Trichotillomania is a mental disorder that, according to the modern classification, belongs to disorders of habits and desires.
With trichotillomania, a person occasionally pulls out their hair, which leads to significant hair loss. In ICD-10, trichotillomania is coded F63.3 and belongs to the section “Disorders of habits and impulses not specified in other sections,” along with pyromania, kleptomania and gambling addiction (pathological urge to gambling).
Trichotillomania is a compulsive symptom (compulsive behavior) and is essentially a variant of obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, this symptom can also occur in the structure of other diseases, for example, schizophrenia. It can also be combined with anxiety and depressive disorders (comorbidity).
A common feature of these disorders is the patient’s regular performance of obsessive and irrational actions that cause him harm and discomfort, as well as the inability to self-control.
Process Features
The main purpose of depilation with tweezers is to remove hair from the follicles, which will stop their growth forever. The first few sessions give inconsistent results. However, over time, the hairs in the frequently treated area thin out, become thin and light, and then stop growing completely. For this reason, you should not abandon the procedure, giving preference to a less labor-intensive method. Using tweezers, you can remove those hairs that cannot be removed during other procedures, such as shaving or sugaring.
When buying tweezers for work, you need to pay attention to its shape:
- Rounded. Such a tool is considered the safest due to the absence of the risk of injury. However, not all hairs can be captured with rounded tweezers.
- Beveled. This option is also safe and suitable for use both in the clinic and at home. A beveled tool is more effective than a rounded one.
- Spicy. With its help you can capture even the shortest hairs. The disadvantage of the tool is the high risk of injury.
- Straight. The least convenient tweezers for removing hair at home.
The photo shows three types of tweezers: with straight, beveled and pointed edges
Trichotillomania - treatment
Treatment for trichotillomania in children is shaving or cutting the hair short, which can help stop the behavior. Shaving a limited area of hair manipulation on a weekly basis (“hair growth window”) may have similar diagnostic and reassuring benefits. It should be remembered that shaved (trimmed) hairs are not all in the actively growing anagen stage, and it may take several weeks before full regrowth is noted.
When it comes to trichotillomania in adults, treatment is difficult and disappointing and is best done in psychiatric clinics.
It is unclear how well antidepressants and tranquilizers work for trichotillomania. Well-documented reports in the psychiatric literature show that clomipramine produces short-term improvement in adult patients who are severely affected by trichotillomania and whose disorder interferes with their daily life.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using tweezers:
Versatility. The method is suitable for removing soft and hard hair from 2 mm.
Minimum number of contraindications.
Low cost of the procedure. Having bought tweezers once, a girl can use them for many years.
The ability to permanently get rid of unwanted hair. The effect of the first procedures lasts for two weeks. For some girls it lasts no more than a week. However, repeated depilation will damage the hair follicle and prevent hair from growing.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
Traumaticity . Careless movement with tweezers can damage the skin. In some cases, minor bleeding may occur.
Inability to remove hairs shorter than 2 mm and vellus hairs . Such hairs are difficult to grab with tweezers.
Inflammatory processes in the treated area . Inflammations are possible if hygiene requirements are not followed. But even with proper treatment, slight swelling and red dots remain.
Diagnosis of trichotillomania
Hair pulling is not a health-threatening phenomenon, but these obsessive actions worsen a person’s quality of life and lead to social maladjustment. This disorder requires treatment.
Diagnosis of trichotillomania is based on certain criteria:
- a person pulls out hair in such an amount that leads to baldness or significant thinning of the hairline;
— independent attempts have been made repeatedly to get rid of obsessive hair pulling or reduce its intensity, but they did not lead to a positive result;
- pulling out hair causes suffering to the patient, depresses him, and reduces his ability to function normally.
Skin preparation
Before starting the procedure, it is necessary to clean the desired area of skin from possible contaminants. If the intimate area is to undergo the procedure, it is advisable to take a warm shower, but not earlier than 1 hour before the procedure.
We will remove the hair of our programmer, who voluntarily expressed a desire to help 
To relieve pain from plucking, you can use a special cooling gel or Emla cream, which is applied 20-30 minutes before work and then washed off after a few minutes. Before the session begins, the skin is treated with an antiseptic. The tweezers also need to be treated with an antiseptic, after washing them with soap and running water.
You can clean the tweezers before the procedure with soap.
A week before the procedure, the area of skin selected for hair removal can be shaved, since the hairs that grow back after this procedure are thicker. They are easier to grab with tweezers. You should not shave your facial hair.
Also, before the procedure, tweezers can be treated with an antiseptic chlorhexidine
Clinical manifestations of trichophagia:
Let's try to list the manifestations that may indicate the development of trichophagia in a person:
- Annoying thoughts, strong desire to eat hair;
- Apparently tension and anxiety increase before eating hair;
- Relief after eating hair
- Constant tearing out of hair on the head, armpits, and groin;
- No vomiting or nausea after eating hair.
In the first stages of the development of the disease, a person may chew hair for a long time without swallowing, and the phenomenon may look like a harmless habit. As the pathology develops, the patient eats hair more and more confidently and shamelessly. Moreover, over time, a certain semblance of dependence on one’s own (or other people’s) hair is formed. When the experience of eating hair is significant, the listed symptoms are accompanied by signs of closure of the intestinal lumen - paroxysmal pain, dizziness, vomiting. Unfortunately, most patients with trichophagia seek medical help only in extremely severe conditions.
Execution technique
The hair must be grabbed as close to the root as possible and pulled out in the direction of its growth. Do not pull on the tip or middle. This way the hair can be broken. Its root will remain under the skin. The hair will grow back and may become ingrown. Under no circumstances should you pull sharply, otherwise the hair may break off! Excessively sharpened tweezers can lead to biting the hair, which is also not desirable.
In the image you can see step by step how to remove hair correctly. Image is clickable
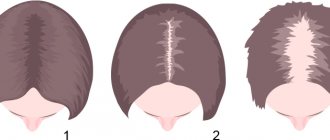
What is trichotillomania?
Currently, trichotillomania is recognized as not as rare and harmless as previously thought. Patients studied in dermatology clinics appear normal in their daily behavior, except for the habit of pulling out hair, causing baldness (alopecia). In younger patients, alopecia is largely considered a dermatological condition and is diagnosed by a specialist. As a rule, the further prognosis of the condition is quite good. However, in a small group of adult patients who have suffered from trichotillomania for years, the alopecia is usually extensive and difficult to treat, even with psychiatric intervention.
Among children, this disease most often occurs in boys, and in adolescence and adulthood - in girls and women.
Aftercare
After the session, the skin should be treated with an antiseptic, and then with lotion or anti-inflammatory ointment or cream, for example, Panthenol, Synthomycin or Levomekol.
After hair removal, you can use Levomekol, it is relatively inexpensive and very effective
To avoid bleeding, you can use a cold compress to constrict the capillaries. Decoctions of medicinal plants (celandine, chamomile) are suitable for compresses.
Treatment of the hair removal site with Levomekol
For several days after hair removal, it is not recommended to sunbathe, swim in the river (sea), or visit the solarium or sauna. It is allowed to take a cool or warm shower. However, you should not rub the treated area with a washcloth or scrub.
General recommendations for hair loss in women
What women experiencing hair loss need to remember is that the universal trigger for hair loss is stress. Sometimes the problem of hair loss can be eliminated by seeking help from a psychotherapist and reducing the level and intensity of negative experiences, depression, and irritation. In addition, it must be remembered that often in women, hair loss is not an independent disease, but a symptom of more serious disorders in the body. In this regard, in case of hair loss, you should consult a gynecologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, therapist, dermatologist, and undergo a comprehensive health check to exclude the presence of pathologies that provoke hair loss. If a pathology is detected, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease and use external hair restoration products until the cause of hair loss is eliminated.
“To make a correct diagnosis, it is very important to carefully collect anamnesis and conduct an external examination of the entire scalp. Case study: a 33-year-old female patient has been experiencing hair loss for 3 years. History of polycystic ovary syndrome, autoimmune thyroiditis. After collecting complaints and anamnesis, she suggested a diagnosis: androgenetic alopecia. Trichoscopy in the parietal area did not reveal a typical picture. She examined the entire head and found that the patient had alopecia areata. On the scalp there are multiple small round and oval-shaped foci of baldness with a diameter of 0.3-0.5 cm. It turned out that there was a single foci of baldness in childhood, which resolved spontaneously. She ordered a blood test for syphilis, the result was negative. Having confirmed the diagnosis of alopecia areata, I chose the appropriate treatment tactics, although initially, it would seem, there were all the signs of androgenetic alopecia.”
Olga Fedina Doctor of the highest category, dermatologist, trichologist.
Possible problems
Why do most people, when they cut a hair with a razor or break off the hair under the base soon after epilation, hair grows quickly and the hairs become stiffer and thicker?
Hair growth is a natural physiological process. Hair is a keratinized formation of the epidermis located in the pores, where the sebaceous glands are also located, and serves to remove secretions, the so-called sebum, through the lumen to the surface of the skin to soften and moisturize it, as well as the toxins it contains. The removal of sebum is a very important process, it is necessary so that the secretion does not accumulate in the pores and does not interfere with tissue respiration, and the accumulation of secretion serves as a good environment for the development of microbial flora and the subsequent occurrence of inflammation! Thus, the cells of the hair follicles begin to actively divide so that the hair can again emerge through the surface of the skin and continue to perform its main function.
It is worth noting that there are pores without hair; sweat glands are located there; their secretion is not so thick, so it does not need to be drained. However, even in such pores, outflow can be impaired if the pores are clogged from the outside with foreign particles, for example particles of powder or other loose makeup products, as well as when using too greasy creams, oils and improper cleansing of the skin.
Features of using the method for various areas
When working with different parts of the body, you need to take into account the sensitivity of the skin and the location of the area: the more accessible it is for depilation, the better the effect can be achieved. If the zone is inaccessible for some reason, you should use other methods.
Face
On the face, eyebrows are most often corrected. However, some women need to get rid of the mustache above their upper lip. It is necessary to remove unwanted hair gradually, over several sessions, to avoid the appearance of swelling and redness on the face.
Bikini area
Before plucking your hair, you need to steam your skin. It is recommended to use a scrub or washcloth soaked in warm water to lift the hairs. Such measures will help make the procedure less painful and free ingrown hairs. If the hairs in the bikini area are longer than 4-5 mm, they need to be shortened with scissors or a trimmer. For effective removal, the skin should be pulled with your fingers in the direction opposite to the growth of the hairs and the movement of the tweezers.
The procedure should not be carried out during menstruation, as the pain threshold is greatly reduced, which will increase the pain from manipulation.
You can remove hair with tweezers both in the classic and deep bikini areas. However, in the latter case, the use of tweezers should be replaced by other methods.
Axillary area
Tweezers are rarely used for the armpit, since plucking will have to be done in an awkward position. You can work in front of a mirror. But if possible, you should look directly at the vegetation, and not at its reflection. To do this, you need to turn your head in the right direction and bend it slightly. When you stay in this position for a long time, dizziness appears and your limbs become numb. For this reason, it is necessary to pause for 5-10 minutes.
Manifestations of trichotillomania
People suffering from this disorder usually experience significant tension or anxiety immediately before they begin to pull out hair, and feel some relief after performing this action.
Symptoms can vary in intensity between different people and within the same person throughout life.
Trichotillomania is diagnosed when hair pulling causes hair loss and the person's repeated compulsive attempts to stop hair pulling do not improve the condition. It is important to note such manifestations of trichotillomania as depression and anxiety caused by the inability to control one’s behavior, and deterioration in social functioning.
The first manifestations of trichotillomania are usually recorded shortly before or shortly after puberty.
Hair pulling in trichotillomania is a behavioral disorder where a person pulling out hair does not mean eliminating some kind of cosmetic defect or improving appearance. Usually the scalp, eyebrows or eyelashes are affected, but hair can be pulled out on any other part of the body.
The intensity of hair pulling and the areas of the body affected by trichotillomania vary from person to person. Some patients have areas of complete baldness or loss of eyebrows or eyelashes. Others experience thinning hair or alternation of affected areas of the body.
Some people with trichotillomania automatically pull out their hair without thinking about it. Others are aware of the irrationality of their actions, but cannot resist their obsessive impulses. Hair pulling is not due to their desire to change their appearance (which can occur with body dysmorphic disorder). Before the act of hair pulling, a person may feel increasing tension and anxiety, and the action itself brings short-term relief.
Compulsive (obsessive) actions may accompany other manifestations of trichotillomania. Some people look for and pull out a certain type of hair, or twirl the hair in a special way around their finger, or pull with their teeth, or bite. It is not uncommon for people with trichotillomania to eat plucked hair. This can lead to the formation of tangles (trichobezoars) in the gastrointestinal tract, causing a false feeling of fullness or nausea, pain or other symptoms from the digestive system.
In areas where the patient pulls out hair, the skin may become damaged or become infected.
It has been noted that manifestations of trichotillomania are often accompanied by other forms of self-harm: scratching the skin, biting nails or the inner surface of the cheeks, etc. Hair pulling is often associated with depression, anxiety or other types of mental disorders, or is part of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
In most cases, people with hair pulling disorder recognize the irrationality of their behavior. They are embarrassed by their compulsions (obsessive actions), ashamed of their appearance, try to disguise hair loss by using hats, scarves, scarves, and try to pull out hair from those parts of the body that are hidden under clothing. They tend to avoid situations in which others might notice the hair loss.
Typically, people with trichotillomania do not pull out their hair in front of other people except their loved ones. They suffer greatly from their inability to cope with their bad habit and make numerous attempts to stop their actions or pull out their hair less often, but still cannot control their behavior, which leads to an increase in internal tension.
There may also be a desire to pull out hair from other people or animals or threads from fabrics.