Capgras syndrome is a personality disorder in which a person develops and propagates the idea that a loved one or animal has been replaced by a completely different creature in an old guise. Capgras syndrome is often called “delusional syndrome” because a person experiences delusions that involve misrecognizing people or other objects. The disorder can take place in the following forms:
- acute form;
- transitional form;
- chronic form.
Delusional thoughts most often occur in patients diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia. There are cases when the above manifestations occur due to a head injury. The syndrome is often detected in people with acquired or congenital diseases of the nervous system, especially at an older age.
Medical studies have shown the relationship between the development of this disorder, diabetes mellitus and migraine. According to research, scientists have found that Capgras syndrome affects women about 20 percent more often than men. The information collected during the research gave scientists an understanding of the differences in neuroanatomy between a healthy person and someone suffering from this pathology.
Clinical picture of the disease
To better understand what Capgras syndrome is, we will give several examples in which the clinical picture of the disease is clearly visible.
A 70-year-old married housewife was recently discharged from a local psychiatric hospital. After some time, she again ended up in the same psychiatric hospital for re-examination. A woman was diagnosed with Capgras syndrome - due to her belief that her husband was replaced by a completely different person. Because of this, she refused to sleep with him, locked herself away from him in the bedroom and asked him to give her a weapon to defend herself from the impostor. She also resisted when hospital staff tried to send her to a medical facility. Against the background of her husband's mistaken recognition, she recognized other family members well.
The girl Diana was convinced that there were two completely exact copies of one person in the world. Moreover, the first copy always wanted good, and the other, on the contrary, only evil. Against this background, she was given a psychiatric diagnosis - schizophrenia with Capgras syndrome.
Symptoms of the disease
The presence of the disease can be determined by the following manifestations:
- Due to the rapid fusion of the sutures, the skull receives a large number of deformations and malformations. The forehead becomes convex and quite high, the eyes are set deep and wide, the lower jaw protrudes strongly, and the root of the nose expands.
- The fingers and toes grow together, leaving only the thumb free. The fusion can be membranous, skin or bone.
- Dwarf growth is often determined, the cause of which is improper development of bone tissue.
- The internal organs of the child are also subject to pathologies, as a rule, these are dysplasia of the kidneys, pancreas and genitals, heart defects, hearing loss, malformations of the vertebrae and external ear.
- On the part of the visual system, cataracts, strabismus, pigmentary degeneration of the retina, lens luxation, hypertelorism, deformations of the palpebral fissures, nystagmus, and exophthalmos are observed.
Apert syndrome and disability are closely related, but everything depends on the severity of the disease. Primary diagnosis is carried out by external signs; for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to conduct a genetic study.
Causes of Capgras syndrome
Capgras syndrome is complex in nature and varies from patient to patient. It is impossible to identify the causes of the development of this disorder in a particular person without detailed studies of the neural damage that is associated with the syndrome.
The first studies on this topic were related to the possible relationship of brain injuries with Capgras syndrome. Allegedly, after injury, patients are not able to recognize faces consciously, even if they recognize other objects that they knew before. A study dating back to 1984 revealed impaired recognition during autonomic arousal of the brain. It became clear that there are two ways of developing Capgras syndrome - conscious and unconscious.
Studies have also shown the relationship between the presence of doubling paramnesia and the development of Capgras syndrome. This is because these two syndromes can affect the same areas of the brain and for this reason may have the same manifestations (signs).
Since paramnesia most often develops with injury to the frontal lobe of the brain, scientists have suggested that the development of Capgras syndrome is also associated with the condition of the frontal part of the brain. They also noticed that if the connection between another part and the frontal part is disrupted due to injury, this can also cause the development of Capgras syndrome.
Treatment rules
Crumpies themselves do not pose a threat to life or health. However, they are extremely painful and cause a lot of trouble. The symptoms accompanying cramps are varied, so the efforts of the doctors at the CELT clinic are aimed at identifying the underlying disease. Treatment of this disease, as well as the abolition of excess medications, can quickly improve health outcomes.
Emergency relief for pain relief consists of passive stretching of the contracted muscle or voluntary active contraction of the antagonist muscle. So, when there is a cramp in the calf muscle, you need to stand up, leaning on the irritated leg, and when the muscles of the fingers contract, straighten them with your hand.
To prevent cramps after physical activity, you need to raise your legs high from a lying position. In this position, venous outflow improves and the likelihood of convulsive contraction decreases. If electrolytes are lost through sweat or diarrhea, potassium and magnesium supplements are recommended.
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary method, in particular the following methods:
- physical therapy aimed at general strengthening of muscles;
- contrast water procedures, massage and hardware types of physiotherapy.
If the effect of physiotherapeutic procedures is insignificant, the doctor may prescribe medication.
Glossary of terms
In this section we have collected all the terms that you might encounter in this article. Gradually, we will collect from these explanations a real dictionary of a narcologist-psychiatrist. If some concepts remain unclear to you, leave your comments under the articles on our site. We will definitely help you figure it out.
Affective flattening
– a disorder of affect associated with a significant weakening of emotional reactions, insensitivity, spiritual coldness, and indifference. Affective flattening can be either an independent symptom (with autism, schizophrenia, depression, dementia and other diagnoses) or a side effect of taking certain types of medications or drugs.
Migraine
– a neurological disease characterized by severe and painful headaches in one or both hemispheres. However, there are no obvious reasons for migraines - such as recent head injuries or bruises, strokes and brain tumors, etc. Typically, migraine pain is pulsating and is caused by vascular problems rather than tension. In addition, migraine headache is not associated with changes in blood pressure or intracranial pressure.
Paramnesia
– memory disorders associated with false memories – the patient may confuse the present and the past, real and fictitious events. Many patients tend to overestimate their own participation (both guilt and merit) in certain events of the past. Paramnesia is considered a qualitative perversion of memory.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- a type of schizophrenia, which is characterized by a predominance of hallucinations and delusions, but phenomena such as catatonic syndrome, speech problems, affective flattening and others may not manifest themselves (or manifest themselves weakly). Paranoid schizophrenia is the most common. A mandatory symptom is paraphrenic, paranoid or paranoid delusions. The behavior of patients can be hostile and aggressive, most of them become suspicious, tense, intolerant of others, and irritable.
Paranoid delusions
- one of the main symptoms
of paranoid schizophrenia
. Usually associated with persecutory delusions combined with verbal hallucinations.
Paranoid delusion
– delusion associated with an exaggerated idea of simple life situations. The patient’s statements with this type of delusion are logical, consistent and have strong argumentation.
Paraphrenic delirium
- figurative nonsense of fantastic content. Often accompanied by other mental disorders, such as paramnesia, affective flattening, perceptual deception, etc.
Duplicating (reduplicating) paramnesia
- a type of paramnesia in which the patient thinks that there are two (or more) identical places (for example, somewhere there is exactly the same hospital). Typically, reduplicating paramnesia is associated with damage to the frontal lobe.
Treatment
- Dohn HH, Crews EL Capgras syndrome: a literature review and case series //Hillside Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. – 1986.
- Hines A., Stewart JT, Catalano G. A case of Capgras syndrome related to hypothyroidism // Journal of Psychiatric Practice. – 2015. – T. 21. – No. 6. – pp. 445-448.
- Hirstein W., Ramachandran VS Capgras syndrome: a novel probe for understanding the neural representation of the identity and familiarity of persons //Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences. – 1997. – T. 264. – No. 1380. – pp. 437-444.
- Klein CA, Hirachan S. The masks of identities: who's who? Delusional misidentification syndromes // Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law Online. – 2014. – T. 42. – No. 3. – pp. 369-378.
- Lucchelli F., Spinnler H. The case of lost Wilma: a clinical report of Capgras delusion //Neurological Sciences. – 2007. – T. 28. – No. 4. – pp. 188-195.
- Sharma A., Garuba M., Egbert M. Capgras syndrome in a patient with multiple sclerosis: a case report //Primary care companion to the Journal of clinical psychiatry. – 2009. – T. 11. – No. 5. – pp. 274-274.
Story
The syndrome was first described by Joseph Capgras in 1923. He used the phrase “illusion of doubles” as a name, but it did not catch on because the word “illusion” in psychiatry had a different meaning. As a result, the disorder, in which patients mistook relatives and other people for doubles, received its name - “Capgras syndrome.”
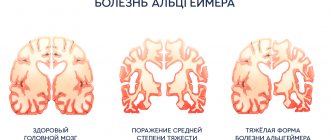
It is more common in people with schizophrenia, head injuries, and in combination with various types of dementia. It may appear with age; there have been cases of Capgras syndrome in children. The disorder was once identified as a result of ketamine abuse. In a ratio of 3 to 2, it occurs more often in women than in men.
Diagnosis and treatment
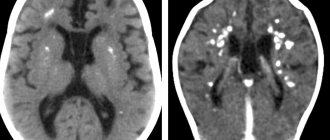
An experienced psychiatrist will always notice alarming symptoms; diagnosing a deviation includes observing the patient and collecting complaints. The doctor notes which ideas prevail in the patient and also interviews his relatives. An X-ray of the brain shows the presence of an organic substance in the human body that affects the functioning of the nervous system.
Any image enters the fusiform gyrus, where recognition of living and nonliving objects occurs. The finished result goes to the amygdala, which is responsible for emotions. If there is damage to the organ, then the connection between perception and mental reactions is broken.
Fregoli delirium is difficult to treat. Not only drug therapy for the disease is important, but also a friendly environment in the patient’s family. A common mistake made by relatives is to try to explain to the patient that he is wrong and that the persecutor does not exist in reality.
Such actions will worsen a person’s well-being, since the delusions of a positive double are accompanied by the ward’s confidence in his own rightness. Psychiatrists associate this illness with delusions of grandeur.
Treatment of Fregoli delirium takes many years. The prognosis of the disease depends on the following factors:
- duration of medication use;
- the presence or absence of other diseases;
- patient's age.
Specialists have to do a lot of work assessing the patient’s condition and drawing up a treatment plan for him.
What is the disease?
As already mentioned, Capgras syndrome is relatively rare in modern psychiatric practice. If you have such a disease, a person is sure that someone from his environment (spouse, one of his children or parents) has been replaced by a double.
In some cases, the patient is confident in the presence of his own double, and it is this fictitious personality that is responsible for the actions performed by the patient. It is worth noting that the patient can see the double or consider him invisible. Sometimes, in complete strangers, a person with this pathology recognizes relatives, acquaintances, people with whom he has known for a long time.
Possible complications
The further development of the disease largely depends on its causes and the presence of concomitant diseases. For example, in schizophrenia, Capgras syndrome can progress rapidly, and other mental disorders often appear.
The feeling of fear and threat makes the patient aggressive. Anger and violence in this case are a defense mechanism. If left untreated, people with this pathology can undoubtedly be dangerous to others, because they easily become angry and can pursue or even attack imaginary doubles. In some cases, the disease leads to the desire to commit suicide.
Valera, love, hope and faith...
An unsuccessful performance at the European Championships made the departure of Stanislav Cherchesov more than likely. The problem wasn't even the exit from the group - the team's play was forced, there was no thought in it, and the players themselves seemed to not believe in themselves. And although such an achievement as reaching the quarterfinals of the World Cup is still vivid in the people’s memory, Cherchesov has not done anything in recent months for which the masses of football fans would be ready to rise in a single impulse to his defense.
The appointment of a new coach was supposed to determine the concept of further development of the main Russian team, to show what kind of football was expected from it. Insiders spoke in every possible way that negotiations were being conducted with experienced foreign specialists who would be able to pull the team out of the quagmire of lack of ideas.
Question answer
Football coach Valery Karpin. Dossier Against this background, the news of Karpin’s appointment became a real cold shower. However, sports journalists began to look for advantages in such a decision.
But just as there is no point in looking for a missing black cat in a dark room, there is no point in looking for advantages in Karpin’s arrival as head coach. He is the worst thing that could happen to the Russian team right now.