Pediatric epileptology is a subsection of neurology devoted to epilepsy at a young age. This is a disease in which repeated attacks occur - paroxysms. The diagnosis can be made only if at least two seizures have occurred, and no other causes other than epilepsy could lead to them.
The fact is that in young children, convulsions can occur when the temperature rises during infectious diseases, intoxication, or the administration of certain medications, as a reaction to vaccinations. Seizures may accompany metabolic disorders such as diabetes.
Children often suffer from this disease: statistics say that it occurs in 7 out of 1000 children under the age of 16. In addition, in childhood the disease occurs with certain characteristics. It is for this reason that pediatric epileptology was singled out.
Signs of epilepsy
Pediatric epileptology identifies the following main symptoms of the disease:
- Grand mal seizure. This is the main symptom of epilepsy. It can begin suddenly, but more often it is preceded by an “aura” - specific sensations, for example, the feeling of a breath of wind, sparks before the eyes, some kind of unclear sound. After this, the patient makes a sharp sound caused by a spasm of the glottis, then he begins to have convulsions that take over the whole body, his breathing becomes noisy, and foam comes out of his mouth. The attack ends on its own, after which the patient may fall asleep and not remember what happened to him, or remain conscious, remaining confused for some time. Seizures may occur rarely or several times a day.
- Minor convulsive seizure. During it there are no general convulsions. The patient makes automatic movements: turning the head, chewing movements and other automatisms. With them, a short-term partial disorder of consciousness is observed.
- Absence. This symptom most often occurs in children, and more often in girls than in boys. It manifests itself in the fact that the child disconnects from reality: he stops speaking and moving, freezes, his gaze is fixed at one point, he does not react to external stimuli. There are no convulsions in this case.
In addition to these striking manifestations, epilepsy in children may be accompanied by:
- sleepwalking;
- mood disorders, the appearance of irritability, sudden changes in mental state;
- a change in character, the appearance of hypertrophied pedantry and accuracy.
Epileptic seizures can occur both while awake and during sleep, quite often when falling asleep or waking up.
Mechanism of occurrence of an epileptic seizure
The root cause of epilepsy is excessive activity of brain cells. It usually occurs in a certain area - the epileptic focus, in the cells of which the excitation processes are modified.
Causes of epilepsy in children
The opinion that epilepsy is an exclusively hereditary disease is not supported by modern doctors. Some of its forms are not inherited, some are a consequence of structural damage to the brain (focal cortical dysplasia, congenital anomalies of brain development, tuberous sclerosis, gangliomas, etc.). It is also impossible to say unequivocally that any diseases suffered by a person lead to epilepsy, but they can accelerate the onset of the disease. These factors are:
- birth injuries, the occurrence of oxygen deficiency at birth;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- neoplasms in the brain (cysts, hematomas, tumors);
- brain abscess;
- infectious, parasitic, viral diseases;
- meningitis, encephalitis.
What is the danger of epilepsy in children?
- During an attack, a child can be seriously injured, choke on vomit, or bite their tongue or cheek.
- In addition, children have frequent and severe attacks at short intervals, when they simply cannot recover.
- Due to constant attacks, chronic pneumonia can form and mental retardation can develop.
What symptoms require a pediatric epileptologist?
The symptoms of epilepsy are very varied. A classic epileptic seizure looks like this:
- The child loses consciousness - after the aura or without it. An aura is a complex of neurological symptoms before the next attack (nausea, speech impairment, tinnitus, numbness of the tongue, etc.).
- The muscles of the chest contract, the glottis sharply narrows, which is accompanied by a cry.
- Tonic convulsions appear - all muscles spasm, the head is thrown back, breathing is delayed, the jaw clenches tightly.
- After 10-20 seconds, tonic convulsions turn into clonic - the muscles of the torso and neck contract rhythmically.
- Sometimes there is a discharge of foamy blood from the mouth.
This attack lasts 2-3 minutes. Then all the muscles relax. In this case, involuntary bowel movements or urination may occur.
Absence seizures are often observed in children with epilepsy. These are short-term episodes of loss of consciousness. The child freezes for a few seconds, not responding to any external stimuli during this time. He then continues to play or engage in other activities without realizing that he has just had an attack. The frequency of such epileptic seizures can be high – dozens of times daily.
Other possible manifestations of epilepsy:
- hallucinations;
- cessation of speech;
- Strong headache;
- feeling of electric shock;
- involuntary laughter or crying;
- sudden increase in heart rate;
- involuntary movements;
- loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the body.
All these situations require consultation with an epileptologist to exclude or confirm the diagnosis of epilepsy.
Diagnosis of epilepsy
- Before making a diagnosis of epilepsy, a specialist in pediatric epileptology finds out all the nuances of the course of attacks: their frequency, what preceded them. Talking to parents who can describe their child's seizure in detail is one of the key points in diagnosing epilepsy.
- To exclude any other causes of seizures, laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed, as well as consultations with highly specialized specialists - a cardiologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and others.
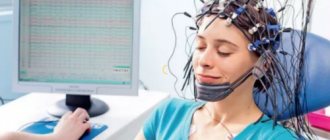
- To clarify the diagnosis, electroencephalography (EEG) is performed. With its help, the bioelectrical activity of the brain is assessed and the area of increased excitability is determined.
- A study such as Video-EEG monitoring is also used, in which, simultaneously with the instrument readings, the behavior and paroxysms described by the patient’s parents are recorded on a video camera.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be prescribed.
Treatment of epilepsy
Epilepsy is treated using conservative methods. Medications are aimed at preventing recurrent attacks. This therapy is effective in approximately 75% of patients. The effectiveness of conservative treatment tends to increase, because global pharmaceutical companies are developing new drugs for epilepsy. The doctor selects the optimal drugs for each clinical situation individually, which allows achieving the best treatment results.
Advantages of treatment with a pediatric epileptologist:
- the doctor knows the specifics of the child’s body - in most cases, special medications are used, not the same as in adults;
- a pediatric epileptologist carefully monitors the safety of therapy (the risk of side effects is assessed, and the function of internal organs is monitored using tests);
- In childhood, there are many special forms of epilepsy that an adult epileptologist never encounters.
Can epilepsy be cured?
The prognosis of the disease is directly related to its form. Benign forms of epilepsy that occur in childhood do not necessarily require drug therapy and disappear with age. In the process of treating adults, when it is possible to achieve the disappearance of attacks and remission, the doctor may decide that there is no need to continue taking antiepileptic drugs. But there are also forms that require medication for almost the entire life of the patient, even despite complete remission.
In our clinic, appointments are conducted by neurologists who have high qualifications and practice in the field of neurology, as well as titles, degrees and state awards. You can receive other qualified medical care at the Neuro-Med pediatric and adult neurology clinic in Moscow.
FAQ
How to make an appointment with a neurologist?
You can sign up for Dr. Gruzdev’s Clinic in two ways: call us by phone or click the “Sign up” button in the upper right corner of the site and fill out a simple form.
If you want to go to a neurologist at a municipal clinic, then first you need to get a coupon to see a therapist, who, if indicated, will give a referral to this specialist.
Who treats neuroses, a neurologist or a psychotherapist?
Neuroses are treated by both of these specialists at the same time.
Who treats shingles, a neurologist or a dermatologist?
Shingles is treated by either a dermatologist or a neurologist.
Who treats depression and prescribes antidepressants, a neurologist or a psychiatrist?
Depression often accompanies neurological diseases; it may be a symptom of organic brain damage. It always worsens the clinical picture of a neurological disease and reduces the patient’s recovery options.
Depression is detected after a stroke, in Parkinson's disease, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer's disease. And, conversely, with long-term depression without treatment, changes occur in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala.
Therefore, a neurologist treats depression. However, he must redirect the patient to a psychiatrist if:
- there is a severe form of depression;
- the patient has suicidal thoughts;
- bipolar depressive disorder is present.
A neurologist can independently treat minor and subsyndromal depression.
The neurologist also prescribes antidepressants, but he prioritizes the minimum of side effects and negative interactions with other medications over the clinical effectiveness of the drugs. The antidepressant should not adversely affect a neurological disease, cause an increase in blood pressure, impair cognitive function, or cause hypotension.
Who diagnoses “dysarthria” and treats the disease, a speech therapist or a neurologist?
Both of these specialists treat dysarthria and can make this diagnosis.
Who treats Alzheimer's disease, a psychiatrist or a neurologist?
It is best if both of these specialists are involved in maintaining the normal condition of the patient, each in his own profile. This will help you adapt better and improve your quality of life.
Personal qualities of the profession of epileptologist
In order to work as an epileptologist, you must not only be passionate about medicine and science, have a specialized education and appropriate training, but also have certain character traits:
- responsibility;
- discipline;
- stress resistance;
- inner rod;
- emotional resilience;
- desire to help people;
- ability to connect with patients and their families;
- desire for self-development;
- erudition.
Epileptologist - description, doctor's advice:
E Zh Ts Sh Shch Yu Ya
Children's doctors
- Who is an Epileptologist
- What is the competence of an Epileptologist?
- What diseases does an Epileptologist treat?
- What organs does an Epileptologist deal with?
- When should you contact an Epileptologist?
- When and what tests should be done
- What are the main types of diagnostics usually performed by an Epileptologist?
- Advice from an Epileptologist
- Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
Who is an Epileptologist?
Specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy and rehabilitation of epileptic patients.
What is the competence of an Epileptologist?
An epileptologist studies disorders of brain function that manifest as sudden, recurring seizures. Epilepsy is the oldest disorder of brain function known to date; it accompanies the human race throughout its existence. Its external manifestations have already been described in ancient Egyptian papyri and Indian books.
What diseases does an Epileptologist treat?
Epilepsy.
What organs does an Epileptologist deal with?
Brain.
When should you contact an Epileptologist?
The main, or cardinal, sign of epilepsy is a grand mal seizure. The seizure is preceded by a short-term state called an aura, as if a signal about its onset. The aura is expressed differently: sometimes the patient feels like a breath of wind (hence the name “aura”), sometimes he feels some smell, sometimes he sees sparks, sometimes he hears thunder, etc. The attack itself begins with an inarticulate cry caused by a convulsive spasm of the vocal cord. cracks. The patient loses consciousness and falls, convulsions seize all the muscles, the body tenses, then begins to beat convulsively. The face turns blue, breathing is held at first, then becomes noisy, saliva is not swallowed, foam appears on the lips. Often during convulsions a person may bite his tongue, lips, or cheek. But then he begins to breathe calmly, his face turns pink - the seizure most often ends in sleep. If the patient gets up immediately after a seizure, then his consciousness is not entirely clear, his gaze wanders, and he does not immediately recognize those around him and does not immediately orient himself in the situation. His speech at this time is very poor: he speaks little, gets by with a few words. If the patient falls asleep, then upon awakening he does not remember anything and guesses that there was a seizure, either by a feeling of weakness, or by bites in the mouth. The frequency of grand mal seizures varies. Sometimes they happen daily or several times a day, sometimes once a week, once a month and even once a year. Naturally, this limits a person’s ability to work - he cannot be at heights, near fire, near water, near moving mechanisms, or in transport. If a seizure occurs under these conditions, the patient may die or be seriously injured. In addition to grand mal seizures, there are also so-called minor seizures, in which they do not fall, there are no general convulsions, but there are quickly passing disturbances of consciousness, when the patient turns pale or red, becomes covered in sweat, and sometimes convulsively makes some automatic movements, for example chewing, turning. heads, etc.
When and what tests should be done
— Hematological (general) blood test. — Study of liver enzymes (AlAT, AST, etc.). — Blood electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca++, Mg++) and osmolarity. - Amylase. — Concentrations of anticonvulsants in the blood. — Biochemical profile (AST, ALT, glucose, K+, Na+, Cl-, Ca++, osmolarity). — Anticonvulsants (concentration, drug monitoring). - GGT (gammaglutamyl transferase). — total alkaline phosphatase (ALP). - Total bilirubin. - Direct bilirubin. - Cholinesterase (ChE). - Haptoglobin. - Alpha 1-antitrypsin. — Pro-BNP. - LDH (lactate dehydrogenase). — CPK – total (creatine kinase). — CPK – myocardial fraction (CK-MB). - Amylase.
What are the main types of diagnostics usually performed by an Epileptologist?
— Electroencephalography (EEG); — Test with hyperventilation; — EEG with photostimulation; — EEG with sleep deprivation; - EEG during sleep; — Video-EEG; — Brain mapping; - CT scan; - Magnetic resonance imaging.
Advice from an Epileptologist
Epilepsy has been known since ancient times. The disease knew no boundaries of professional, social, age, or intellectual. Here is a far from complete list of famous figures of history, science and art: - Pythagoras, - Gaius Julius Caesar, - Apostle Paul, - Napoleon Bonaparte, - Peter I, - Charles Dickens, - Nicolo Paganini, - Isaac Newton, - Van Gogh. Let's mentally try to protect some of the above-mentioned individuals from society! Is it really difficult?! Therefore, it is worth remembering: epilepsy is not a death sentence. As a rule, after a child is diagnosed with epilepsy, he is prescribed drugs that prevent the occurrence of seizures - anticonvulsants. They are used for a long time, in a strictly calculated dosage depending on the weight of the child. Children regularly undergo an electroencephalogram - a study of the bioelectric activity of the brain. When the indicators of this type of study normalize, the use of anticonvulsant drugs is gradually stopped. While taking anticonvulsants, the number of epileptic seizures in a sick child first decreases, and then they disappear completely. Of course, such children are prohibited from physical education - the increased and inevitable hyperventilation of the brain can provoke an attack. They are also prohibited from working with a computer (much less playing computer games!). TV viewing should also be limited as much as possible. But in no case should children be protected from the group - in kindergarten or at school! There are some forms of epilepsy that are accompanied by rapid destruction of the intellect, but, fortunately, there are not many of them, and they occur infrequently.
Epileptologist |
Is something bothering you? Do you have questions or need an inspection? You can make an appointment with an Epileptologist by choosing the clinic that is most suitable for you in the “All Medicine” section. For any other questions, the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic: Phone number of our clinic in Kiev: (+38 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our coordinates and directions are listed here. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on its personal page.
| (+38 |
If you have previously performed any studies, be sure to take their results for a consultation with an Epileptologist. If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is necessary to take a very careful approach to your overall health. There are many diseases that at first do not manifest themselves in our body, but in the end it turns out that, unfortunately, it is too late to treat them. undergo examination by an Epileptologist several times a year in order not only to prevent a terrible disease, but also to maintain a healthy spirit in the body and the organism as a whole.
If you want to see a doctor, use the online consultation section, perhaps you will find answers to your questions there and read the Epileptologist’s advice on caring for yourself . If you are interested in reviews about clinics and doctors, try to find the information you need on the forum - perhaps after that you will no longer be bothered by the question “ recommend a good Epileptologist ”. Also register on the Euro lab to be constantly aware of the latest news and updates on the site, which will be automatically sent to you by email.
Other medical specialties starting with the letter “E”:
| Embryologist |
| Endodontist |
| Endocrinologist |
| Endoscopist |
| Epidemiologist |
If you are interested in any other medical specialties or have any other questions or suggestions, write to us, we will definitely try to help you.
Epilepsy, types of seizures
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition. The disease is characterized by repeated seizures caused by epileptic activity of brain neurons. Such attacks occur spontaneously and last several seconds or minutes. They manifest themselves as episodes of “freezing,” muscle twitching, convulsions, and disturbances of consciousness.
Epilepsy attacks are divided into 2 types:
- generalized - epileptiform activity covers both cerebral hemispheres;
- focal (partial) - the spread of epileptic activity is limited to one area of the brain.
It happens that an attack begins as focal, but becomes generalized due to the spread of epileptiform activity to other parts of the brain.
In the event of an epileptic attack, the victim needs medical assistance: consultation with a specialist in this field - an epileptologist.