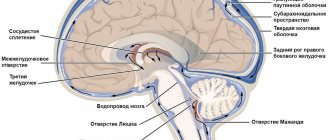
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is a disorder within the cranial cavity and head. According to norms, the brain makes up 85%, blood volume - 8%, cerebrospinal fluid - 7% of the volume of the cranial cavity. With this proportion, the fluid pressure is determined from 7 to 15 mmHg for a person in a supine position. When loss of ratio occurs, intracranial pressure on the brain increases or decreases.
Causes of intracranial pressure - description, factors
The main etiology is a violation of the outflow of fluid into the brain. The condition worsens if the brain
- blood from the veins arrived in a larger volume;
- a lot of spinal substance got in.
Intracranial compression exists in the form of:
1. Hypertension, when the pressure rises to 20 or 25 mmHg and fluid enters the brain in the walls of the skull:
- spinal;
- tissue due to brain tumors;
- blood with stagnation in the veins;
- foreign during the period of brain tumors.
The reasons that cause increased intracranial pressure in the patient are: situations of traumatic injury (TBI), tumors, effusion of blood inside the skull, meningoencephalitis (the brain is affected), hydrocephalus (“dropsy” due to cerebrospinal fluid), excess weight, excess fluid, as well as others factors when cerebrospinal fluid increases.
An increased degree of pressure on the brain (over 40 mmHg) threatens human life.
If pressure on the brain increases in adults, it is necessary to undergo examination and rule out a malignant tumor.
2. Intracranial hypotension, when the pressure on the brain, on the contrary, is reduced.
In this case, the prerequisites are:
- the state of destruction of the bones of the skull, membranous membranes, which are caused by injuries, combined with an outpouring of cerebrospinal fluid;
- taking dehydrating diuretic medications in larger quantities than necessary;
- loss of cerebrospinal fluid due to lumbar puncture or external drainage of the lateral ventricles of the brain.
Treatment of high intracranial pressure
Living with increased intracranial pressure is quite difficult, and also dangerous. If the disease is not treated, the patient develops hormonal imbalance, the nervous regulation system is disrupted, and intellectual abilities decrease.
The basis of the treatment program is the use of drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid and activate the process of its absorption. In severe cases, doctors decide on the need for surgical bypass surgery.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
The symptoms of increased blood pressure are so vivid and strong that they affect the entire life and activity of the individual:
- pressing pain spreading to all areas;
- pain that occurs in the morning and intensifies throughout the day, not relieved by conventional analgesic medications;
- signs of sleep disturbance;
- nausea, vomiting;
- slowdown in heart rate;
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- lack of ability to focus on small objects;
- decreased memory and attention.
If the headache occurs due to a significant pathology, the patient should maintain bed rest. Otherwise, dizziness, lapses of consciousness, and memory loss begin.
With reduced ICP, symptoms are observed:
- constant mood swings, lethargy, indifference, asthenia, dissatisfaction, fatigue;
- vertigo, sometimes fainting after minor sports activities;
- headache;
- with a general lack of fluid, blood pressure simultaneously decreases;
- decreased ability to see, cloudy spots in the eyes;
- lightheadedness, abdominal pain;
- pain in the heart area.
Intracranial pressure in children of different ages
In children, hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure are expressed by the following pathologies:
- Strong crying. A special feature is the relatively normal condition of the patient throughout the day. In the evening and at night, the baby cries and becomes restless. In a supine position, the outflow from the veins is inhibited, and the vessels of the skull are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates and causes the development of intracranial pressure on the brain and pain.
- Increased anxiety, difficulty falling asleep, constant awakenings, insomnia;
- Nausea, severe and frequent regurgitation;
- Signs of bulging or very long fusion of the fontanelle, excessive increase in head circumference, divergence of the bones of the skull;
- The appearance of a vascular network under the skin;
- The child mostly lies down and cannot play with friends;
- Delays in psycho-emotional and physical development.
In children under ten or eleven years of age, any signs of intracranial pressure on the brain are associated with trauma during childbirth. Of course, they can provoke symptoms of intracranial pressure and pain. However, first of all, it is necessary to identify or exclude signs of dropsy, which manifests itself at a very young age. The diagnosis is made based on constant measurements of head circumference and assessment of the rate of head growth.
Symptoms
The development of this pathology can be suspected even in the prenatal period if there are severe infections in the mother, fetal hypoxia, birth asphyxia, prematurity, or birth injuries.
The main signs of intracranial hypertension in newborns and infants include:
- bulging and pulsation of the fontanel;
- excessive growth of the head with disproportionate size;
- divergence of the sutures of the skull;
- convulsions;
- well-defined venous pattern on the skin – “marbling”;
- chin tremor;
- copious and frequent regurgitation, vomiting, resulting in poor weight gain;
- restlessness, crying, sleep disturbance;
- delay in psychomotor development.
Diagnostic methods
A unique and most reliable way to measure the intracranial pressure on the patient’s brain in a few minutes is a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid: a special puncture is made and a catheter is inserted into the lower back or into the brain. CSF flows out under pressure and measurements are taken. The normal value is from 60 to 200 mm of water column in a supine position.
There are also indirect studies:
- The ultrasound radiation method is carried out exclusively for babies whose fontanel has not yet fused and the brain is visible through the sensor;
- A method of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, where the image shows the brain in full three-dimensional layout;
- The echoencephalography method allows you to determine the coefficient of filling and beating of arteries in the brain;
- Rheoencephalogram method - examines the outflow of blood from the veins in the vessels of the brain;
- X-ray - used for a sluggish diagnosis of hydrocephalus, mostly performed in adults and children over one year of age.
What is intracranial pressure?
Nature acted wisely, placing the brain in a durable bone shell, thereby protecting it from external mechanical influence. No less wise was the decision to surround the brain with a special liquid - cerebrospinal
, which protects it from impacts on the internal surfaces of the skull bones. But for this “shock absorber” to work properly, there must be just enough fluid so that the brain is constantly exposed to a certain, same pressure, which is called intracranial pressure (ICP).
To measure or not to measure pressure?
It’s unlikely that anyone would ever think of running to the doctor when they have a headache, saying that it will hurt and stop. Hypertensive patients will immediately measure their blood pressure (fortunately, everyone has blood pressure monitors at home) and take the medication prescribed to them. Those who do not suffer from hypertension will regard their health as a reaction to weather changes or magnetic storms and will take painkillers. And no one thinks that pain in the head can be a consequence of increased ICP, which often leads to unpleasant consequences.
Just as blood flows endlessly through the vessels of our body, so too the cerebrospinal fluid—the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord—is not a frozen substance, but is renewed, forming in the designated parts of the brain and flowing into others. Then some part of it is absorbed into the venous blood, with which it leaves the brain. The other part moves into the spinal canal. Every day, up to a liter of cerebrospinal fluid is formed in the body: after all, it is needed not only as a “shock absorber”, like an airbag in a car, but also participates in the metabolic processes of the brain, and even has antimicrobial properties.
Traditional treatment of pathology
It is best to treat a patient with blood pressure in a hospital setting.
At home, it should be prescribed based on the results of diagnosing hypertension. After a TBI, the patient should be given complete rest, offered light food, drink more fluids, and take anti-inflammatory drugs. In situations of hematomas and brain tumors, surgery is required.
Similar measures should be taken for hydrofecal cerebral effusion. To drain excess fluid during ICP, a catheter is installed. Liquor should be removed several times depending on the child’s growth, and the latter should be constantly monitored. Gradually, interference with blood pressure will disappear.
Treatment with medications during pathology is prescribed to make you feel better:
- hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- agents that protect neurons - affect blood flow and gas exchange in the brain;
- diuretics - for the outflow of excess contents;
- osmodiuretics - reduce the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
However, the drugs affect the intracranial disorder signal itself, and not its cause. At the same time, an important stage of treatment is the treatment of the pathogenesis of intracranial pressure.
Causes of pathology
In the first months of life, the main role in the formation of ICP is played by infections suffered by the baby during intrauterine development. These include rubella, herpes, syphilis, as well as malformations of the central nervous system. In some cases, the cause of changes in intracranial pressure in children under one year of age is birth trauma. Experts also associate ICP with prematurity and oxygen starvation of the baby during childbirth.
Common factors that can cause ICP are:
- various non-infectious brain lesions;
- acute neuroinfections;
- hydrocephalus;
- benign and malignant neoplasms (tumors, cysts);
- cerebrovascular accident due to thrombosis, hematopoietic diseases;
- traumatic brain injury;
- acute poisoning;
- abnormalities of brain development;
- hormonal pathologies;
- pathologically early closure of the fontanel;
- obesity;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- abrupt cessation of treatment with certain medications.
Uncontrolled increased intracranial pressure can lead to irreversible changes in the child’s nervous system, depression of cognitive functions, disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, mental retardation, asthenic syndrome and death.
How does osteopathy treat intracranial pressure?
But the best way to correct pressure on the brain is craniosacral osteopathic actions. They have this name because “cranium” in Latin means “skull”, and “sacrum” means sacrum. The word "osteopathy" also consists of two Greek words: osteo - "bone" and patio - "disease". There is an erroneous interpretation of it as something related only to bones, and doctors in this specialty are likened to chiropractors and chiropractors.
In fact, the term means that the causes of any disease consist of a disorder in the integrity of the anatomical systems of the human body.
In the forties of the last century, osteopath William Sutherland put forward the theory that small, gentle manipulation around the skull and neck leads to relief from a wide range of health problems. In the 1970s, his follower, physician John Upledger, identified a separate area - craniosacral osteotherapy.
Treatment methods have proven effective in eliminating increased cranial fluid. According to neurosonography, the number of signs indicating hypertension decreased.
Regardless of who the patient is, after surgery or not, in children and adults after this treatment there is always a decrease in pain, intracranial pressure decreases, cerebrospinal fluid decreases, and an improvement in condition appears. On the fourth or fifth day of treatment, a patient with ICP usually achieves stabilization of hypertension, normalization of well-being, and pain subsides.
An osteo-practitioner leads to a reduction or elimination of obstacles to blood flow and lymphatic drainage of blood vessels, and adjusts the circulating cerebrospinal fluid. The number of manifestations of pathology decreases, headaches, nausea, increased pressure in the eyes, visual impairment, and tinnitus go away.
The above is also relevant in order to correct the baby’s intracranial pressure. You need to see an experienced doctor as soon as possible. The earlier treatment is started, the stronger the lasting effect is achieved. In many situations, it is possible to make people’s quality of life much better, help them get rid of migraines and poor sleep, removing obstacles to the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
To do this, they use special options for working on the structures of the skull, the membranes of the brain, blood vessels, and so on, worked out and verified over several decades. Thanks to the doctor’s manipulations, clients are able to avoid taking medications, many of which have side effects, and recover from pressure on the human brain in a natural and safe way.
The principles of osteopathy are also good after surgery or a course of medical pills. They help neutralize possible symptoms of ICP and consolidate a positive outcome. As a result of gentle bodily influence, pathologies in adults that have their roots in distant childhood and during childbirth are eliminated.
Craniopathy techniques are aimed specifically at eliminating the cause of hypertension; they give impetus to independent rehabilitation of the body after ICP. Following this, the symptoms of pain and fluid pressure on the brain gradually disappear. This is where they differ from classical medicine. The important thing is that the treatment is carried out without pain, drugs, the use of additional instruments, noise and fear for the small patient.
Osteopathy sessions are healing methods performed only with the help of manual influences on the brain, with proven effectiveness in eliminating increased intracranial pressure.
What causes intracranial hypertension in children?
In order to understand this issue, let's turn to anatomy. The brain in the skull is located movably. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid are in constant motion, bathing the brain, supplying it with nutrients and oxygen. From the spinal canal, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the ventricles of the brain and then returns through the venous sinuses. The speed of movement of cerebrospinal fluid and blood may vary depending on a person’s physical activity. In this case, there is an increase in intracranial pressure , but this is a variant of the norm, it is physiological. About 85% of the skull is occupied by the brain, 8% by blood, and 7% by cerebrospinal fluid. Standard values of intracranial pressure are achieved by maintaining these proportions. If the volume of the brain increases, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, which causes impaired blood circulation and increased intracranial pressure. And this is a very serious pathology.
Craniosacral methods for relieving ICP
At first, the most superficial opinion, it seems that a session with a specialist in craniosacral therapy looks like an elementary massage of the head and face area. However, this statement is incorrect.
Real healing of pressure on the brain using a procedure can only be carried out by a modern qualified osteopath with extensive experience, who can listen to the so-called “primary rhythm” and adjust the techniques of the hands and fingers to it. In addition, the doctor must perfectly know the structure of the human brain. High efficiency and security of the session are guaranteed only if these conditions are met.
During the massage, the client is placed on a horizontal couch. Then the specialist begins to slowly press on the scalp with his fingers. With such movements, the intracranial pressure of the brain is first opened and then corrected. The doctor's movements are very light, painless, smoothing, almost imperceptible. There will be no discomfort during the session.
On the contrary, almost 100 percent of people indicate pleasant sensations: the disease goes away and fresh strength increases. The first procedure immediately entails that pain, increased pressure on the brain, and visual disturbances are relieved. The whole condition is normalized. The therapist spends about one hour, but this time is enough to achieve the identified effect in ICP and maintain it. Then you will need several sessions, because ICP requires quite a long treatment.
The above approach is absolutely effective in healing the symptoms of any disease. It is absolutely not dangerous to health and becomes the only possible option of salvation when the patient is not ready to take medication for any reason.
Indications and contraindications for osteopathic therapy
Here is just a small list of body ailments for which a specialist appointment is indicated:
- various injuries;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- dysfunction of childbirth;
- pain of various etiologies;
- pain in internal organs;
- states of the nervous system;
- curvature of posture;
- intracranial vascular disorder;
- increased intracranial hypertension;
- pregnancy planning.
Contraindications for manipulation:
- strokes, heart attacks;
- bleeding in the brain;
- cardiac, renal, hepatic, respiratory failure during decompensation;
- infections in the acute stage;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- untreated hematomas;
- mental illness;
- blood diseases;
- oncology, tumors.
The doctor will not be able to immediately cure high blood pressure and pain in adults and children, but after an acute period of the disease, during the rehabilitation stage, he will help to recover faster. In our Center, every visitor is treated with close attention and care. An individual approach and an atmosphere of trust between doctor and patient are proof of successful healing.