Serotonin molecule
The pineal gland (pineal gland) is a tiny cerebral process that belongs to the central endocrine system.
The main hormones of the pineal gland are serotonin and melatonin. These active substances play a leading role in regulating a person’s circadian rhythms and restoring the body during sleep. They also affect the function of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, gonads, pancreas (insulin production), nervous system function and emotional state.
The other two hormones are less well known. Adrenoglomerulotropin regulates kidney function, and dimethyltryptamine (DMT) regulates the emotional and mental sphere.
Serotonin
The main regulator of sleep and wakefulness processes. It is produced only during daylight hours under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Refers to neurotransmitters and tissue hormones. This means that it is involved in the conduction of nerve impulses, but also “works” in tissues and organs.
The mechanism of action of serotonin
Serotonin as a neurotransmitter
It is sometimes called the hormone of joy, but this is not entirely true. Dopamine is largely responsible for the emotions of joy, while serotonin rather suppresses the center of negative emotions, preventing the development of depression.
In addition, it reduces sensitivity to pain. People with a high pain threshold have fairly high levels of serotonin and many serotonin receptors.
It has an inhibitory effect on the nervous system - this is due to its anti-stress and general calming effect.
Serotonin is important for blocking weak sensory signals so that the mind does not “hear” distracting sounds, and a person can focus on tasks that are important to him.
Together with dopamine, serotonin is involved in the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, stimulating the production of prolactin and other pituitary hormones.
Serotonin as a tissue hormone
The tissues contain a large amount of serotonin and receptors for it. It affects blood vessels, the digestive system, smooth muscles, and immunity.
Serotonin constricts blood vessels and thickens the blood if you need to quickly stop bleeding and form a blood clot. It also plays a big role in the formation of allergic and inflammatory reactions - it increases vascular permeability, stimulates the movement of leukocytes to the site of inflammation, and increases the level of eosinophils in the blood.
Serotonin contracts smooth muscles, enhancing intestinal motility, participates in the metabolism of lactobacilli, improves digestive processes, and also causes uterine contractions during childbirth.
Interesting! The pineal gland synthesizes 5–10% of the total amount of serotonin, the rest is produced by the intestines.
Peptide for the pineal gland Endoluten
This drug is a representative of the category of cytomax peptides of natural origin. It is based on peptide compounds obtained from the pineal gland of small calves. It should be noted that pineal gland peptides provide the opportunity to restore pineal gland tissue at the cellular level and regulate important biorhythms of the body. They are a powerful and effective means for increasing life expectancy, as well as reducing the risk of developing cancer by 3-5 times. The result of consuming Endoluten is the restoration of the synthesis of one’s own hormones to the levels of a young and completely healthy body.
Taking the drug in question is recommended for:
- High risk of cancer;
- The influence of negative external factors;
- Complicated passage of the menopause;
- Diseases of the reproductive system;
- Prevention of early aging.
The use of Endoluten will ensure the functioning of the pineal gland in the way it was originally intended in the cells of its DNA. Negative factors (stress, unsatisfactory and unbalanced nutrition, problems with maintaining a daily routine, as well as poor ecology, etc.) negatively affect the human body. As a result, metabolic processes in cells slow down. As a result, the functioning of the pineal gland becomes significantly worse. This in turn leads to the appearance of various diseases and early aging. Biological regulators based on peptides provide the opportunity to “invigorate” the pineal gland, ensuring its functioning at 100%.
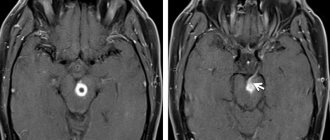
Disorders of the pineal gland
Disorders of the function of the pineal gland are often associated with tumor processes - pinealomas. In this case, its hyperfunction or hypofunction may develop - an increase or decrease in hormone production. Failure in the synthesis of pineal gland hormones leads to obesity, hypothyroidism, diabetes, and other endocrine disorders.
Pinealomas are common in childhood, especially in boys. Hyperfunction of the gland leads to underdevelopment of the genital organs in children, and hypofunction, on the contrary, leads to early puberty.
Tumors require surgical removal, and malignant tumors require additional radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Functional hypofunction of the pineal gland. It often occurs in older people and is one of the most common causes of sleep disturbance (insomnia). With this pathology, the organ itself does not have organic lesions, but its function is reduced, and patients suffer from irritability, anxiety, increased fatigue, memory loss, a tendency to colds, and hormonal disorders.
Desynchronoses. These conditions are characterized by an imbalance in the melatonin production cycle. They develop when the usual routine changes, as well as with somatic and mental illnesses. Severe illnesses can lead to a complete absence of diurnal changes in melatonin levels.
Desynchronosis is also called "pilot's disease"
External desynchronosis, caused by a rapid change in time zone when flying to another hemisphere, does not require treatment, but time for adaptation.
Internal desynchronoses caused by long-term violations of the daily routine and illnesses lead to a disorder of the body's adaptability, the development of acute and exacerbation of chronic diseases, and nervous disorders.
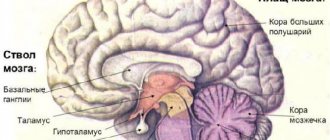
Pituitary and pineal gland
In the previous article, we discussed the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which are closely related to each other. The hypothalamus secretes liberins and statins, which regulate the activity of the pituitary gland. Now we will take a closer look at the structure of the pituitary gland and the hormones it secretes.
Pituitary
The pituitary gland (lower cerebral appendage, pituitary gland) is an endocrine gland located at the base of the skull. Consists of three lobes: anterior, intermediate (middle) and posterior. The pituitary gland is called the “conductor” of the endocrine glands, since its hormones influence their work.
In the anterior part of the pituitary gland (adenohypophysis), tropic hormones (from the Greek tropos - direction) are produced and released into the blood:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - stimulates the release of hormones by the thyroid gland (lat. glandula thyroidea - thyroid gland)
- Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) - stimulates the adrenal cortex (from Lat. adrenalis - adrenal and Lat. cortex - bark)
- Gonadotropic (GTG) - affects the secretion of sex hormones by the gonads and the maturation of eggs/sperm in the gonads (lat. gonas - sex gland)
- Somatotropic (GH) - growth hormone, affects the growth and development of all cells of the body (Greek soma - body)
- Prolactin - stimulates the development of the mammary glands and the formation of milk in them in nursing mothers
Let's pay special attention to growth hormone - growth hormone. Violation of its secretion leads to serious diseases, as it affects the growth and development of the body. The secretion of GH can be increased, in this case they speak of hyperfunction of the adenohypophysis (Greek hyper - above), or decreased, in this case they speak of hypofunction of the adenohypophysis (Greek hypo - below). In childhood and adulthood, the consequences of hypo- and hyperfunction differ.
With hyperfunction of the adenohypophysis (high growth hormone) in childhood, excessive bone growth occurs and gigantism develops, while body proportions are preserved. With gigantism, a person's height can reach 2 meters or more. With this pathology, the gonads and joints are most prone to diseases, and the psyche is often disturbed.
In adulthood, hyperfunction of the adenohypophysis is not accompanied by an increase in growth, since the growth of most of the bones is complete. However, those bones that have a cartilaginous layer begin to grow excessively: the phalanges of the fingers, the lower jaw. The lips and nose thicken, and the internal organs enlarge. This condition in adulthood is called acromegaly (Greek: akron - limb and megas - large).
With hypofunction of the adenohypophysis (reduced secretion of growth hormone), dwarfism develops in childhood - growth retardation. With dwarfism, the body has the correct proportions, height is no more than 1 meter, and the psyche is normal. This condition can be corrected by a doctor by prescribing growth hormone in the form of a medicine in time (in childhood!).
With hypofunction of the adenohypophysis in adulthood, metabolic changes develop, which can lead to both exhaustion and obesity.
The intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland synthesizes and secretes melanotropic (melanocyte-stimulating hormone). You already know that melanocytes are located in the basal layer of the epidermis; their pigment, melanin, gives the skin a dark color. Melanotropic hormone stimulates the activity of melanocytes: they synthesize melanin, skin pigmentation increases.
The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland - the neurohypophysis - does not synthesize (!), but only releases two hormones into the blood: vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone - ADH) and oxytocin. These hormones are synthesized by neurons of the hypothalamus and descend along the processes of neurons into the neurohypophysis, where they enter the blood.
Vasopressin increases the reabsorption (absorption) of water in the nephron tubules, thereby reducing its excretion in the urine. If the secretion of ADH is impaired, the volume of urine can increase to 20 liters per day! This condition is called diabetes insipidus because, like diabetes, it is characterized by increased diuresis (volume of urine) and extreme thirst.
Oxytocin plays an important role during childbirth - it stimulates uterine contractions, promoting the movement of the fetus along the birth canal. In nursing mothers, oxytocin promotes lactation (milk secretion) in the mammary glands during feeding.
Pineal gland
The epiphysis (pineal body) is an endocrine gland of internal secretion, anatomically related to the diencephalon. Depending on the light intensity, pineal gland neurons synthesize and secrete the hormone melatonin, which is involved in the regulation of the body’s circadian and seasonal rhythms. Light inhibits the production of melatonin.
© Bellevich Yuri Sergeevich 2018-2021
This article was written by Yuri Sergeevich Bellevich and is his intellectual property. Copying, distribution (including by copying to other sites and resources on the Internet) or any other use of information and objects without the prior consent of the copyright holder is punishable by law. To obtain article materials and permission to use them, please contact Yuri Bellevich
.
How to normalize the functioning of the pineal gland
Peptide bioregulators will help restore normal activity of the pineal gland during functional hypofunction and desynchronosis. The drug Endoluten is designed specifically to correct the function of the pineal gland, and contains its peptide complex A-8.
As a result of taking Endoluten, the functioning of the entire neuroendocrine system is normalized: circadian rhythms are restored, the immune system is strengthened and the body is rejuvenated.
Cellular structure
The pineal gland is a small organ colored grayish-red. On the outside, it is covered with a dense capsule of connective tissue. The capsule forms so-called trabeculae, which penetrate inside the gland and divide it into small lobules. This is exactly what the human pineal gland looks like - its structure can be considered quite simple.
The internal part of the gland consists of parenchyma and connective tissue elements. The main structural elements in the pineal gland are pinealocytes - polygonal parenchymal cells. In addition to them, four more types of cells were discovered: pineal gland neurons, interstitial endocrinocytes, also peptidergic neuron-like structures and perivascular phagocytes.
It is worth noting that at the beginning of a person’s life, the pineal gland grows rapidly, but around the time of puberty, the growth of the pineal gland gradually fades. Moreover, as the human body grows and ages, the gland involution occurs.