pharmachologic effect
An antihypoxic agent that has three types of effects: metabolic, neuroprotective and microcirculatory.
Actovegin increases the absorption and utilization of oxygen; The phospho-oligosaccharides contained in the drug inositol have a positive effect on the transport and utilization of glucose, which leads to an improvement in the energy metabolism of cells and a decrease in the formation of lactate under ischemic conditions. Several ways to implement the neuroprotective mechanism of action of the drug are being considered.
Actovegin prevents the development of apoptosis induced by beta-amyloid (Aβ25-35).
Actovegin modulates the activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), which plays an important role in the regulation of apoptosis and inflammation in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Another mechanism of action involves the nuclear enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). PARP plays an important role in the detection and repair of single-stranded DNA damage, but excessive activation of the enzyme can trigger cell death in conditions such as cerebrovascular disease and diabetic polyneuropathy. Actovegin inhibits PARP activity, which leads to functional and morphological improvement in the central and peripheral nervous system.
The positive effects of the drug Actovegin, affecting the processes of microcirculation and the endothelium, are an increase in the speed of capillary blood flow, a decrease in the pericapillary zone, a decrease in the myogenic tone of precapillary arterioles and capillary sphincters, a decrease in the degree of arteriovenular shunt blood flow with preferential blood circulation in the capillary bed and stimulation of the function of endothelial nitric oxide synthase , affecting the microvasculature.
In the course of various studies, it was found that the effect of the drug Actovegin occurs no later than 30 minutes after taking it. The maximum effect is observed 3 hours after parenteral and 2-6 hours after oral administration.
Indications for use
Despite their different origins, both drugs are used for the following conditions:
- Brain infarction.
- Cerebrovascular disease and its consequences.
- Intracranial injury.
In the treatment of these pathologies, the reparative effect, which is characteristic of the above-mentioned drugs, is important.
When used together, an increase in the positive effect is observed.
In addition to the above, Cortexin can be used in the complex treatment of speech disorders, memory disorders, emotional status disorders, increased anxiety and epilepsy. This is explained by the drug’s ability to improve impulse transmission between nerve cells, normalizing cognitive processes (memory, speech, thinking).
Actovegin is used as a reparator for many pathologies: vascular diseases, skin lesions, wounds and burns. It accelerates metabolism, increasing the energy status of cells and stimulating biosynthesis.
These medications are used parenterally.
Cortexin is available in bottles in the form of a dry white-yellow powder. Before use, it must be diluted in water for injection, saline or local anesthetic. The route of administration is intramuscular.
Actovegin is produced in ampoules in the form of a solution that can be used immediately. The solution contains an excipient - water for injection. Routes of administration: intramuscular and intravenous.
Cortexin is produced by the Russian company Geropharm. Actovegin is produced by the Japanese company Takeda and produced in factories in Austria and Russia. Both drugs are in the same price category.
Side effects with these medications are rare, however, when using Actovegin there is a slightly greater risk of developing allergic reactions in the form of rashes, skin hyperemia and the development of anaphylactic shock.
Dosage
The drug is taken orally before meals. Do not chew the tablet, take it with a small amount of liquid.
In the acute period of ischemic stroke (starting from days 5-7) - 2000 mg/day intravenously, up to 20 infusions, switching to tablet form, 2 tablets. 3 times/day (1200 mg/day). The total duration of treatment is 6 months.
For dementia - 2 tablets. 3 times/day (1200 mg/day). The total duration of treatment is 20 weeks.
For peripheral circulation disorders and their consequences - 1-2 tablets. 3 times/day (600-1200 mg/day). Duration of treatment is from 4 to 6 weeks.
For diabetic polyneuropathy - 2000 mg/day IV drip, 20 infusions with switching to tablet form, 3 tablets. 3 times/day (1800 mg/day). Duration of treatment is from 4 to 5 months.
What is better for an adult and a child?
This question cannot be answered unambiguously, since everything depends on the pathology that a particular patient has.
It is preferable to treat diseases of the nervous system with Cortexin, since it has a targeted effect specifically on nerve cells.
Actovegin helps improve metabolism in general, and can be used both in the complex treatment of neurological disorders and for injuries of another nature.
Despite their differences, these drugs have a good reputation. But you must use them only as prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
The frequency of side effects was determined according to the classification of the Council of International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS): very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000); frequency unknown (cannot be estimated from available data).
From the immune system: rarely - allergic reactions (drug fever, symptoms of shock).
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rarely - urticaria, sudden redness.
Reviews from doctors
Mikhail, neurologist, Kursk: “I often prescribe Cortexin both in monotherapy and in combination with other nootropic drugs for psychosomatic and mental disorders, organic and neurological lesions of the brain. Sometimes allergic reactions occur, but generally it is well tolerated.”
Valentina, psychotherapist, Vladivostok: “I prescribe Actovegin for depressive disorders, and often with other vascular drugs. It has a mild antidepressant effect. Rarely, discomfort may occur after taking the medication.”
special instructions
Clinical data
In the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ARTEMIDA trial (NCT01582854), which examined the therapeutic effect of Actovegin on cognitive impairment in 503 patients with ischemic stroke, the overall incidence of serious adverse events and death was similar in both study groups. Although the incidence of recurrent ischemic strokes was within the expected range in this patient population, there were more cases in the Actovegin group compared with the placebo group, but this difference was not statistically significant. The relationship between the incidence of recurrent stroke and the study drug has not been established.
Use in pediatrics
Currently, there is no data on the use of the drug Actovegin in pediatric patients, so the use of the drug in this group of people is not recommended.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Not installed.
Material and methods
A total of 257 patients with IS were included in the study, of which 152 (59.1%) were men, 105 (40.9%) were women. The median age in the overall group was 60 (55; 72) years. Speech impairments were represented by motor ( n
= 113, 44.0%) and sensorimotor (
n
= 144, 56.0%) aphasia.
Criteria for inclusion in the study: AI within 24 hours from the onset of the first symptoms; stroke in the dominant left hemisphere; the presence of speech disorders such as aphasia; initial severity from 9 to 20 points on the NIHSS (National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale); no indication of a history of cognitive impairment.
Non-inclusion criteria: hemorrhagic stroke; transient ischemic attack; repeated cerebrovascular accident; right hemisphere stroke in left-handed people, ambidexterity; indication of a history of severe traumatic brain injury or neuroinfection; the presence of focal changes in the brain according to the results of neuroimaging in the period preceding the development of stroke; disturbance of consciousness; the presence of post-stroke depressive disorders (more than 6 points on the Hamilton Depression Scale); mild speech impairment more than 12 points on the speech questionnaire scale.
At the first stage of the study, within 1 day from the onset of the disease, all patients were examined by a neurologist and speech therapist. We assessed the initial severity of stroke and aphasic disorders, tested for impairment of expressive and impressive speech, and determined the type of aphasia. The severity of speech disorders was assessed using a standard speech questionnaire (Speech Questionnaire - SQ) [29]. Over the next 3 weeks, the patients received the full range of treatment and rehabilitation measures provided for by the standards, including neuroprotective therapy and speech therapy classes to restore speech, reading and writing.
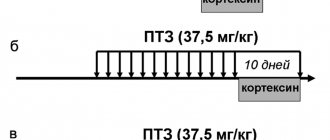
Neuroprotective therapy was represented by drugs with metabolic, antioxidant, neuromodulatory and neurotransmitter effects in monotherapy or various combinations. Thus, 38 patients received Actovegin in monotherapy, 39 - Mexidol, 42 - Mexidol in combination with Ceraxon, 39 - with gliatilin, 34 - with Cortexin. Cerakson monotherapy was prescribed to 30 patients, gliatilin monotherapy to 35. All drugs were used in standard dosages recommended for the treatment of patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents:
- Actovegin: 20 ml (800 mg) intravenously in 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution once a day;
- Mexidol: 5 ml (250 mg) intravenously in a stream or drip per 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution 2 times a day;
— cerakson: 4 ml (1000 mg) intravenously in 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution 2 times a day;
- gliatilin: 4 ml (1000 mg) intravenously in 50 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution once a day;
— Cortexin: 10 mg intramuscularly in 2 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution once a day.
The duration of therapy was 10 days.
At the second stage, the level of restoration of speech function in patients was assessed on the 21st day from the onset of the disease, after a course of rehabilitation, neuroprotective therapy, and logotherapy. The degree of speech restoration was characterized by the level of increase in the score on the SQ scale from the initial one (ΔSQ).
Based on the data obtained, all patients were divided into two groups: group 1 - 143 (55.7%) patients with an increase in score on the speech questionnaire ΔSQ≤6 (low level of recovery); Group 2 - 114 (44.3%) patients with ΔSQ>6 (high level of recovery).
Both groups were comparable in terms of gender, age, and initial level of speech impairment (Table 1).
Table 1. Brief characteristics of patients Note. *—statistically significant differences.
Statistical data processing was carried out using MS Win 8.1/MS Office 2013 Pro Ru and IBM SPSS Statistics 22 software. The nature of the distribution of quantitative characteristics was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Since the distribution of characteristics in all study groups differed from normal, quantitative characteristics were described using the median (Me) and interquartile range (25th, 75th percentiles) in the Me format (LQ; UQ). The work used a standard speech questionnaire that has discrete scales; they are also described by the median (Me), interquartile range and presented in Me format (LQ; UQ).
When statistically processing the data, nonparametric statistics methods were used: for comparison of several independent groups (with the number of characteristic values more than 5) - Kruskal-Wallis rank analysis of variance (H), for two independent samples - Mann-Whitney test (U). Qualitative characteristics are presented in the format of absolute and relative values (frequencies). Frequency comparisons were made using the Pearson χ2 test and the Fisher test for analysis of four-field tables.
When testing null hypotheses, the critical value of the level of statistical significance was taken equal to 0.05. If the achieved significance level is exceeded ( p
) statistical criterion for this value, the null hypothesis was accepted.
Patient reviews of Cortexin and Actovegin
Alena, 25 years old, Yaroslavl: “My child at 4 years old practically did not speak. His hearing and psyche are fine. The neurologist recommended the drug Cortexin, but it needs to be injected. I diluted it with sodium chloride to increase its effectiveness. The result gradually began to appear, and a sharp jump in speech occurred towards the end of the course of treatment. There were no side effects."
Margarita, 38 years old, Bryansk: “2 years ago my son started having severe headaches. With age, this problem only worsened, and we consulted a doctor. The diagnosis is vegetative-vascular dystonia. The drug Actovegin was prescribed. You need to drink it in courses 1-2 times a year. After the first week of taking it, the headaches practically stopped, and then completely disappeared.”
How does Cortexin work?
Manufacturer: Geropharm (Russia). The release form of the drug is a lyophilisate intended for the preparation of a solution for injection. The drug can only be administered intramuscularly. The active ingredient is the substance of the same name. Cortexin is a complex of polypeptide fractions that are highly soluble in water.
Cortexin is a neurometabolic stimulant that affects mental performance.
The lyophilisate contains glycine. This substance is used as a stabilizer. You can purchase the drug in packages containing 10 bottles (3 or 5 ml each). The concentration of the active ingredient is 5 and 10 mg. The indicated amount is contained in bottles of different volumes: 3 and 5 ml, respectively.
Cortexin belongs to the nootropic group of drugs. It is a neurometabolic stimulant that affects mental performance. It restores memory. Additionally, the drug stimulates cognitive functions. Thanks to the drug, the ability to learn is enhanced, and the brain’s resistance to the effects of negative factors, for example, oxygen deficiency or excessive stress, increases.
The active substance is obtained from the cerebral cortex of cattle. A drug based on it helps restore brain metabolism. The therapy has a pronounced effect on bioenergetic processes in nerve cells. The nootropic drug interacts with the neurotransmitter systems of the brain.
The active substance also exhibits neuroprotective properties, due to which the level of negative influence of a number of neurotoxic factors on neurons is reduced. Cortexin also exhibits antioxidant properties, due to which the process of lipid oxidation is disrupted. The resistance of neurons to the negative effects of a number of factors provoked by hypoxia increases.
During therapy, the function of neurons in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system is restored. At the same time, there is an improvement in the functioning of the cerebral cortex. The imbalance of amino acids characterized by inhibitory and stimulating properties is eliminated. In addition, the regenerative function of the body is restored.
Indications for use of Cortexin:
- decreased intensity of blood supply to the brain;
- trauma, as well as complications that develop against this background;
- recovery after surgery;
- encephalopathy;
- impaired thinking, information perception, memory and other cognitive disorders;
- encephalitis, encephalomyelitis in any form (acute, chronic);
- epilepsy;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- developmental disorders (psychomotor, speech) in children;
- asthenic disorders;
- cerebral palsy.
The safety and effectiveness of the drug during therapy during pregnancy have not been proven. This means you should refrain from taking Cortexin. The drug is contraindicated for breastfeeding women for the same reason. This product should not be used if a negative individual reaction to the components occurs.
In most cases, the drug does not cause side effects. However, there is a risk of developing hypersensitivity to the active component of the drug.
Who should not take nootropics?
Treatment with nootropic drugs is prohibited in case of intolerance to the components of the drug and their active substances, during an acute phase hemorrhagic stroke, or renal failure.
In general, tablets and injections of nootropic drugs are well tolerated by adults and children. This can be seen in the descriptions and reviews of patients on blogs and medical websites. On the Internet you can also read reviews about drugs and their effects on forums. Despite the fact that drugs (Actovegin, Cortexin, Cerobrolisini and others) are highly effective, their independent administration may be unsafe.
Patients may experience headaches, drowsiness, anxiety, irritability, and insomnia. It is possible that blood pressure may increase and the symptoms of coronary insufficiency may worsen (especially in older people). Allergic reactions, psychopathological symptoms, and gastrointestinal dysfunction (loose or hard stools, nausea) may occur.