Location and anatomy of the back of the head in humans
Blood circulation, innervation, muscles of the occipital part
The occiput is the back part of the head, located above the cervical region and under the crown. The bone that forms it borders on the sphenoid, parietal and temporal bones. It is convex on the outside and concave on the inside. Consists of four different elements:
- Scales. It looks like a triangular plate. It has a concave part on one side and a convex part on the other side. Due to the attachment of muscle fibers and ligaments to its surface, it has a rough texture.
- Articular condyles located in the lateral parts. Responsible for the fusion of the skull with the spine.
- Main body. Fuses tightly with the sphenoid cranial bone by the age of 17-20. The shape resembles a quadrangle, the back of which forms one of the sides of the occipital foramen. In children, it has clefts filled with cartilaginous tissue. Gradually they harden.
- Big hole. It is localized between the three listed parts, forming a passage between the spinal column and the cranial cavity. The perfect combination of its shape with the first cervical vertebra results in a strong interaction between two important skeletal segments.
If in humans the occipital bone acts as a single system, then in animals it can consist of several interconnected bone structures.
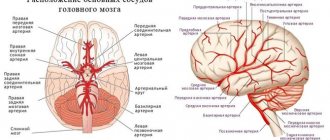
The blood supply to the occipital part of the head is carried out by the posterior auricular artery. Innervation occurs due to the nerve endings of the greater occipital nerve, which is formed from the posterior branch of the second cervical spinal nerve. The skin is also innervated by the greater occipital nerve, which arises from the cervical nerve plexus.
Types and shape of the back of the head
Shapes of the back of the head
When assessing the shape of the skull, experts pay attention to the structure of the forehead, crown, occipital part and the tubercles located on them. The anatomy of the back of the human head is the same for all people, regardless of race, gender, mental and physical abilities. However, the types of napes may differ. This part of the skull can be:
- round, in which the occipital line smoothly curves, and its protruding part is located in the middle;
- flat (straight, vertical), when the occipital line is closest to a straight line;
- oblique, in which the occipital line goes in an obliquely straight direction;
- angular, where the nuchal line is slightly curved in the middle at an angle;
- protruding, noticeable in people whose nuchal line arches sharply, protruding at the top.
The position of the occipital line is often determined in profile relative to a vertical line. It passes through the most prominent point of the back of the head along an inclination when the contour of the back of the head is tilted forward, vertically if the contour coincides with the vertical, with a protrusion when the contour extends beyond the vertical.
It is believed that a highly developed forehead in combination with a cut off (underdeveloped) back of the head is found in people prone to self-centeredness and a craving for loneliness. They have poor contact with society and lose their connection with the Cosmos. And, conversely, adult men and women with a well-developed occiput are distinguished by their education and sociability.
Anomalies and damage to the occipital region
If significant deviations are noticed, for example, missing bone fragments, this condition is attributed to a genetic pathology, which is always associated with serious diseases. Based on the disturbed structure and anatomy of the cranial bones, the doctor can make a diagnosis. For example, during examination, you can identify:
- partial or complete fusion of the condyles with the first vertebra;
- change in the weight of the occipital protrusion;
- formation of extra sutures, condyles, bones.
When examining newborns, dolichocephaly is diagnosed based on the shape of the back of the head (protruding or flat). Also considered an anomaly is a low border of hair growth in the occipital part of the skull.
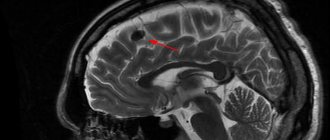
The integrity of the occipital bone can be damaged due to an accident, a fall from a height, a gunshot or knife wound, or injuries to adjacent bone structures. Swelling and hematomas form at the fracture site. In this case, the victim experiences the following symptoms:
- vascular spasm;
- severe pain in the damaged area;
- nausea, vomiting;
- impaired pupil reaction to light;
- difficulty breathing;
- fainting, loss of orientation in space.
Fractures of any skull bones can be fatal, so the patient needs emergency medical care and proper treatment.
If the examination does not reveal the presence of hematomas or signs of brain damage, surgery will not be necessary. The victim is treated with antiseptics, painkillers and sedatives are administered. If X-ray images reveal bone displacement, the patient undergoes surgery, since fragments can damage brain tissue and provoke the development of epilepsy and other serious diseases.
Symptoms
The presence of certain symptoms depends on the reasons that cause the pain syndrome. For example, with osteochondrosis, the pain will be constant and will eventually move to the back of the head. In addition, nausea, vision problems and other unpleasant symptoms may appear.
The development of osteochondrosis is gradual. It is divided into three stages:
- No symptoms. The pain is unnoticeable and therapy is not needed. Sometimes you may experience discomfort in the back area.
- Vertebral displacement. The patient experiences discomfort in the back and spine. The general condition is characterized by fatigue. At this stage, the disease is treatable. Drugs based on NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors and other drugs help.
- The last stage is characterized by disc rupture with further deformation of the spine. The nerve roots also begin to become severely pinched. In this situation, pain in the base of the skull and neck will not go away without surgical intervention. The patient needs surgery.
If we talk about migraine, it appears due to a combination of a number of unfavorable factors. It manifests itself in the form of a headache. May be accompanied by other symptoms. For example, an unpleasant pulsation occurs in the back of the head, sensitivity to sounds and light increases, and the feeling of a lump in the throat increases. Separately, one can highlight such a symptom as a rapid increase in sensitivity if you press on certain places.
Hypertension is accompanied by squeezing pain, which usually manifests itself in the morning. In addition, a strong heaviness is felt in the head, the person begins to feel sick. Sudden changes in blood pressure can trigger vomiting. The heart rate also increases. Painful sensations intensify when turning or tilting the head.
Unpleasant sensations most often begin to bother you due to unhealthy blood circulation in the muscles and prolonged exposure to a draft. If we talk about myositis and myogelosis, then these diseases can begin to develop if you sleep in the wrong position. In a patient with myositis, the back of the head, shoulders or shoulder blades may be affected. With myogelosis, frequent dizziness and muscle tightness appear.
If the neck hurts in the back right at the base of the head, then the sensation most often occurs due to a sharp turn of the head, increased physical activity, hypothermia, etc. Painful sensations often accompany professional athletes. Similar pains also appear as a result of violations of the rules of healthy sleep. This is one of the main causes of pain. Separately, it is worth saying that such problems do not require serious therapy. They usually go away within a few days.
The sudden appearance of pain is a consequence of the development of an intervertebral hernia. Pain can also occur due to displacement of the cervical vertebrae. Typical symptoms are weakness in the arms.
Occipital neuralgia is accompanied by severe pain. They appear due to pinching of nerves by intervertebral discs.
Another cause of severe pain in the cervical region is spondylosis, which is a degenerative disease. If you complain of a burning sensation in the neck or back of the head, then it is possible that this is due to the proliferation of vertebral bone tissue and the development of osteophytes. The amplitude and overall mobility of the head are also seriously limited. If you have pain between your neck and head and you try to forcefully turn your head, the pain will intensify. In some cases, heaviness radiates to the heart.
It is necessary to mention other diseases that can cause pain in the cervical spine. Painful sensations may be a consequence of sore throat. If you have suffered a severe illness, complications may arise. For example, cervical lymphadenitis. With it, a pathological process begins in which the lymph nodes are affected. With poor quality treatment of angina, these processes cannot be stopped.
Diseases that cause pain in the back of the head
Pain in the back of the head is often associated with overexertion, overwork of the neck muscles, and increased intracranial pressure. Unpleasant symptoms are observed against the background of psycho-emotional tension, stress, anxiety, and depression. This problem can be dealt with by self-massage, taking sedatives, painkillers.
The back of the head can also hurt for other reasons related to diseases of the spinal column:
- Osteochondrosis. It is characterized by the destruction of the cervical vertebrae, which disrupts their depreciation and compresses the artery supplying the brain. In addition to headaches, patients complain of frequent attacks of dizziness, nausea, ringing in the ears, and numbness of the extremities.
- Neuralgia of the occipital nerve. Develops as a result of severe hypothermia or against the background of other diseases of the spine. A person experiences severe shooting pain, which intensifies when turning or tilting the head.
- Cervical spondylosis. The growth of bone tissue due to the ossification of salts, taking the form of spines. They put pressure on healthy tissues and blood vessels, impairing neck mobility, causing dull pain that worsens with exercise.
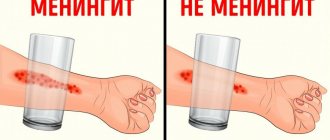
The back of the head reacts to pathological processes as acutely as other parts of the body. It can hurt due to vascular spasms, surges in blood pressure, stroke, meningitis, tumor formations, and concussion. Diseases of the ENT organs, teeth, and eyes make themselves felt by pain in the occipital area.
Causes of pain in the back of the head
Irregular pain in the back of the head can occur due to excessive consumption of coffee or drinks with harmful ingredients (for example, energy drinks), prolonged uncomfortable head position, stress and severe hunger. The main causes of pain in the back of the head may be the following:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - pain is combined with discomfort in the neck, nausea, tinnitus and the appearance of a veil (“fog”) before the eyes;
- hypertension (regular increase in blood pressure) – the pain is pulsating in nature and is accompanied by dizziness, increased heart rate, and vomiting;
- high intracranial pressure - diffuse and bursting pain, which can occur in the eyeballs, intensifies in bright light or too sharp, loud sounds;
- cervical myositis – pain spreads to the neck, shoulder girdle, can be observed in the area of the shoulder blades, intensifies when trying to tilt or turn the head, is asymmetrical in nature;
- vascular diseases - severe, throbbing pain that intensifies with any movement of the head.
Pain in the back of the head and temples can appear after experiencing strong emotions - both positive and negative. It always occurs suddenly, often accompanied by darkening of the eyes, tremor (shaking) of the hands, rapid breathing, pulse and heartbeat.