limbs on one side of the body, a distortion of the face, speech disorder, or lack of coordination. If you have other alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor as planned. You should also see a neurologist if you are taking too many pain medications or if your headaches are affecting your quality of life.
Top 9 drugs for headaches depending on its cause.
June 1, 2021
10878
3.3
1
Content
- Why does my head hurt?
- Groups of drugs for headaches
- Analgesics
- Antispasmodics
- Vasoconstrictor drugs
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- The most effective pills for headaches
- Aspirin
- Paracetamol
- Citramon
- Tempalgin
- Pentalgin
- Spazgan
- Nurofen
- No-Shpa
There is probably not a single person who has not experienced a headache at least once in his life. Moreover, this also applies to absolutely healthy people. Headache varies in severity, often impairing quality of life and reducing performance. Therefore, there are head pills in every home medicine cabinet.
But you need to understand that there is no universal remedy for headaches, because there are about 40 causes that cause them. And only a doctor can determine exactly why you have a headache. If you need to quickly relieve pain, we suggest you at least figure out which headache medication you need to take in a particular case.
Read also How to treat migraine: the best drugs Top 5 best drugs against migraine
Ways to prevent headaches
Pain in the right occipital part of the head can be prevented at home. To do this, you should follow several rules recommended by doctors:
- monitor your posture while walking and working in a sitting position;
- devote time to physical activity every day, carry out moderate loads;
- get rid of excess weight - it becomes a source of problems with joints, blood vessels, and metabolic disorders;
- Maintain a healthy diet with sufficient vitamins and minerals.
Pain in the back of the head on the right is a symptom that is important to pay attention to in time. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain recommend contacting for diagnosis at the initial stages. Most diseases that cause headaches can progress and lead to dangerous consequences. However, this can be prevented if the cause is addressed in the early stages.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 17 votes
Share article on social networks
We turn to folk knowledge
You should not neglect proven folk methods. But we must remember that all home remedies are designed to maintain and enhance the basic traditional treatment. Before starting therapy, consultation and obtaining permission from the treating doctor is required.
- Oregano will help cope with headaches. Regularly drinking medicinal tea can reduce muscle tension and help blood vessels.
- A decoction of medicinal herbs will strengthen your defenses. Pour boiled water over lilac flowers, cornflowers and thyme and leave for 50 minutes. Drink 2 times a day.
- Infusion of onion peels. Pour boiling water (1 cup) over the husks and let it brew for 2 hours. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day. Prepare fresh product every day.
If the back of your head begins to hurt on one side (the pain is sharp and growing), do not self-medicate, remember that this can be dangerous.
Why at night?
At night, the human body works differently than during the day. He is more relaxed, the metabolic and restoration processes work practically without external irritants. Therefore, malfunctions in the human body and brain manifest themselves more clearly, more intensely - in the form of pain. This is a kind of signal that not everything is in order and measures need to be taken. Therefore, it is strongly recommended not to simply endure the pain, drowning it out with analgesics or using sleeping pills.
Night pain can be especially dangerous if it is accompanied by dizziness; worse when sneezing, coughing; if you notice the system in their appearance (for example, at a certain time of the night); if they roll on suddenly and very strongly. With such night headaches, it is better not to delay treatment!
A special case is night migraine. Many people are familiar with these long and frequent pains in the head, for which there are no apparent reasons. Moreover, migraine can be inherited, most often through the female line. Its causes have not yet been fully studied, but modern doctors are good at reducing the strength and frequency of such pain.
Night pain may be accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, increased heart rate, pain in other parts of the body, and panic. In addition, pain causes prolonged and chronic insomnia. This can be dangerous to your health and even life!