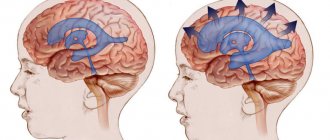
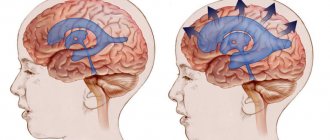
Ventriculomegaly is a pathology that affects the ventricles of the brain. The function of these parts of the organs is to maintain intracranial pressure and ensure normal blood circulation to the human cerebral cortex.
Most often, the disease occurs in unborn babies, less often in children of preschool and school age. Ventriculomegaly in adults develops in exceptional cases, since the disease is congenital.
Let's take a closer look at what ventriculomegaly is, the causes of its occurrence and how it is treated.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
According to medical research, ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles occurs due to the following reasons:
- Hereditary prerequisites. If any of the child’s close relatives (mother, father, siblings/cousins) suffered from a similar disease, the likelihood of its occurrence in the newborn increases to 25% compared to a baby in whom no one in the family had such a disease;
- Ventriculomegaly in the fetus often develops as a side disease along with another disease, such as Down syndrome;
- Pathology is provoked by intrauterine infections, as a result of which the ventricles of the brain enlarge.
Causes
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is mainly a consequence of chromosomal abnormalities and genetic abnormalities in the expectant mother.
Other causes of the disease:
- Infections suffered by a woman and negatively affecting the intrauterine development of the fetus;
- Physical injuries;
- Obstructive dropsy (hydrocephalus) of the brain. It occurs against the background of partial or complete blockage of the pathways through which cerebrospinal fluid should normally be drained;
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Hemorrhage (bleeding from blood vessels);
- Destructive damage to different parts of the brain;
- Heredity.
Ventriculomegaly is congenital in most cases. In exceptional cases, pathology can occur in older children, for example, with untreated rickets.
In older age, the cause of dilation of the cerebral ventricles is considered to be bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
Ventriculomegaly predisposes to the development of Down and Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), gonadal dysgenesis.
The disease negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system and leads to disorders in all parts of the brain and in the musculoskeletal system.
The likelihood of having a child with ventriculomegaly increases with age in women. Pregnant women over the age of 35 are born with such children 3 times more often than younger women.
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
Symptoms
Ventriculomegaly in a child is accompanied by symptoms, depending on the degree of the pathological process.
Mild disease is accompanied by:
- increased excitability;
- severe irritability.
The average course of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- seizures;
- the head increases in size;
- veins are clearly visible in the frontal part of the head;
- the child is lagging behind in physical development;
- mental retardation.
During this period of development, the disease can be combined with other abnormalities, such as ventricular asymmetry and agenesis of the corpus callosum.
In severe cases, in addition to severe dilatation of the ventricles, the following is observed:
- strong intracranial pressure, which occurs due to the asymmetry and large size of the ventricles, which compress the surrounding tissues;
- frequent headaches;
- speech disorders.
When the pathological process becomes irreversible, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, Down syndrome and hydrocephalus are added to the existing symptoms.
Diagnosis of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain
Ultrasound procedure of a child’s brain
Depending on the age of the patient, various methods for diagnosing pathology are used:
- The disease can be detected in the fetus starting from the 17th week of pregnancy. For diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the mother’s abdominal cavity;
- Ventriculomegaly in an infant is confirmed after an ultrasound of the head;
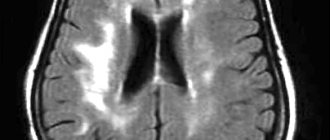
- To diagnose an adult, an MRI of the brain is prescribed.
All procedures are aimed at examining the ventricles of the brain and identifying lateroventriculoasymmetry (violation of ventricular symmetry).
FOR SPECIALISTS
The lateral ventricles of the brain have a complex three-dimensional architecture, which furthermore undergoes significant developmental changes during pregnancy. Sonographic assessment of these structures has been the subject of many sonographic studies, and many different approaches to the definition and diagnosis of intrauterine fetal function have been proposed from time to time. Control charts were established for all different parts of the lateral ventricles, measured both in standard axial planes and in coronal and sagittal sections. However, currently preference is given to measuring the transverse diameter of the ventricular atrium at the level of the glomus choroid plexus or at the level of the parietal-occipital groove. The measurement is easily obtained and reproducible. Various studies have given very similar results in mid-trimester, reporting a mean ventricular width of about 7 mm and a standard deviation of about 1 mm. In the third trimester, the sizes of the ventricles are often smaller than normal values. Some degree of lateral ventricular asymmetry exists in the human fetal brain and is found in utero. Male fruits are slightly but larger in size than female fruits. It is clear that there is no 100% sensitive or 100% specific ventricular value that absolutely distinguishes between the normal and abnormal group. Ventriculomegaly is dynamic, and there is no doubt that fetuses with normal ventricular measurements early in pregnancy may become abnormal. Likewise, there are fetuses with mild ventriculomegaly that were later found to be normal. Currently, however, clinical series indicate that a ventricular atrium measurement of less than 10 mm should be considered normal, while a measurement of 10 mm or more indicates an increased risk of developing brain malformations and/or extracranial anomalies and warrants further investigation. Other secondary findings that may be helpful in diagnosing ventriculomegaly include disruption of the choroid plexus from the ventricular wall. Mahoney et al. described fetuses with an abnormal result where there was 4 mm or more between the choroid plexus and the ventricular walls. The outcome was usually normal in this population, but they felt that the finding of separation of the choroid plexus from the ventricular wall could be associated with an abnormal outcome even if the ventricular width is 10 mm or less. That's a moot point. The current prevailing view is that ventricles less than 10 mm in the second or third trimester should be considered normal. Finally, the choroid plexus has been noted to hang down in the ventricle when there is true ventriculomegaly or hydrocephalus. The intersection of the long axis of the inferior part of the choroid plexus and the long axis of the midline structures forms the choroid angle, which usually ranges from 16 to 22 degrees. If the choroid angle is greater than 29 degrees, it usually indicates ventriculomegaly. In most cases, this torn choroid is easy to recognize and no specific measurements are taken. It is also important to note the location of the choroid plexus in all cases of possible ventriculomegaly. During the second trimester of pregnancy, the cerebral hemispheres appear hypoechoic, falsely giving the appearance of hydrocephalus, which is actually pseudohydrocephalus. However, with pseudohydrocephalus, the choroid plexus never droops (because the ventricles are not enlarged). Thus, noting that the choroid plexus does not droop is helpful in distinguishing true hydrocephalus from pseudohydrocephalus.
Information for parents
The entire surface of the brain and spinal cord is bathed in a clear, colorless fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Cerebrospinal fluid is a clear, watery fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and is also found in all ventricles (brain cavities and tunnels). Liquor softens the brain and spinal cord from shocks. Ventriculomegaly is when the fluid-filled structures (lateral ventricles) in the brain are too large.
What is the prognosis for a fetus with ventriculomegaly?
The prognosis of ventriculomegaly depends on several factors, including the actual size of the ventricles, regardless of whether there are any other findings on ultrasound, such as agenesis of the corpus callosum and amniocentesis results. In general, the outcome is worse when the ventricles are larger, the amniocentesis is abnormal, or there are other problems seen on ultrasound. Best results are usually seen when: 1.) the fetal ventricles are only slightly enlarged (measure 10 to 15 millimeters in size, 2.) when there are no other problems seen on ultrasound, and 3.) genetic testing results are normal - this is called "Isolated" mild ventriculomegaly." The exact prognosis for your baby's health is difficult to know. The most common change in a child is developmental delay. This appears to be related to the size of the ventricles. Fetal MRI is now being studied to see if information from fetal MRI can tell us about the possibility of disability and can provide families with more information about what to expect in their child's health and development. This information will help parents make decisions during pregnancy and prepare in advance for the challenges their baby and family may face.
How serious is ventriculomegaly?
If your doctor sees ventriculomegaly, you may be referred for several tests. These include a more detailed ultrasound (expert ultrasound), amniocentesis and/or microchip (to look at the genetic makeup of your fetus and look for any signs of infection) and fetal magnetic resonance imaging (fetal MRI). Fetal MRI is another way to look at the brain safely. It provides images of the fetal brain using different technologies. Fetal MRI can detect other problems in the fetal brain that may not be detected by ultrasound. Then the results of all the tests are looked at together, and your doctor will tell you what the results mean.
What are the choices during this pregnancy?
There is no treatment before birth for fetuses with ventriculomegaly. Treatment after birth involves managing the baby's symptoms. During pregnancy, it is important to obtain a detailed diagnosis (using detailed ultrasound, amniocentesis and MRI) to determine if there are any additional problems. If there is evidence of more serious deficiencies that require long-term care, we can help refer you to appropriate specialists. If tests show that your baby's cerebrospinal fluid is not being drained well, hydrocephalus is indicated. Hydrocephalus is a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid that causes pressure on the brain. In such a situation, a ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VP shunt) can be recommended. Hydrocephelus is a progressive problem, so the fluid usually builds up slowly over the weeks after your baby is born. In most cases, we will know by 6 months if your child will need a VP shunt. A VP shunt is the surgical implantation of a small plastic catheter that drains cerebrospinal fluid into a part of the body that can easily absorb fluid, such as the abdomen or peritoneum (the membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity). The VP shunt procedure will be performed by a pediatric neurosurgeon. This is a very safe procedure that can help your baby's development as it helps relieve pressure on the brain caused by a build-up of cerebrospinal fluid. Your child will not have to stay in the hospital because the shunt lives under the skin. Many people live their lives well with a VP shunt. Patients with a VP shunt will require regular follow-up with a neurosurgeon to ensure that the shunt continues to function properly.
© Website of Dr. Natalia Vasilievna Khramchenko
Expert research in prenatal ultrasound diagnostics, ultrasound doctor, pediatrician. International certificate FMF ID: 99271
The information on the site is not a public offer and is for reference only. There are contraindications. Consult your doctor.
Copying of site materials is possible only with written permission from the site administration.
A hyperlink to www.echoploda.com is required.
Severity of ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles
Doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of pathology:
- First: an increase in the ventricles of the brain to 11-12 mm. Patients are diagnosed with “ventriculodilation” - a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain in newborns and preschool children;
- Second: enlargement of the ventricles up to 15 mm. Against this background, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and impaired blood flow to the affected areas are often observed;
- Third: enlargement of the ventricles up to 20 mm. At this stage, irreversible changes occur in the structure of the brain.
In addition, the child may be diagnosed with “borderline ventriculomegaly,” which means an increase in the lateral ventricles by no more than 9 mm.
Ventriculomegaly 1st degree
At the first stage of development of the disease, there are no pronounced symptoms. Only a neurologist can detect it after diagnosis. Most parents notice that the child becomes excitable and irritable. Unfortunately, no other symptoms appear.
Moderate ventriculomegaly
The second stage of the disease is also called “moderate ventriculomegaly.” As a rule, it is combined with other ailments, for example, ventriculomegaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum often occur together. Also in this case, lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain (asymmetry of the ventricles) occurs. The following symptoms are also observed:
- Periodic convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures;
- Increase in head size;
- The presence of bulging veins on the forehead;
- Slow physical development;
- Mental retardation.
Severe ventriculomegaly
In addition to abnormal expansion of the ventricles of the brain, the following symptoms are present:
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the asymmetric shape of the ventricles;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Speech disorders.
Additional diseases are often added to the pathology: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome or hydrocephalus.
Types of Ventriculomegaly
According to the nature of the course, ventriculomegaly is divided into three types:
- MILD FORM OF DISEASE. Changes are detected only in one ventricle, deviations in size do not exceed 12 mm. With this type of pathology, treatment may not be required;
- MODERATE FORM OF DISEASE. The ventricles increase in size to 15 mm, disturbances in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid are noted;
- SEVERE FORM. The cerebral ventricles are significantly expanded in size, which causes serious pathologies of the central nervous system and brain.
Ventriculomegaly can be either an isolated defect or combined with other common fetal developmental anomalies. The disease often accompanies chromosomal abnormalities (for example, Down's disease) and can be one of multiple congenital defects.
Isolated ventriculomegaly almost does not cause serious consequences. When combined with other anomalies in the fetus, the pathology is severe.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
The disease is most often congenital, so it can be detected even before the birth of the child. To do this, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, based on the results of which the degree of pathology is determined. In the third degree, the woman is offered an abortion, since the risk of miscarriage is high.
In other cases, doctors begin searching for the cause of the pathology:
- A woman must be tested for infectious diseases;
- The fetus is checked for the presence of congenital pathologies (cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc.);
- If no abnormalities are found, the pregnant woman is prescribed potassium tablets. It saturates the fetus with oxygen, which improves its condition.
With ventriculomegaly in the fetus, the consequences depend on the promptness of treatment at the stage of pregnancy.
Danger and consequences of the disease
After birth, ventriculomegaly in a child may manifest as increased agitation and moodiness, or, conversely, an overly calm, inhibited state.
In severe cases, the pathology leads to an increase in the size of the head, the appearance of frequent cramps, and noticeable protrusion of the veins.
The danger of the disease and the likelihood of serious consequences depend on how dilated the cerebral ventricles are. If their size is up to 15 mm, then the diagnosis is made as moderate ventriculomegaly; with appropriate and timely treatment, this pathology does not lead to severe disorders.
When the ventricles are larger than 15 mm and hydrops of the brain increases, the fetus may develop severe congenital anomalies of the central nervous system and, in some cases, death.
Most often, a disappointing prognosis corresponds to the early development of ventriculomegaly and its rapid increase with the transition to hydrocephalus.
With a moderate type of pathology, in 80% of children no developmental deviations are observed in the future, in 8% of cases the deviations are not critical, in 10% the pathology causes disorders that cannot be corrected, leading to disability.
The risk of adverse neurological disorders with ventriculomegaly is significantly higher if the fetus is female.
Possible complications of ventriculomegaly include the likelihood of serious NS pathologies in the fetus:
- Down syndrome;
- Edwards syndrome. Refers to chromosomal pathologies and is characterized by multiple malformations of intrauterine development;
- Turner syndrome. Physical abnormalities in this disease are combined with sexual infantilism;
- Severe hydrocephalus.
The prognosis for ventriculomegaly in the fetus also depends on the underlying cause of the pathology. An unfavorable prognosis is given if the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired due to genetic diseases, since the underlying disease can negatively affect the viability of the child.
If the ventricles of the brain expand under the influence of infectious processes and lead to hypoxia, then psychoneurological disorders or the development of cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) cannot be ruled out in the future.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
With a mild degree of pathology, no therapy is prescribed: the mother only needs to carefully monitor the child’s condition and, at the slightest deviation from the norm, contact a neurologist.
The second stage is treated with medication: the child is prescribed drugs that accelerate processes in the brain:
- Vitamin B tablets;
- Diuretics are drugs that remove excess fluid from the body;
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to walk with your child in the fresh air more often and perform minimal physical exercise with him.
Surgery
The third degree of pathology is treated surgically, since taking medications will not give any results. The asymmetric shape of the ventricles is corrected by performing ventriculo-peritoneal shunting.
This is an operation during which shunts are installed to remove excess fluid. After surgery, children recover quite quickly: insomnia disappears and appetite returns.
What is ventriculomegaly in an infant?
Ventriculomegaly is a congenital malformation of the fetal brain, in which the size of the lateral ventricles of the brain pathologically increases, causing neurological disorders to develop. These special cavities in the human brain contain the so-called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and normally their depth should be from 1 to 4 mm. With ventriculomegaly they expand to 12-20 mm.
The reasons for the development of ventriculomegaly are not fully understood, but women over 35 years of age have such children three times more often than young mothers. Many doctors consider the expansion (dilatation) of the lateral ventricles of the brain not to be an independent pathology, but a pathological condition that indicates a failure of intrauterine development and accompanies various diseases. She can:
- appear on its own. This happens in premature babies and those babies whose mothers suffered a severe infection, injury or late bleeding during pregnancy;
- combined with chromosomal abnormalities (Down, Edwards, Turner syndromes) and non-hereditary malformations.
In infants, dilatation of the cerebral ventricles can occur as a complication of rickets and, in turn, lead to neurological disorders. Thus, in older children and adults, dilated ventricles of the brain are observed in some mental illnesses - schizophrenia, bipolar disorder. But it is not entirely clear whether this pathology is a symptom, consequence or cause of mental illness.
Types of dilatation of the cerebral ventricles
To assess the correct development of parts of the brain, doctors use special tables, and diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. It is done during pregnancy and according to indications for a newborn baby.
Ventriculomegaly can be asymmetrical and right-sided. It is also classified by severity and location.
- Light type. The ventricles of the brain are expanded to 10-12 millimeters.
- Medium type. The intracerebral cavities are expanded to 15 mm; the outflow of brain fluid is disrupted, and the child experiences neurological disorders.
- Severe form. The cerebral ventricles of an infant are enlarged to 16-20 mm or more, and serious pathologies of brain development occur, such as hydrocephalus.
By location, lateral dilatation of the ventricles is distinguished (left + posterior); pathology of the III (in the area of the visual hillocks in the front of the forehead) and IV ventricle (in the occipital part - in the medulla oblongata and cerebellum).
Symptoms and diagnosis
Anomalies of brain development are clearly visible during intrauterine ultrasound. But if ventriculomegaly in the fetus is not combined with other pathologies, then it is much more difficult to notice it in an infant with a mild degree. In addition, it is impossible to predict how the baby’s brain will “behave” in a month, two, three, six months or a year! Has ventricular dilation managed to interfere with the normal development of the little man? Will they continue to increase, and if so, how quickly?
The answers to these questions will be given by time and careful observation of the baby. The child needs to be examined if:
- he began to sit and walk later than others his age;
- he does not babble, does not try to pronounce sounds and words at the appropriate age;
- suffers from headaches, seizures;
- he has a large head;
- the difference between the head circumference and the chest circumference of the child exceeds three centimeters.
In children with delayed motor or speech development, the diagnosis of ventriculomegaly is sometimes made “to be on the safe side.” But after some time, such children catch up with their peers in development, lead a normal life, and even in the distant future they do not develop any neurological symptoms.
Treatment
A baby with moderate ventriculomegaly is prescribed preventive treatment or observation only. On average, 80% of such children develop without physical or mental disabilities. The remaining infants with moderate, moderate and severe pathology have various neurological disorders - from minor to serious.
Drug treatment depends on the severity of the disease and its characteristics in each individual baby. Medications do not affect the size of the ventricles of the brain, but help the child’s body compensate for abnormal processes occurring in it. Usually the child is prescribed:
- nootropic drugs that improve cerebral circulation;
- antihypoxants (increase tissue resistance to lack of oxygen), diuretics to reduce the amount of fluid in the body, and accordingly, in the cavities of the brain;
- drugs that retain potassium in the body - they help prevent neurological disorders; vitamins.
Children are also prescribed massage and special physical therapy - static exercises that load the pelvic muscles and pelvic floor. After timely treatment, a child with moderate ventriculomegaly will develop completely normally; with moderate pathology, he may still have some neurological impairments, but his development will improve. In severe cases, the baby undergoes surgery: a special drainage shunt tube is installed in his skull to drain excess fluid from the brain.
Diagnostics
Ventriculomegaly is detected during a routine ultrasound examination between 17 and 30 weeks. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to observe the process over time, and for this, repeated diagnostics are prescribed. After a few weeks, if the suspicions are confirmed, the patient is referred to a geneticist for consultation.
Additional genetic studies are carried out, karyotyping is prescribed, which will help to clarify the structure of the anomaly and the composition of the chromosomes.
Additionally, the patient undergoes a blood test to determine the presence or absence of an infection that could affect the deviation of intrauterine development.
The fetus or newborn is checked for congenital abnormalities.
A magnetic resonance thermogram of the child is performed, and if a mild or moderate degree is detected, then neurosonography is performed to track the process over time.
If no abnormalities are detected, therapy is prescribed in the form of potassium tablets, which will replenish the cells with the missing oxygen.
If a severe pathology is detected, the pregnancy is terminated, and in the case of a mild to moderate degree, therapeutic measures are used.