The problem of vascular diseases of the brain is socially significant. The main cause of cerebrovascular pathology (from initial signs of cerebrovascular insufficiency to strokes) remains arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis. Yusupov's disease neurologists diagnose cerebral ischemia, ACA hypoplasia and asymmetry of cerebral blood flow using the latest equipment from the world's leading manufacturers.
Doctors at the neurology clinic use the latest medications to treat patients. With ischemia in the area of the ACA basin, the duration of recovery depends on the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the brain and the adequacy of rehabilitation measures. Rehabilitation clinic specialists use physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, acupuncture, and alternative methods of restorative therapy to restore blood flow through the PMA.
Asymmetry of blood flow in the MCA and ACA can result in ischemic stroke. At the Yusupov Hospital, complex therapy for pathology is carried out, as a result of which blood flow is restored and the brain tissue receives a sufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen. Severe cases of ischemia in the ACA basin are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. Leading neurologists are collectively developing tactics for managing patients with circulatory disorders due to ACA hypoplasia. The medical staff is attentive to the wishes of patients.
Segments
What is PMA of the brain? ACA stands for anterior cerebral artery in medicine. The blood supply to the brain is quite complex. Blood enters the brain through two internal carotid and two vertebral arteries. The carotid arteries form the carotid basin. They begin in the chest cavity: the right one from the brachiocephalic trunk, the left one from the aortic arch. The vertebral arteries form the vertebrobasilar basin. Through them, blood flows into the vessels that provide nutrition to the medulla oblongata, cervical spinal cord and cerebellum. As a result of fusion, the vertebral arteries form the main basilar artery.
The ACA (anterior cerebral artery) begins at the site where the internal carotid artery divides into its terminal branches. At the beginning of its journey, it gives off a number of small branches that penetrate through the anterior perforated substance to the basal nuclei of the base of the cerebrum. At the level of the optic chiasm, the anterior cerebral artery forms an anastomosis (ostium) with the artery of the same name on the opposite side through the anterior communicating artery.
Treatment methods
The treatment tactics for the patient are determined based on the characteristics of the pathology and the degree of its influence on the blood supply to the brain. This can be conservative treatment or surgical intervention.
As a supplement for vascular hypoplasia, experts recommend combining the main treatment with traditional methods. However, self-medication is dangerous, since medications may be incompatible with medicinal plants.
Treatment with medications
Conservative treatment consists of taking medications, the action of which is aimed at improving blood counts and tissue metabolism. In some cases, hormonal agents may be used.
It is important to remember that even if you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, the problem will not disappear, but it will protect the brain from more serious diseases.
Surgery
In an acute condition, when blood flow cannot be restored with drugs, the patient is prescribed surgery.
This is usually an operation using an endovascular technique: a special dilator is inserted into the affected vessel using an endoscope, which will subsequently hold its walls and prevent their spasm.
Hypoplasia of the ACA
The cause of sudden blockage of a cerebral vessel is often an abnormal decrease in its lumen. The reason for this is not cholesterol plaques, but hypoplasia of the cerebral artery - a pathological narrowing of the vessel. The disease is observed in 80% of older people. In addition to their congenital defect, age-related changes in blood vessels are added.
PMA hypoplasia – what is it and how does it manifest? ACA hypoplasia manifests itself in insufficient development of the right cerebral artery. The vessel has an abnormal shape. With this pathology, the structure of the blood vessels supplying intracranial structures may be disrupted. ACA hypoplasia is a congenital pathology that occurs in utero. With hypoplasia of the ACA, the nutrition of the cerebellum, brainstem and occipital lobes is disrupted. As a result of the pathology, the risk of aneurysm formation or stroke increases. Hypoplasia of the ACA is a dangerous condition, to which neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital and neurosurgeons at partner clinics pay special attention.
How to make a diagnosis
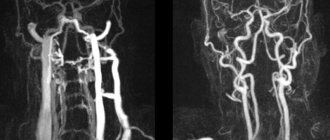
The optimal way to detect hypoplasia of the cerebral vascular system is considered to be classical angiography and its variations, for example selective research. With its help, specialists evaluate the functioning of all arteries and veins of the head, their length, and identify the presence of additional blood flow paths.
Despite the advantages, this research method has a number of contraindications:
- Allergy to iodine (which is a component of the contrast agent);
- Chronic diseases: renal failure, heart failure, pulmonary failure, oncology;
- Inflammatory processes in the body;
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Mental illnesses;
- Pregnancy.
For a pathology such as hypoplasia of the right or left vertebral artery of the brain, a specialist may prescribe Doppler ultrasound (USDG). This non-invasive research method allows you to quickly obtain information about the thickness of the walls of the affected vessel, the nature and phase of blood flow in it, the symmetry of paired structures, blood flow speed and resistive index.
Causes, symptoms and treatment
The process of formation of cerebral arteries, including the ACA, is negatively affected by the following factors:
- Drug or alcohol addiction in a pregnant woman;
- Infection of the fetus during intrauterine development;
- Intoxication of a woman’s body during gestation;
- Burdened heredity;
- Pregnant women taking medications that have a teratogenic effect.
Symptoms of the disease and their severity depend on the degree of underdevelopment of the vessel that supplies the brain. Symptoms may present differently in each patient. Some people only find out that they have hypoplastic ACA during a medical examination. Often the disease is asymptomatic.
Hypoplasia of the PMA can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Headaches of varying intensity;
- Frequent dizziness;
- Decreased or loss of sensitivity of the skin;
- Instability of blood pressure;
- Emotional disorders;
- Disorders of perception and sensations.
All of the listed symptoms indicate insufficient cerebral circulation, so if they occur, contact the neurologists of the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors will first conduct a comprehensive examination, which includes the following diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound examination and Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- Contrast angiography;
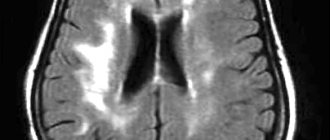
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging.
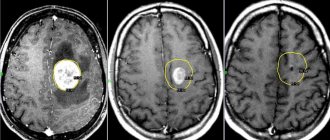
Sonologists use modern ultrasound machines that combine a triplex scanner and a Doppler unit. They make it possible to visualize the extracranial and intracranial sections of the arteries of the vertebral-basilar region and identify the asymmetry of blood flow in the MCA and ACA. To determine the state of neurons during cerebral ischemia, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed using premium devices. CT angiography of cerebral vessels at the Yusupov Hospital is performed on a modern scanner. Using it, not only step-by-step images of cerebral vessels are obtained, but also their three-dimensional model. These images can be viewed on a computer monitor, printed on film, or transferred to a DVD+R disc.
If the symptoms of cerebrovascular accident caused by dysplasia of the ACA are mild, therapy is carried out with drugs that dilate the arteries and normalize cerebral blood flow. Conservative therapy helps reduce the intensity of headaches and improve the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. When a blood clot is detected in an abnormal vessel, the doctor prescribes medications to dissolve it. Neurosurgeons at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital carry out correction of the pathology of the ACA in cases where there is no positive dynamics with drug treatment. The stenting technique is mainly used for ACA hypoplasia.
Underdevelopment of the endocrine system organs
Hypoplasia of any organ of the endocrine system, as well as hypoplasia of the central nervous system structures, is of systemic importance, since many body functions depend on the hormones they produce. Thus, underdevelopment of the adrenal glands provokes disruptions in the production of steroid hormones, without which normal metabolism and immunity are impossible. Hypoplasia of the thyroid gland in women and men is fraught with metabolic disorders. And underdevelopment of the pancreas, which produces insulin, can cause diabetes.
Cerebral vasospasm
Elderly people, middle-aged and brain-aged people are often bothered by headaches, noise and dizziness, increased fatigue, memory impairment, and decreased performance. Often patients do not take such complaints very seriously. Meanwhile, these may be signs of vasospasm in the left cerebral arteries, MCA (middle cerebral artery) and ACA (anterior cerebral artery). Cerebral vasospasm (narrowing of the lumen of the arteries at the base of the brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage due to rupture of a saccular aneurysm) can secondary cause cerebral ischemia.
After an aneurysm ruptures, the patient experiences a temporary period of improvement or stabilization until symptomatic vasospasm occurs. Neurological symptoms of cerebral spasm from the fourth to the fourteenth day after the first rupture of the aneurysm. The resulting neurological symptoms correspond to cerebral ischemia in specific arterial territories. The severity of cerebral vasospasm determines the likelihood of developing cerebral ischemia and infarction.
Signs of vasospasm in the left arteries of the brain, MCA and ACA often occur in those patients in whom early magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the brain showed layers of coagulated blood 1 mm thick or more in the sulci of the brain or spherical blood clots larger than 5 mm3 in the basal cisterns.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine the localization and severity of vasospasm in the ACA and MCA using magnetic resonance or computed tomography. To ensure an accurate prognosis, a CT scan of the brain is performed between 24 and 96 hours after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Clinically pronounced cerebral vasospasm is manifested by symptoms that relate to one or another pool of blood supply to the brain of a certain artery. When the trunk or main branches of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) are involved, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- Contralateral hemiparesis - weakness of the muscles of half the body on the side opposite to the intracerebral hemorrhage;
- Dysphasia is a speech disorder due to spasm of the arteries of the dominant hemisphere of the brain;
- Anosognosia, apraktoagnosia - a recognition disorder due to spasm of the arteries of the non-dominant hemisphere of the brain.
Signs of vasospasm in the left cerebral arteries, MCA and ACA may not be pronounced due to the fact that collateral blood flow is formed in the brain through fusion of areas of adjacent cerebral blood supply.
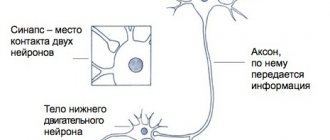
Ischemia due to vasospasm of the ACA is manifested by abulia. The patient is awake, lies with his eyes closed or open, and responds to instructions with a delay. He cannot actively conduct a conversation, but answers questions with short phrases that he pronounces in a whisper, chews food for a long time and often holds it between his gums and cheek. All focal neurological symptoms resulting from cerebral vasospasm in patients may occur suddenly, reaching maximum severity within a few minutes, or develop over several days.
If the entire brain area in the MCA basin (middle cerebral artery) is subject to ischemia or infarction, its edema develops, which can lead to increased intracranial pressure. Early magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the brain can predict an unfavorable outcome if a large blood clot is detected in the Sylvian cistern or in the lumen of the Sylvian fissure and a second significant clot in the basal frontal fissure, located between the cerebral hemispheres. The simultaneous presence of clotted blood in these areas is combined with severe symptomatic spasm of the MCA and ACA. In such a situation, superficial collaterals in the cerebral cortex from the ACA are not able to compensate for ischemia in the MCA territory.
If spasm of the cerebral arteries occurs against the background of subarachnoid hemorrhage, drug prevention and treatment are ineffective.
Because patients with cerebral vasospasm have increased blood volume and swelling of the brain parenchyma, even the small increase in intracranial volume that occurs with vasodilator exposure can aggravate neurological disorders. If a patient has severe symptomatic cerebral vasospasm, neurologists do not prescribe vasodilators.
All efforts of doctors are aimed at increasing cerebral perfusion pressure by increasing mean arterial pressure. This is achieved by increasing plasma volume and prescribing vasopressor drugs (phenylephrine, dopamine). Since treatment aimed at increasing perfusion pressure leads to an improvement in the picture of the neurological status in some patients, but high blood pressure is associated with the risk of recurrent hemorrhage, when using this method of treatment, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital determine cerebral perfusion pressure and cardiac output, and conduct a direct study of the central venous pressure. In severe cases, the patient's intracranial pressure and pulmonary artery wedge pressure are measured.
Administration of the osmotic diuretic mannitol, while maintaining adequate intravascular volume and mean arterial pressure, increases the patient's serum osmolarity. In severe cases, barbiturate coma is used to reduce intracranial pressure.
Underdevelopment of the genitourinary system
Underdevelopment of the genitourinary system manifests itself in the form of:
- kidney hypoplasia (possible underdevelopment of one kidney and absence of the second);
- underdevelopment of the testicles in men and the uterus in women, manifested by reproductive dysfunction.
During intrauterine development, a combination of both disorders is possible - from the urinary tract and the reproductive system.
In men, testicular hypoplasia can be accompanied by a reduction in the penis and scrotum. And in women with uterine hypoplasia, the ovaries, fallopian tubes and external genitalia (clitoris, labia) may not undergo such changes.
A woman’s reproductive function depends on the degree of endometrial hypoplasia of the uterus - if the inner layer of the uterus is underdeveloped, a fertilized egg will not be able to attach to the inner surface of this organ.
Causes of hypoplasia of the vertebral cervical artery segment
In most cases, hypoplasia of the cervical vertebral artery is a congenital pathology associated with a disruption of the process of differentiation of vascular tissue at the embryonic stage of development. Potential reasons could be:
- smoking and drinking alcohol by the expectant mother;
- gross violation of the recommendations of a doctor monitoring the development of pregnancy;
- work in environmentally hazardous production conditions;
- insufficiency of vitamins and minerals in the diet (for example, folic acid).
In an adult, hypoplasia of a segment of the vertebral artery is a common complication of long-term cervical osteochondrosis. This is a dystrophic degenerative disease characterized by the gradual destruction of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. Here, important radicular nerves responsible for the innervation of the coronary and cerebral circulatory system depart from the spinal cord.
Physical deformation of the cervical spine can cause the vertebral arteries to narrow and become deformed as they enter the foramen ovale. Subsequently, the area below is expanded. In this place, gradual hypoplasia begins.
In the practice of a vertebrologist, there are cases of left-sided and right-sided disease. Bilateral hypoplasia is a rare form of pathology. Right-sided vascular pathology is diagnosed in approximately 10% of the adult population of our country. The left-sided form is more common in adolescents and older people.
The reasons for the development of hypoplasia of the vertebral artery are:
- metabolic disease;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and accompanying protrusions, hernial protrusions;
- poor posture in the cervical and thoracic spine;
- displacement of the vertebral bodies (partial dislocation of the first vertebra (atlas) is particularly dangerous);
- absorption of the first cervical vertebra by the occipital bone (assimilation);
- muscle tonic convulsive syndrome;
- spondylosis and ankylosing spondylosis;
- injuries of the neck and collar area.
Predisposing factors for the development of this vascular disease may be:
- work in a static position with tension in the muscles of the neck and collar area;
- wearing clothes with stiff and constricting collars, excessively tightening ties and scarves;
- improper organization of the sleeping place (during night sleep, the neck muscles completely relax, as a result of which the configuration and location of the vertebral arteries changes);
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle, as a result of which the tone of the muscles of the neck and collar area is lost.
Only an experienced doctor will be able to identify the exact causes, who will compare the data from the anamnesis, objective examination and clinical diagnostic studies. After making an accurate diagnosis, it will be possible to carry out comprehensive treatment, which will result in a significant improvement in the patient’s condition.
Treatment of vertebral artery hypoplasia
It is useless to talk about how hypoplasia of the vertebral artery is treated with pharmacological drugs, since such therapy does not give any less positive results. Only an integrated approach can improve the patient’s condition and restore his mental performance. It includes a mandatory search and elimination of the potential cause of the development of vertebral artery hypoplasia. Then the doctor’s main task becomes restoring blood flow to the cerebral structures.
Effective treatment of vertebral artery hypoplasia using manual therapy methods includes:
- pharmacopuncture and reflexology – the processes of restoring the physiological tone of the cerebral blood vessel are launched;
- therapeutic exercises and reflexology – the muscles of the neck and collar area are strengthened, the nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs is enhanced;
- osteopathy and massage - tissue elasticity and their susceptibility to other treatment methods increases.
If you require treatment for vertebral artery hypoplasia, you can sign up for a free initial consultation with a vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. Call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit.