Reasons for development
Factors contributing to the development of atheroma on the head are:
- metabolic disorders leading to changes in the properties of the secretion of the sebaceous glands;
- hair dyeing, head shaving with damage to hair follicles;
- hyperhidrosis (especially in combination with seborrheic dermatitis);
- inflammatory diseases of the scalp;
- low-quality hygiene products for hair care;
- Irregular hair washing with the accumulation of viscous oil on the scalp.
Atheromas often form not only on the scalp, but also around the ears and on the chin.
Types of bumps behind the head depending on the reasons
Masses on the back of the head can occur for a variety of reasons, sometimes accompanied by pain and sometimes by deformation of the scalp. Some of the reasons are given below.
Mass due to head injury
If for any reason the blow is struck from behind, a slightly hard mass and bleeding (hematoma) may form at the site of the blow and under the skin. These bumps usually heal gradually over two weeks.
Cold compresses can be used to reduce swelling for minor injuries. Using painkillers is also a great help in reducing pain.
But in the event of a severe injury, a person may suffer a concussion. Symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, extreme tiredness or drowsiness, and memory loss are important and should be treated by a doctor.
Sebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a major group of cysts that are divided into two types.
Epidermal cyst
Epidermal cysts are made of creatine and fat and affect the thin outer layer of skin called the epidermis. These cysts can be the result of mild skin damage or acne and have certain symptoms.
- These are round cysts that slowly grow up to five centimeters.
- Cysts are not painful unless they become infected.
- They are not cancerous
- They usually do not need treatment and go away on their own.
- If treatment is required, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, steroid injections, or drainage of the cyst.
Pilar cyst
Pilar cysts are made of creatine and are present in the outer hair follicle or hair follicle. These cysts form around the front and back of the hairline. They are from half to five centimeters in diameter and usually:
- They are not cancerous.
- They are hereditary.
- It is more common in women than in men.
- In most cases they go away without treatment.
- Antibiotics are prescribed or, if necessary, the cyst is drained.
Folliculitis
Inflammation of the hair follicles, or folliculitis, forms as noticeable red or white lumps around the hair follicle. This lesion is more common in the head, especially the back of the head. Folliculitis can be caused by a bacterial, fungal, viral infection, or inflammation of the skin during hair growth. People with diabetes are very prone to inflamed hair follicles.
Bacteria can infect hair follicles and lead to folliculitis.
Treatment for folliculitis varies depending on what causes it. Antibiotics, antifungals and proper diet are effective in improving it. In addition, when treating this mass, the head should not sweat as much as possible and hair creams and shampoos should not be used.
Pilomatricoma
Pilomatrixoma is the name for a hair follicle tumor that is abnormal but usually harmless. This mass is caused by an overproduction of hair matrix cells.
Pilomatrixoma appears as dome-shaped lesions that are monochromatic or purple in color and can grow up to several centimeters. This mass is one of the most common types of lumps on the back of the head and neck and occurs in both children and adults.
To treat a hair follicle tumor, a sample is taken and then the mass is completely removed through outpatient surgery.
Lipoma
A lipoma is a soft mass of fat under the skin that moves in place. This mass slowly grows to two centimeters. A lipoma is a harmless mass that can be found on different parts of the body. Of course, it appears less on the back of the head and neck.
Doctors do not know the exact cause of lipoma, but in many cases it occurs in people between the ages of 40 and 60. It is slightly more common in men than in women.
Lipomas do not require special treatment and will go away on their own, but if they grow or harden, they should be checked by a doctor.
Seborrheic keratosis
Seborrheic keratoses are wart-like, non-cancerous bumps that usually appear on the head and neck of older people. These bumps are often harmless and therefore rarely treated. If the doctor is concerned that these lumps are cancerous, he will remove them using cryotherapy or electrosurgery.
Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node swelling, or lymphadenopathy, occurs when a lymph node behind the ear becomes inflamed due to external factors. Skin or ear infections are the main cause of swelling in these nodules. This swelling usually goes away on its own, but if the swelling lasts more than two weeks, you should see a doctor.
Mastoiditis
The part of the skull bone behind the ear is called the mastoid process. If bacteria infect this area of the skull, it can cause mastoiditis. This infection occurs in the air spaces of the bone.
Mastoiditis is more common in children than in adults and is a serious infection that requires prompt medical treatment. The disease appears as soft red bumps on the back of the ear, which can cause the ear to pop out.
Other symptoms include mastoiditis. For example, discharge from the ears, possible hearing loss, high fever, feelings of nausea and irritability, headache.
Doctors prescribe antibiotics to treat mastoiditis, and sometimes surgery is required to open the mass and drain the infection.
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis means premature healing of the skull joint. This is a birth defect in which one or more of the fibrous joints between the bones of a baby's skull fuse together prematurely. In this case, the baby's umbilical cord is formed when brain development is not yet complete. Because the baby's brain is still growing but the skull is closed, pressure is applied to the skull bone and the skull becomes deformed.
Surgery is necessary to treat craniosynostosis and correct head deformities so that the brain can grow normally. Early diagnosis and treatment creates enough space for the brain to develop.
Masses caused by bone growth
Bone growth (exostosis) is a benign bone tumor that is rarely found in the skull. This complication is caused by long-term irritation, arthritis, infection or injury and is sometimes accompanied by chronic pain. The best treatments for this type of mass are pain medications, physical therapy, and surgery.
Skull bone tumor
Sometimes back bumps can be caused by a bone tumor. One of the most common types of skull cancer is chordoma. This tumor grows from the bones at the base of the skull.
If the cordoma is small, it has no obvious symptoms, but if it is large, it is accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty walking and balance, headache, and problems with hearing and vision. In some cases, the tumor may spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment for skull tumors will depend on a number of factors, including whether the tumor is benign or malignant, the size of the tumor, the location of the tumor cells, and other individual variables.
Masses caused by subcutaneous hair
Sometimes hair grows into the skin as it grows. In this case, a small, hard, red bump appears on the surface of the skin. This noticeable mass is caused by pus from subcutaneous hair growth. Pimples are usually harmless and go away with hair growth. In some cases, it needs to be removed from under the skin with a special hair product.
Clinical picture
The cyst is a soft lump with rounded contours, located subcutaneously. Even small atheromas are clearly visible if you part your hair and carefully examine the changed skin.
Non-inflammatory atheromas are painless and do not cause discomfort, but if an infection occurs (which almost always happens with an accidental injury), the symptoms become more obvious. Suppuration of the cyst leads to its increase in size, intense pain, redness of the skin, and local swelling. The skin in the area of the inflamed atheroma is hot, and pus may be released from the outlet of the sebaceous duct.
Probable causes
Bumps occur anywhere in the human body and are often ignored until a certain point due to lack of time.
A lump that bothers you is the result of a person’s careless attitude towards their health. or small size.
The main complaint upon treatment is usually the word hurts, but it cannot become the basis for a reliable diagnosis.
It is necessary to undergo an examination and establish the real cause of the lump.
To determine the etiology, you need to find out the nature and intensity of the pain, conduct an external examination, and do laboratory tests.
The appearance of a lump may be due to:
- folliculitis (an inflammatory process that leads to the formation of an abscess, abscess or abscess);
- atheroma (which existed before, but now hurts due to the emerging purulent-inflammatory process);
- hemangioma (the cause of which is a pathological plexus of blood vessels and not only on the head);
- fibroma (a benign neoplasm, in some cases capable of transforming into malignant fibrosarcoma);
- lipoma (usually they are painless, and they hurt if they put pressure on blood vessels or nerve endings during the growth process);
- trichoepithelioma (benign neoplasm, sometimes inherited);
- wart (a characteristic sign of damage by the papilloma virus, dormant in the body, arising due to weakened immunity);
- enlarged lymph nodes caused by a general somatic disease of the body;
- osteoma (benign bone cyst).
A tumor (or lump) may also appear in the plural, in which case this is an even more alarming sign.
Small lumps are often the result of a bruise or injury. The bumps may be associated with insect bites.
Physiological seals are accompanied by other characteristic signs (nausea, dizziness, nausea and vomiting if there has been a traumatic brain injury), or they itch and hurt when pressed.
Treatment
The most effective way to remove atheromas with minimal risk of recurrence is radio wave excision using the Surgitron device (USA). The procedure does not require shaving the hair; removal takes place under local anesthesia in 30 minutes. Bleeding does not occur due to instant coagulation of blood vessels. The scalp and hair are not damaged. Removal of the formation is non-contact; after the procedure, the doctor carries out an antiseptic treatment and a follow-up examination of the patient. The procedure is outpatient and does not require hospitalization.
Other possible causes of tumors on the head
If you feel a lump behind your ears or on the back of your neck, it could be an enlarged lymph node. Such bumps most often occur in young children, as the immune system adapts in the first months of life. Most often, such a lump grows during infectious diseases and decreased immunity. Such a formation must be shown to an immunologist; he will be able to determine what caused it and prescribe medications for treatment, if necessary.
If skin care is not taken care of, a sebaceous gland cyst may appear. With such a tumor, you must definitely visit a doctor, since you need to have surgery. Among the benign ones are:
- Lipoma is a tumor that is a clot of adipose tissue, or a wen. Rarely it can become malignant, turning into liposarcoma. It is treated on an outpatient basis, by removal under local anesthesia.
- Hemangioma - formed from blood vessels. Has a dark tint. Hemangioma most often appears due to heredity, progression of vascular disease, or exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Treatment methods: cryotherapy, injections, hormonal therapy, removal, radiation, cauterization, electrocoagulation.
- Fibroma is a tumor of connective tissue. Fibroids appear with excessive use of beta blockers, due to hereditary predisposition, diabetes, chronic diseases of the reproductive system, hormonal imbalance, parasites. The fibroid is removed if it causes discomfort and does not pose a threat to life. Treatment is carried out in the form of laser or radiation therapy, surgical removal.
Malignant tumors are like a ball under the skin. They have mobility and often uneven edges, are accompanied by pain and enlarged lymph nodes. Appear on the back of the head, neck and other parts of the head. Surgical treatment, radiation or chemotherapy are carried out.
Causes of rickets
The main cause of rickets is a lack of vitamin D, which is responsible for calcium-phosphorus metabolism in the body. It is found in minimal quantities in food, but the main share is produced in the layers of the epidermis under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, mothers are advised to take their children for walks in the fresh air more often.
Other factors also influence the absorption and delivery of nutrients to bone tissue:
- gastrointestinal disorder;
- disorders of the liver and kidneys;
- gene mutations (characteristic of hereditary forms of rickets).
Risk factors
There are also risk factors that can provoke the disease.
For the mother, these are the following factors:
- too young or mature age (pregnancy before 18 and after 40 years);
- insufficient exposure to sun and fresh air during pregnancy;
- chronic diseases;
- improper or inadequate nutrition;
- lack of physical activity;
- the interval between births is less than two years;
- third and subsequent births;
- multiple pregnancy.
The child has:
- disturbances in fetal development during gestation;
- improper organization of feeding: underfeeding, overfeeding, selection of food not according to age;
- poor absorption of formula components during artificial feeding;
- digestive problems;
- nervous system disorders.
Treatment and prevention of rickets
For the treatment and prevention of rickets, children are prescribed vitamin D: at least 1000 IU per day for infants, 1500-2000 IU for children from one to three years old. Regular walks, massage, therapeutic exercises, and exercises are also recommended. The child should be breastfed or an adapted formula, and complementary foods should be introduced in a timely manner. The diet of older children should be based on foods rich in phosphorus and calcium.
If the disease is caused by disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, then therapy is first aimed at eliminating this pathology.
It is important to understand that such measures are effective only in the early stages. If rickets is detected at the stage of skeletal deformation, it will not go away without consequences. Surgery may be required.
Rickets: symptoms
If the symptoms of rickets are not noticed early, it can lead to bone deformities and developmental delays. The first bells appear from the age of two months:
- frequent and causeless mood swings;
- restless sleep: trembling, convulsions, crying;
- lethargy and poor appetite;
- sweating and itching, especially in the scalp, resulting in hair loss on the back of the head;
- flattening of the back of the head and soft edges of the fontanelle;
- congenital hip dysplasia.
At this stage, violations can be corrected without serious consequences. In the future, the symptoms become more pronounced and dangerous:
- developmental delays: inability to hold head up, sit, stand, crawl, walk;
- short stature and slow weight gain;
- elongated skull with bumps on the forehead and crown of the head;
- rounded tubercles - “rosary beads” at the border of costochondral thickenings;
- an arched depression under the ribs called Harrison's groove;
- “bracelets” on the wrist joints;
- O and X-shaped curvature of the legs;
- convex “frog” belly;
- late teething;
- rachitic hump in babies who were seated early.
Diagnosis of pathology
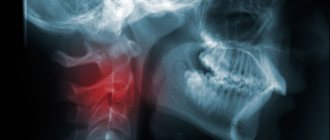
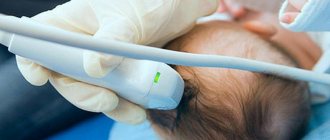
Birth injuries are not uncommon. The bones of the skull are subject to enormous stress as they pass through the birth canal. The newborn is carefully examined by a neonatologist, who diagnoses pathology if it is present. To clarify the diagnosis of cephalohematoma, ultrasound, head X-ray and other examinations are performed (we recommend reading:).
It is easiest to identify a hemangioma by its appearance and characteristic red color. In the future, the surgeon should monitor it, monitor its growth and dynamics.
If you find a ball-shaped lump on the back of a child’s head after a bruise, it is better to immediately show it to the doctor. The main criteria that the doctor focuses on during the examination:
- size;
- number of cones;
- location;
- color;
- amount of blood leaked (in case of injury);
- general condition of the patient.
By comparing all the parameters and assessing the possible risk of damage or danger to the brain, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis. Only with light blows can you do it yourself.
Diagnostic methods
An ultrasound of a child's head allows one to establish the etiology of a neoplasm.
To find out the reasons for the appearance of a neoplasm, the doctor conducts an examination. The specialist takes into account the number, color and size of the balls, location, and assesses the general condition of the patient.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- clinical blood test to identify signs of an inflammatory process;
- general urine analysis;
- CT, MRI of the head;
- tumor marker test;
- allergy tests;
- For cephalohematoma, an ultrasound of the head is performed.
Based on the diagnostic results, consultation with a surgeon, allergist, or ENT specialist may be required.
When urgent medical attention is needed
If after an injury the child is weak and sleeps a lot, he needs to be shown to a doctor and an MRI done. It is
immediately necessary to show the child to a doctor if, after a fall or blow, drowsiness, dizziness, convulsions, loss of consciousness, double vision are observed.
Other reasons to urgently consult a doctor:
- a lump on the skull of a newborn; when pressed, the baby turns his head and cries loudly;
- the size and number of tumors increases;
- the ball or nearby tissues are swollen, bright red;
- pus or watery fluid is released from the cone;
- the sleep-wake pattern is disrupted, the psycho-emotional state is unstable;
- the pupils are dilated or have different sizes, strabismus is observed;
- bleeding.
Such symptoms indicate the development of a dangerous pathological process in the body. When they appear, you should not self-medicate, warm up the tumor, or use folk remedies.
Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons why tumors may appear:
- Injuries and bruises. The most common problem after which bulges appear on the head. In this case, a small painful swelling appears, which looks like a growth from the outside.
- Allergic reaction to an insect bite. Depending on the degree of reaction to an insect bite, the neoplasm can be from 5 mm to several centimeters in diameter, accompanied by itching and unpleasant but tolerable sensations. To relieve itching and redness, you will need to use antiallergic medications; you should consult a specialist.
- Inflammation of soft tissues:
- Furuncle (purulent neoplasm, appears from a staphylococcal infection).
- Abscess (subcutaneous accumulation of pus, appears due to a focal bacterial infection).
- Enlarged lymph nodes (inflamed when adenoviral infections penetrate the body).
- Subcutaneous formations:
- Atheroma (cyst). Formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland, it is painless and can reach the size of a fist. When infected and suppurated, it is accompanied by a feeling of pulsation at the site of the tumor and an increase in temperature.
- Lipoma (fat). Appears due to excess fat deposition in the skin, consists of fat cells and does not cause pain.
- Wart. Caused by the human papillomavirus, it usually appears on the head due to weakened immunity.
- Fibroma, sarcofibroma. Fibroma is hard to the touch and is itself a benign tumor. Sarcofibroma is malignant.
- Osteoma (benign tumor formed from bone tissue).
Symptoms and signs
Inflamed atheroma requires surgical intervention.
If a lump on a child’s head does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician.
Often, when formed on the back of the head, additional signs appear on the forehead:
- pulse quickens;
- pale skin;
- the lump hurts, there are signs of an inflammatory process;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- the pain does not go away within 20 minutes or is increasing;
- weakness, attacks of nausea, dizziness;
- the child complains of discomfort when turning his head;
- speech is incomprehensible.
With infectious pathologies, the temperature rises, appetite disappears, a rash appears or the throat becomes inflamed. Enlarged lymph nodes can be felt.