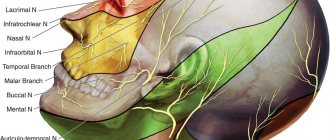
The facial nerve is responsible for the activity of all facial muscles. This nerve provides the ability to express emotions, squint, smile, etc. A person with facial paralysis does not have this option.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow offers services for high-quality diagnostics, effective treatment of facial paralysis, as well as successful rehabilitation of patients after an illness.
Facial nerve paralysis: causes of development
The exact cause of this disease has not been determined to date. However, it is known that the trigger for the development of facial paralysis can be damage to the following infectious viral pathologies:
- herpes infection;
- chickenpox and herpes zoster;
- adenoviral infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus);
- cytomegalovirus;
- Coxsackie virus;
- rubella.
In addition, paralysis of the facial nerve can occur with hypothermia, alcohol abuse, cancer in the brain, severe stressful situations, hypertension, head injuries (ears, face), atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, dental diseases, diabetes, otitis media and sinusitis.
The risk group for the development of facial nerve paresis includes women during pregnancy and after childbirth, elderly people, especially those with weakened immune systems. The incidence of the disease increases during viral epidemics.
Among experts there is also an opinion about hereditary factors of the disease.
Pharmacotherapy
Numerical studies of LLN, including meta-analyses, have compared steroid therapy in patients treated with acyclovir or placebo. One of them, having accumulated the results of four published studies, showed a significant improvement in facial weakness with the use of glucocorticoids. Another meta-analysis, which included randomized controlled follow-up studies, showed that the initiation of hormone therapy at intervals of up to 7 days led to the development of permanent paralysis of half the face. There was a 17% increase in swelling (P = 0.005) compared with placebo. Evidence is available to show that corticosteroids reduce the incidence of permanent mimetic paralysis, although further research is needed to determine whether their use with antiviral drugs may be changing vagi.
The purpose of the rest for Bell's paralysis seems entirely logical. Acyclovir, a nucleotide analogue, blocks HSV DNA polymerase and suppresses replication. As a result of its low bioavailability (15–30%), new drugs are being tested, zocrema valacyclovir, famciclovir and sorivudine, which may have a better dosing regimen and therapeutic response in the treatment of herpetic infections ій.
The remaining systematic analysis shows that patients with NLN, treated with a combination of acyclovir and prednisolone, have a slightly better prognosis than those who found it without hormone therapy, although the results are not they looked around at Cochrane. The main determinant of the differential therapeutic response was the treatment of the ear at intervals of up to 3 days before the onset of the disease. There was also no difference in effectiveness between different routes of administration of the above-mentioned drugs. Their systemic administration should be considered in case of immunosuppression or massive herpetic infection of the central nervous system.
Facial nerve paralysis: symptoms
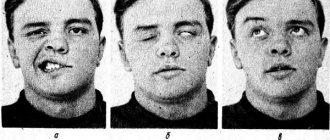
The development of facial paralysis is characterized by an acute onset: the condition of patients worsens quite sharply.
However, initial symptoms can be detected at an early stage of the disease, one to two days before visual manifestations appear.
Facial nerve palsy may present with the following symptoms:
- soreness in the area of the auricle, extending to the back of the head or face;
- pain in the eye from the affected area.
The appearance of the first signs is associated with an increase in swelling of the nerve column and its gradual compression.
Then more pronounced signs of facial paresis appear:
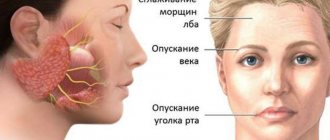
- violation of facial symmetry;
- lack of facial expressions and emotionality on the affected side of the face;
- drooping of the corner of the mouth, smoothing of the nasolabial fold, frontal folds on the affected side of the face;
- increased facial symmetry when trying to smile, speak, or cry;
- inability to completely close the upper eyelid;
- difficulty keeping liquid food and drinks in the mouth, pouring them from the affected side of the mouth - while the patient can chew and swallow normally;
- chewing food may be accompanied by biting the inside of the cheeks, which is associated with a lack of sensitivity in one’s own cheek;
- drying of the mucous membrane, decreased salivation (in some cases, on the contrary, its increase);
- impaired speech function associated with inactivity of certain parts of the mouth and lips;
- impaired blinking function, half-opening of the eye on the affected side, drying of the eye mucosa or, conversely, the appearance of excessive tearing;
- increased hearing on the affected side, changes in the perception of sounds (they seem louder to patients than usual);
- Patients have impaired taste sensations on the affected side of the tongue.
Electrophysiological research
Improper renewal of motor functions of facial expression and synkinesis in certain diseases associated with the inheritance of NLN. They can be transferred based on the relevance of early clinical improvement to the results of neuromyography; Such restraint may lead to permanent facial paralysis. In this case, the amplitude of the folding potential of the action is observed on both sides. After compression or repeated traumatic rupture of the nerve, axonal degeneration becomes obvious within a few days. In addition, electrodiagnostic procedures should be carried out 3 or more days after the onset of paralysis.
Among the patients who did not have 90% of degeneration over the first 3 tiers, in 80–100% the function was restored to a level of 1 (normal strength) or 2 points (minimal motion) weakness) on the House-Brackmann scale. In particular, during the first 3 years, small degenerative changes at the level of 90% or more, less than half, prevented a good improvement in motor functions. Then the level of intensity determines the forecast; for example, patients with 90-day degeneration on the 5th day of illness have a worse prognosis, less than 14. The value of neuromyography of the past, if they are prescribed in the intervals of up to 2 days after the formation of the total mimetic paralysis.
Facial paralysis: forms
There are several types of facial paralysis:
- Congenital facial paralysis occurs when the process of brain formation is disrupted in the prenatal period. In patients with this form of paralysis, there is a drooping of the corner of the mouth, a mask-like facial expression on the affected side, opening and moistening of the palpebral fissure. The skin on the cheek is smooth; during exhalation, the cheek on the affected side swells. The most severe form of congenital paralysis is Mobius syndrome;
- peripheral paralysis of the facial nerve - occurs if the patient has impaired motor function of the nerve trunk. With this type of paralysis, asymmetry occurs, complete immobility of the muscles of the affected part of the face;
- central paralysis of the facial nerve is caused by pathological changes in the cerebral cortex. The disease is most often localized in the lower part of the face. The main symptoms of central facial paralysis are: seizures, as well as involuntary muscle movements (a kind of tic).
DESIGNS OF INNOCENCE
Several episodes of NLN have been associated with ischemia associated with atherosclerosis or diabetes, which may explain the increasing frequency of this disease in the elderly. At the same time, most episodes of Bell's palsy are most likely associated with HSV type 1. The DNA of this organism is, apparently, even specific for the named illness; fragments of it are not detected in the human body in cases of the disordered Ramsay Hunt syndrome. An increase in the incidence of NLN occurs in parallel with seroconversion to HSV. Since seropositivity has been well established in adulthood, in which Bell's palsy has even expanded, the disease itself, perhaps, more likely reflects a viral reactivation from latency at the node of the ring, rather than the initial infection ktsіyu. This virus completely damages the facial nerve and makes it invisible.
Large randomized, double-blind studies are needed to better assess the effectiveness of glucocorticoids, antiviral agents, their combinations, as well as the treatment of surgical decompression in patients with a high risk of permanent facial palsy. Zokrema, it is very important for us to celebrate that hour-long moment, since celebration will no longer yield anything. In addition, additional data are required to determine which pharmacotherapy regimen (hormonal monotherapy or polypharmacy) is optimal. In this regard, we maintain continued caution that the long-term renewal of peripheral vestibular functions in vestibular neuronitis is also likely to be associated with HSV infections. It was strongly felt when taking corticosteroids rather than valacyclovir.
Facial nerve paralysis: complications and consequences
In the absence of competent therapy, which requires a considerable amount of time and patience, facial paralysis can be aggravated by the development of the following complications:
- muscle atrophy (thinning and weakening of muscles), caused by prolonged dysfunction and impaired tissue trophism. This process is irreversible: restoration of atrophied muscles is impossible;
- facial contractures (muscle elasticity is lost on the affected side), spastic shortening of muscle fibers, muscle spasms. Visually, tension on the affected side and squinting of the eye are noted;
- facial muscle tics, spastic twitching (hemispasms, blepharospasms);
- associated movements (syncinesia) - characterized by the release of tears during chewing food, raising the edges of the lips when squinting the eyes;
- inflammatory processes in the conjunctiva or cornea of the eye, the development of which is associated with drying out of the eye mucosa as a result of its prolonged stay in an incompletely closed state.
Facial nerve paralysis: diagnosis
An experienced neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital can diagnose facial paralysis after the first examination of the patient. However, to determine the cause of the development of this disease, a general blood test may be prescribed to identify the inflammatory process and additional instrumental studies:
- magnetic resonance imaging for the possible detection of tumor processes, vascular disorders, inflammatory changes in the membranes of the brain, cerebral infarction;
- computed tomography - x-ray examination to identify the probable causes of the disease: post-stroke conditions, tumors, consequences of mechanical damage to the brain, disturbances of perinuclear blood flow;
- electroneurography - to determine the speed of passage of nerve impulses, which makes it possible to establish muscle atrophy, damage to the nerve branch, and the inflammatory process;
- electromyography with neurography - to identify the quality of intramuscular impulses for the diagnosis of muscle atrophy and contractures.
During the diagnostic process, facial nerve paresis must be differentiated from such pathologies as: stroke, Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, inflammatory processes in the mastoid process and middle ear, Lyme disease, temporal bone fractures, carcinomatosis or leukemia affecting the nerve trunk, chronic meningitis, tumor processes , multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Facial nerve paralysis: treatment
The main method of treating facial paresis in the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is complex drug therapy using modern drugs of various effects:
- diuretics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticoids;
- antiviral drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- neurotropic drugs;
- vitamin preparations;
- agents for inhibiting cholinesterase.
Drug treatment of facial paralysis in the Yusupov Hospital in-patient department is carried out under the strict supervision of a neurologist, who can promptly adjust the dosage or replace the drug.
3. Treatment of the disease
Depending on the degree of paralysis and the rate of progression of muscle atrophy, a decision is made on the method of treatment. Conservative care
sometimes it helps prevent the situation from getting worse, but most often it is impossible to do without
facial nerve plastic surgery
. Despite the fact that drug and physical therapy are more preferable, it should be borne in mind that long-term muscle atrophy (more than a year) creates the preconditions for the irreversibility of the resulting paralysis even after restoration of nerve conduction.
Indications for facial nerve plastic surgery are:
- progressive paralysis of part of the face;
- absence or low effectiveness of conservative treatment of facial nerve damage;
- increasing atrophy of the facial muscles for more than 6-8 months.
Contraindications
are any infections, especially localized in the cervicofacial area. In addition, signs of positive dynamics in the restoration of sensitivity and mobility of the paralyzed area of the face cast doubt on the advisability of surgical treatment. In this case, dynamic observation, drug support and physiotherapy are recommended.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!