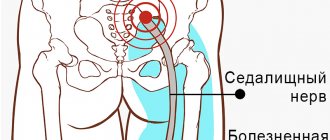
The concept of carpal tunnel syndrome is not universal for the wrist area; this condition can also manifest itself in other anatomical areas where the nerves lie quite superficially and close to the bone structures at the same time. The syndrome in question manifests itself in the form of a decrease or absence of sensitivity in the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger, as well as impaired motor function in them.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common pathology and occurs in 1-3% of the population, mainly in people whose occupation is associated with fine, monotonous motor skills of the hand. Half of all those suffering from this syndrome are people whose type of employment involves using a computer. Also, this disease can be considered an occupational pathology in musicians, tailors, office workers, etc. The syndrome occurs in the active working population at an already mature age (40-60 years), and in 105 cases at a younger age. Scientists concluded that heavy PC users have a 15% higher risk of developing the syndrome, especially in women.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The median nerve in the hand area passes through a tunnel formed by the transverse ligament and the carpal bones of the hand. Compression of the nerve in the canal can be caused by:
- Traumatic injuries to the hand.
Bruises, dislocations, sprains, and fractures can cause swelling of the ligaments and muscles or even displacement of the wrist bones. All this can put pressure on the nerve in the canal and cause disruption of its function. With proper treatment, all these processes are reversible, but if help is not provided in time and correctly, then contractures of muscles and ligaments, as well as bone deformation, may be irreversible.
- Arthrosis, arthritis and other pathological joint processes of various etiologies and genesis.
The swelling and inflammatory reactions caused by these pathologies, including tissue necrosis, can also cause compression of the nerve. With the permanent occurrence of inflammation and the progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes, the articular surfaces of the wrist lose their properties and wear out, resulting in deformation and compression of the nerve in the canal by bone structures.
- Inflammation of the tendons or tenosynovitis.
Inflammation can be septic (caused by microorganisms) and aseptic (caused by stress, hypothermia, etc.). Septic inflammation can be provoked by diseases such as purulent wounds of the hand, including felons, improper technique for drawing blood from a finger, etc. Non-infectious inflammation can be caused by chronic traumatic stress, for example, frequent monotonous motor skills of the hand, static load on it, and temperature trauma.
- Diseases that lead to water retention in the body
, can cause swelling of the extremities and, as a result, lead to an increase in the volume of soft tissues and compression of the median nerve. Violation of the water-electrolyte composition can be caused by: pregnancy, taking hormonal contraceptives, menopause, kidney disease, etc.
- Rare, but do occur tumors of nervous tissue and median nerve
in particular. Most of these are benign neoplasms (schwannomas, neurofibromas, perineuromas), but there are also malignant ones arising from the nerve sheaths. With its growth, the tumor puts pressure on the nerve, which leads to its damage.
- Diabetes.
Under the influence of the enzyme protein kinase C, sorbitol and fructose accumulated during the disease begin to be destroyed in nerve tissues. Because of this, as well as due to a violation of the trophism of neurons and their processes, aseptic inflammation of the nerves and surrounding tissues occurs. Swelling increases, which in turn leads to compression of the nerves, including the median nerve.
- Acromegaly.
As a result of the prolonged and intense growth of a person suffering from acromegaly, processes of disproportionate growth of bone and soft tissue occur. The median nerve can be pinched in the narrowed carpal tunnel due to increased bone volume and narrowing of its lumen.
- Congenital malformations
. The transverse carpal ligament may be thickened from birth, and poor tendon lubrication production may occur. One of the factors predisposing to carpal tunnel syndrome may be an anatomical feature of the structure, the so-called “square wrist”.
Causes
Tunnel nerve syndrome is both a congenital anomaly and a disease associated with a person’s activity and lifestyle.
Among the main causes of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- maintaining an uncomfortable hand position for a long time (this may be associated with professional activities, for example, working at a machine);
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalances caused by pregnancy, menopause;
- inflammatory processes;
- benign, malignant tumor in the canal area.
The causes of tunnel syndrome include diseases such as arthrosis, diabetes, arthritis, and thyroid diseases. Patients may encounter this problem due to metabolic disorders, after fractures, frequent injuries, or bruises.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Feeling of numbness in fingers.
The syndrome in question, as a rule, develops gradually and the lesion mainly manifests itself unilaterally. Basically, the pathological process occurs in the limb that is the leading one; in right-handed people, the right hand, and in left-handed people, the left hand. The development of carpal tunnel syndrome occurs gradually. However, a two-way process can also be observed, with diseases of the endocrine system, pregnancy, etc. - Paresthesia
. They manifest themselves as tingling sensations and loss of sensitivity in the fingers. They appear in the morning, after waking up, and disappear within a few hours. But over time, these manifestations become more stable and intense and can already become permanent. This can lead to disruption of the normal function of the limb: strength, dexterity, etc., the patient has to change hands when performing actions, and give rest to the affected limb. Particular inconvenience is caused by manipulations requiring static tension of the limb.
- Pain.
When the disease manifests itself, a burning and tingling sensation may appear in the hand, which can be quickly eliminated by lowering the limb down and shaking it. Blood flow in the arm is restored and the pain goes away. As a rule, this occurs during sleep due to the static position of the hand, or during monotonous work performed by the limb. The pain is not specific to any specific joints and is widespread. As the disease progresses, pain can affect not only the fingers, but the entire hand and arm up to the elbow joint, which often makes diagnosis difficult. The patient is unable to perform his duties because the pain may occur during the daytime.
- Loss of dexterity and strength.
Over time, if the disease is not treated, the limb begins to lose strength and dexterity in movements. It is difficult for the patient to hold objects in his hands, especially small ones; they seem to spontaneously fall out. The ability to perform fine motor skills (grasp small things, position the thumb, etc.) is lost.
- Decreased sensitivity.
Over time, the patient may begin to notice that he has difficulty distinguishing the temperature of objects, and ceases to feel touches or even injections. A painful burning sensation and numbness appear in the hand.
- Amyotrophy.
In advanced forms of the syndrome, atrophy of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the arm may develop; muscles and ligaments not only lose strength, but also decrease in size. Over time, the hand becomes deformed and takes on a shape resembling a monkey's paw.
- Change in skin color.
Due to the fact that when the innervation of the hand is disrupted, the nutrition of skin cells also occurs, the color of the skin changes, they become lighter and unevenly colored.
Symptoms
It is not difficult to independently determine whether you have carpal tunnel syndrome. Damage manifests itself for the first time both during work activity and at rest at night; sudden pain can wake a person. Or at some point he simply cannot handle the keys, fasten the buttons and perform other basic actions.
The sensitivity of the palm and fingers decreases, they cannot be controlled, difficulties appear in holding things, and a noticeable, often painful tingling sensation spreads.
Sometimes the temperature of the hand surface changes, remaining significantly higher or lower than normal, and the skin tone changes.
If you shake or rotate a numb limb, control over it returns due to a rush of blood, but after some time the situation repeats itself. Gradually, attacks become more frequent, and self-help measures and treatment are less effective. Ultimately, the elbow and shoulder are also affected, affecting bundles of nerve fibers up to the brachial plexus.
With carpal tunnel syndrome, its carrier also faces deterioration in sleep, persistent fatigue, decreased productivity and motivation, helplessness, work pressures, loss of a favorite activity, inability to concentrate on anything other than one’s illness, and ultimately depression.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
For an accurate diagnosis, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. In this case, the doctor conducts a number of specific tests, and laboratory and instrumental research methods can also be used.
Tests for carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Tinel test.
In the narrowest place of the carpal tunnel, on the side of the palm, when tapping, an unpleasant tingling sensation occurs. - Phalen test.
When the hand is bent to the maximum, pain and paresthesia appear in the wrist area within a minute or less. - Cuff test.
A blood pressure cuff is placed on the forearm and inflated as much as possible. Within one minute, if the test is positive and the syndrome is present, a feeling of numbness and tingling appears. - Raised hands test.
The upper limbs are raised vertically and held in this position for a minute. If the result is positive, unpleasant sensations appear within 30-40 seconds.
All of the above tests can be done at home, and if you have at least one positive test, be sure to consult a doctor.
The following instrumental research methods are used:
- electroneuromyography;
- X-ray examinations;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound.
To identify the causes of the disease, the patient is prescribed a blood and urine test:
- blood biochemistry;
- blood and urine test for sugar;
- analysis for thyroid-stimulating hormones;
- clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin-O;
- blood test for circulating immune complexes;
- blood test for antistreptokinase.
Diagnostics
To correctly diagnose the disease, the doctor communicates with the patient and takes into account his complaints. Afterwards, the limbs are examined, tests and instrumental examination are prescribed.
The main tests include:
- Tinnel;
- Vest;
- Fallena.
The patient is also prescribed an ultrasound, computed tomography, and MRI, which makes it possible to determine (or refute) the presence of tumors. Before prescribing treatment, the specialist is faced with the task of determining how affected the nerve is. For this purpose, electroneuromyography is prescribed.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
The most important thing in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is compliance with measures to prevent the development of the disease. Even with the best and highest quality treatment, you cannot do without preventive measures, because the effect may simply not be achieved.
- Preventive measures for carpal tunnel syndrome.
When the first signs of the disease occur, it is necessary to firmly fix the hand so that there is no possibility of movement in the joint and, as a result, injury to the nerve. The fixator can be applied by a doctor or purchased an elastic bandage at the pharmacy for temporary use. For two to three weeks, you must avoid activities that aggravate the symptoms of the disease. It is also recommended to apply cold to the wrist area for 2-3 minutes 2-3 times a day to reduce swelling. In the subsequent period, treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the pathological process and its severity. If this is necessary, then treatment is based on the treatment of the underlying disease (traumatic injury, hypothyroidism, diseases of the urinary system, diabetes mellitus, etc.) causing compression of the nerve in the canal. - Local treatment.
Includes the use of compresses and the introduction of medications into the canal cavity. These procedures can quickly relieve painful symptoms and relieve local inflammation.
- Drug therapy.
Drug therapy in each case is selected individually depending on the underlying or concomitant disease. In this case, B vitamins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vasodilators, diuretics, anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants, etc. are often prescribed. - Physiotherapy.
It can be used both during drug therapy and in the postoperative period during rehabilitation. In this case, the following is used: acupuncture; manual therapy techniques; ultraphonophoresis; shock wave therapy. Before using physiotherapeutic procedures, you should consult a specialist for any contraindications.
Clinical manifestations
Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by pain, numbness, paresthesia and weakness in the arm and hand.
Pain and numbness extend to the palmar surface of the thumb, index, middle and 1/2 ring finger, as well as to the dorsum of the index and middle finger. Initially, symptoms occur when performing any activities using a brush (working on a computer, drawing, driving), then numbness and pain appear at rest, sometimes occurring at night. The following tests are suggested to verify the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Tinel test: tapping the wrist (above the median nerve) with a neurological hammer causes a tingling sensation in the fingers or pain radiating (electrical shooting) to the fingers (Fig. 2). Pain may also be felt in the tapping area. A positive Tinel sign is found in 26–73% of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome [Al Zamil M.H., 2008]. Durkan's test: compression of the wrist in the area of the median nerve causes numbness and/or pain in the 1st–3rd, half of the 4th fingers (as with Tinel's symptom). Phalen Test: Wrist flexion (or extension) 90 degrees produces numbness, tingling, or pain in less than 60 seconds (Figure 3). A healthy person may also develop similar sensations, but not earlier than after 1 minute. Opposition test: with severe thenar weakness (which occurs at a later stage), the patient cannot connect the thumb and little finger (Fig. 4); or the doctor (researcher) can easily separate the patient’s closed thumb and little finger.
Surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired effect for 6 months or more, then it makes sense to think about surgical resolution of the disease. The main goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the median nerve by widening the carpal tunnel.
Most operations are performed under local anesthesia. The following methods are used:
- Open access:
The carpal ligament is dissected through a 5mm incision in the area of the carpal canal.
- Endoscopic surgery.
There are two types of endoscopic intervention, through two incisions and through one. In the first case, an endoscope is inserted into one incision, and an instrument is inserted into the second to cut the ligament. In the second case, both instruments are inserted alternately through one hole.
At the end of the surgical intervention, a plaster cast is applied to the arm to immobilize the limb. After the cast is removed, a course of physical therapy and physiotherapy is carried out. As a rule, complete restoration of hand function occurs within six months. After recovery, the patient can return to work, subject to a protective regime, so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease. In the modern world, where computer technology has already been introduced everywhere, the pathology we are considering is becoming more and more common. Timely and qualified assistance and prevention in the event of carpal tunnel syndrome allows one to achieve remission completely and with sufficient stability.
Treatment methods
How treatment will proceed depends on the stage of the disease.
- If you occasionally experience unpleasant but weak sensations, especially during or immediately after exercise, you need to reduce tension, take frequent breaks from work, optimize your work space, and do not forget about joint exercises.
- The second stage is spoken of when the symptoms already cause serious inconvenience: tingling and pain wake you up in the middle of the night, and during work activities the limb periodically “fails,” forcing its owner to take sick leave. It is with this development of events that the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs or injections, physiotherapeutic measures and fixes the affected area. Pain relievers and relaxers are also prescribed.
- The extreme degree is characterized by an almost absolute loss of mobility and unbearable lumbago and burning, which can only be relieved briefly with medication. The only salvation is an operation to expand the tunnel channel.
Surgery and the above therapy can help and alleviate symptoms until a feeling of complete recovery. However, it is worth remembering that medications do not have a local effect on the affected area, so unwanted reactions are possible.
If the tunnel symptom complex arose as a consequence of an internal disease or provoking factors and bad habits persist, most likely very soon it will make itself felt again.
Relapses have a worse prognosis than the newly diagnosed syndrome.
Is it so easy during and after treatment to abruptly and permanently quit smoking and alcohol, engage in physical exercise on a regular basis and control the minutes and hours spent doing activities that overload a vulnerable area? How about trying to eliminate deep-seated problems in health? Or not go through with surgery at all, because the results are essentially unpredictable.
No matter how gentle the operation, it is a violation of the integrity of the tissue, and the subsequent scar is an injury that gives rise to a chain of new failures in the future.
Complex treatment requires the participation of various specialized specialists, each of them is responsible only for “their” organs and systems. And the patient came simply with discomfort in the wrist. It is difficult to imagine that for the sake of his diagnosis a council will gather and consider the problem from the perspective of the unity of the body. Apparently, they will simply treat the source of his suffering.
Osteopathic medicine offers gentle procedures for correcting the syndrome through rehabilitation of all vital systems.
Treatment
At the initial stages of the disease, conservative treatment is carried out.
Changing the load on the elbow and eliminating elbow flexion as much as possible can significantly reduce pressure on the nerve. It is recommended to fix the elbow joint in an extension position at night with the help of orthoses, hold the car steering wheel with your arms straightened at the elbows, straighten the elbow when using a computer mouse, etc. If the use of traditional drugs (NSAIDs, COX-2 inhibitors, splinting) for 1 week does not have a positive effect, an injection of an anesthetic with hydrocortisone is recommended. If the effectiveness of these measures is insufficient, then an operation is performed. There are several techniques for surgical release of the nerve, but all of them in one way or another involve moving the nerve anteriorly from the internal epicondyle. After surgery, treatment is prescribed aimed at quickly restoring nerve conduction. Guyon's tunnel syndrome Guyon's tunnel syndrome develops due to compression of the deep branch of the ulnar nerve in the canal formed by the pisiform bone, the hook of the hamate, the palmar metacarpal ligament and the palmaris brevis muscle. There are burning pains and sensitivity disorders in the 4th–5th fingers, difficulty in pinching movements, adduction and extension of the fingers.
Tunnel ulnar syndrome is very often the result of prolonged pressure from working tools, for example, vibrating tools, screwdrivers, pliers, and therefore occurs more often in representatives of certain professions (gardeners, leather cutters, tailors, violinists, people working with jackhammers). Sometimes the syndrome develops after using a cane or crutch. Pathological factors that can cause compression also include enlarged lymphatic ganglia, fractures, arthrosis, arthritis, ulnar artery aneurysm, tumors and anatomical formations around Guyon's canal. Differential diagnosis. The difference between Guyon's canal syndrome and ulnar canal syndrome is indicated by the fact that when a nerve is damaged in the hand area, pain occurs in the hypothenar and base of the hand, as well as intensification and irradiation in the distal direction during provoking tests. In this case, sensitivity disorders occupy only the palmar surface of the 4th–5th fingers. On the back of the hand, sensitivity is not impaired, since it is provided by the dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve, which arises from the main trunk at the level of the distal third of the forearm.
When making a differential diagnosis with radicular syndrome (C8), it should be taken into account that paresthesia and sensitivity disorders can also appear along the ulnar edge of the hand. Paresis and hypotrophy of the hypothenar muscles are possible. But with C8 radicular syndrome, the zone of sensory disorders is much larger than with Guyon’s canal, and there is no hypotrophy and paresis of the interosseous muscles. If the diagnosis is made early, limiting activity may help. Patients can be recommended to use fixators (orthoses, splints) at night or during the day to reduce trauma. If conservative measures fail, surgical treatment is performed aimed at reconstructing the canal in order to free the nerve from compression.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome are pain, numbness and/or tingling. Pain and paresthesia are felt in the lateral part of the shoulder and radiate to the little finger and half of the fourth finger. At first, discomfort and pain occur only when pressure is applied to the elbow or after prolonged bending. In a more severe stage, pain and numbness are felt constantly. Another sign of the disease is weakness in the arm. It manifests itself as a loss of “confidence” in the hand: suddenly objects begin to fall out of it during some habitual actions. For example, it becomes difficult for a person to pour water from a kettle. In advanced stages, the hand on the sore arm begins to lose weight, and pits appear between the bones due to muscle atrophy.
Treatment
In mild cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, ice compresses and a decrease in load can help. If this does not help, the following measures must be taken: 1. Immobilization of the wrist. There are special devices (splints, orthoses) that immobilize the wrist and are convenient to use (Fig. 1). Immobilization should be carried out at least overnight, and preferably for 24 hours (at least in the acute period). 2. NSAIDs. Drugs from the NSAID group will be effective if the inflammatory process dominates in the pain mechanism. 3. If the use of NSAIDs turns out to be ineffective, it is advisable to inject novocaine with hydrocortisone into the wrist area. As a rule, this procedure is very effective. 4. In outpatient settings, electrophoresis can be performed with anesthetics and corticosteroids. 5. Surgical treatment. For mild or moderate carpal tunnel syndrome, conservative treatment is more effective. In cases where all conservative treatment options have been exhausted, surgical treatment is resorted to. Surgical treatment consists of partial or complete resection of the transverse ligament and releasing the median nerve from compression. Recently, endoscopic surgical methods have been successfully used in the treatment of carpal syndrome.