General information
Vestibulopathy is a disorder of the normal functioning of the vestibular apparatus , in which characteristic symptoms appear.
The ICD-10 code for vestibulopathy is H81 (Vestibular function disorders). The normal orientation of a person in space and his balance in a vertical position is ensured by the vestibular apparatus. Disturbances in its work lead to a person experiencing confusion, dizziness , and the inability to remain in a standing position. This condition is also called labyrinthopathy. It can develop due to various reasons and diseases, developing at any age in every person. Sometimes vestibulopathy is a congenital pathology.
It may manifest itself as a separate syndrome or as a sign of neuropsychiatric disorders. In the second case, it is more difficult to treat this disease. How this pathology manifests itself, and what treatment methods are advisable to practice, will be discussed in this article.
Motion sickness syndrome
Problems in the vestibular system can also manifest as motion sickness syndrome. Motion sickness in transport can occur in practically healthy people or serve as a manifestation of one or another disease of the autonomic nervous system or gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory diseases of the hearing aid, etc. In this case, a thorough examination and treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. As you recover, the unpleasant sensations that arose while traveling on a bus, train or car often disappear.
Pathogenesis
Vestibular insufficiency can occur at any age. Sometimes this is a congenital pathology. The pathological process is localized in the inner ear. The vestibular apparatus, which is a complex receptor of the vestibular analyzer, consists of three arches. They are located at an angle of 90 degrees to each other. They contain liquid, which is distributed through the channels depending on the position of the human body, gravity, the force of attraction, as well as the influence of a number of other factors. The brain receives impulses that determine the movements of different parts of the body. Vestibular insufficiency develops when the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
Vestibulopathy can develop with a variety of pathogenetic variants of damage to the peripheral or central part of the vestibular analyzer, which performs three important functions - maintaining balance, spatial orientation, and image stabilization.
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE VESTIBULAR APPARATUS AND METHODS OF TRAINING IT
№20, 02.07.2019
Pedagogical Sciences
Miftakhov Almaz Faridovich
Tolibova Mokhinur Fayzullo Kizi
Key words: VESTIBULAR APPARATUS; MOVEMENT COORDINATION; healthy lifestyle; TRAINING; EQUILIBRIUM; VESTIBULAR; COORDINATION; HEALTHY LIFESTYLE; EXERCISE; BALANCE.
Abstract: This article reveals the importance of such a human organ as the vestibular apparatus.
Its training is needed not only by those who plan large overloads and flights into space. It is the vestibular apparatus that provides us with an exceptional evolutionary feature - upright posture. The study describes the structure of the vestibular apparatus, its impact on a person’s well-being and orientation in space, its significance both in everyday life and for athletes and astronauts. We also describe the main ways to strengthen the vestibular system for better health. The structure of the vestibular apparatus
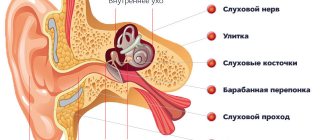
The mechanism of operation of the vestibular apparatus is very complex; it is a small organ in the inner ear that provides us with a sense of balance. This mechanism monitors changes in the position of the head and body, sending signals to the brain - “up”, “down”, tilt.” It is he who is responsible for coordinating processes such as running, walking, jumping. Many animals, for example cats, have a vestibular apparatus that is more developed than that of humans. For example, in turtles it is less developed. However, our vestibular apparatus is significantly different: it is thinner than all others, since it synchronizes the simultaneous work of hundreds of muscles and ligaments to ensure balanced movement of the body on two points of support [1]. The peripheral section of the vestibular analyzer is a part of the inner ear, consisting of semicircular canals located in three mutually perpendicular planes, and statocyst organs - two sacs - oval (uterus) and round, located closer to the cochlea. One end of each semicircular canal expands, this expansion is called an ampulla. The ampoules of the semicircular canals contain a crescent-shaped bone ridge. Directly adjacent to the scallop is a membranous labyrinth and an accumulation of two rows of cells: supporting and sensitive, having at the upper end 10-15 long hairs, glued together by a gelatinous substance into a brush (flap). The oval and round statocyst sacs of the vestibule are lined on the inside with flat epithelium, with the exception of some areas (spots). The spots consist of columnar epithelium, where supporting and sensitive hair cells are located. Supporting cells form many fibers, which include calcareous pebbles - otoliths adjacent to the hair cells. The sacs and semicircular canals are filled with endolymph. The hair cells of the crests of the semicircular canals and the spots of the statocyst sacs are connected with the fibers of bipolar neurons located in the Scarpa vestibular node, located deep in the internal auditory canal [2].
The mechanism of operation of the vestibular apparatus is that with various movements of the head, the endolymph and otoliths move, which irritates the hair cells of the semicircular canals and statocyst sacs. Centripetal impulses arise there, which are transmitted along the vestibular nerve to the medulla oblongata, and then to the cerebellum, midbrain, diencephalon and temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. The semicircular canals, in turn, are irritated at the beginning and end of rotational movements of the head. Statocyst sacs, in turn, perceive the beginning and end of uniform rectilinear movement, linear acceleration and deceleration, changes in gravity and centrifugal force, shaking, rolling - they mainly regulate posture.
Unfortunately, there are cases when the vestibular apparatus is highly sensitive, and as a result, in the case of prolonged vestibular influences, so-called motion sickness is observed, associated with a deterioration in well-being and vegetative disorders, the totality of which is called seasickness.
Let us note that the excitability of the human vestibular apparatus manifests itself from the very day of birth, and its functions are trained by rhythmic stimulation (rocking and carrying).[3]
The importance of training the vestibular system
The simplest tip for improving the functioning of the vestibular system is to lead a healthy lifestyle. The good news is that many exercises can be done at home. For example, it is recommended to practice holding various objects on your head, walking along a curb, or walking backwards. Further, if a person successfully copes with these tasks, you can begin systematic training of the vestibular apparatus.
Nowadays, there are many ways to train coordination of movements: you can practice with exercise machines, swings, rocking chairs, and also in an equipped gym.
The following exercises are best done daily for 10-15 minutes to achieve a systematic approach: • Tilt your head down and exhale, lift your head up and inhale. • Turn your head left and right 10-15 times. • Tilt your head to your left shoulder, take the starting position, tilt your head to your right shoulder 10-15 times. • Make circular movements with your head from left to right and from right to left. When lowering your head, exhale, raising your head, inhale[4].
It is important to note that there are the following tips: 1. Exercises should always be performed at a calm pace, sudden movements are not allowed. 2. You should breathe through your nose, and your breathing must be deep. 3. The key to success is consistency in training, breathing control and, if possible, fresh air. If classes are held in a building, it must be well ventilated.
After some time, in order to complicate the tasks, you can begin to perform the exercises with your eyes closed. Coordination for athletes
Most sports, such as martial arts, require a well-developed vestibular system. The following exercises to overcome dizziness differ in complexity from the initial level and are recommended for athletes in the absence of contraindications: • Do several somersaults, stand up and try to cope with dizziness by choosing a certain point in space and concentrating on it. You should not overuse the exercise to the point of nausea. The number of somersaults in the approach should be gradually increased.
• Raise your head up and extend your hand with your index finger, which you need to focus on when circling. Start circling around your axis. This exercise is for a while. After 30 seconds, you should perform the following task: stop and cope with the dizziness. [5]
This sports training will help in achieving stability, making quick movements, and the ability to easily recover from missed blows during wrestling.
Vestibular apparatus and yoga
Yoga classes play a special role in training the vestibular apparatus.
It is believed that a set of stretching exercises, and especially coordination and static balance, has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Thanks to yoga, harmony of thoughts with the body is achieved, since the psychological state also affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Conclusion
Thus, a strong vestibular apparatus makes a person’s life better. People with a weak vestibular system are contraindicated from traveling on buses, planes, and ships in order to avoid dizziness and motion sickness. No matter how difficult it may be, it is quite possible to combat this problem. To maintain the health of such people, in this article we have presented the main methods of improving a person’s health by performing exercises, from the simplest to the rather complex.
Classification
Depending on the nature of its origin, vestibulopathy is divided into several types:
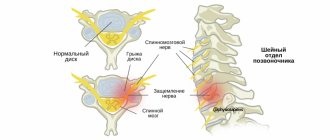
- Vertebrogenic – develops against the background of pathologies of the cervical spine. It can be observed with osteochondrosis , osteoporosis , intervertebral hernia , etc. This form is the most common. This condition is characterized by prolonged dizziness and a feeling of head instability. When trying to focus your gaze on moving objects, discomfort occurs. Spontaneous attacks of eye rotation may occur when a person tries to turn his head sharply. They last no longer than 30 seconds.
- Peripheral - develops as a consequence of the inflammatory process in the nerve ganglia in the inner ear. Most often this occurs due to allergies or infections. With such a lesion, in addition to vestibular disorders, the patient may experience tinnitus and causeless fear. Prolonged dizziness and bouts of eye rolling are noted.
- Central - develops if disturbances occur in the function and structure of the vestibular nuclei of the medulla oblongata and cortex.
- Post-traumatic – develops after traumatic brain injury if hemorrhage occurs in the labyrinth of the inner ear. As a result, tissue damage is noted. The eardrums may also be damaged, and the ganglia of the brain may be shaken and damaged. In this case, both dizziness and other characteristic signs are noted - spontaneous eye movements, nausea, vomiting. In addition, a patient with such a lesion has an unstable gait - it is difficult for him to stand on his feet.
Cochleovestibular syndrome is also distinguished . In this condition, auditory and vestibular function is impaired. Cochleovestibular disorders are accompanied by tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, and imbalance.
Diseases of the vestibular apparatus
Doctors count more than 80 different diseases that in one way or another may be associated with a violation of the balance apparatus. Examples include diseases of the endocrine system, traumatic brain injuries, cardiovascular pathologies, and serious mental disorders. At the same time, for all diseases of the vestibular system, doctors will have an explanation, a description of the symptoms and ways to check them.
Meniere's disease
This disease of the balance apparatus can be described using only four signs: dizziness, noise or congestion in the ears and hearing loss. The first three symptoms peak within a couple of minutes, gradually subsiding over several hours. The decrease in sound perception at an early stage is reversible. In some patients, Meniere's syndrome may be accompanied by a brief loss of consciousness or balance.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
This deviation can occur at any age, but most often affects the elderly. It is caused by infections, traumatic brain injuries or coronary heart disease, sometimes the source cannot be determined. In patients with this diagnosis, a feeling of dizziness, loss of balance and other symptoms appear with every turn, tilt of the torso or head.
Basilar migraine
The syndrome is short-lived and usually affects patients under 20 years of age. Basilar or teenage migraine is especially common in girls entering the period of formation of the menstrual cycle. Headaches, dizziness and nausea in a teenager appear suddenly and in rare cases the development lasts more than one hour.
Vestibular neuritis
The disease is possible at any age. Often its appearance is accompanied by an acute respiratory infection, so doctors attribute the disease to a viral nature. Neuritis of the vestibular apparatus is accompanied by severe rotational dizziness, vomiting and nausea, and twitching of the eyelid. With the right treatment, the deviation goes away in 3-4 days, but full recovery will take up to several weeks.
Causes of vestibular apparatus disorders
The causes of dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus can be very different. Basically, vestibulopathy is provoked by the following factors:
- Cervical osteochondrosis - due to displacement of discs and vertebrae, the functioning of the vertebral artery is disrupted, which impairs blood supply. In addition, with osteochondrosis, the nerves are pinched, which also leads to dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus. Also, problems with the vestibular apparatus can be observed with intervertebral hernia, osteoporosis, etc.
- Pathologies of the inner ear - this may be a violation of lymph flow in the middle ear, inflammatory processes, otitis media, etc.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammatory disease that provokes the development of periodic dizziness.
- Meniere's disease - during the development of the disease, pathological changes in the inner ear are noted.
- Infarction of the labyrinth – leads to impairment of hearing and function of the vestibular apparatus.
- Vestibular neuronitis is a consequence of herpetic damage to nerve fibers. If a person is diagnosed with vestibular neuronitis, it should be taken into account that signs of the disease appear periodically - during exacerbation. As a rule, this happens in spring and autumn. Also, vestibular neuritis can develop as a consequence of acute respiratory infections, influenza , etc.
- Migraine - with this disease, the symptoms are similar to vestibulopathy, but the hearing does not change.
- Diseases of the central nervous system - can cause pathological processes in the membranous labyrinth.
- Traumatic damage to the thin bone membranes of the labyrinth , in which the eardrum ruptures or hemorrhage in the middle ear - this can happen with severe coughing, straining, diving.
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency - manifests itself mainly in older people, causing damage to the vestibular analyzers. With this pathology, the blood vessels, cerebellum and brain stems are affected. The duration of such an attack is several minutes, during which the person loses balance and orientation in space, he develops weakness, and his limbs go numb.
- Intoxication of the body due to taking certain medications.
- Neurotic disorders.
- Neuromas are tumors that form and grow from nerve cells.
- Occupational diseases – working in conditions of constant vibration or noise.
“Failures” of the vestibular apparatus: symptoms of disorders.
Everyone has experienced problems with the vestibular system in their life. Someone cannot travel in public transport, sail on a ship, fly on an airplane, or ride a carousel in the park. This so-called “seasickness” is a fairly common phenomenon. But its manifestations do not mean that a person is sick: in ordinary life he does not experience any discomfort, he just has a weak vestibular apparatus, and the symptoms quickly pass. Vestibular apparatus disorders are characterized by:
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- vibration of the eyeballs (nystagmus);
- loss of balance;
- sweating;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- instability of blood pressure, pulse rate and breathing;
- blurred vision, feeling of a veil before the eyes;
- sometimes fainting.
If these symptoms occur for no apparent reason and persist for more than a day, then you need to sound the alarm and seek help from a doctor.
Symptoms of vestibulopathy
The basis of vestibulopathy are four main symptoms:
- systemic dizziness;
- vegetative manifestations - nausea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis , heart rate disturbances, etc.;
- imbalance;
- spontaneous nystagmus .
However, disorders of the vestibular system can manifest themselves differently in different diseases. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the following manifestations:
- I feel dizzy from time to time, and this symptom occurs quite often.
- Difficulties appear in maintaining balance - it seems that the body “does not obey” while walking or trying to move.
- Vision deteriorates, spots and goosebumps appear in the eyes.
- of migraines increases .
- Hearing deteriorates, tinnitus bothers me.
- Nystagmus is periodically observed - the movement of the eyeballs in one direction.
- Periodic nausea and vomiting.
If a person does not know what vestibular neuritis and how it manifests itself, then he can ignore the symptoms of vestibular neuritis for a long time, believing that these are just signs of overwork.
Transmission of nerve impulses
Nerve impulses arising in the receptor cells of the vestibular apparatus are transmitted along the sensitive nerve fibers of the VIII pair of cranial nerves to the brain and first enter the vestibular centers of the medulla oblongata. From here, signals are sent to many parts of the central nervous system: the spinal cord, cerebellum, cerebral cortex, oculomotor nerve nuclei, reticular formation and autonomic nuclei.
Thanks to connections with the spinal cord, vestibular reflexes are carried out to maintain body balance, which involve the muscles of the neck, torso and limbs. As a result of these reflexes, muscle tone is redistributed and balance is maintained. Connections with the cerebellum give movements smoothness, precision and proportionality.
Signals that are sent from the vestibular centers to the nuclei of the oculomotor nerves make it possible to maintain the direction of gaze when changing the position of the head. This also explains nystagmus in cases of imbalance - involuntary rhythmic movements of the eyeballs in the direction opposite to rotation, followed by their spasmodic movement back. The characteristics of nystagmus serve as an important indicator of the state of the vestibular apparatus, therefore they are analyzed in aviation, marine and space medicine, and studied experimentally and clinically.
Tests and diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the patient must see a doctor, who first conducts a detailed survey and examination. Further, if necessary, further studies will be prescribed.
The study of the vestibular apparatus can be carried out using different methods. There are three main tests to check how the vestibular apparatus works: rotational , thermal and mechanical . In addition, you can undergo simple testing to determine the presence of coordination disorders.
With the help of such tests, a study of the functions of the vestibular apparatus for VVC in Moscow (Khimki, etc.) and other cities is carried out.
- Rotation test - to conduct it, a person sits in a chair and tilts his head forward. After this, 10 rotations are carried out over 20 seconds, then the chair suddenly stops. After this, nystagmus develops. Having measured its duration, the procedure is repeated again with rotation in the opposite direction. Normally, nystagmus will last the same amount of time - 20-50 seconds. If the difference between the two results is 25%, then we can talk about balance disorders.
- Mechanical examination - for this purpose, a rubber bulb is used, with the help of which the external auditory canal is filled with oil to displace the air from it. Next, the pear is compressed and unclenched, checking for damage to the bone capsule of the labyrinth.
- Thermal examination - the patient's ear canals are washed with water for 30 seconds.
At this time, nystagmus occurs, and assessing its duration makes it possible to determine the sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus.
Tests are carried out to determine coordination. This could be walking in a straight line with your eyes closed, trying to touch the tip of your nose with your eyes open and closed, etc.
There are other tests to determine whether the vestibular apparatus is weak or strong.
- Nystagmus can be measured using so-called Frenzel glasses . These are special magnifying glasses with bulbs equipped with light bulbs that illuminate the eyes.
- Also for this purpose, the method of electronystagmography - measuring nystagmus using electrodes.
- A neurological examination is also carried out, aimed at determining the condition of the nerve trunks of the eyeball and the muscles of the facial skull.
- MRI allows you to determine the condition of the spine.
- The inner ear and eardrum are also examined.
Other studies may be prescribed. The doctor will tell you during the consultation where to undergo such a study and what the conclusion looks like.
Autonomic reactions
Through a set of nerve structures located in the central parts of the brain stem (medulla oblongata and midbrain, visual thalamus), the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract and other organs are involved in vestibular reactions. With strong and prolonged stress on the vestibular apparatus, autonomic reactions occur in the form of a slowing pulse, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, cold hands and feet, pale face, cold sweat, etc. Similar symptoms are possible with seasickness or going up in a high-speed elevator. This is due to the fact that a person is accustomed to movements in the horizontal plane, but movements up and down or to the sides are unusual for him. Special training (swings, rotation) and the use of medications reduce the excitability of the balance organ and prevent undesirable effects.
Treatment with folk remedies
Some folk remedies can be used as auxiliary methods during the period of treatment and recovery for vestibulopathy.
- Melissa tea . 1 tbsp. l. Dried lemon balm pour 1 cup boiling water. After 10 minutes, drink with honey. It is recommended to drink this tea for dizziness twice a day.
- Infusion of parsley seeds . Finely grind parsley seeds, 1 tsp. pour the raw material into 1 glass of water and leave for 8 hours. Drink 50 ml 4 times a day.
- Infusion of nettle leaves . 1 tbsp. l. Pour dry nettle leaves into a thermos and pour 200 ml of boiling water. After two hours, strain by squeezing out the nettle leaves. Combine the resulting liquid with the same amount of fresh apple juice. Drink throughout the day. Take for two weeks.
- Essential oils . Mix 50 ml of camphor oil with 25 ml of fir oil and 10 ml of juniper. Mix thoroughly and lubricate the lymph nodes on the neck, nose and mouth with the resulting product. Please note that this product should not be applied to open wounds.
- Infusion of mistletoe and Japanese Sophora . The dry raw materials of both plants need to be crushed and mixed with 15 g of each component. Pour 500 ml of boiling water. When the product is infused, drink 100 ml before meals.
How to strengthen the vestibular apparatus?
There is probably no child who doesn’t like to tumble, run, jump, or ride on a swing-carousel, but among adults only a few can do all this without difficulty. All children naturally have a good vestibular system, and in order to preserve and strengthen it, adults need constant training:
- Sports activities that keep the whole body in good shape are required;
- if possible, ride on a swing, at first swing not too much, increasing the amplitude every day;
- rotational movements of the head: clockwise, counterclockwise, bending forward, backward, 10 times of each type of exercise, gradually increase the speed of rotation;
- walk a few meters forward, then back: you need to do this first with your eyes open and then with your eyes closed;
- stand upright for a while with your eyes closed, then stand on your toes and stand again.
Such exercises need to be repeated 5-6 times a day, and after 2-3 months of regular training you can see the result. It is necessary to train the vestibular apparatus not only for those who have problems with coordination, but also for all people for prevention.
Prevention
The following prevention methods should be practiced:
- Limit situations that provoke an attack of vestibulopathy.
- Eat right, avoiding lack of vitamins and minerals. If necessary, take vitamin-mineral complexes periodically.
- Get proper rest, sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Exercise daily, do yoga, Pilates, swimming.
- Treat bacterial and viral diseases in a timely manner.
- If vestibulopathy occurs, consult a doctor.
Diet
Salt-free diet
- Efficiency: 5-10 kg in 13 days
- Time frame: 13 days
- Cost of products: 4500-8000 rubles for 13 days
For some diseases that provoke vestibulopathy, it is recommended to adhere to a salt-free diet or limit the amount of salt in the menu.
In general, nutrition should be rational and varied, and the diet must include fresh fruits and vegetables, meat, fish, dairy products, nuts, and vegetable oils.
You should give up alcohol.
Consequences and complications
A severe complication of vestibulopathy can be purulent labyrinthitis , which, in turn, sometimes develops into meningitis . Therefore, inflammation in the inner ear must be treated under the close supervision of a doctor.
Vestibulopathy, moreover, negatively affects the overall quality of life. Dizziness and migraines impair work ability. In addition, such manifestations can cause accidents and traffic accidents.
In advanced stages, the auditory nerve may be affected, leading to the development of hearing loss.
This condition can also lead to cognitive impairment.
What are the signs of damage to this system?
When any part of the vestibular system is affected (tumor, inflammatory and vascular processes), specific symptoms arise. The main manifestations of vestibular disorders are a feeling of dizziness and twitching of the eyeball - nystagmus. In addition, nausea, vomiting, imbalance, changes in breathing rhythm, pulse, fluctuations in blood pressure, increased sweating, paleness or redness of the face and neck may occur. Most often, vestibular symptoms occur suddenly, with more or less regular intervals between attacks.
List of sources
- Zamergrad M.V., Grachev S.P., Gergova A.A. Acute vestibular vertigo in old age: stroke or peripheral vestibulopathy. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2018; 118(6-2): 46-49.
- Parfenov V.A., Abdulina O.V., Zamergrad M.V. Differential diagnosis and treatment of vestibular vertigo // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 49-54.
- Suslina Z.A., Varakin Yu.Ya., Vereshchagin N.V. Vascular diseases of the brain. M. 2006.