Everyone is familiar with the feeling of sharp pain as a result of an elbow strike. It’s as if an electric current shoots through the arm from the elbow joint to the little finger, sometimes radiating up the shoulder. This occurs due to contusion of the ulnar nerve. Compression of the nerve at the elbow joint is called cubital tunnel syndrome or cubital tunnel syndrome.
The disease is the second most common among carpal tunnel syndromes, second only to carpal tunnel syndrome.
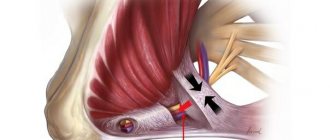
Anatomy of the ulnar nerve and cubital tunnel
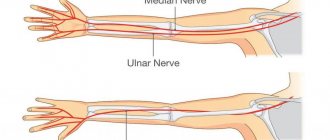
The ulnar nerve originates in the cervical plexus, being one of the three main nerves of the upper limb. It runs along the inner surface of the shoulder, then lies in the canal formed by the olecranon process, the internal epicondyle and the ligament that connects these two bone formations, forming a rather narrow cubital canal.
Next, the nerve passes through the intermuscular space of the forearm, flowing into another channel, this time on the wrist. This canal is called the Guyon Canal. It is at the level of this canal that the ulnar nerve begins to divide into 3, sometimes 4 branches, ending with the sensory branches of the 5th and inner half of the 4th fingers, as well as the motor branches of the 3-4-5 lumbrical muscles of the hand.
Causes of cubital tunnel syndrome
The cause of this particular disease is compression of the nerve in the cubital canal. In this article we do not discuss nerve injury.
There are several causes of cubital tunnel syndrome:
- repeated trauma to the ligaments and bone structures of the elbow joint that form the canal,
- intense sports,
- arthritis, arthrosis of the elbow joint
- synovitis of the elbow joint or hemarthrosis
- repeated monotonous activities,
- consequences of fractures can also be the causes of the syndrome.
For drivers, the disease can be caused by the habit of placing their elbow on the window opening of the car door. When symptoms appear, this habit will have to be eradicated.
At the computer, you should pay attention to the position of your hand when working on the keyboard and mouse. When doing this type of work, the forearm should rest completely on the tabletop. You can put something soft under the sore elbow.
Compression of the ulnar nerve in the canal can be caused by inflammatory processes not only in the nerve tissue, but also in the soft tissue component of the cubital canal wall. For example, with medial epicondylitis, inflammation in the projection of the internal epicondyle can cause swelling and compression of the nerve. Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner and delays in starting treatment can lead to organic damage to the wall and the process becoming chronic. As a result of the thickening of the nerve sheath, the transmission of nerve impulses may become difficult, leading to loss of sensation and motor function in some muscles of the hand and forearm.
Treatment for elbow pain
For pain in the elbow, drug blockade with GCS can be used. An alternative to drug treatment may be physical therapy. The use of peripheral magnetic stimulation with a frequency of 3-5 Hz and the maximum intensity that the patient can withstand. At first, even mild stimulation may be unbearable. In this case, the intensity should be increased gradually. To make the treatment effective, ultrasound with corticosteroids, high-top above and below the elbow joint, and acupuncture are added.
Treatment of elbow pain in Samara is carried out by neurologists and orthopedists at the FIRST NEUROLOGY clinic.
Signs and symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome
Symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include each of the following:
It is not necessary to have all the signs.
- Stiffness, loss of sensation, or significant dull or sharp pain in the ulnar part of the hand, 4th and 5th fingers.
- Pain and weakness when attempting to grasp an object with a brush.
- Discomfort in the elbow area.
Such symptoms indicate ischemia (lack of blood supply) of the nervous tissue. These symptoms are most pronounced in the morning, after the hand has been resting overnight. After some time, when the patient performs a certain amount of movements, the pain and numbness slightly recedes.
Active lateral neck tilt
While sitting on a chair, keep your back and neck straight. Slowly tilt your head to the side so that your right ear is as close as possible to your right shoulder, the movement should be smooth until you feel pain in the muscles, and then return to the starting position. Relax and repeat the movement in the other direction. Make sure that you do not twist your head or raise your shoulder while doing the exercise. Repeat this exercise 10 times in each direction.
Diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome
When examining the elbow joint by a doctor, the patient may notice a significant increase in pain. A painful examination is necessary for a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis:
- If the nerve is compressed in the canal, there will be a positive Tinnel's sign, which is manifested by the sensation of a current shooting through the nerve into the little and ring fingers when the doctor taps with a neurological hammer - although this can happen when the nerve is without pathology, with a strong blow.
- The doctor will check to see if the nerve slips out of the canal when the patient bends the arm at the elbow.
- Tests sensitivity and strength in the hand and fingers.
If the doctor has doubts about the causes of cubital tunnel syndrome, the patient may be recommended to undergo additional examinations, such as MRI, ENMG, and radiography.
Radiography. Based on radiographs, it is possible to determine bone exostoses in the projection of the canal, which compress the nerve. But most of the causes of compression of the ulnar nerve cannot be seen on x-ray, since they are of soft tissue etiopathogenesis.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG). This study makes it possible to determine how well the impulses are transmitted along the nerve and to determine at what level and how much the nerve is compressed.
During nerve conduction testing, the nerve is stimulated proximally and the time required to conduct the impulse is measured and compared with normal values.
Clinical manifestation of elbow pain
This symptom may occur in segments controlled by the ulnar nerve. If it is due to Guyon's bone, which is being pressed by a tubercle, or a rupture or injury in another area, then such pain is of secondary importance. But here there is damage to the motor nerve, for example, muscle contraction and muscular dystrophy. If pain, numbness or tingling in the wrist joint extends to the ring finger, and especially to the little finger, then it is necessary to examine the aforementioned Guyon's bed. Patients usually complain of an unpleasant tingling sensation in the ulna bone when they write or use a computer mouse. The examination method is quite simple. Apply pressure to the ulnar nerve between the epicondyle and the olecranon to check for severe pain, similar to an electric shock. The examination is carried out by comparing symptoms on both sides. If you lightly hit the area located on the inside of the triceps muscle 10 cm above the olecranon process, you may experience pain like an electric shock, radiating to the little finger. If this test is positive, the neck should be examined. If the above symptom is detected, the neck must be treated. It is especially important to stimulate the area between the cervical and thoracic vertebrae. In many cases, a favorable treatment outcome is ensured by the use of peripheral magnetic stimulation in this area (C7-T1 facet joint).
Treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome
The vast majority of such cases of the disease require non-surgical treatment. Non-surgical treatment options for cubital tunnel syndrome include:
- load reduction,
- temporary refusal of intense training,
- taking anti-inflammatory non-hormonal drugs.
Good remedies for treating cubital tunnel syndrome are anti-inflammatory non-steroidal ointments, taking vitamins and the patient undergoing a course of physiotherapy.
Surgical treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome is prescribed if therapeutic methods have not produced results after 12 weeks. During surgery, segments of the canal wall are removed from the patient and the tendon arches are cut. If it is impossible to expand the canal surgically, the nerve is completely removed from it, placing it between muscle tissue and fatty tissue.
Treatment of elbow arthritis
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate pain and suppress the progression of the disease. For this purpose, an individual complex of conservative therapy is prescribed, which includes medicinal and non-medicinal methods.
In the absence of a positive result from conservative treatment of arthritis of the elbow joint, various types of surgical intervention are prescribed.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Drug therapy
Drug treatment for arthritis of the elbow joint is selected taking into account the patient’s main diagnosis, his general condition and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. Drug therapy includes:
- Elimination of pain syndrome. For this purpose they prescribe:
- medications of the NSAID group - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nise, etc.) in the form of injections (injections), tablets or capsules for oral administration, rectal suppositories; the choice of a particular drug and its dosage form depends on the patient’s condition and the intensity of the pain syndrome; ointments, creams, gels with analgesic properties are prescribed externally (Fastum-gel, Voltaren, etc.);
- if the pain is not relieved, swelling increases, glucocorticoid hormones (Prednisalone, Betamethasone, etc.) are prescribed in short courses;
- To eliminate muscle spasms that increase joint pain, muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) are administered as part of drug therapy.
- To improve metabolic processes in case of elbow arthritis, the following is prescribed:
- chondroprotectors (Dona, Structum) – restore cartilage tissue;
- vitamins and minerals – activate metabolic processes.
- For rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, medications that suppress the autoimmune process are prescribed - Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide. More modern products that contain biologically active substances (antibodies, cytokines, etc.) - MabThera, Redditux - are also effective in this direction.
- If the cause of arthritis is an infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
- To restore local blood circulation - Trental.
Drugs for the treatment of elbow arthritis and the introduction of a medicinal solution into the joint cavity
Traditional methods of treatment
The attending physician may also include folk remedies as part of the complex treatment of elbow arthritis. They act more gently and have almost no side effects. Such means include:
- juice from celery stalks - take 15 - 20 ml 3 times a day (with honey) 30 minutes before meals for a month; has excellent analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- salt applications; Moisten a napkin with 10% saline (10 g of salt per 100 ml of water), apply to the inflamed elbow and hold until dry (you can bandage it and leave it overnight); relieves inflammation and swelling of tissue.
Non-drug methods
Treatment of elbow arthritis is also carried out using non-drug methods:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis and phonophoresis with medicinal solutions, UHF, paraffin, laser and magnetic therapy. Physiotherapy procedures are contraindicated for malignant tumors.
- Massage and physical therapy (physical therapy) improve blood circulation, promote joint restoration, and prevent the development of ankylosis. Exercises for training are selected individually and are initially performed under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor.
- Reflexology is a method of influencing points on the human body that are reflexively associated with the tissues of the elbow.
Surgery
Indications for surgical treatment of elbow arthritis are failure of conservative treatment, compression of the ulnar nerve, and progressive impairment of joint function. The following operations are carried out:
- synovectomy
- removal of part of the overgrown synovial membrane; often its implementation is combined with debridement - removal of damaged necrotic or infected tissue of ligaments, adhesions, etc.; in the early stages, this operation is often performed endoscopically, using an arthroscope; - endoprosthetics
– replacement of a destroyed joint with an artificial one.