This group of mental disorders includes diseases associated with short-term or permanent disturbances that occur to a person against the background of the influence of various traumatic factors on the brain.
These may be causes directly affecting the brain (trauma, neurotropic viruses, toxins), or factors associated with secondary lesions (blood or vascular diseases that lead to starvation of neurons and inhibition of their activity, endocrine diseases, brain tumors and etc.).
The causes of organic damage can be:
- Traumatic brain injuries (concussion, bruises, slaughter)
- Degenerative diseases (Alzheimer's, Pick's, Huntington's, senile dementia)
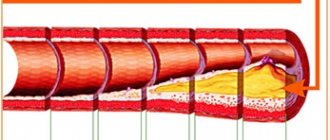
- Vascular pathology (hypertension, cerebrovascular accidents - ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, rheumatic diseases)
- Brain tumors
- Infections (tick-borne encephalitis, syphilis, HIV, herpes virus)
- External intoxication (alcohol, drugs, toxic substances - glue, household solvents)
Features of pathological disorders in childhood
One of the common causes of neurological disorders in childhood is intrauterine infection. The most severe lesions occur with congenital rubella, cytomegaly, toxoplasma, and syphilis. The consequences that result from infection of the fetus depend not so much on the type of pathogen, but on what month of intrauterine development this infection occurred. If the fetus is infected in the third trimester of pregnancy, the child may be born completely healthy. But already in the neonatal period or a little later, general and focal symptoms of brain damage appear:
- child's restlessness, tearfulness, interrupted night sleep, refusal to eat;
- increased sensitivity to touch, sound, light;
- the appearance of vomiting;
- increase in body temperature within 37.5 – 38°C;
- weight loss;
- increased muscle tone;
- tension of the large fontanelle;
- convulsions.
Other focal symptoms of organic damage: severe convergent or divergent strabismus, facial asymmetry, involuntary oscillatory movements, voice formation and swallowing disorders, muscle weakness, etc. Many children with the consequences of early brain damage exhibit features of dysplasia (impairments in the development of tissues, organs or parts of the body): deformation of the skull, facial skeleton, ears, widely spaced eyes, high palate, abnormal growth of teeth, protruding upper jaw, etc. . Common consequences of early brain damage are cerebrasthenic syndrome, neurosis-like syndrome, hyperactivity syndrome. (A syndrome is a collection of specific symptoms.)
Cerebrasthenic syndrome
Cerebroasthenia is one of the manifestations of organic psychosyndrome. Increased fatigue is combined with headaches, dizziness, weakening of memory, and increased exhaustion of intellectual and cognitive activity. The syndrome is characterized by vegetative disorders: intolerance to heat, stuffiness, travel in transport, flickering outside the window when moving; When bending the body, weakness, darkening of the eyes, and a feeling of lightheadedness easily occur.
Neurosis-like syndrome
In early childhood one can rarely observe clear-cut pictures of neurosis. More often these are short-term neurotic reactions due to fear, an unpleasant prohibition from the parents for the child. Symptoms of organic brain damage in a child and an adult are different. In an adult, psychiatric disorders include neurasthenia, hysteria, and obsessions. In the child, somatovegetative and movement disorders predominate: enuresis, stuttering, tics. A common manifestation of childhood neuroses is fear. In early childhood, this is a fear of animals, fairy-tale characters, and movie heroes. In preschool and primary school age - fear of darkness, loneliness, separation from parents, death of parents, fear of starting school. In adolescents, this is a growing concern for their health, fears or a passionate conviction of the presence of a physical defect in themselves that is unpleasant for others (“ugly legs”, “a nose like Buratino’s”, “protruding ears”), sometimes the fear of death.
Fears more often arise in children with an anxious and suspicious character and increased impressionability, suggestibility, and timidity. The emergence of fears is influenced by parental overprotection (constant anxious fears for the child), quarrels, and conflicts in the family.
There are no detailed pictures of hysterical neurosis in children. More often these are affective respiratory attacks with loud crying, at the height of which respiratory arrest develops. The child turns blue and loses consciousness for a few seconds. Such psychogenic reactions occur with equal frequency in boys and girls.
Hyperactivity syndrome
Hyperkinetic disorder (hyperdynamic syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is a relatively common developmental disorder. Usually occurs in the first 5 years of life, much more often in boys. Characterized by excessive activity, mobility, distractibility, impaired attention, which interferes with regular classes and the assimilation of school material. The work started is not completed. With good mental abilities, children quickly lose interest in the task, lose and forget things, and get involved in fights. They cannot sit in front of the TV screen, they constantly pester others with questions, push, pinch and pull parents and peers. There is a lack of organization and will. Behavior returns to normal between the ages of 12 and 20. But to prevent the development of illegal behavior, it is necessary to begin treatment as early as possible. Therapy is based on persistent, structured education: strict control by parents and educators, regular exercise. In addition to psychotherapy, psychotropic drugs are prescribed.
Organic brain damage – relationship with functional disorders
Historically, earlier in psychiatry, all mental illnesses were divided into organic (in which the substrate can be identified - the site of the lesion, the cause of the process) and functional (which are caused exclusively by social and behavioral factors).
However, with the development of medicine, this division lost its relevance and showed that exclusively organic and exclusively functional disorders are rarely encountered.
For example, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) used to be considered purely functional, since its cause was the direct fact of suffering mental trauma. Now it has been proven that the emergence and development of PTSD is associated not only with the presence of mental trauma, but also with certain characterological characteristics of the individual, including those of an organic nature, the so-called. pathoplastic basis (organic lesions at the subclinical level, preceding the manifestation of PTSD, such as post-infectious processes, trauma during childbirth, etc.).
Modern instrumental studies have now proven that patients with panic disorder exhibit diencephalic insufficiency.
According to G.L. Voronkov, there are practically no organic mental disorders in their pure form; they are always a combination and interpenetration of organic and functional symptoms.
Symptoms
Organic brain diseases do not have characteristic symptoms due to their complex genesis. The following changes in behavior are recorded: activity worsens, sloppiness, problems with concentration, and apathy appear.
Old patients often forget the names of their relatives, what day or date it is, and problems with speech appear. As the disease develops, words are forgotten and the ability to maintain a conversation becomes difficult. Let's consider the types of emotional states: lack of emotions, aggressive behavior, attacks of hallucinations.
Organic brain lesions may appear during perinatal development. During the process of intrauterine development, the central nervous system has not yet become stronger, so all provoking factors can cause serious illnesses. The reasons for the transformation include: hypoxia, alcohol, psychotropic drugs, nutritional problems, chronic disorders, birth injuries, asphyxia, premature birth, infection in the newborn’s body.
If girls become pregnant at too young an age, the fetus may have difficulty developing. When a baby is born, problems in the functioning of his brain can be identified.
Sometimes situations arise when the level of brain disorder is too low; it can only be determined with the use of suitable equipment. In such cases, the disease is difficult to cure and cannot be controlled. Gradual development is observed if the disease is not detected in a timely manner.
Organic damage to part of the brain in children manifests itself in the form of migraines, sleep problems, and inability to concentrate. If left untreated, cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and neuropathy may occur.
Are some forms of organic damage to the cerebral cortex normal for age?
It is safe to say that old age is a risk factor for the development of atrophic processes in the brain and dementia. But when examining older people, it is discovered that most of them still do not have signs of this pathology. Based on this, it can be assumed that senile dementia and other organic brain lesions due to degenerative, vascular, and endocrine age-related disorders are not the age-related norm, despite the predisposition of older people to these diseases.
If we consider dementia, its clinical manifestations depend on a number of additional aspects: the causes of occurrence, premorbid personality traits (the character of a person before the disease), the social environment. Thus, a patient with certain types of dementia with a prosperous family environment, who is partially socially adapted, thanks to the support of loved ones, can function for a long time, unlike patients who are deprived of this opportunity.
Diagnostic methods
Organic diseases in areas of the brain are regularly monitored. This applies to treatment and elimination of negative symptoms. Main stages of diagnosis:
- The doctor collects anamnesis.
- A neurologist examines a patient.
- Performed .
A correctly collected anamnesis makes it possible to consider the temporal duration of the disease, the degree of its progression, and heredity.
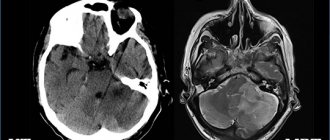
CT makes it possible to determine inflammatory processes in such situations. For damage to the frontal lobe. Convulsions, paralysis of the muscle tissues of the body, eyes, mental problems may appear, and the person ceases to smell. The parietal region is characterized by malfunctions of all receptors, convulsions, deterioration of concentration, seizures, a person may forget how to read and count.
When exposed to the temporal lobes, hearing is often lost, it is difficult to distinguish smells, epileptic seizures and increased emotionality occur. If the reference lobes are damaged, there is a possibility of disruption and loss of visual function, coordination of movements noticeably deteriorates, balance is often lost, convulsions and hallucinations appear.
Topography of organic damage
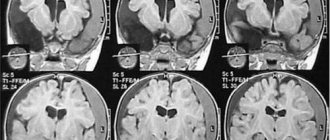
Thanks to the availability of modern instrumental imaging methods (computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography), it becomes possible to compare the clinical picture of an organic disorder and the localization of the lesion.
If the process involves predominantly the frontal parts of the brain, then aspontaneity (lack of impulses for motor, speech, mental and
other activities), as well as depressive symptoms. Previous attachments disappear, and behavior becomes disinhibited, moral standards are lost, anosognosia is observed - a complete lack of criticism of one’s actions. These patients may be characterized by moria syndrome, when they become complacent, euphoric, with a tendency to make inappropriate, vulgar and rude jokes, and play pranks.
If the orbital sections are affected, then impulsivity and lack of self-control may prevail - the character acquires features of psychopathic behavior.
When the temporal lobes are affected to a greater extent, memory is usually affected first, and mood may change.
When the parietal lobes are damaged, we can see first of all in the patient agnosia (loss of accumulated knowledge and the inability to acquire new ones), apraxia (loss of skills, such as drawing, sewing, professional developments), paralysis, paresis, etc.
Acceptable treatments
Neural connections cannot be restored if organic brain restoration in children progresses. Proper treatment helps control the progression of the disease. It is necessary to stimulate the work of areas of the head. The patient needs to be explained what changes are affecting his body.
Treating an organic brain disease of complex origin requires the use of different groups of medications:
- Means to protect normal nerve cells, you need to activate the brain, improve memory function.
- Neuroprotectors. They contain peptides that stimulate blood circulation and remove dirt from the blood.
- Anticonvulsants.
In addition to drug therapy, you can do a massage that stabilizes the blood supply to the tissues in the brain to eliminate spasms, and physical therapy is performed. If you have problems with speech or a complex emotional state, it is advisable to work with speech pathologists and psychologists.
After therapy or in its absence, the following results are possible:
- Full recovery, when the brain damage is minor, defects are difficult to notice.
- Lack of ability to work. The patient's life is saved, but his capabilities are limited; the person cannot take care of himself or work.
- Disability. It becomes difficult for a person to live without his caregiver.
- A fatal outcome is possible in the case of a complex lesion; this result is often influenced by age and lack of professionalism of doctors.
To make a diagnosis, the disorder will have to be characterized.