Spinal stroke is a type of myelopathy (diseases of the spinal cord of a neurological nature). Among all strokes it accounts for 1-1.5% of cases. Also, as in the case of the brain, it has two forms:
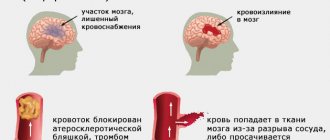
- Ischemic stroke (infarction) of the spinal cord - cessation of blood supply to a certain area of the brain and hypoxia.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of a blood vessel and bleeding into the spinal cord.
Transient disorders of the spinal circulation and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes) can also be observed.
A distinctive feature of a spinal stroke is that it usually occurs at a younger age than a cerebral stroke, at 30-50 years. Without adequate treatment, it is extremely rarely fatal, but often leads to disability.
| Treatment in a hospital setting | |
| Complex treatment in the rehabilitation department of the 3rd category of complexity (1 day)* | 6600,00 |
| Complex treatment in a rehabilitation center of category 2 (1 day)* | 7900,00 |
| Complex treatment in a rehabilitation center of 1st category of complexity (1 day)* | 12300,00 |
| Accommodation of an accompanying person in the ward (1 day) | 1750,00 |
| Stay in the department (1 hour) | 110,00 |
| Individual care from a nanny at home (1 day) | 2300 |
| Additional care by a junior nurse (1 day) | 600,00 |
| Individual post of a junior nurse (1 day) | 1100,00 |
| Mechanotherapy | |
| Stander BALANS (duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| Motomed (duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| KRD (cardio training, duration 30 min.) | 600,00 |
| Rehabilitation therapy | |
| Locomotor therapy (duration 60 min.) | 750,00 |
| Locomotor therapy (duration 30 min.) | 580,00 |
| Kinesiotherapy (duration 60 min.) | 750,00 |
| Kinesiotherapy (duration 30 min.) | 630,00 |
| Occupational therapy (duration 60 min.) | 630,00 |
| Occupational therapy (duration 30 min.) | 520,00 |
| Speech therapy (duration 60 min.) | 550,00 |
| Speech therapy (duration 30 min.) | 450,00 |
| Speech therapy in the department | 450,00 |
| Psychological correction | 550,00 |
*Comprehensive treatment in the department includes:
- comfortable stay in the ward;
- balanced individual nutrition;
- constant medical and advisory assistance from the attending physician;
- classes in kinesiotherapy and ergotherapy halls using special equipment (balance trainer, bobat tables, motomed, wheelchair).
The Center also provides services:
- consultations with narrow specialists;
- laboratory diagnostic examinations;
- injections, manipulations and procedures.
Causes of spinal stroke
The causes of a spinal cord stroke do not lie in the spinal cord itself, but in problems with the blood vessels that supply it. Provoke the development of the disease:
- atherosclerosis and blockage of arteries,
- rupture of a blood vessel due to injury or due to blockage,
- physical compression of the arteries (osteochondrosis, vertebral listhesis, herniated discs, tumors in the spine,
- congenital anomalies of vascular development, vascular malformations,
- aneurysms (often of the aorta),
- phlebeurysm,
- myocardial infarction and a sharp drop in blood pressure,
- bleeding disorders (hemophilia, thrombocytopenia)
Development of stroke
The process of development of ischemic spinal stroke will always depend on the reasons that caused the arrest of blood circulation in the spinal cord. If the latter occurred due to a detached blood clot, then symptoms will develop literally over the next few minutes. In other cases, symptoms will appear completely within a few hours.
Further symptoms of a developing ischemic stroke will depend on which particular vessel has stopped the flow of blood to the spinal cord. If there is a blockage of the spinal artery, then paralysis of the limbs begins, the normal activity of the bladder and intestines is disrupted, the skin becomes not as sensitive as before, especially on the arms and legs.
If the main focus of the stroke is concentrated in the cervical spinal cord, then the patient is characterized by a flaccid type of paralysis in the upper limbs, which is usually accompanied by a decrease in muscle tone. Spastic paralysis may also occur in the lower extremities, which is characterized by increased muscle tone. In case of damage to the thoracic spinal cord, paresis of the legs or flaccid paresis of the legs with fecal retention begins (if the lesion is localized in the lumbosacral region).
Symptoms of a spinal stroke
Signs of a spinal cord stroke can vary depending on the location and extent of the injury. The most characteristic neurological symptoms are:
- back pain (region of the spinal column),
- if the upper spine is affected - paresis or paralysis of the arms,
- leg pain, instability, transient lameness,
- paresis and paralysis of the legs are possible,
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (random urination or defecation),
- sensory disturbances in the back and limbs.
Difficulties in diagnosis arise due to the fact that pain can radiate to different parts of the body. Also, due to the connection of the spinal cord with the internal organs, many non-specific (non-neurological) symptoms are observed, and therefore a stroke can be mistaken for multiple sclerosis, spinal hernia, radiculitis, nephritis, inflammation of the bladder, gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, duodenitis , colitis), “women’s” diseases and so on.
Types of spinal stroke and their signs
Circulatory disorders of the spinal cord can occur in hemorrhagic, ischemic and mixed types. Ischemic stroke is more often recorded in people over 50 years of age; it is formed as a result of compression or blockage of a vessel. Symptoms of ischemia increase gradually, long-term consequences become apparent within a week to several months. Focal symptoms depend on the location of the damage and its volume. The most commonly diagnosed symptoms are:
- Weakness in the limbs that goes away on its own;
- Loss of sensitivity in the limbs;
- Pain in the muscle area;
- Urinary disorders;
- Pain in the spine.
There are certain syndromes that can be used to suggest the location of the damaged area. Ischemia of the spinal and vertebral arteries is manifested by bilateral paralysis of the limbs, sensory disturbances, sphincter paresis, and respiratory distress. Damage to the posterior spinal artery is accompanied by disturbances of superficial sensitivity, tremors of the hands, and paresis of the legs. Damage to the vertebral and radicular arteries causes paresthesia, disruption of muscles and joints, and convulsive muscle twitching. Ischemia of the radicular arteries leads to the appearance of girdle pain, changes in temperature sensitivity, increased knee reflexes, decreased abdominal reflexes and other signs.
A hemorrhagic stroke of the spinal cord is formed due to the rupture of a vessel and further hemorrhage under the membranes (hematorachis) or into the brain tissue. When hemorrhaging into the substance of the spinal cord, the patient experiences girdle pain, paralysis of the limbs of varying degrees, sensitivity disorders, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs. Hemorrhage under the membranes is recorded extremely rarely; it is accompanied by sharp pain and symptoms of brain damage, which lasts several days.
If unfavorable symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, since the outcome and consequences of the disease depend on the speed and quality of care. You can undergo a full examination, comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital.
Diagnosis of spinal cord stroke
As already mentioned, a spinal stroke can masquerade as many other conditions, but the common symptom that is always present is back pain. Of course, there are a huge number of causes of back pain, but the presence of such a symptom should always be alarming. Therefore, if there is such a complaint, an experienced neurologist will immediately prescribe:
- x-ray of the spine
- computed tomography of the spinal cord
- revazography or vascular Doppler
- electroneuromyography
- spinal tap
- laboratory blood tests
Based on the results of the studies, a repeated consultation with a neurologist is carried out and treatment is prescribed.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing spinal strokes, it is important to determine the stage of development of the pathological process and the mechanism of its triggering. The list of instrumental examinations includes:
- computed tomography of the spinal column;
- collection of cerebrospinal fluid (lumbar puncture);
- spinal angiography;
- electroneuromyography of muscle tissue.
The reason against which the disease began to develop is determined together with highly specialized doctors and general practitioners (therapist, hematologist, endocrinologist, etc.). Laboratory diagnostics involves a detailed blood test, coagulogram, etc.
Treatment of spinal stroke
As in the case of a stroke of the brain, in case of a spinal stroke the main actions in the acute period are aimed at maintaining the vital functions of the body, eliminating the cause of the stroke, restoring the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and normalizing blood pressure. Blood thinners are prescribed (if the cause was a blood clot), myelorelaxants, and neuroprotectors. In some cases, surgical restoration of damaged vessels may be required. If the patient is paralyzed, bedsores and congestive pneumonia are prevented.
Kinds
Spinal cord stroke occurs in several forms:
- ischemic. Ischemia is a circulatory disorder caused by prolonged spasm, compression or narrowing of the lumen of the artery supplying nervous tissue. As a result, a section of the spinal cord deprived of nutrients gradually dies, that is, undergoes necrosis;
- hemorrhagic. This type of stroke occurs as a result of hemorrhage caused by a violation of the integrity of the arterial wall;
- mixed. The pathogenesis of mixed spinal stroke is as follows: first, bleeding develops, which leads to reflex vascular spasm and the development of an ischemic zone.
Damage to the vessels supplying the spinal cord can lead to spinal stroke
Rehabilitation after spinal stroke
Depending on the complexity of the disease, the consequences of a spinal cord stroke may be completely unnoticeable or minimal (mild tremor of the fingers, transient loss of sensation in the skin of the back). However, a stroke is often accompanied by impaired motor functions of the limbs and even paralysis. To return the patient to normal life, physical rehabilitation cannot be neglected. The Aximed Neurology Clinic offers the services of its rehabilitation center.
- The neurologist will assess the patient’s condition and determine whether it is possible to begin rehabilitation measures (the optimal start of rehabilitation is 1-3 weeks after the patient’s condition has stabilized).
- The rehabilitator will draw up an individual program of physical exercises and physiotherapeutic procedures, and will adjust it as the course progresses.
- The rehabilitation room is equipped with the latest simulators, orthoses and robotic rehabilitation complexes.
- You can visit the hall while staying in a “full” hospital setting or as a day hospital.
It is important to remember that after a spinal stroke, the spine forever remains the “weak spot” of the body. During the recovery period, it is worth taking care of supporting corsets and orthopedic mattresses/pillows. However, over time, the corset will need to be abandoned, since constant wearing of it can cause dystrophy of the back muscles, can cause curvature of the spine, disc instability and increased stress on the spinal cord.
Also, for patients who have suffered a spinal cord stroke, in order to avoid repeated circulatory disorders (including the brain, because there is only one area of the disease), it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet, monitor your weight, blood pressure and sugar levels / cholesterol in the blood), take a daily walk in the fresh air, give the body light physical activity, and harden up.
Spinal stroke: who is at risk and what the consequences may be
There are not many residents of our country diagnosed with spinal stroke - only 1-1.5% among both women and men. Age category – from 30 to 70 years inclusive. But the rhythm of modern life shows that many diseases, including spinal cord stroke, are getting younger.
In order to reduce the likelihood of this disease occurring, you must:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- eat right, watch your weight;
- get rid of bad habits;
- if you have chronic diseases, follow the recommendations of your doctor;
- Monitor your health and undergo medical examination on time.
Causes and types of damage to the spinal column
The following can lead to acute disorders of spinal circulation:
- acquired or congenital pathological changes in the blood vessels of the spinal cord;
- neoplasms, broken vertebrae due to injuries, enlarged internal organs and other processes that exert external pressure on the blood supplying vessels of the spine;
- complications after surgery on the aorta or spine.
As a rule, the disease does not occur on its own, so when making a diagnosis it is important to determine the main factor that caused the pathology and the form of the stroke.
There are hemorrhagic and ischemic forms of stroke.
The first form is characteristic of relatively young patients and is a hemorrhage directly into the spinal cord. This pathology often occurs due to high blood pressure and weak vessel walls. The clinical picture is characterized by rapid development and requires emergency care. According to indications, surgical intervention is often required.
The second form is more common in elderly patients and is characterized by necrosis of part of the spinal cord tissue due to cessation of blood supply as a result of compression of blood vessels or their blockage by a blood clot. It is important to remember that ischemic lesions in the initial stages are reversible.
Prevention of pathology is carried out in the following areas:
- early detection and treatment of the disease;
- cholesterol control;
- preventing the development of atherosclerosis;
- prevention and treatment of back diseases such as osteochondrosis, protrusion , spinal hernia
; - visiting a doctor at the slightest deviation in the functioning of the back or other organ;
- weight control;
- active lifestyle.
You need to be attentive to yourself and your loved ones, and if discomfort occurs, do not endure the pain - contact a specialist, because it is much easier to prevent serious consequences than to restore precious health.
Symptoms of a spinal stroke
Symptoms appear suddenly: from a few minutes (less often hours), but it is not easy to diagnose, the symptoms are similar to the manifestations of other diseases:
- short-term weakness;
- numbness;
- burning and tingling muscles;
- impaired coordination of movements and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system;
- problems in the functioning of the body's cardiovascular system.
The main difference is considered to be a disorder of the pelvic organs, which includes impaired urination, the manifestation of pathological processes in the brain (loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, general weakness).
If such signs are present, you should immediately call an ambulance, ensure that the patient is in a horizontal position, rest, and an influx of fresh air before it arrives, and do not allow panic. The sooner you seek professional help, the fewer consequences the disease will have. Only early diagnosis and timely treatment will avoid tragic consequences.
Main directions of treatment
The patient is hospitalized in a hospital, where a full medical examination is carried out. The choice of one or another direction of treatment is made only after a high-quality and complete history collection. A full examination is necessary to more accurately determine the location of the rupture or occlusion. For this purpose, advanced methods are used, such as computed and magnetic resonance imaging, blood clotting analysis, blood sugar level measurement, and in exceptional cases, cerebrospinal fluid is taken. To determine the cause, consultations with specialists such as a cardiologist, therapist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, and hematologist are required.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, eliminating edema and compression of the vascular walls. The patient needs to take the prescribed painkillers, decongestants and venotonic drugs in a disciplined manner.
Additional measures include the appointment of physical therapy, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, ozorkit and paraffin applications, magnetic therapy), spinal massage
, wearing a corset and sleeping on a thick mattress.
What's next?
Pathology has a positive outcome in most cases. It should be remembered that the earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis of the disease.
If a person seeks help late, this leads to large-scale death of nerve endings and entails all sorts of problems:
- muscle weakness;
- lack of sensitivity (partially or completely) in the limbs or the body as a whole, loss of two-dimensional spatial sense is not excluded;
- problems in the functioning of the excretory system of varying degrees;
- decreased potency.
The recovery period lasts for several years.
Twice a year, drug treatment, massage courses, acupuncture, physiotherapy and regular exercise therapy are prescribed, in some cases the wearing of orthopedic shoes is required. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms
Spinal ischemic stroke develops in four stages, each with its own clinical picture.
Stage 1: precursor stage
The duration of the stage can be anything: from several minutes to several months. A short duration of the stage most often occurs when a vessel is blocked or when an artery is compressed during an injury. And in the case when a slow cessation of blood circulation occurs, for example, a tumor grows, which gradually blocks the ability of blood to circulate normally, this is a long period of precursors.
Symptoms of this stage include the following changes:
- Pain in the spine.
- Intermittent claudication, in other words, weakness and numbness in the legs during prolonged walking or standing. The symptom occurs due to oxygen starvation of the spinal cord, which is responsible for the movement of the lower extremities, as well as due to poor blood circulation in the vessels.
- Feeling of pain or discomfort in the areas where the roots branch (pins and needles or numbness).
Stage 2: development of stroke
In this case, the speed of development of the pathology depends on the cause that provoked the attack. When a blood clot or embolus breaks off, symptoms appear within a few minutes. If the cause is different, symptoms may appear within a few hours.
Symptoms also depend on the type of vessel in which blood has stopped circulating and entering the spinal cord. Therefore, if there is a blockage of the anterior spinal artery, the following symptoms appear:
- dysfunction of the bladder and rectum;
- paralysis of limbs;
- lack of skin sensitivity in symmetrical areas of the limbs.
If a stroke develops in the cervical spine, the symptoms are as follows:
- decreased muscle tone in the arms (flaccid paralysis);
- increased muscle tone in the legs (spastic paralysis).
When a stroke affects the thoracic spinal cord, the following changes occur:
- spastic paresis of the legs.
If the source of the stroke is localized in the lumbosacral segments of the spinal cord, the following symptoms appear:
- flaccid leg paresis;
- retention of urine and feces.
Stage 3: reverse development
This stage begins a month after the onset of the attack, and characteristic of this stage is the reverse development of symptoms. During this period, partial recovery occurs, and blood gradually begins to flow into the damaged area. This process occurs due to the flow of blood through the arteries from other large blood vessels, also due to the restoration of the functions of neurons that remained alive in the lesion.
At this stage, the symptoms of the disease begin to disappear and everything gradually returns to normal. How quickly the stage will develop and how well functions will be restored depends on the location where the stroke occurred and the size of the affected area.
Stage 4: residual effects
A person who has experienced an attack reaches this stage approximately 24 months after the onset of the disease. During this period, a person has persistent neurological disorders, but they do not have pronounced dynamics.
Rehabilitation
After completing treatment for a spinal stroke, the patient requires long-term work with a rehabilitation physician. Rehabilitation is aimed at rapid restoration of impaired neurological functions.
In many ways, the prognosis after a spinal cord stroke depends on the rehabilitation program
The following rehabilitation measures are used:
- physical therapy classes;
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation of damaged nerve fibers, acupuncture, reflexology).
No ads 3
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the likelihood of developing a spinal stroke and prevent its recurrence, the following measures are recommended:
- regular physical activity that is feasible for the patient. Nordic walking and long walks will be especially useful;
- rational distribution of the load on the spinal column. It is not recommended to lift weights or perform strength exercises. To prevent recurrent spinal stroke caused by vertebral displacement, you should wear a special corset that evenly distributes the load on the spinal column;
- It is desirable to get rid of excess weight. Obesity increases the load on the spinal column and contributes to the development of intervertebral hernias and osteochondrosis;
- to give up smoking. Nicotine causes vasospasm, which can provoke ischemia;
- giving up alcohol. Alcohol impairs liver function, which, in turn, can cause bleeding disorders and hemorrhage in the brain and spinal cord;
- If you suspect a spinal stroke, it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the likelihood of rapid rehabilitation.
Spinal cord stroke is an urgent condition requiring emergency medical care. It is important to remember that early initiation of therapy can prevent complications that can make a person disabled and permanently bedridden.
Treatment methods
During the treatment of a disease, the doctor and the patient have several goals, namely:
- improve blood flow to the spinal cord;
- eliminate factors that provoked blood flow disturbances;
- restore spinal functions that were lost due to a stroke.
To achieve all the goals, the doctor prescribes a number of drugs, namely vasodilators, antiplatelet agents, venotonics, decongestants and drugs that improve the resistance of spinal cord tissue to oxygen starvation. This list is primarily aimed at improving blood circulation.
The factors that provoked the disease are eliminated using conservative and surgical methods. How a person is treated depends on the cause itself. In cases where a vessel is blocked by a blood clot, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are used. If the stroke occurred due to compression of the artery by an intervertebral hernia, the doctor prescribes an orthopedic corset, exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
If this type of treatment does not bring positive results, then surgery is used. This treatment method is also used if the stroke is caused by tumors.
To restore spinal functions, massage, exercise therapy, treatment in sanatorium-resort conditions, manual therapy are prescribed, and all this begins at the stage of reverse development, so that in the end there is the most positive result.
Sensory disorders
A spinal cord stroke causes sensory disturbances. With extensive damage, sensitivity in the segment innervated by the damaged area disappears completely. Possible dysfunction of the pelvic organs, involuntary defecation and urination, decrease or disappearance of potency.
Symptoms of spinal stroke depend on the level of nerve tissue damage
If the pathological process affects half of the transverse section of the spinal cord, Brown-Séquard syndrome develops. On one half of the body, located on the same side as the damaged area. In this case, disturbances in the motor sphere and loss of deep sensitivity are observed, that is, the patient loses the ability to feel the movements of his muscles and does not feel pressure on the body. On the opposite side of the body, the so-called superficial (pain, temperature) sensitivity disappears.
If the artery supplying the anterior side of the spinal cord is damaged, the patient loses sensitivity to pain and also develops constipation. If the artery supplying blood to the back of the spinal cord is damaged, muscle spasms and loss of vibration sensation in the legs may occur. This type of spinal cord stroke is quite rare.
No ads 1
How to carry out prevention
This problem can affect any person, but older people are at risk. Therefore, to protect yourself from this disease, you need to follow several recommendations:
- identify and treat cardiovascular diseases in the early stages;
- control blood cholesterol levels and prevent the development of atherosclerosis;
- treat and prevent spinal osteochondrosis;
- consult a doctor promptly if you detect even one symptom signaling the development of a spinal cord stroke;
- lead an active lifestyle and avoid obesity.
Listen to your body, do not ignore any signals that may indicate problems with the spinal cord and remember that in any case, timely help is important!