Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
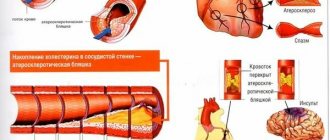
— Cardiovascular diseases — Vascular diseases of the brain
Even at rest, the human brain consumes up to 25% of the oxygen entering the body; To ensure its operation, about 15% of the total volume of circulating blood is required. Vascular diseases, narrowing of their lumen leads to hypoxia and neuron death.
People without special education cannot always recognize the first symptoms of cerebrovascular accident and miss the time when therapeutic or preventive care is most effective.
Blood supply to the brain
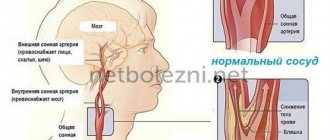
Four large arteries are responsible for the transport of oxygen and nutrients to the brain tissues: two internal carotid and two vertebral. The vertebral arteries are responsible for supplying blood to the brain stem. At the base of the brain they merge into the basilar artery.
Each internal carotid artery is divided into anterior and posterior. These vessels supply the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
At the base of the brain, the internal carotid branches, the basilar artery and the branches connecting them form a closed circle of Willis. It is named after the English doctor Thomas Willis. This anatomical formation ensures the redistribution of blood and the preservation of nutrition of parts of the brain during blockage of blood vessels. The outflow of blood from the cranial cavity occurs through the jugular veins.
Brain diseases occur when large and small vessels are damaged. Depending on the cause, symptoms occur acutely and require immediate medical attention or develop gradually, slowly leading to a deterioration in a person's quality of life.
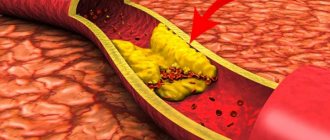
The main causes of arterial damage include atherosclerosis and hypertension. In the first case, plaques form on the inner surface of the vascular wall, narrowing the lumen of the arteries. They have a thin cover and contain lipids inside. When such plaques rupture, blood platelets adhere to the damaged surface, leading to blockage of the lumen (thrombosis). The provoking factor is often vasospasm.
Arterial hypertension also damages the walls of blood vessels: they become denser, and areas of expansion (aneurysms) appear. These vulnerabilities can cause arteries to rupture or become blocked.
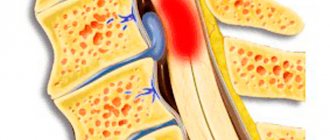
A condition in which small cerebral arteries are affected and the blood supply to the brain is affected is called discirculatory encephalopathy. Nerve cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients and die. A developed network of arteries cannot solve this problem. The process is not limited to any one area of the brain; lesions are found in various parts.
What does a CT scan of the vessels of the head and neck show?
Thanks to the CT scan of the brain and neck vessels, you can:
- study the features of the structure and relative position of veins and arteries;
- set the diameter of the vessels;
- identify atherosclerosis of artery walls;
- diagnose vasoconstriction and make an assumption about the possible cause of this pathology;
- identify the presence of collaterals (bypass routes of blood flow).
The pictures will show:
- developmental defects (malformations, aneurysms, etc.);
- stenosis, thrombosis, embolism;
- vascular networks of neoplasms;
- vasculitis;
- angiopathy of various etiologies;
- atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of the arteries;
- traumatic vascular injuries.
CT scan of the cervical arteries. On the left is a two-dimensional image, on the right is a three-dimensional image. Arrows indicate stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery
Risk factors for cerebrovascular diseases
Assessing the likelihood of vascular damage, neurologists and cardiologists say that some people are more predisposed to this group of diseases. Risk factors include such conditions, diseases and lifestyle features as:
- low physical activity;
- hypertonic disease;
- heart disease;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- smoking;
- regular stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- frequent drinking of alcohol.
In addition, the risk group includes people with a family history of hypertension, heart attack, stroke in close relatives.
Symptoms
The first signs of vascular damage to the brain may appear already at a young, working age. In this case, patients tend to ignore painful symptoms and not consult a doctor. And even when visiting a therapist or neurologist, the condition often remains unrecognized.
Among the early signs:
- absentmindedness;
- memory loss;
- fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- headache;
- noise in the head;
- episodes of dizziness;
- weather sensitivity.
Signs of circulatory problems may appear one by one. Young patients often associate them with overwork, as they believe that it is too early for them to be sick.
Over time, negative lifestyle factors lead to a deterioration of the condition - normal activities begin to suffer, severe weather sensitivity worries, and a person’s character “deteriorates.”
But sometimes the situation changes dramatically. In such cases, they speak of acute cerebrovascular accidents. How to recognize typical vascular diseases?
Encephalopathy
This diagnosis has already become “the talk of the town”: it is used to scare patients with hypertension, and it is “gifted” to old women who make scandals in pharmacies, clinics and on the street. And no wonder. The first symptoms of the disease are often noticeable behavioral, emotional and volitional disturbances. Thus, patients experience:
- irritability;
- emotional lability;
- sleep disorders;
- fatigue;
- depressive symptoms.
Relatives may notice that such a relative has become angry, sensitive to changes in weather, and his personality traits have become “sharpened.” Sentimental people become whiny, punctual people become pedantic, thrifty people become frankly stingy.
Over time, productivity begins to suffer: memory and attention deteriorate. The person becomes absent-minded, “constantly writes down so as not to forget,” but still forgets. Episodes of inappropriate, rude behavior are possible.
Discirculatory encephalopathy progresses, the course can be uniform or with sudden episodes of deterioration. It cannot be cured, you can only slow down the development of the disease. Severe encephalopathy is characterized by the development of dementia. Such a patient has completely lost self-care skills, in some cases cannot control physiological functions, and needs constant care and supervision.
Osteochondrosis often provokes or intensifies the manifestations of encephalopathy, as it impairs blood flow to the brain due to narrowing of the lumen of the vertebral arteries. Slow personality changes due to vascular damage also occur in systemic diseases accompanied by vasculitis.
Stroke
Stroke is one of the most common causes of death in people around the world. In fact, this is an acute circulatory disorder in the cerebral vessels, in which the entire brain lesion dies. According to the mechanism of development, there are 2 types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
In ischemic stroke, the lumen of the vessel is blocked. Brain cells are very sensitive to hypoxia. At first, they try to provide for themselves through anaerobic glycolysis; within a few hours, the pathological processes are reversible. But decay products gradually accumulate, and the pH of the tissue changes to the acidic side. Neurons swell, their membranes cease to perform their functions and are destroyed. The final formation of the stroke focus occurs within 2-7 days; specialist assistance is most effective during the first 3-6 hours.
With a hemorrhagic stroke, the integrity of the vessel is compromised. Blood pours under the membranes, into the parenchyma (tissue) of the brain, and breaks into the ventricles. The cause of such a catastrophe is changes in the structure of the vascular wall and fluctuations in blood pressure. Congenital or acquired cerebral aneurysm can cause sudden death or severe disability. Until it reaches a large size, there is no pressure on the brain, and there are no clinical manifestations. The condition may worsen acutely, the patient is concerned about:
- headache;
- nausea;
- double vision;
- convulsions;
- disturbances of consciousness.
A special place is occupied by transient ischemic attacks, or as they say - micro-strokes. The name “microstroke” is unscientific; it reflects the reversibility of what occurs in the patient’s tissues. Some people who have had ischemic attacks are not aware of this. Thus, patients are greatly surprised to learn about them when describing a routine computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. (“I thought it was a simple hypertensive crisis!”)
Symptoms and prognosis for cerebrovascular accidents depend on the volume and location of the lesion. It is worth recalling obvious signs, the detection of which requires immediate medical attention:
- severe headaches, often with dizziness, tinnitus;
- asymmetry of the face, it is impossible to raise your hands, smile, show your teeth;
- weakness, numbness in the arms and legs, unsteadiness of gait;
- violation of pronunciation and perception of addressed speech;
- nausea and vomiting;
- disturbance, loss of consciousness.
Treatment methods
Medication
This method is prescribed if the disease is at an early stage of development.
Typically, the patient is prescribed a whole list of medications, which includes the following types of medications:
- antioxidants;
- means aimed at narrowing blood vessels;
- satins - drugs intended to reduce cholesterol levels in the body;
- fibrates - agents that prevent lipids from concentrating in the blood;
- antidepressants;
- tranquilizers.
What is vasoconstriction and how to deal with this pathology is described in the video:
Surgical
This method is used if the vessels have narrowed by more than 60%.
The following surgical options are used to treat the disease:
- carotid endarterectomy;
- angioplasty;
- stenting.
The first option is scraping plaques from the walls of blood vessels. The second is the dilation of blood vessels, which occurs due to the installation of a special catheter. The third method is to fix a special wire frame that straightens the narrowed area.
From the editor: Game exercises for the development of memory in primary schoolchildren
Massage
This method can be considered as restorative and preventive against new diseases. Only a professional who takes into account physiological characteristics can give a massage.
He will need to provide pictures of the spine so that the specialist knows which areas need to be worked on. Typically a massage consists of stroking, rubbing and kneading movements.
This method helps relieve spasms, improve blood flow into the vessels, as well as cells and tissues of the body.
ethnoscience
In folk medicine, there is a wide variety of recipes that will help reduce the manifestation and sometimes completely eliminate vasoconstriction. However, this is only possible if the patient adheres to proper nutrition.
Hawthorn tincture:
- Pour 2 tablespoons of hawthorn fruit into 0.2 boiling water.
- Infuse the composition for half an hour.
- Afterwards, the infusion needs to be cooled and strained.
- You need to add water so that you get 1000 ml of water.
- Next, add 1 kg of sugar and one chopped lemon.
- After this, boil the mixture for 5 minutes.
- Take 1 tablespoon once a day.
A mixture of garlic and lemon.
Grind 0.5 kg, place in a one and a half liter jar and fill completely with water. Leave for 10 days to infuse. Stir the contents every day. After this, add 0.5 kg of lemon to the garlic. Mix everything thoroughly.
Take one tablespoon daily after meals.
Physiotherapy
When treating vasoconstriction of the cervical spine, an important fact is the use of physiotherapy, which includes the use of:
- pulsed magnetic fields;
- acoustic shock waves;
- mineral showers and baths;
- magnetic therapy;
- dosed exposure to electric current;
- detensor therapy;
- low-intensity laser radiation;
- ultrasound therapy.
Nutritional Features
Patients with this diagnosis need to limit their intake of foods that contain large amounts of cholesterol and fatty foods. Include more fruits and vegetables in your diet.
Animal fats, butter and even margarine are of particular benefit to patients. There should be a lot of meat.
Also, do not forget about dairy and fermented milk products, preferably low in fat. The body needs porridge and spices.
It is better to avoid pasta and coffee drinks. Herbal teas (both green and black) are of great benefit.
Diagnosis of vascular diseases of the brain
To “take care of your health and get examined,” you don’t need to wait until you reach pre-retirement or retirement age - many vascular disorders begin to develop in young people. What do we have to do? It is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations, even if “nothing bothers you,” and do not be embarrassed to “bother” the doctor with complaints about a change in condition.
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular pathology includes:
- Analysis of patient complaints. You should tell your doctor even such “minor” symptoms as: fluctuations in blood pressure, headaches, dizziness, forgetfulness, and weather sensitivity.
- Anamnestic information: age, presence of risk factors, rate of development of symptoms, concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes, systemic and rheumatic lesions).
- Examination of the patient with analysis of neurological symptoms, examination of the fundus. Body mass index assessment.
- Laboratory data: blood sugar, blood lipid profile, coagulogram, platelet count assessment. CSF analysis to detect hemorrhagic stroke.
- Instrumental diagnostic methods: CT or MRI of the head, scanning of the vessels of the head and neck, ECG.