Home / Articles / Deterioration of vision due to nervous conditions
The importance of vision can hardly be overestimated; through it we receive the most information about the world around us. The human eye is a surprisingly balanced, but at the same time quite fragile structure. Therefore, when exposed to negative factors, the balance of this system can be disturbed, which often becomes the cause of the development of eye diseases. One of the reasons for the deterioration of vision is the ever-accelerating pace of life, constant tension, stress and worries that accompany modern people.
Why does vision deterioration occur due to nervousness?
If we consider the structure of the human eye, we can see that various muscles are responsible for its proper functioning, which constrict the pupil, change the curvature of the lens - the natural lens of the eye that ensures focusing of vision, etc. In addition, the good functioning of the visual organs depends on the normal circulation of intraocular fluid, as well as sufficient blood supply and tissue nutrition.
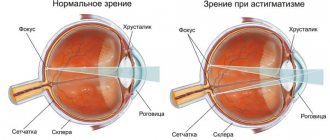
Mental experiences and stress lead to excitation of the nervous system, as a result of which excessive tension of the eye muscles occurs, the shape of the eyeball changes, vasoconstriction occurs, and the tissues begin to experience a lack of blood supply. The constant overstrain of the eye muscles that occurs due to nervous conditions causes their improper functioning, leading to the development of refractive errors - myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism. In this case, people usually resort to wearing glasses or contact lenses, but as a result, the eye muscles weaken even more and the problem gets worse. And insufficient blood supply to the retina and optic nerve leads to the emergence of pathological processes that threaten the development of glaucoma and other very serious diseases.
How to eliminate vision problems with VSD
Problems with visual impairment and eye pain can occur with high intracranial pressure, high blood pressure, stress, and physical inactivity. When visiting an ophthalmologist at the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will undergo the necessary tests of intraocular pressure, blood pressure, and an examination of the condition of the visual organs. With VSD, the nervous regulation of all structures of the body changes, including those responsible for the position and movement of eye structures. Hypotonicity and hypertonicity of the muscles responsible for the condition of the lens of the eye, smooth muscle muscles of blood vessels leads to a change in the refractive function of the eye lens, affects the photoreceptors of the retina, and discoordination of the smooth muscles of the iris occurs. Spasm of the muscles of the walls of the small blood vessels of the eye leads to disruption of the nutrition of the cells of the eye structure, causing visual impairment.
The doctor will determine what diseases cause vision deterioration and what causes the pain in the eyes. During the examination, the main symptoms will be determined: different pupil sizes, changes in the fundus, swelling and bruising around the eyes, red eye syndrome, blurred vision. If a patient has VSD, prevention is of great importance. To avoid a decrease in visual acuity, you should maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and avoid stressful situations. In the rehabilitation department of the hospital, dystonics will be able to take courses in physical therapy and breathing exercises. Dystonics will be able to undergo treatment of diseases against which VSD is diagnosed in a neurology clinic. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
How to avoid vision deterioration
In order to maintain good vision, you need to try not to succumb to stress and relax more often. To relieve overstrain, especially if your professional activity involves working on a computer, special eye exercises are well suited, which are best performed on a regular basis.
Eye exercises:
- Close your eyes and then open your eyes wide. Repeat the exercise 5-6 times.
- Look up, down, to the sides without moving your head. Repeat 3 times and then do the same with your eyes closed.
- Rotate your eyes clockwise and in the opposite direction. Repeat 3 times, then perform the exercise with your eyes closed.
- Blink rapidly for a minute.
- Stand near the window, look for some point or scratch on the glass. Look at it for 15 seconds, then for the same time, turn your gaze to some distant object outside the window. Borrow back to the point on the glass. Repeat 3-5 times.
- Rub your palms until they become hot. Then close your eyes for a few minutes, relax and imagine something pleasant, for example, the seashore or a forest landscape.
Proper nutrition is of great importance for eye health. The diet must include foods rich in vitamins A, C, D and E. Experts especially recommend eating fresh blueberries, which contain a substance that restores visual pigment. You can take special vitamin and mineral complexes for eye health, drink herbal teas that strengthen vision and have a calming effect on the nervous system.
The ARTOX Clinic offers diagnosis and treatment of any eye problems at affordable and affordable prices. Our experienced specialists will help you regain and maintain good vision.
View prices
Making an appointment with an ophthalmologist
Why does vision decline sharply: what symptoms cannot be ignored?
When vision deteriorates gradually, it can be difficult to notice. Our cunning brain manages to adapt to changes, and a person does not experience any particular inconvenience, and therefore does not worry. But if your vision drops sharply, there is something to panic about. Let's figure out why this could happen.
It’s not necessarily a “failure”, perhaps it’s overwork
Prolonged excessive strain on the eyes can short-term but greatly impair vision. For example, if you worked or played at the computer for many hours, studied information on the small screen of your smartphone for a long time, or watched several films in a row. It will inevitably become more difficult for your eyes to focus, the outlines of objects will become blurred, and your color perception may even change. So it's time to relax!
A similar situation can arise against the background of severe stress or general fatigue, with systematic lack of sleep, and exhaustion of the nervous system.
The loss of vision in these cases is natural - and temporary. After proper rest, vision should return to its previous levels. We wrote in this article how to help your eyes recover faster after overstrain.
But if you notice that your vision deteriorates periodically or drops steadily over a period of time, it means that there is a serious pathology and you should consult a doctor.
If you notice that your vision is falling, do not self-medicate! This can cause serious complications.
You should not self-medicate, since the rapid deterioration of vision is due to the acute form of the disease, and you need to examine the state of the visual system as quickly as possible and begin therapy in order to prevent the development of severe complications.
Symptoms that should alert you
The most important symptom is, of course, the suddenness of the deterioration of vision. It suddenly becomes difficult for a person to focus his gaze on objects far and near. Focus is more difficult to maintain and contours become blurred. Other symptoms may also appear:
- narrowing the field of view;
- cloudiness of the image, veil;
- sparks, flashes, spots before the eyes;
- doubling of the contours of an object;
- poor vision at night and in twilight;
- redness of the eyes;
- Pain in the eyes;
- pain or tension in the temporal area;
- headache;
- weakness in the body and limbs.
Vision may be impaired in only one eye. And this is a serious reason to contact a specialist to check the visual system.
Symptoms may periodically recede, weaken, and then return. Sometimes vision decreases in only one eye. And then the symptoms appear on the affected side.
The main causes of sudden deterioration in vision
The etiology of the decline in visual function can be different. Conventionally, the reasons can be divided into ophthalmological and other.
Injuries and physical stress in combination with congenital or acquired vascular pathology often provoke a decrease in vision - for example, heavy sports activities, prolonged labor. The nutrition of the eye tissues is disrupted, and vision decreases.
Ophthalmological reasons:
- injuries to the visual organs - damage from foreign objects, chemical burns, excessive insolation;
- hemorrhage into the vitreous or retina;
- retinal detachment, retinal tears (especially dangerous in the central zone);
- macular degeneration (insufficient nutrition of the vessels in the center of the retina leads to impaired central vision);
- optical neuropathy (the optic nerve atrophies);
- infectious eye diseases (keratitis, blenorrhea and others);
- diabetic retinopathy (diabetes mellitus affects small vessels, including the vessels of the eye, and vision inevitably declines over time).
Other factors of vision impairment (there are a lot of them, let’s highlight the main ones):
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- osteochondrosis;
- damage to the base of the skull;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the pituitary gland area;
- toxic effects of drugs, low-quality alcohol;
- hormonal disorders of various types.
What to do if your vision is rapidly deteriorating?
Visit a doctor! Only a specialist will be able to understand the reasons for what happened and prescribe competent treatment.
Before visiting an ophthalmologist, try to give your eyes some rest: stop watching TV, don’t read in poor lighting, and reduce computer work to a minimum. This will not only help stop the deterioration of vision, but will also enable the doctor to more reliably determine the cause.
If you have experienced severe stress, walk more in the fresh air, try to get more than 8 hours of sleep.
Treatment
During the examination, the doctor assesses the general condition of the patient and conducts a comprehensive ophthalmological diagnosis. Even if vision is poor in only one eye, the other eye will also be carefully examined.
Depending on the clinical picture of the disease, the doctor will prescribe medications. Certain destructive processes (for example, retinal detachment, macular degeneration and others) will require surgical intervention.
If the problem lies outside of ophthalmology, the doctor will refer you to another specialist. Perhaps the efforts of different specialists will need to be combined and a joint treatment developed. The most important thing is to have time to stop the acute course of the disease and prevent the development of complications. The sooner therapy begins, the greater the chance of successful vision restoration.
Be more attentive to your health.
Good vision to you!
Symptoms of neurosis
There are two large groups of signs of neurosis: psychological and physical. The first include:
- emotional instability, frequent and causeless mood swings;
- lack of initiative, indecision;
- inadequate self-esteem: overestimation or underestimation of one’s own abilities;
- obsessive thoughts, uncontrollable fears;
- irritability, aggressiveness;
- constant feeling of anxiety, restlessness;
- a cynical attitude towards others, a desire to criticize everyone and for any reason;
- inconsistency of desires and needs;
- tearfulness, vulnerability, excessive impressionability, touchiness, suspiciousness.
A person in a state of neurosis concentrates heavily on traumatic events. In other words, this or that situation does not let the patient go; he constantly thinks about it, considers himself guilty, even if there is no reason for this. It’s almost impossible to focus on work or positive life moments. In this state, it is impossible to perform the amount of work that is normal for a healthy person. Labor productivity is falling. Because of this, a conflict situation at work may arise. This will worsen your mental state.
The most common symptom of neurosis is insomnia. It becomes increasingly difficult for a person to fall asleep at the usual time. If he does fall asleep, he has nightmares and wakes up in a cold sweat. In the morning you feel very tired, and drowsiness persists throughout the day.
Sometimes neurosis is accompanied by increased sensitivity to sounds. Loud voices and music irritate the patient. Photophobia and meteosensitivity develop. These factors are associated with the physical manifestations of neurosis. Among them:
- headache that hardly goes away, dizziness;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- digestive problems;
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness and trembling of hands;
- decreased appetite;
- excessive sweating;
- frequent need to urinate;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- decreased sex drive;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes, blurring of vision, and a decrease in its acuity.
These symptoms are quite common and characteristic of many diseases. It’s difficult to call them specific. Consequently, when they appear, the doctor does not always look for reasons in the psychological state of the patient. Because of this, neuroses are always very long lasting.
Symptoms
VSD has one feature - its course has no specific signs and has extensive symptoms. Nervous system failure manifests itself differently in each person. This also applies to visual dysfunctions - there is no clear clinical picture here, everything is very individual.
The most common symptoms of vision problems that patients with VSD complain about:
- If a person suddenly changes body position, flashes of light and darkening may appear. Sometimes this is accompanied by loss of balance and noise in the temples.
- During panic attacks or severe nervous excitement, vision seems to float, blur, and become unclear.
- When the patient is very tired, spots appear in the eyes, especially if the person concentrates on an object for a long time and then suddenly changes the position of his gaze.
- The image may be distorted, the contours of objects change, and a person will perceive straight lines as broken.
- In some cases, painful sensations in the eyeballs may occur, especially with prolonged strain. Pain can be triggered by various factors, such as a flash of light, touching the eyes, or due to blinking.
- The sufferer sometimes blurs the background, the object on which the gaze is concentrated. A person sees clearly, but everything around this object becomes cloudy.
- It is sometimes difficult for the patient to focus on one object for a long time, gradually the gaze weakens and defocus occurs.
Causes of neurosis
There are several theories, each of which suggests considering certain factors that provoke neurotic disorders. So, from the physiological point of view, neurosis is a pathology of the body, the cause of which is a malfunction in the nervous system. Excessive mental activity, accompanied by a large number of nervous processes, can contribute to the destabilization of the psychological state.
There is another theory, according to which the cause of neurosis is a combination of an irritant and personality characteristics. For example, there is a stressful situation. People may perceive it differently. Some may treat it indifferently or with great patience, others are not always able to adequately respond to various stimuli.
General health is also important. People who do not take care of their health, smoke, eat poorly, abuse alcohol, do not have a clear regime and daily routine, often get sick, are constantly overworked physically and mentally, and are more susceptible to neuroses. In the event of a stressful situation, they are especially vulnerable. At the same time, not only negative factors can provoke a disorder. Even positive emotions can lead to the development of neurosis. The sharp and constant alternation of positive and negative factors has an even worse effect on the psyche. Thus, in childhood, a neurotic disorder can be the result of a “carrot and stick” type of upbringing.
There is also a psychoanalytic theory. Neurosis, according to its postulates, is the result of an internal conflict that arose due to the dissatisfaction of a basic need.
Moreover, the foundations of conflict can be laid at any age. Subsequently, they manifest themselves in the form of an unstable psychological state.
In general, the causes of neurosis in certain cases are the following factors:
- isolation of a person from society;
- conflict between instinctual drives and moral standards;
- strong pressure and control from others;
- a person's strong need for protection or recognition;
- a thirst for power, glory that cannot be satisfied;
- striving for ideality, perfectionism;
- inability to rest, uncontrolled workaholism;
- lack of life experience and skills to adequately perceive stressful situations.
These are psychological reasons. Physiological diseases include diseases of infectious or inflammatory etiology, addictions, including alcoholism and smoking. These factors reduce immunity, and therefore the body’s resistance to the external environment. How does a neurotic disorder manifest itself? Is it possible for vision to deteriorate with neurosis?