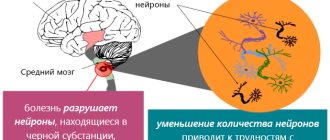
Parkinson's disease is a serious disease of the nervous system that affects neuron cells in the brain. Parkinson's disease is progressive. From a medical point of view, it is manifested by motor disorders, namely, weak motor activity, limited movements, muscle mobility in a state of complete rest, tremors of the limbs. The disease is also accompanied by the development of mental disorders - a person’s mental abilities decrease, and the state of depression increases.
The causes of Parkinson's disease can be different; the disease cannot be treated. Only through drug therapy can the symptoms of Parkinson's disease be relieved.
Medical prescriptions include a structured lifestyle, as well as physical exercises for balance and stretching. Speech problems will be corrected by a speech therapist.
Stages of Parkinson's disease
As the number of cells in the cerebral cortex that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine decreases, Parkinson's disease progresses more and more actively. As a result, the functioning of those parts of the brain that control involuntary movements of the limbs decreases.
Based on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, parkinsonism is divided into several stages . Each stage is characterized by its own characteristics and specific treatment. The Hoehn-Yahru scale is used to differentiate the stages of Parkinson's disease. According to this scale, the following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Zero – the person has no obvious signs of pathology.
- The first is that there are slight disturbances in the movements of the fingers and hands, trembling of some limbs, which stops in a state of sleep or rest, depression, lethargy appears, and sleep is disturbed.
- The second is that motor disturbances appear on both sides, facial expressions worsen, the functioning of the sweat glands worsens, and processes associated with sweat secretion are disrupted. A person performs his daily work, but his movements are already becoming slow.
- Third, the face takes the form of a mask; a person acquires a certain pose in which he begins to be constantly; this pose is called the pose of a supplicant; muscle tone and tension increases; motor activity becomes very low.
- Fourth – there are disturbances in coordination of movements when walking, a person’s ability to maintain balance in one position or another decreases, problems appear with the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, in everyday life a person needs help and support from outside. At this stage, signs of dementia may appear.
- Fifth - obvious signs of a nervous system disorder - a person cannot move, eat, or control urination without the help of others. A person at this stage completely needs the care of loved ones; the speech he pronounces is difficult to perceive and understand.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Main symptoms of Parkinson's disease:
- Tremor of the limbs is often the first sign of pathology. At rest, the patient’s hands tremble uncontrollably, and in more severe stages also the tongue, lower jaw, and eyelids;
- slow, stiff movements, shuffling gait;
- quiet and emotionless speech;
- constant tension in the muscles;
- mask effect on the face (hypomimia). The facial muscles stop moving normally, so the person looks devoid of emotions;
- difficulties with coordination and maintaining balance; in later stages, the patient may fall when trying to move without assistance;
- disturbances in the functioning of the salivary, sweat, sebaceous glands, loss of smell.
As the disease progresses, these symptoms may intensify and multiply. Sometimes the above-mentioned manifestations are accompanied by sleep disturbances, pain, depression and other symptoms.
Main signs and symptoms
It is impossible to prevent the occurrence of the disease in advance, since its occurrence is not associated with genetic predisposition. However, identifying signs of the disease in the early stages makes it possible to stop the further progressive course. At the initial stage, it is extremely difficult to detect the disease, because the nerve cells are just beginning to gradually deteriorate. With the transition of the disease to a new stage, new symptoms of nervous system disorders are observed. Parkinsonism changes a person at lightning speed.
Signs of Parkinson's disease at the initial stage
At the moment when the disease has not yet declared itself, it is difficult to determine the initial stage of destruction. But if you take a very strict approach to your health, you can detect the first signs of Parkinson's disease:
- the appearance of a slight trembling in the hands, which the patient may not feel at all,
- movements become slower
- a person may fall into a state of depression, have problems sleeping, and disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
When you notice the appearance of signs such as tremor, when walking, your arms do not make the usual sweeping movements, they remain pressed to the body, the motor activity of the limbs is disrupted, stooping when walking, poor facial expressions, which means that the brain cells have begun to produce less of the neurotransmitter dopamine and the pathology becomes wide coverage. Serious disorders of the nervous system appear.
Diagnostics
Timely diagnosis is an important stage in the treatment of the disease. In addition to a neurological examination, diagnostic measures include a number of modern instrumental and laboratory methods:
Instrumental diagnostics:
- PAT.
- MRI. CT.
- SPECT or SPECT.
- Transcranial sonography.
Laboratory methods:
- Detection of Lewy bodies (LBB).
- Detection of genetic pathologies.
- Levodopa test.
If necessary, the diagnostician prescribes a consultation with a neurologist and psychologist.
Causes of Parkinson's disease
To date, a complete list of the causes of Parkinson's disease has not been fully identified. However, we can mention some factors that could trigger the development of this disease. Among them: aging, ecology (external environmental factors), heredity. There are cases when parkinsonism occurs as a result of a person having certain diseases.
Causes of Parkinson's disease:
- physiological old age of the body, in which case there is a natural decrease in the number of neurons that are responsible for the production of the neurotransmitter domafin;
- heredity;
- long-term residence near highways, operating enterprises or near railways;
- vitamin D deficiency, obtained from exposure to ultraviolet rays on our body, and also protects the structural cells of our brain from destruction;
- poisoning of the body with chemicals (for example, ethanol, carbon monoxide, technical alcohol, etc.);
- previous neuroinfections (for example, encephalitis);
- tumors and frequent brain injuries.
Our clinic has opened a treatment room for Parkinson's disease and extrapyramidal disorders.
Extrapyramidal disorders are diseases characterized by movement disorders. They can be either primary (occurring independently) or a consequence of other diseases.
Extrapyramidal diseases include diseases such as:
- Trembling of hands, head;
- Violent movements in the limbs and torso;
- Gait disturbances;
- Memory disorders.
The office is attended by highly qualified doctors - doctors and candidates of medical sciences, specializing in this section of neurology. We carry out a comprehensive clinical differential diagnosis of conditions associated with impaired motor functions, establish the cause of extrapyramidal disorders and prescribe adequate specialized treatment. The health status of patients is monitored.
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment (drug therapy, use of botulinum toxin), patients experience long-term and stable remission, lost functions are restored and the quality of life is significantly improved.
Registration is carried out by phone
Causes
The exact reasons for the development of this pathology are unknown, however, based on research data, it has been proven that one of the main factors in the occurrence of parkinsonism is genetic predisposition. Thus, in more than 20% of all registered cases of the disease, close relatives of the patient also suffered from this pathology.
In addition, the following factors contribute to the formation of parkinsonism:
- Pathogenetic changes in mitochondria in brain cells.
- Vitamin D deficiency.
- Congenital pathological structure of blood vessels.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases affecting brain structures.
- Acute brain intoxication.
- Atherosclerosis.
- TBI of varying severity.
- Medicines of certain groups.
- Alcohol abuse.
As a result of clinical studies, it has been established that the development of parkinsonism is influenced by unfavorable ecology in the region of residence.
Who is at risk
In most cases, this disease develops after 60 years of age, but it happens that the disease occurs between the ages of 20 and 40 years, and the juvenile form develops in childhood and adolescence (up to 14 years).
Prevention of Parkinson's disease
In order to reduce the risk of developing Parkinson's disease, it is necessary to perform certain preventive actions:
- Promptly identify and promptly treat vascular pathologies of the brain that may appear due to injuries or previous infections.
- Do not forget to take special medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Seek medical advice if any signs of illness appear.
- Include a large amount of apples and citrus fruits in your diet, as these fruits contain substances that can protect brain neurons from damage.
- Try to avoid stressful situations, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and do physical exercise.
- Many scientists have proven the fact that smokers and coffee drinkers are least likely to suffer from this disease. But this does not mean that for safety reasons you need to start smoking and drinking large quantities of coffee. If there are no contraindications, you can drink coffee in small portions daily.
- It is recommended to expand your diet with foods rich in B vitamins and fiber.
- Avoid contact with chemicals such as carbon monoxide, manganese, etc. Since they have a strong influence on the development of the disease.
What do people with Parkinson's disease look like?
People who suffer from Parkinson's disease have difficulty moving. As a rule, their arms are always bent at the elbows, the body is tilted forward, and the head is slightly extended. Sometimes you can notice trembling of the body and limbs. Due to the fact that the facial muscles are affected, the face resembles a “mask” without any emotions. It is rare to see a patient blink or smile.
Walking in sick people is slow and clumsy, the steps are very small, and during movement the arms are always pressed to the body. Weakness, malaise, and constant depression appear.
Disability groups for Parkinson's disease
The disability group is established based on the results of a medical examination, during which the basic systems of the body are assessed, and the ability to care for oneself independently, communicate with people, move, and engage in work activities is tested.
There are 3 groups of disabilities, each of which has its own characteristics of the patient’s behavior:
- Group 1 – the patient is unable to care for himself or move independently. Labor activity is contraindicated and bed rest is prescribed.
- Group 2 – the person is partially able to take care of himself, symptoms of bilateral instability appear. Labor activity is limited.
- Group 3 – a person is fully capable of independent care. Labor activity is reduced.
Life expectancy with Parkinson's disease
The life expectancy of a patient suffering from parkinsonism is determined by a timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment. If the disease is detected at an early stage, effective treatment is prescribed, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, diet and a healthy lifestyle are prescribed, the patient’s life expectancy can significantly increase.
But you need to understand that Parkinson's disease cannot be completely cured. Therefore, the prognosis for this disease is extremely disappointing. Doctors are unable to stop the progressive development of the disease. It is caused by a number of genetic, physiological, and environmental factors. But, nevertheless, by following all the recommendations and prescribed treatment by the doctor, the development of the disease can be slowed down and the quality of life can be significantly improved.
Is treatment possible?
Treatment for Parkinson's disease is carried out with two goals: to relieve the symptoms of the disease and to delay the worsening of the condition. It is impossible to completely cure the pathology and restore the affected brain cells, but supportive treatment can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
What 3 areas does classical therapy include:
- Drug treatment. The doctor can select drugs that will partially compensate for the lack of dopamine in the body and stimulate its production. Due to this, it is easier for the patient to walk and perform any actions, and the tremor of the limbs becomes less pronounced.
- Non-medicinal methods - massage, physical therapy, physiotherapy. These techniques are gentle, have no contraindications and complement the main therapy.
- Neurosurgical treatment. In severe cases, when medications are poorly tolerated or do not bring improvement, surgery may be prescribed.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
This disease is practically untreatable, but modern medicine, as well as high achievements in the field of neurology, help cope with severe symptoms of the disease. Each specific case of treatment of a disease is considered by a doctor individually. The following treatment methods are currently used in medicine:
- drug therapy,
- surgical intervention,
- physical therapy and massage.
Medicines
Medicines help overcome difficulties with walking, movement and tremors. These drugs increase or replace dopamine, a specific signaling chemical (neurotransmitter) in the brain that is deficient in patients with Parkinson's disease. But dopamine cannot be given directly because it does not enter the brain. Let's take a closer look at what a disease such as Parkinson's disease is like and its treatment.
To increase dopamine levels, the following are prescribed:
- Carbidopa/Levodopa, the most effective antiparkinsonian drug. The substances included in its composition penetrate the brain, promoting the production of dopamine.
- Carbidopa-levodopa infusion is a combined drug in the form of a suspension; is supplied to the duodenum via an infusion pump. Recommended to alleviate the condition of patients with advanced disease.
- Dopamine agonists. Unlike levodopa, they are not converted into dopamine, but reproduce dopamine effects in the brain. Their effectiveness is not as high as that of levodopa, but the effect is longer.
Often prescribed together with levodopa to smooth out the side effects of the latter.
- Dopamine agonists: pramipexole (Mirapex), ropinirole (Requip), and rotigotine (Neupro). A short-acting dopamine agonist, apomorphine (Apokyn), has been developed for rapid relief.
- MAO-B inhibitors. These include selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar) and rasagiline (Azilect). They slow down the destruction of dopamine by inhibiting brain monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).
When added to carbidopa-levodopa, these medications increase the possibility of hallucinations.
- Catechol-o-methyltransferases (COMT inhibitors). Entacapone (Comtan) is the main drug in this class. It gently prolongs the effect of levodopa by blocking the enzyme that breaks down dopamine.
- Tolcapone (Tasmar); another COMT inhibitor that is rarely prescribed due to the risk of serious liver damage and liver failure.
- Anticholinergics. Helps control limb tremors. Several anticholinergic drugs are available, such as benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl.
Their modest benefits are often offset by side effects: memory loss, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and urinary problems.
- Amantadine. Doctors may prescribe amantadine alone to provide short-term relief from symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson's disease. In later stages, they may be prescribed together with carbidopa-levodopa to control involuntary movements (dyskinesias) caused by carbidopa-levodopa.
Folk remedies
For the complex treatment of this disease, herbal decoctions are used. They are used both externally and internally. Decoctions of fern roots are used for foot baths, and hands are rubbed with jasmine flower oil. Depending on what symptom of the disease you want to cope with, various medicinal herbs are used.
It is also important to maintain an active lifestyle during the treatment period, supplement your diet with vegetables and fruits, and stop drinking and smoking. The diet must contain foods that will activate the brain (for example, nuts, seafood). In the absence of contraindications, you can increase the amount of fluid consumed. Failure to eat a balanced, proper diet can overload the body.
Physiotherapy
The effectiveness of physical therapy in treating the disease has been proven by many. It increases blood circulation and motor activity of the limbs. Good for relieving limb tremors. When treating Parkinson's disease, you can perform the following simple exercises:
- stretching,
- circular movements of the hands and shoulders,
- twisting the body in a standing and sitting position,
- tilts of the head, body,
- raising your legs parallel to the floor,
- neck stretch.
Doctors recommend several useful approaches to treating the disease that will help cope with the further development of the pathology. This includes frequent stay in the fresh air, physical activity; to control speech, you can read books out loud to monitor the correct pronunciation.
Massage
With an integrated approach to treating the disease, it is effective to undergo massage sessions, which are carried out using special techniques and techniques. This makes Parkinson's disease easier. The impact on different muscle groups of the limbs helps restore their activity and has a positive effect on the nervous system.
Surgical intervention in treatment
Often Parkinson's disease, regardless of the causes and methods of treatment, progresses. In this case, deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used. Electrodes are implanted in the brain and connected to a generator, which is implanted in the chest near the collarbone. The device transmits electrical signals to the brain; as a result, symptoms become less severe.
The doctor adjusts the settings depending on the patient’s condition. Surgery comes with risks, including infection, stroke or brain hemorrhage.
DBS can stabilize the effects of medications, reduce or stop reflexive movements (dyskinesias), reduce tremors, and improve and slow movements. But although DBS relieves the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, the procedure is not able to stop the development of the disease.
How dangerous is Parkinson's disease from a medical and everyday point of view?
The dangers of this serious disease can be divided into several groups.
The first group is severe manifestations of symptoms of the disease:
- loss of motor and speech activity;
- loss of vision and control over body functions;
- muscle pain;
- progressive disconnection from real life.
The second group is household hazards:
- risk of serious injury to yourself due to loss of control of movements and loss of vision;
- the dangers of not following a diet and following bad habits;
- the inability to exist without outside help, for example, a guest nurse.
The third group is the consequences of using potent drugs that produce side effects in the form of nausea, vomiting, pressure surges and other unpleasant phenomena.