Home > Cancer treatment in Israel > Treatment of meningioma in Israel
Meningioma is a tumor that develops from the membranes covering both the brain and spinal cord. In terms of frequency, it ranks first among benign intracranial neoplasms – it accounts for 25% of all diagnosed cases. As a rule, the tumor is characterized by a slow growth rate, and it can be localized in different parts of the nervous system due to the fact that the meninges cover both the brain and the spinal cord.
Typically,
patients have one primary focus of meningioma , but in rare cases, tumors form in several parts of the central nervous system
.
Most often, meningiomas occur in women aged 40 to 70 years, but men over 35 years of age also suffer from the pathology. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed accidentally, during a test for another reason, or when the formation significantly increases in size and the symptoms become severe. There are 3 types of meningiomas: benign, atypical and malignant. Benign meningiomas do not invade surrounding tissue, grow slowly and in many cases do not require treatment, but only regular monitoring. Atypical and malignant meningiomas - they account for about 5-10% of the total - are characterized by rapid infiltrative growth. It is malignant types of meningioma that are more common in men.
Malignant tumors are mainly localized in:
- cavernous and parasagittal sinuses;
- pyramid of the temporal bone;
- wings of the sphenoid bone;
- foramen magnum;
- cerebral hemisphere zone;
- tentorial notch;
- cerebellopontine angle.
Malignant meningiomas require immediate medical attention at the first signs of the disease.
To ensure an accurate diagnosis and receive the most effective medical care, you need to choose the right clinic. Israeli clinics are among the leading cancer centers in Europe: the best oncologists and neurosurgeons are gathered here, and all conditions for a comfortable stay are created for patients. Israel also attracts medical tourists due to the affordable cost of medical care combined with the opportunity to undergo a full examination, therapy and rehabilitation in one medical facility. You can evaluate the benefits of our clinic’s offers by sending an online request or contacting us at the phone number indicated on the website.
Consult an Israeli specialist
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the formation of tumors and their transformation into malignant lesions have not been clearly established. However, doctors are aware of the negative impact of certain factors that increase the risk of meningioma. Among them:
- unfavorable family history, in particular, the presence of multiple hemangiomatosis or neurofibromatosis in close relatives;
- being female - the female body produces hormones that contribute to the development of tumors;
- age over forty years;
- exposure to radiation, both in high and low doses. The risk of meningiomas is increased in patients who have previously received radiotherapy for brain tumors.
In the majority of patients, with timely and adequate treatment, which consists of radical removal of the meningioma, their health is completely restored, and relapses are extremely rare. The likelihood of relapse is high in patients with malignant meningiomas and tumors growing in the area of the venous sinuses, which makes their removal difficult.
Meningioma is not a brain tumor because it is formed from its membrane. At the same time, by squeezing brain tissue as it grows, it can cause symptoms characteristic of brain tumors
.
Causes of the disease
Presumably, the following factors may contribute to the appearance of a neoplasm:
- genetic predisposition;
- negative impact of poor environmental conditions;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- exposure to x-rays or radiation;
- skull injuries, including intrauterine and birth injuries;
- hazardous working conditions: working with nuclear waste and chemicals;
- regular consumption of nitrates in food;
- brain infections;
- other types of cancer.
People with reduced immunity and those who have undergone internal organ transplantation are at greater risk of developing the disease.
Symptoms and treatment of brain meningioma
In the initial stages, most meningiomas are completely asymptomatic. Signs of the disease appear when the tumor grows, compresses the brain or spinal cord and interferes with normal blood circulation. In such situations, the following may occur:
- pressing headache that worsens at night or in the morning;
- visual disturbances (double or blurry vision);
- memory impairment;
- hearing loss, ringing in the ears;
- loss of smell;
- convulsions;
- weakness or partial paralysis of the limbs;
- change in emotional state (depression, euphoria).
With a certain localization of meningiomas, more specific symptoms are noted:
- in the area of the tubercle of the sella turcica – a sharp deterioration in vision;
- in the temporal lobe – visual and hearing impairment;
- in the area of the tentorium cerebellum – coordination and movement disorders;
- in the convexital area – epileptic seizures.
If you notice one or more neurological symptoms in yourself, your spouse or a relative, do not delay getting tested. Moreover, in our clinic it will take only a few days for a doctor’s consultation, diagnostic measures and preparation of an individual treatment program.
Help is needed? Doctor online. Consultation is free+972-52-651-26-54
Help is needed? Doctor online. Consultation is free+972-52-651-26-54
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
After surgery to remove brain meningioma, the patient is under medical supervision for some time. After discharge, both the patient and his relatives must monitor their health and follow the doctor’s recommendations. As a rule, in order to achieve a complete cure after surgery, the following are prescribed:
- courses of radiation therapy (in particular for incomplete excision of meningioma);
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Recurrence of benign type brain meningioma occurs in only 3%, of atypical type - about 40%. If the tumor is malignant – 78%, but even in this case, after complex treatment and removal of the tumor, the patient’s life can be made easier for several years.
Our clinic will select the optimal treatment methods. Diagnostic prices and the cost of meningioma removal can be found on the website.
Disease detection
To choose the optimal treatment strategy and assess the prognosis, the doctor needs to get the most complete picture of the disease. For this purpose, all patients with suspected meningioma undergo a thorough diagnosis using the most modern equipment.
Before instrumental tests are started, the patient is examined by a neurologist. During the examination, the doctor assesses:
- state of the vestibular apparatus;
- reflexes;
- vision and hearing;
- coordination of movements and other cerebellar functions.
In addition, the doctor will carefully study the medical history and medical documentation provided by the patient, familiarize himself with the data of previously performed medical examinations and test results.
As part of the diagnosis, blood tests are required - general clinical, as well as a special analysis for tumor markers. Most patients are prescribed electroencephalography, a study of the electrical activity of the brain. This is an absolutely safe and painless procedure lasting about half an hour.
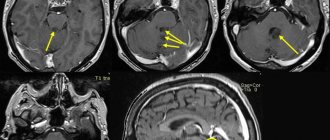
Medical imaging techniques are recognized as the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of meningiomas: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Both diagnostic procedures are usually performed with contrast enhancement to assess the size and location of the tumor, its location in relation to critical brain structures, and resectability (the possibility of removal during surgery).
| CT scan | creates a layer-by-layer image of brain structures, allowing you to identify deviations from the norm; |
| magnetic resonance imaging | a modern technique used as an alternative to CT to obtain a detailed picture of the affected organ; |
| angiography | The procedure involves the introduction of a special contrast agent into the blood to monitor the blood supply system of the tumor. This method is mainly used before surgery for the most accurate planning of surgeons’ actions; |
| biopsy | study of the morphological characteristics of a tumor based on a sample of tumor tissue. Biopsy and histological analysis help differentiate benign from malignant meningiomas. At the Assuta clinic, when performing a biopsy, the most modern equipment is used, which allows it to avoid affecting vital areas of the brain. |
4. Methods for removing meningioma
The most effective way to treat a tumor is surgery
, during which the surgeon completely removes it. However, if the tumor is localized in a hard-to-reach place, or is closely adjacent to vital areas, it cannot be completely removed. This factor is one of those that causes relapses.
Surgical removal of meningioma is aimed at ensuring that all surrounding bone tissue is subjected to thorough resection. The dura mater adjacent to the meningioma must be removed using surgical plastic surgery
replaced by patient tissue or artificial grafts. The surgical intervention is carried out under the control of special microscopic and neuronavigation equipment.
In some cases, when for one reason or another traditional surgery is impossible, radiosurgery
, in which the tumor is removed by powerful targeted ionizing radiation.
Effective assistance from Israeli doctors
The effectiveness of treatment of meningioma in the best medical facilities reaches almost 100% due to the work of first-class world-famous neurosurgeons. Thanks to their skill, as well as the most modern and effective treatment methods, Assuta patients quickly return to everyday life, forever forgetting about their terrible diagnosis - meningioma.
The therapeutic course includes several stages:
- consultation with a specialist, examination, medical history;
- detailed diagnostics (laboratory tests, computer and magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography);
- drawing up an individual treatment plan.
When planning treatment, the doctor takes into account the characteristics of the tumor (size, location, histological type, proximity to large vessels or vital centers), as well as the general condition of the patient (age, presence of concomitant diseases, severity of symptoms).
Diagnosis of meningioma
Diagnosis is made by CT, MRI or PET/CT. MRI with contrast is considered the most informative method for detecting benign meningiomas of the spine and brain. It allows you to see the relationship of the tumor with surrounding tissues and assess the condition of the blood vessels. CT detects up to 90% of tumors, shows bone changes and calcifications in the tumor.
PET/CT is used to detect malignant forms; the examination helps to assess the metabolic rate in the tumor, and therefore determine the likelihood of its malignant degeneration.
The PET center performs PET/CT diagnostics of meningiomas using fluorine-18-fluoroethyltyrosine. The advantage of the study is its safety and high information content; it allows you to detect even small foci of malignant cells.
Do you need additional information on PET CT diagnostics? Get a free consultation from our specialists Get a consultation
Treatment of meningioma without surgery - Cyber and Gamma knife at the Assuta clinic
Surgery is the highest priority method of combating the tumor, since this is the only way to remove it entirely, preventing the development of relapse.
The operation is indicated if the meningioma has already reached an impressive size, but its removal does not pose a danger to the life and health of the patient. For example, it is not always possible to perform resection of meningiomas adjacent to large blood vessels, venous sinuses, brain stem, etc. Assuta specialists recommend treating meningiomas that are difficult to reach or adjacent to critical structures using conservative methods that reduce the risk of complications to almost zero and do not injure healthy tissue.
Using a radio wave cyber knife instead of a traditional scalpel makes the procedure for destroying a tumor absolutely painless. In addition, there is no need for general anesthesia. The proven effectiveness of the cyber knife is 95%, and the course of treatment takes from one day to several months, depending on the size of the tumor and the individual characteristics of the body.
A gamma knife can be used to remove very small tumors. Gamma therapy is a modern non-invasive, gentle method of meningioma removal, practiced in medicine in Israel. It involves targeted irradiation of the lesion from different sides with small doses of radiation, which are focused directly in the area of tumor growth. The accuracy of the gamma knife is amazing - 0.3mm (for the cyber knife - 1.0mm).
After removing the meningioma using any of the above methods, the patient is observed for some time at the Assuta clinic and undergoes repeated checks. If there are residual tumor cells, a stereotactic course of radiation is prescribed, during which they are completely destroyed.
Israeli doctors do not recommend using chemotherapy and external beam radiation therapy to treat meningiomas due to the low effectiveness of these techniques. Chemotherapy is rarely used for inoperable meningiomas that are resistant to radiotherapy.
Treatment of meningioma in the most popular Assuta clinic in Israel is carried out under the close supervision of experienced neurosurgeons - Zvi Ram, Zvi Cohen, Moshe Adani, Dvora Blumenthal.
1.What is meningioma?
Meningioma
- this is, in most cases, a benign tumor that grows from the arachnoid membrane of the brain, or more precisely, from the arachnoid endothelium, and is not, as was previously believed, a tumor of the dura mater. The term “meningioma” was introduced in the 20s of the last century by Harvey Cushing, an American neurosurgeon.
Meningioma is a dense brain tumor surrounded by a capsule, often round in shape, although in some cases horseshoe-shaped and flat tumors are found. Tumor size
can vary from a few millimeters to 15 centimeters. The neoplasm capsule consists of cells of the tissues surrounding it. Statistically, these brain tumors more often affect women than men. They are rare in children.
Most often, meningiomas form either on the convexital surface of the brain or at the base of the skull.
. The surface of the brain located in the area of the frontal, parietal and occipital bones of the skull is considered to be convexital. Much less often, the presence of meningiomas is noted in the intraventricular cavities or on bone tissue.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Prices for treatment of brain meningioma at the Assuta clinic
Basic screening program for brain tumors in Israel:
| Description of the procedure | Cost ($) |
| advanced blood tests | 440 |
| field of view | 350 |
| consultation with a neurosurgeon | 550 |
| preoperative preparation (ECG + x-ray of the lungs + consultation with an anesthesiologist) | – |
| navigation MRI | 1350 |
Therapy includes:
| Description of the procedure | Cost ($) |
| surgery and 4 days of hospitalization in the neurosurgery department (1 day in intensive care) | 23900 |
| use of neuro-physiological monitoring | 1450 |
| surgical materials and equipment | 2250 |
| rapid biopsy during surgery and final histopathology of the tumor | 1250 |
After completion of the operation and during the further rehabilitation period, the patient is advised not to leave Israel for fourteen days. During this period, Israeli doctors will develop an individual program of further medical observation and treatment for you.
4.Methods of treatment of parasagittal meningiomas
The most effective treatment is complete removal of the brain tumor using radical surgery.
using craniotomy. The surgical tactics chosen by the surgeon will depend on whether the meningioma is unilateral or bilateral, and whether there is invasion of the superior sagittal sinus.
During the operation
To prevent relapse, all affected tissue is carefully excised and the tumor is removed. If the tumor has managed to grow into the sagittal sinus and falx (a fold of the dura mater separating the two hemispheres), effective removal of meningioma is only possible with the use of resection of the affected parts of these areas. Such operations pose a certain risk for the patient, since there is a great danger of circulatory impairment in large parts of the brain.
Moreover, there is good news for such patients: recent advances in neurosurgery in the field of improving operating techniques have demonstrated the high effectiveness of a new method for removing complex parasagittal meningiomas using a laser with a specific wavelength
. This type of radiation is capable of penetrating tumor tissue up to 5 mm, being absorbed by the blood and performing a coagulating function.
Rehabilitation periods: goals, therapy, duration
At each stage of rehabilitation, different therapeutic and recreational methods are used with different periods:
The early period is 1-2 weeks
. The main goals are to relieve swelling and pain, prevent complications, and speed up wound healing. During the first days, it is necessary to remain in bed, take antibiotics and neurometabolic drugs, and treat the surgical suture. Mandatory actions: wearing a corset, breathing exercises, gentle exercise therapy.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
The late rehabilitation period lasts up to 2.5 months
. During this time, the ligamentous-muscular system is strengthened, the functions of the spine are restored, and the patient gradually returns to normal life. Drug treatment is prescribed only if necessary; therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, and special exercises in the pool are indicated. During active activities, it is possible to wear a corset.
The deferred period can last up to 9 months (the terms are determined individually). Particular attention is paid to strengthening the body, complete restoration of vital functions, and prevention of relapses. The plan of activities consists of exercise therapy, aqua gymnastics, manual therapy, mineral baths and mud therapy.
Rehabilitation is complemented by sanatorium-resort treatment, which is preferably done once a year. If the recovery process for some reason did not go as planned and did not produce the expected results, the patient is sent for a medical examination. Having the examination and analysis data in hand, the specialist decides on a course of further action.
Asymptomatic meningioma - to treat or not to treat?
We have already written about when a tumor requires mandatory treatment and how dangerous it is to rely on dynamic monitoring of growing meningiomas.
Meningiomas are considered the most common tumors of the central nervous system - 7 cases per 100,000 population. However, their detection is often accidental during CT or MRI. Most often, such asymptomatic tumors do not exceed 25 mm in diameter, but in a quarter of all cases they can increase significantly in volume over several years.
The dynamics of meningioma growth can be represented as a sinusoid, in which the initial and final growth phases are noted. A small tumor discovered by chance can be either in the initial phase of its growth or in the final phase. In both cases, the likelihood that it will increase sharply in a short period of time is small, but understanding what the prospects for the behavior of a particular tumor significantly changes medical tactics.
There is still no consensus on the tactics of treating asymptomatic meningiomas: some scientists believe that decisive action should be taken when neurological symptoms appear or there are signs of progressive tumor growth; others are sure that there is no point in waiting until the tumor begins to grow and take all necessary measures as early as possible.
In order to standardize the approach to the treatment of asymptomatic meningiomas, several tumor assessment scales and criteria have been developed.
First, it should be noted that the generally accepted standard for assessing the growth of intracranial tumors is to measure the volume rather than the linear dimensions of the tumor (diameter). The dynamics of tumor growth is assessed using the AGR (Absolute Percentage of Growth) criterion, which shows the rate of tumor growth in cubic centimeters per year.
Secondly, a risk group has been identified in which the possibility of increasing tumor size is higher:
- Age less than 60 years
- Male
- Sizes over 25mm
- Absence of calcifications in the tumor
- Presence of an area of edema
- T2 hyperintense signal on MRI
- Localization at the base of the skull
- Symptomatic course
Thirdly, in 2021, the AIMSS (Asian Intracranial Meningiomas Grading System) diagnostic scale was developed.
This system evaluates volume, presence of calcification, peritumoral edema, and T2-weighted MRI intensity. The assessment results assign the tumor a low, intermediate, or high risk of rapid growth.
Thus, deciding on the management of asymptomatic meningioma requires evaluation of many factors. But even if the risk of further growth is very low, this does not eliminate the need for periodic monitoring.
Stereotactic radiosurgery using Gamma Knife allows you to quickly and effectively stop the growth of asymptomatic meningioma in the initial stages of its growth, avoiding trephination and long-term hospitalization.
Timely treatment will help avoid the consequences of uncontrolled tumor growth, which can lead to severe complications and disability.
Classification of the disease
Meningiomas are conventionally classified into three large groups:
- benign meningioma - has clear boundaries, a bumpy surface, and grows slowly. Over time, it changes its structure - it becomes softer and then gel-like. Often located along the venous sinuses directly on the surface of the brain;
- atypical meningioma - it is also called semi-benign. In its structure it resembles benign, but the cells in it are different in size and shape, there are small necrotic, that is, dead zones;
- malignant meningioma - the set of chromosomes in the cells is incorrectly formed, they are heterogeneous in size and shape, the structure of the diseased tissue is disturbed, it contains a large number of dead areas. These tumors are aggressive, quickly increase in size and metastasize.